Which of the following statements is are correct with regard to computer flight ? [ Study Manual ]
Question 96-1 : Statement 2 only both statements statement 1 only neither statement
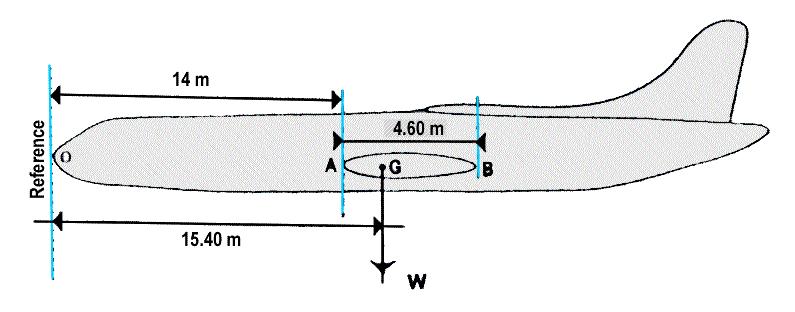 Statement 2 only
Statement 2 only In the ats flight plan item 7 for a radio equipped aircraft the identifier must ?
Question 96-2 : Be the rtf callsign to be used include the aircraft registration marking include the operating agency designator include an indication of the aircraft type
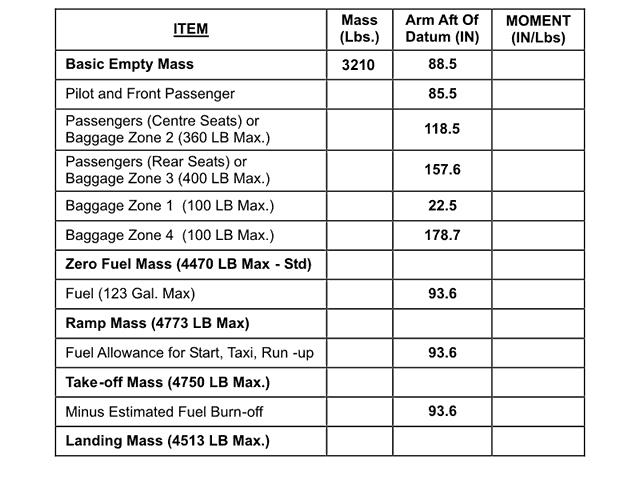 Be the rtf callsign to be used.
Be the rtf callsign to be used. It is possible in flight to .1 file an atc flight plan .2 modify an active ?
Question 96-3 : 1 2 3 4 1 2 4 1 2 3 2 3 4
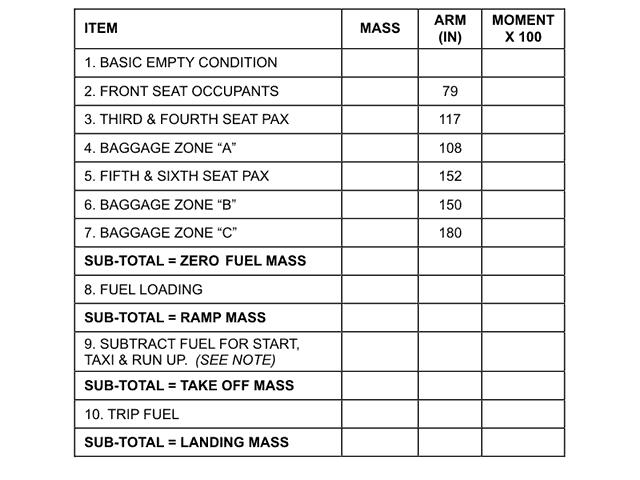 1, 2, 3, 4.
1, 2, 3, 4. On an atc flight plan the letter 'y' is used to indicate that the flight is ?
Question 96-4 : Ifr followed by vfr vfr followed by ifr ifr vfr
 Ifr followed by vfr.
Ifr followed by vfr. The navigation plan reads .trip fuel 136 kg.flight time 2h45min .calculated ?
