Compared with balanced field calculations for an aerodrome with no stopway or ? [ Validation Marking ]
Question 98-1 : Increase the field length limited take off mass not affect the value of the field length limited take off mass increase the value of v1 not affect the value of v1
 Increase the field-length-limited take-off mass.
Increase the field-length-limited take-off mass. The relationship of the reference landing speed vref to the reference stalling ?
Question 98-2 : 1 23 vsro vsro 1 1 vsro 1 32 vsro
 1.23 vsro.
1.23 vsro. The vertical interval by which a class a aeroplane must avoid all obstacles in ?
Question 98-3 : 2000 ft 1000 ft 1500 ft 35 ft
 2000 ft.
2000 ft. Cs 25 the correct formula is . remark ' ?
Question 98-4 : Vmcg 1 05 vmc 1 05 vmcg< vef v2min
 Vmcg
Vmcg Calculate the one engine failed climb gradient of a four engine aeroplane given ?
Question 98-5 : 7 8 % 6 8 % 14 7 % 3 4 %
 7.8 %
7.8 % For jet propelled aeroplanes the maximum endurance speed corresponds with the ?
Question 98-6 : Minimum drag speed mach maximum range mach long range minimum power and minimum drag speed
 Minimum drag speed.
Minimum drag speed. Complete the following statement regarding the take off performance of an ?
Question 98-7 : I v1 ii 2 seconds iii accelerate stop distance available i v2 ii 3 seconds iii take off distance available i v1 ii 1 seconds iii accelerate stop distance available i v1 ii 2 seconds iii take off distance available
 (i) v1 (ii) 2 seconds (iii) accelerate-stop distance available
(i) v1 (ii) 2 seconds (iii) accelerate-stop distance available Performance class a take off .by mistake the take off speed are selected for a ?
Question 98-8 : A tail strike might occur the selected take off speeds are higher than the current speeds the actual accelerate stop distance is increased the accelerate go distance is shorter than calculated
 A tail strike might occur.
A tail strike might occur. A 'balanced field take off' means ?
Question 98-9 : One engine inoperative asdr = one engine inoperative todr one engine inoperative asda = one engine inoperative toda all engines operating asrd = one engine inoperative todr all engines operating asrd = all engines operating todr
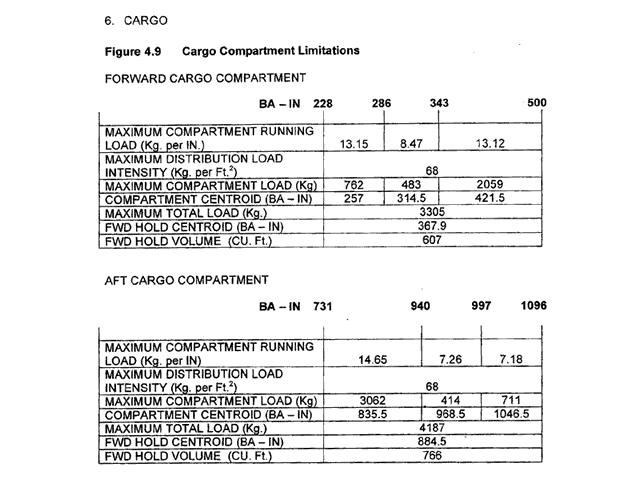 One engine inoperative asdr = one engine inoperative todr.
One engine inoperative asdr = one engine inoperative todr. The quick turnaround limit weight qtlw is the maximum landing weight for which ?
Question 98-10 : There is no minimum ground time required with respect to possible fuse plug melting before executing a subsequent takeoff there is no more guarantee for sufficient brake energy absorption in case of a long landing the landing gear structure will resist between two successive landings
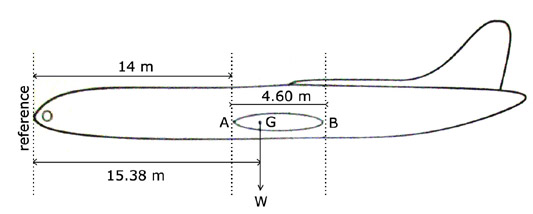 There is no minimum ground time required, with respect to possible fuse plug melting, before executing a subsequent takeoff.
There is no minimum ground time required, with respect to possible fuse plug melting, before executing a subsequent takeoff. The purpose of the 'quick turnaround limits' is to ?
Question 98-11 : Avoid brake overheat and fuse plug problems that could result from repeated landings at short time intervals or a rejected takeoff enhance the carbon brakes life protect the wheel fuse plugs from melting during landing reduce the time between full unloading and full reloading an aircraft
 Avoid brake overheat and fuse plug problems that could result from repeated landings at short time intervals or a rejected takeoff.
Avoid brake overheat and fuse plug problems that could result from repeated landings at short time intervals or a rejected takeoff. Is credit given for the use of reverse thrust in a rejected take off on a dry ?
Question 98-12 : No only for the torr only for the todr only for the asdr
What is the one second interval for in the engine failure at take off ?
