Given .distance from departure to destination 250 nm.gs out 130 kt.gs home 100 ? [ Diploma registration ]
Question 92-1 : 109 nm 141 nm 125 nm 192 nm
 109 nm.
109 nm. Given .distance from departure to destination 550 nm.endurance 3 6 h.true track ?
Question 92-2 : 231 nm 305 nm 116 nm 319 nm
 231 nm.
231 nm. Given .distance from departure to destination 180 nm.endurance 2 h.tas 120 ?
Question 92-3 : Distance 118 nm time 53 min distance 79 nm time 45 min distance 59 nm time 30 min distance 62 nm time 28 min
 Distance: 118 nm, time: 53 min.
Distance: 118 nm, time: 53 min. Given .distance from departure to destination 2500 nm.gs out 540 kt.gs home 470 ?
Question 92-4 : 129 min 171 min 28 min 149 min
 129 min
129 min Given .distance from departure to destination 875 nm.true track 240 .wind ?
Question 92-5 : Distance 394 nm time 43 min distance 481 nm time 64 min distance 716 nm time 78 min distance 438 nm time 53 min
 Distance: 394 nm, time: 43 min.
Distance: 394 nm, time: 43 min. The forecast period covered by the paris/charles de gaulle tafs totals hours . ?
Question 92-6 : 27h 9h 18h 20h
 27h.
27h. If cas is 190 kts.altitude 9000 ft.temp isa 10°c.true course tc 350°.w/v ?
Question 92-7 : 1213 utc 1221 utc 1233 utc 1203 utc
 1213 utc
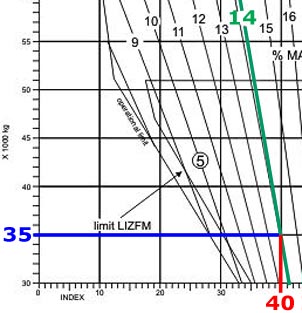
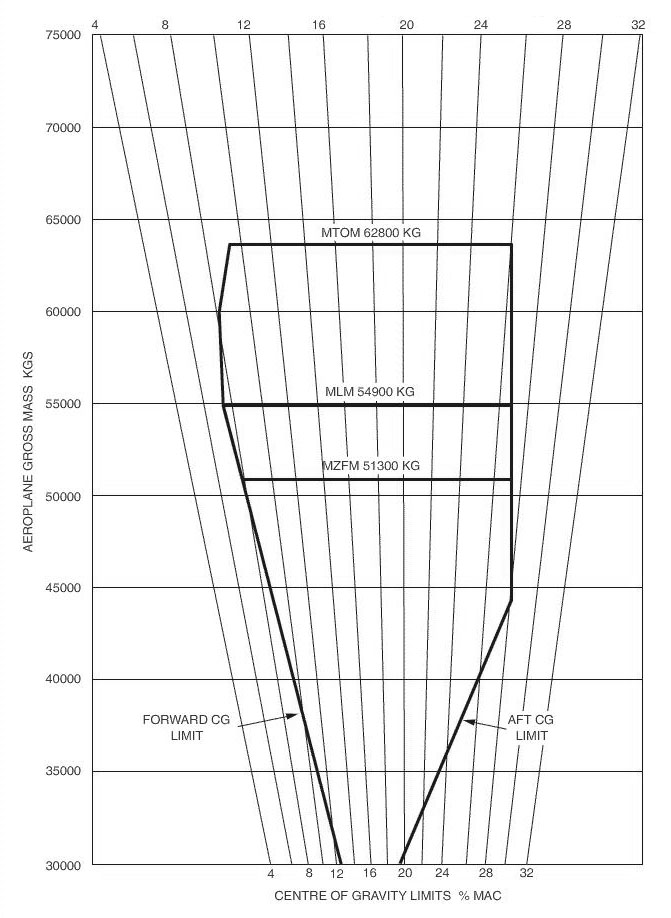
1213 utc At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 4.planning a flight ?
Question 92-8 : 48 125 kg 2 250 kg 48 675 kg 49 250 kg
 48 125 kg.
48 125 kg. Given .distance from departure to destination 1385 nm .gs out 480 kt .gs home ?
Question 92-9 : 74 min 128 min 96 min 50 min
 74 min.
74 min. Given .distance from departure to destination 256 nm .gs out 160 kt .gs home ?
Question 92-10 : 104 nm 152 nm 128 nm 176 nm
 104 nm.
104 nm. Given .distance from departure to destination 480 nm.safe endurance 5 h.true ?