Question 96-5 : 3h34min 2h45min 2h49min 3h38min
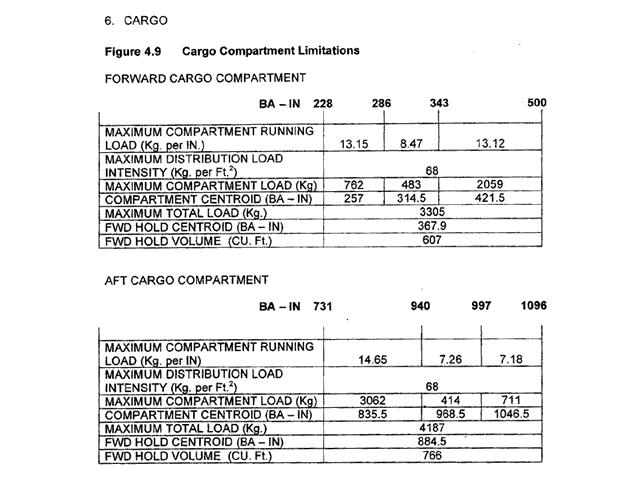 3h34min.
3h34min. When completing item 9 of the ats flight plan if there is no appropriate ?
Question 96-6 : 'zzzz' followed by an entry in item 18 'xxxx' followed by an entry in item 18 the most descriptive abbreviation 'none'
 'zzzz' followed by an entry in item 18.
'zzzz' followed by an entry in item 18. When completing an atc flight plan for a flight commencing under ifr but ?
Question 96-7 : Y x g n/s
 Y
Y In the atc flight plan item 19 if the number of passengers to be carried is not ?
Question 96-8 : Tbn to be notified may be entered in the relevant box the plan should be filed with the relevant box blank an estimate may be entered but that number may not subsequently be exceeded the plan may not be filed until the information is available
 Tbn (to be notified) may be entered in the relevant box.
Tbn (to be notified) may be entered in the relevant box. An aircraft has a maximum certificated take off mass of 137000 kg but is ?
Question 96-9 : Heavy 'h' heavy/medium 'h/m' medium 'm' medium plus 'm+'
 Heavy 'h'.
Heavy 'h'. In the appropriate box of an atc flight plan form corresponding to the ?
Question 96-10 : Go off blocks take off start up pass the departure beacon
 Go off blocks
Go off blocks The planned departure time from the parking area is 1815 utc .the estimated ?
Question 96-11 : 1715 utc 1725 utc 1745 utc 1755 utc
 1715 utc
1715 utc In the ats flight plan item 15 for a flight along a designated route where the ?
Question 96-12 : The letters 'dct' should be entered followed by the point of joining the ats route it is not necessary to indicate the point of joining that route as it will be obvious to the ats unit it is necessary only to give the first reporting point on that route the words 'as cleared' should be entered
 The letters 'dct' should be entered, followed by the point of joining the ats route.
The letters 'dct' should be entered, followed by the point of joining the ats route. An aircraft plans to depart london at 1000 utc and arrive at munich eddm at ?
Question 96-13 : Eddm0215 eddm1415 eddm at 0215 eddm2h35
 Eddm0215
Eddm0215 On an atc flight plan you are required to indicate in the box marked 'speed' ?
Question 96-14 : The true airspeed the equivalent airspeed the indicated airspeed the estimated ground speed
 The true airspeed
The true airspeed The wind direction and velocity °/kt at 50°n 040°e . err a 033 417 ?
Question 96-15 : Is 020/70 is 350/70 is 200/70 is 020/80
 Is 020/70.
Is 020/70. In the appropriate box of an atc flight plan for endurance one must indicate ?
Question 96-16 : The total usable fuel on board the required fuel for the flight the required fuel for the flight plus the alternate and 45 minutes the total usable fuel on board minus reserve fuel
 The total usable fuel on board.
The total usable fuel on board. Item 9 of the ats flight plan includes 'number and type of aircraft' in this ?