Question 98-13 : To recognise and react to the engine failure by v1 it is considered in the all engines take off only the pilot must apply the brakes one second before v1 to stop within the asda it permits the recognition of the engine failure
 To recognise and react to the engine failure by v1.
To recognise and react to the engine failure by v1. If the v1 and field length limited take off mass flltom have been calculated ?
Question 98-14 : V1 increases flltom increases v1 increases flltom remains constant v1 decreases flltom increases v1 increases flltom decreases
 V1 increases, flltom increases.
V1 increases, flltom increases. Flying vfr from peiting 47°48 0'n 010°55 5'e to immenstadt 47°33 5'n ?
Question 98-15 : 32 nm 46 nm 58 nm 36 nm
 32 nm.
32 nm. Flying from edpj laichingen airport 48°30'n 009°38'e to edtm mengen airport ?
Question 98-16 : Magnetic course 202° distance 28 nm magnetic course 022° distance 28 nm magnetic course 022° distance 44 nm magnetic course 202° distance 44 nm
 Magnetic course 202°, distance 28 nm.
Magnetic course 202°, distance 28 nm. Aeronautical chart icao 1 500 000 stuttgart no 47/6 or route manual vfr gps ?
Question 98-17 : Magnetic course 287° distance 41 nm magnetic course 287° distance 60 nm magnetic course 252° distance 41 nm magnetic course 108° distance 60 nm
 Magnetic course 287°, distance 41 nm.
Magnetic course 287°, distance 41 nm. Use route manual vfr gps chart ed 6 .flying from edtm mengen airport 48°03'n ?
Question 98-18 : Magnetic course 288° distance 27 nm magnetic course 108° distance 27 nm magnetic course 108° distance 40 nm magnetic course 288° distance 40 nm
 Magnetic course 288°, distance 27 nm.
Magnetic course 288°, distance 27 nm. Aeronautical chart icao 1/500 000 stuttgart no 47 6 or route manual vfr+gps ?
Question 98-19 : 243° 257° 077° 063°
 243°.
243°. Use route manual vfr gps chart ed 6 .flying from edsz rottweil zepfenhan ?
Question 98-20 : 3760 ft 2605 ft 2920 ft 3331 ft
 3760 ft.
3760 ft. For this question use trm vfr directory for greece 7 3 .what is the local time ?
Question 98-21 : I lt = utc + 2 hours ii lt = utc + 3 hours i lt = utc 2 hours ii lt = utc 3 hours i lt + 2 hours = utc ii lt + 3 hours = utc i lt 3 hours = utc ii lt 2 hours = utc
 (i) lt = utc + 2 hours, (ii) lt = utc + 3 hours.
(i) lt = utc + 2 hours, (ii) lt = utc + 3 hours. Use route manual vfr gps chart ed 6 .flying from edpj laichingen airport ?
Question 98-22 : Magnetic course 243° distance 41 nm magnetic course 063° distance 41 nm magnetic course 063° distance 62 nm magnetic course 243° distance 62 nm
 Magnetic course 243°, distance 41 nm.
Magnetic course 243°, distance 41 nm. For this question use trm vfr aberdeen dyce area chart 19 5 .what is the atis ?
Question 98-23 : 121 85 114 30 121 70 118 10
 121.85.
121.85. Use route manual vfr gps chart ed 6 .what minimum grid area altitude is ?
Question 98-24 : 46 43 1819 ft 1120 m
 46.
46. Use trm vfr aberdeen dyce area chart 10 1v .which of the following frequencies ?
Question 98-25 : 135 17 126 25 119 87 114 30
 135.17
135.17 Use trm vfr aberdeen dyce area chart 10 1v .what is the correct frequency to ?
Question 98-26 : 119 87 126 25 134 10 135 17
 119.87
119.87 For this question use trm esbjerg aerodrome chart 19 2 .what are the dimensions ?
Question 98-27 : 2600m x 45m 8530m x 45m 8530ft x 45ft 2600ft x 148ft
 2600m x 45m.
2600m x 45m. For this question use trm vfr aberdeen dyce information page 19 6 .what is the ?
Question 98-28 : H6 h3 h3 h5
 H6.
H6. Aeronautical chart icao 1 500 000 stuttgart no 47/6 or route manual vfr+gps ?
Question 98-29 : Vor/dme ndb vor tacan
 Vor/dme.
Vor/dme. Aeronautical chart icao 1/500 000 stuttgart no 47/6 or route manual vfr gps ?
Question 98-30 : Munchen information 126 95 mhz munchen information 120 65 mhz frankfurt information 128 95 mhz memmingen information 122 1 mhz
 Munchen information 126.95 mhz.
Munchen information 126.95 mhz. Aeronautical chart icao 1/500 000 stuttgart no 47/6 or route manual vfr+gps ?
Question 98-31 : Vor/dme ndb vor tacan
 Vor/dme.
Vor/dme. Aeronautical chart icao 1/500 000 stuttgart no 47 6 or route manual vfr gps ?
Question 98-32 : 356° 176° 004° 185°
 356°.