Question 92-11 : 280 nm 205 nm 141 nm 199 nm
 280 nm.
280 nm. Given .distance from departure to destination 150 nm .true track 142° .wind ?
Question 92-12 : 79 nm 71 nm 75 nm 134 nm
 79 nm
79 nm A metar reads .1430z 35002kt 7000 skc 21/03 q1024 =.which of the following ?
Question 92-13 : Temperature/dewpoint runway in use day/month period of validity
 Temperature/dewpoint.
Temperature/dewpoint. The wind °/kt at 40°n 020°w is . err a 033 157 ?
Question 92-14 : 310/40 334/40 135/40 155/40
 310/40.
310/40. Given .maximum allowable take off mass 64 400 kg.maximum landing mass 56200 ?
Question 92-15 : 3 000 kg 7 000 kg 5 600 kg 4 000 kg
 3 000 kg.
3 000 kg. What mean temperature °c is likely on a course of 360° t from 40°n to 50°n ?
Question 92-16 : Mean temperature 47°c mean temperature 46°c mean temperature 49°c mean temperature 50°c
 Mean temperature : -47°c.
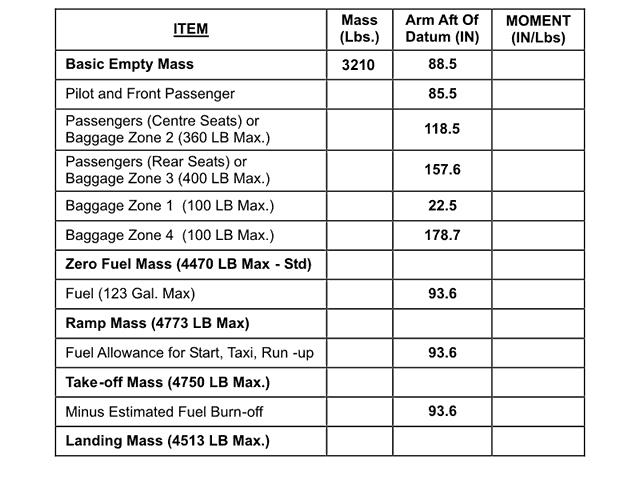
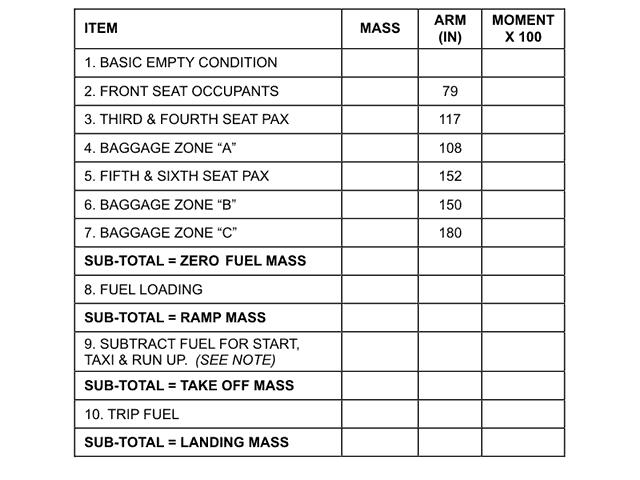
Mean temperature : -47°c. For flight planning purposes the landing mass at alternate is taken as ?
Question 92-17 : Zero fuel mass plus final reserve fuel and contingency fuel landing mass at destination plus alternate fuel zero fuel mass plus final reserve fuel and alternate fuel zero fuel mass plus final reserve fuel
 Zero fuel mass plus final reserve fuel and contingency fuel.
Zero fuel mass plus final reserve fuel and contingency fuel. Given .distance from departure to destination 220 nm.true track 175°.wind ?
Question 92-18 : 116 nm 103 nm 110 nm 136 nm
 116 nm
116 nm At references or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 2 and figure 4 5 3 ?
Question 92-19 : 25000 ft 435 kt 33500 ft 430 kt 33900 ft 420 kt 24000 ft 445 kt
 25000 ft, 435 kt
25000 ft, 435 kt Given .distance from departure to destination 950 nm.gs out 275 kt .gs home 225 ?
Question 92-20 : 93 min 139 min 114 min 39 min
 93 min.
93 min. Given .distance from departure to destination 950 nm .safe endurance 3 5 h .tas ?
Question 92-21 : Distance 622 nm time 117 min distance 528 nm time 79 min distance 311 nm time 52 min distance 328 nm time 62 min
 Distance: 622 nm time: 117 min
Distance: 622 nm time: 117 min Given .distance from departure to destination 1000 nm .safe endurance 4 h .tas ?