Question 96-17 : The number of aircraft flying in a group the registration number of the aircraft the number of aircraft which will separately be using a repetitive flight plan rpl the icao type designator number as set out in icao doc 8643
 The number of aircraft flying in a group.
The number of aircraft flying in a group. On a atc flight plan to indicate that you will overfly the waypoint romeo at ?
Question 96-18 : Romeo/n0120f085 romeo/k0120fl085 romeo/fl085n0120 romeo/f085n0120
 Romeo/n0120f085
Romeo/n0120f085 In the ats flight plan item 19 emergency and survival equipment carried on the ?
Question 96-19 : Crossing out the box relevant to any equipment not carried placing a tick in the relevant box circling the relevant box listing the items carried on the 'remarks' line
 Crossing out the box relevant to any equipment not carried.
Crossing out the box relevant to any equipment not carried. In the atc flight plan item 15 when entering a route for which standard ?
Question 96-20 : Both should be entered in the atc plan where appropriate sids should be entered but not stars stars should be entered but not sids neither sid nor star should be entered
 Both should be entered in the atc plan where appropriate.
Both should be entered in the atc plan where appropriate. Which describes the maximum intensity of icing if any at fl180 in the vicinity ?
Question 96-21 : Severe moderate light nil
 Severe.
Severe. During an ifr flight tas and time appear to deviate from the data in the atc ?
Question 96-22 : Tas 5% and time 3 minutes tas 3% and time 3 minutes tas 5 kt and time 5 minutes tas 10 kt and time 2 minutes
 Tas 5% and time 3 minutes.
Tas 5% and time 3 minutes. In the atc flight plan item 15 cruising speed when not expressed as a mach ?
Question 96-23 : Tas ias cas groundspeed
 Tas.
Tas. In an atc flight plan item 15 route a cruising pressure altitude of 32000 feet ?
Question 96-24 : F320 fl320 s3200 32000f
 F320
F320 On an atc flight plan to indicate that you will overfly the waypoint tango at ?
Question 96-25 : Tango/n0350f280 tango/k0350fl280 tango/fl280n0350 tango/ t350f280
 Tango/n0350f280
Tango/n0350f280 In the atc flight plan item 15 it is necessary to enter any point at which a ?
Question 96-26 : 5% tas or 0 01 mach or more 10 % tas or 0 05 mach or more 20 km per hour or 0 1 mach or more 20 knots or 0 05 mach or more
 5% tas or 0.01 mach or more.
5% tas or 0.01 mach or more. Which of the following statements regarding filing a atc flight plan is correct ?
Question 96-27 : In case of atfm air traffic flow management the flight plan should be filed at least three hours in advance of the eobt any flight plan should be filed at least 10 minutes before departure a flight plan should be filed when a national fir boundary will be crossed a flying college can file repetitive flight plan for vfr flights
 In case of atfm (air traffic flow management) the flight plan should be filed at least three hours in advance of the eobt.
In case of atfm (air traffic flow management) the flight plan should be filed at least three hours in advance of the eobt. For the purposes of item 9 wake turbulence category of the atc flight plan an ?
Question 96-28 : Medium 'm' heavy 'h' light 'l' unclassified 'u'
 Medium 'm'.
Medium 'm'. The navigation plan reads .trip fuel 100 kg.flight time 1h35min.taxi fuel 3 ?
Question 96-29 : 2h 49min 1h 35min 2h 04min 2h 52min
 2h 49min.
2h 49min. You have a flight plan ifr from amsterdam to london in the flight plan it is ?