356°. Flying vfr from villingen 48°03 5'n 008°27 0'e to freudenstadt 48°28 0'n ?
Question 98-33 : 24 nm 46 nm 28 nm 24 km
 24 nm.
24 nm. What are the designated departure routes when using i rwy 34 and ii rwy 05 . ?
Question 98-34 : I h4 ii h4 i h6 ii h4 i h3 ii h3 i h5 ii h3
 (i) h4 (ii) h4
(i) h4 (ii) h4 Which navigation aid is located in position 48°23'n 008°39'e . 2202 ?
Question 98-35 : Vor ndb vor/dme vortac
 Vor.
Vor. What minimum grid area altitude is applicable for edpj laichingen airport ?
Question 98-36 : 43 grid 46 grid 2434 ft 402 m
 43 grid.
43 grid. For this question use trm vfr directory for netherlands 7 3 .what is the local ?
Question 98-37 : I lt 1 hour = utc ii lt 2 hours = utc i lt 2 hours = utc ii lt 1 hour = utc i lt = utc + 2 hours ii lt = utc + 1 hour i lt = utc 1 hour ii lt = utc 2 hours
 (i) lt - 1 hour = utc (ii) lt - 2 hours = utc.
(i) lt - 1 hour = utc (ii) lt - 2 hours = utc. Aeronautical chart icao 1 500 000 stuttgart n°47/6 or route manual vfr+gps ?
Question 98-38 : 127 20 mhz 127 20 khz 128 52 mhz 128 52 khz
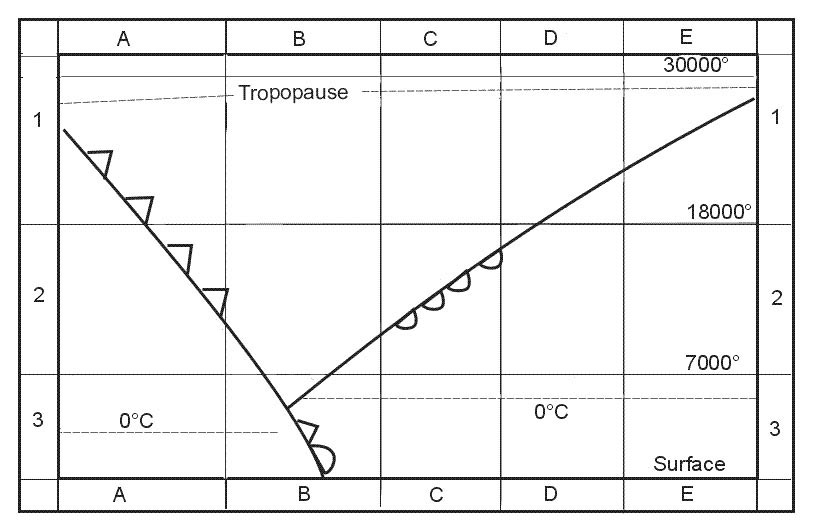 127.20 mhz.
127.20 mhz. For this question use trm vfr aberdeen dyce area chart 10 1v .what is the ?
Question 98-39 : 1733 ft 1245 ft 2105 ft 2025 ft
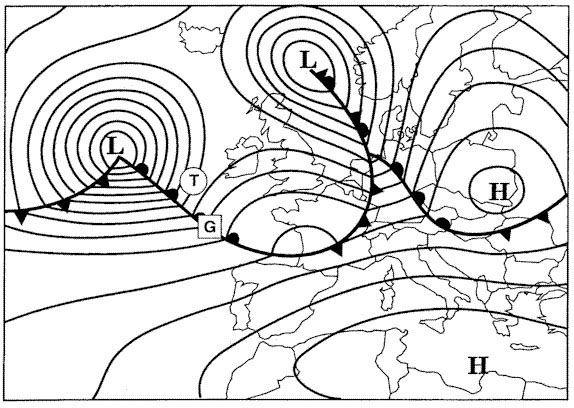 1733 ft.
1733 ft. Use route manual vfr+gps chart ed 6 .flying from edtm mengen airport 48°03'n ?
Question 98-40 : Magnetic course 022° distance 28 nm magnetic course 202° distance 28 nm magnetic course 022° distance 44 nm magnetic course 202° distance 44 nm
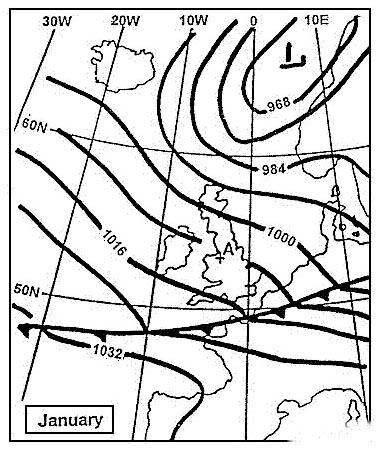 Magnetic course 022°, distance 28 nm
Magnetic course 022°, distance 28 nm ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
3879 Free Training Exam