Question 92-22 : 990 nm 450 nm 495 nm 10 nm
 990 nm.
990 nm. Given .distance from departure to destination 2200 nm.true track 150° .wind ?
Question 92-23 : Distance 980 nm time 115 min distance 1120 nm time 179 min distance 1100 nm time 179 min distance 980 nm time 144 min
 Distance: 980 nm time: 115 min
Distance: 980 nm time: 115 min Route manual chart nap.the initial true course from a 64°n006°e to c ?
Question 92-24 : 271° 259° 247° 279°
 271°.
271°. Which best describes the maximum intensity of icing if any at fl160 in the ?
Question 92-25 : Moderate severe light nil
 Moderate.
Moderate. At reference or see flight planning manual sep 1 figure 2 1. given . fl 75.oat ?
Question 92-26 : 18 nam 15 nm 14 nam 18 nm 16 nam 18 nm 18 nam 13 nm
 18 nam. 15 nm.
18 nam. 15 nm. Given .distance from departure to destination 285 nm .true track 348°.wind ?
Question 92-27 : 154 nm 131 nm 143 nm 123 nm
 154 nm.
154 nm. Given .distance from departure to destination 435 nm .gs out 110 kt .gs home ?
Question 92-28 : 236 nm 199 nm 218 nm 368 nm
 236 nm
236 nm The approximate mean wind component kt along true course 180° from 50°n to ?
Question 92-29 : Tail wind 55 kt tail wind 40 kt tail wind 70 kt headwind 55 kt
 Tail wind 55 kt.
Tail wind 55 kt. The wind direction and velocity °/kt at 40°n 040°e is . err a 033 233 ?
Question 92-30 : 330/75 330/85 150/75 300/75
 330/75.
330/75. In the vicinity of shannon 52° n009°w the tropopause is at about . err a 033 ?
Question 92-31 : Fl 360 fl 350 fl 300 fl 270
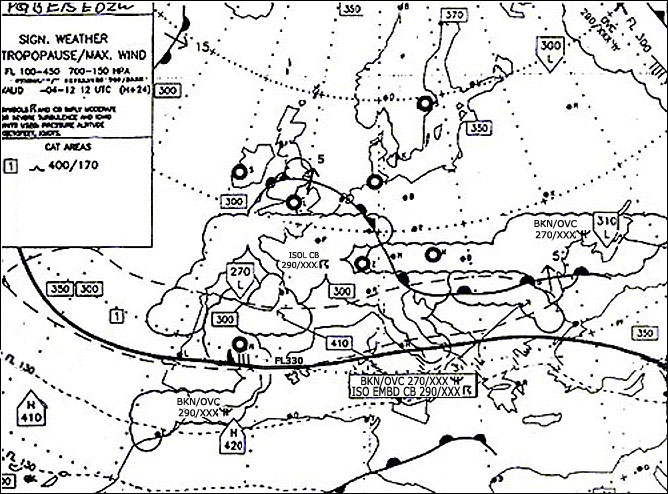 Fl 360.
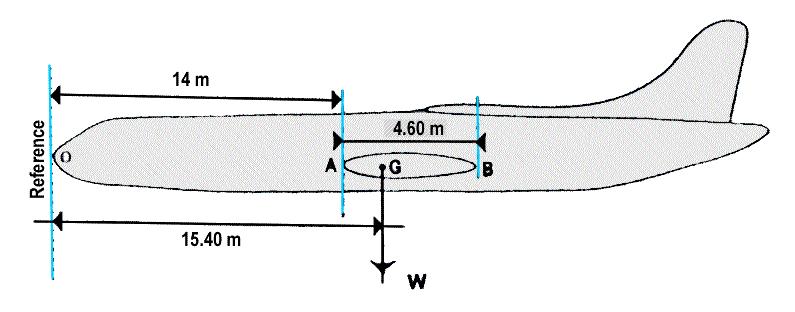
Fl 360. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 5 1.given .brake ?
Question 92-32 : 62 nam 59 nm 59 nam 62 nm 67 nam 71 nm 71 nam 67 nm
 62 nam, 59 nm.
62 nam, 59 nm. Route manual chart nap.the average magnetic course from c 62°n020°w to b ?