Question 96-30 : The route according to the flight plan is accepted it is not allowed to file such a flight plan you will get a separate clearance for the deviation the filed deviation is not accepted
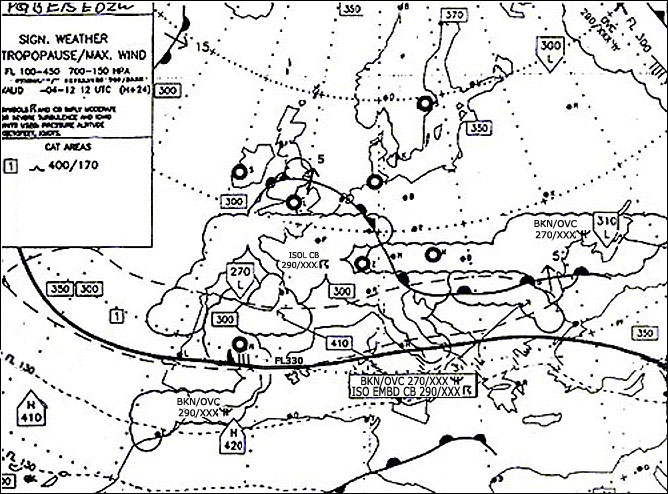 The route according to the flight plan is accepted.
The route according to the flight plan is accepted. In the atc flight plan item 13 in a flight plan submitted before departure the ?
Question 96-31 : Estimated off block time estimated time over the first point en route estimated take off time allocated slot time
 Estimated off-block time
Estimated off-block time Given .planned and actual data as shown in the flight log excerpt .arriving ?
Question 96-32 : 1272 kg 2338 kg 1250 kg 582 kg
 1272 kg.
1272 kg. A turbojet aeroplane flies using the following data .flight level fl 330.flight ?
Question 96-33 : 539 nm 518 nm 471 nm 493 nm
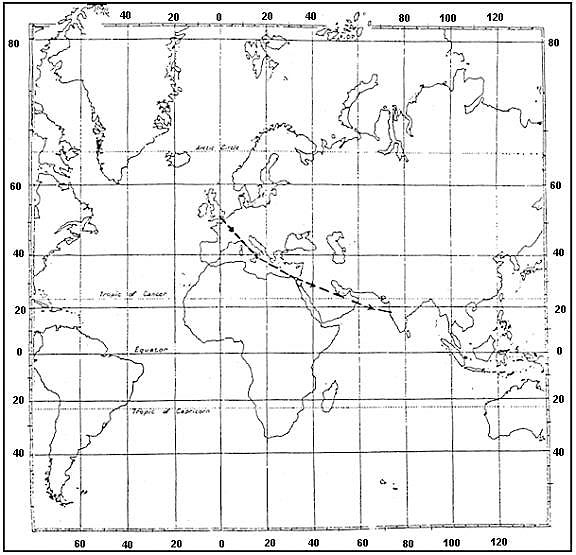 539 nm.
539 nm. Given .true course tc 017°.w/v 340°/30 kt.true air speed tas 420 kt.find ?
Question 96-34 : Wca 2° gs 396 kt wca +2° gs 396 kt wca 2° gs 426 kt wca +2° gs 416 kt
 Wca -2°, gs 396 kt.
Wca -2°, gs 396 kt. The true course is 042° .the variation in the area is 6° w and the wind is ?
Question 96-35 : 052° 044° 040° 058°
 052°.