Question 92-33 : 119° 109° 099° 118°
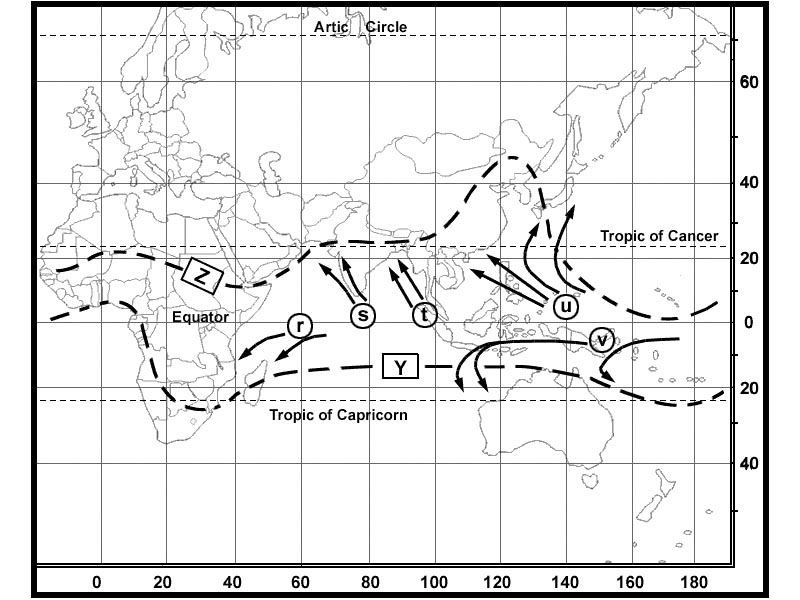 119°.
119°. Given .distance from departure to destination 360 nm .safe endurance 4 5 h ?
Question 92-34 : 308 nm 185 nm 154 nm 52 nm
 308 nm
308 nm What mean temperature °c is likely on a true course of 270° from 025°e to ?
Question 92-35 : Mean temperature is 50°c mean temperature is 48°c mean temperature is 52°c mean temperature is 54°c
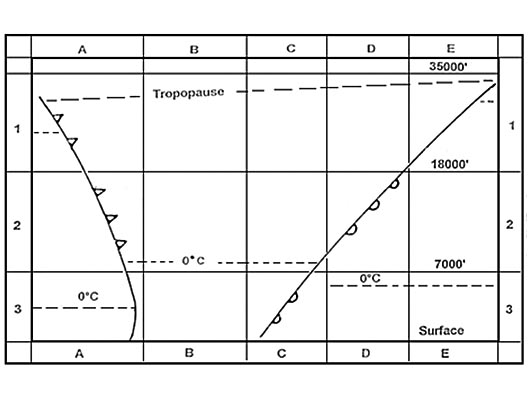 Mean temperature is -50°c.
Mean temperature is -50°c. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 3 3c. given .ground ?
Question 92-36 : 12 400 kg 03h 55 min 12 400 kg 04h 12 min 11 400 kg 03h 55 min 11 400 kg 04h 12 min
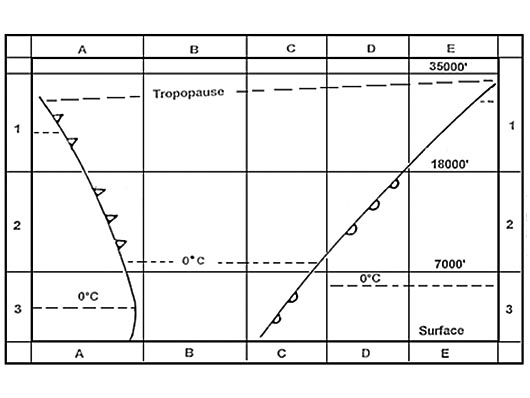 12 400 kg, 03h 55 min.
12 400 kg, 03h 55 min. Given .distance from departure to destination 260 nm .safe endurance 4 1 h ?
Question 92-37 : 213 nm 154 nm 107 nm 47 nm
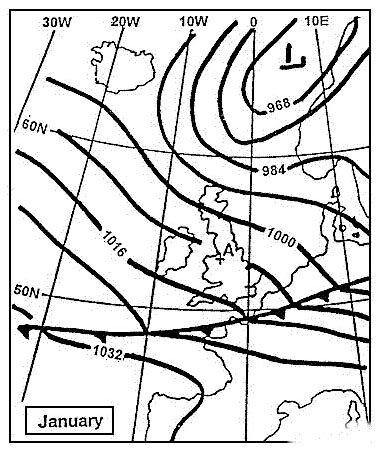 213 nm.
213 nm. Route manual chart nap. the average true course from c 62°n020°w to b ?