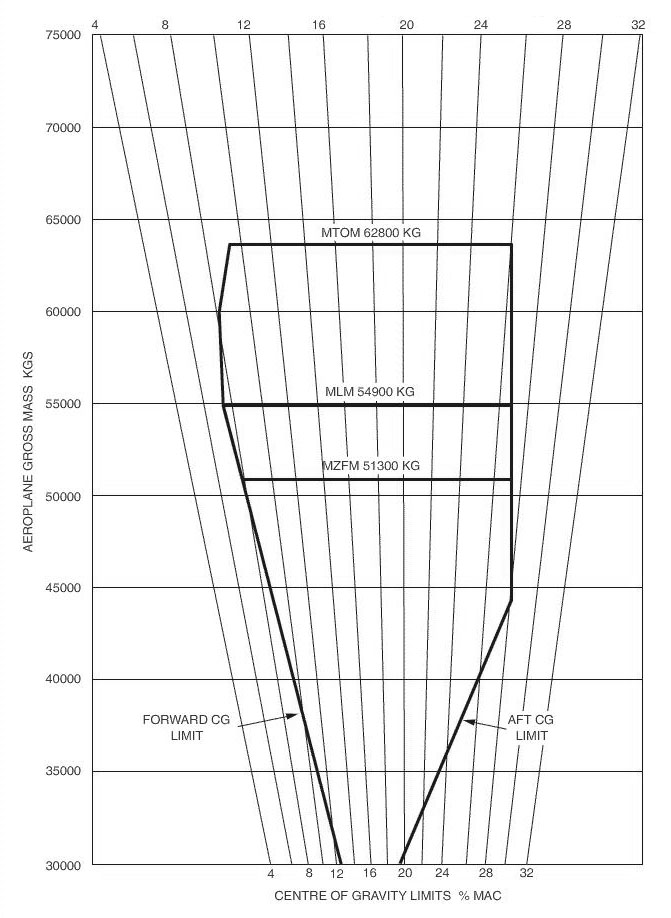
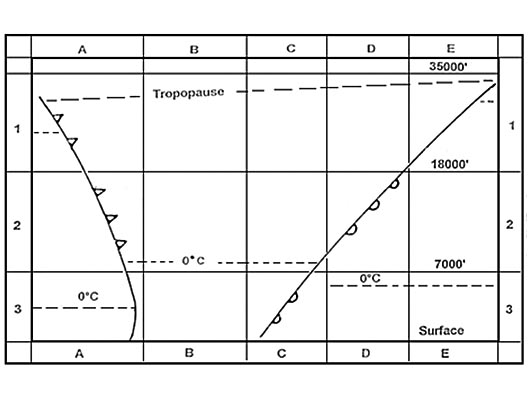
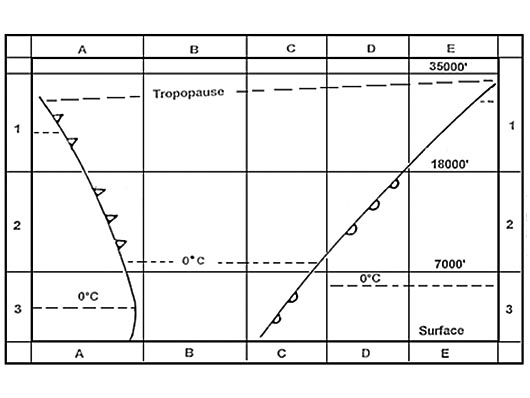
052°. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 3 5 .given a trip ?
Question 96-36 : By 7% by 3% by 4% by 10%
 By 7%.
By 7%. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 5 4 .planning an ifr ?
Question 96-37 : 76 nm 97 nm 65 nm 87 nm
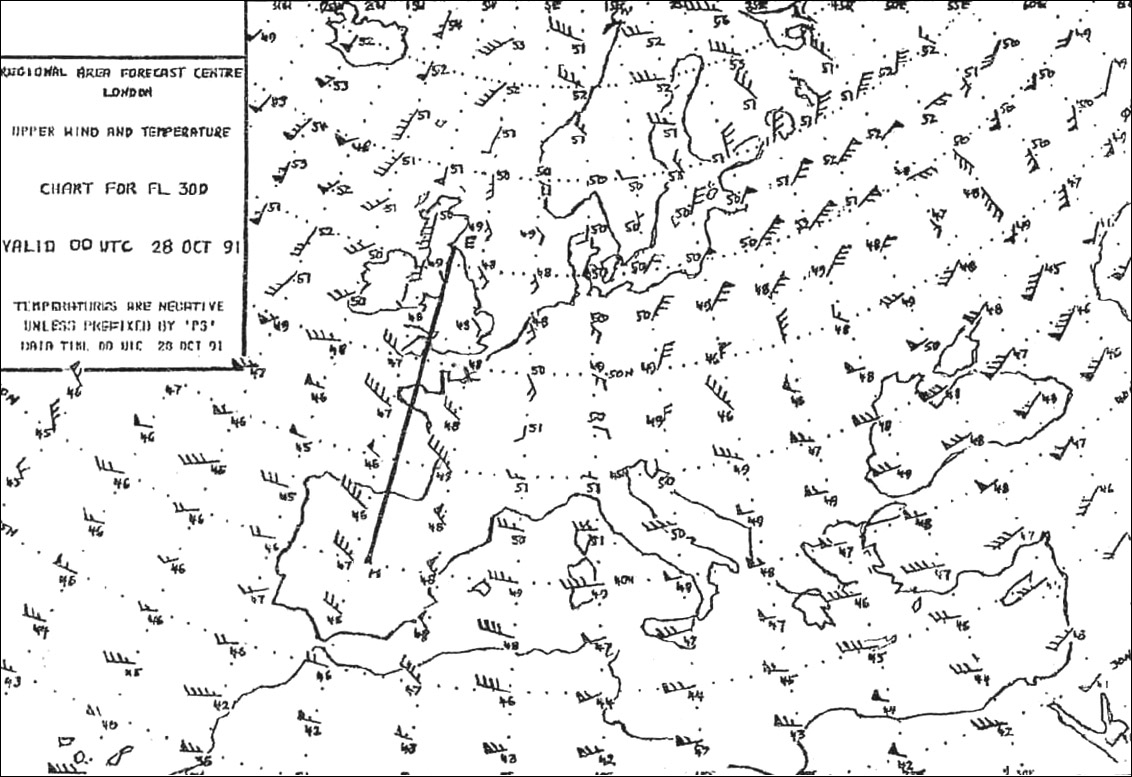 76 nm.
76 nm. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 7 3 .given ?
Question 96-38 : 25000 ft 20000 ft 16000 ft 14500 ft