Question 92-38 : 109° 119° 099° 120°
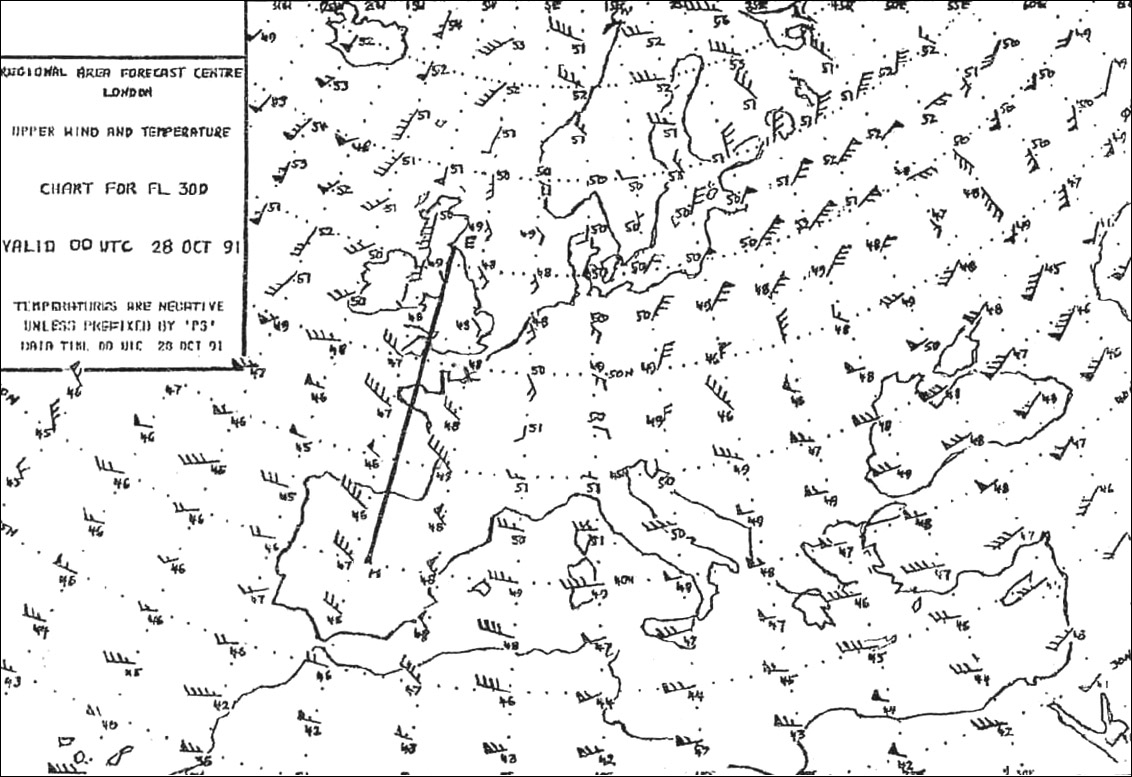 109°.
109°. Given .distance from departure to destination 2450 nm .safe endurance 7 5 h ?
Question 92-39 : 252 min 198 min 111 min 156 min
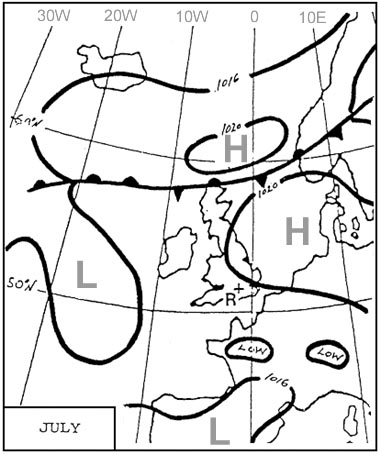 252 min
252 min Which describes the worst hazard if any that could be associated with the type ?
Question 92-40 : Engine flame out and windscreen damage severe attenuation in the hf r/t band reduced visibility there is no hazard
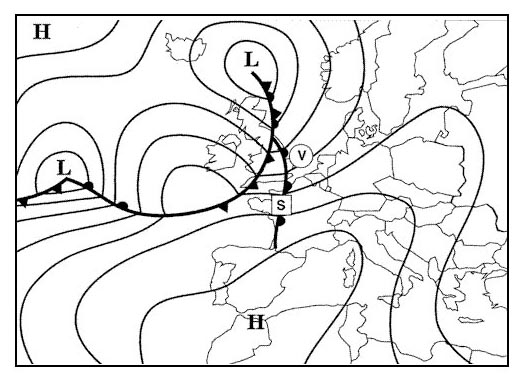 Engine flame out and windscreen damage.
Engine flame out and windscreen damage. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
3639 Free Training Exam