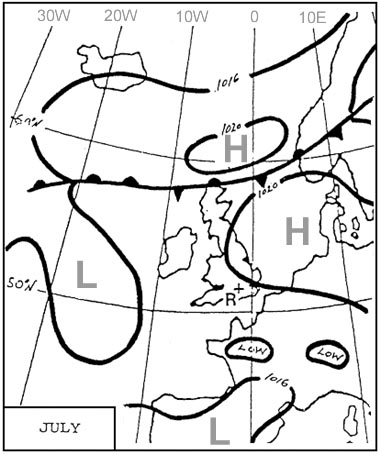 25000 ft.
25000 ft. Flight planning chart for an aircraft states that the time to reach the ?
Question 96-39 : 193 nm 128 nm 157 nm 228 nm
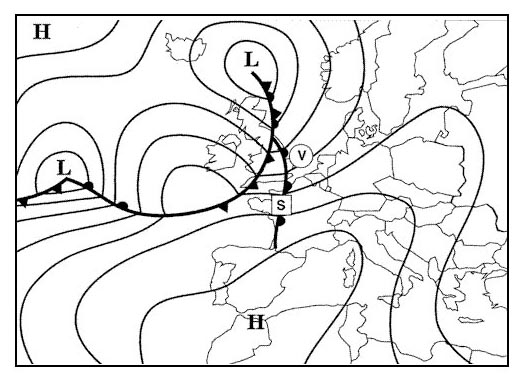 193 nm.
193 nm. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 3 6 .given .distance ?
Question 96-40 : 2800 kg 2550 kg 2900 kg 2650 kg
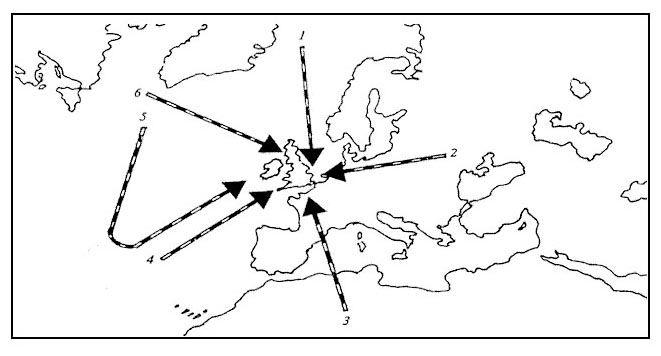 2800 kg.
2800 kg. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
3799 Free Training Exam
