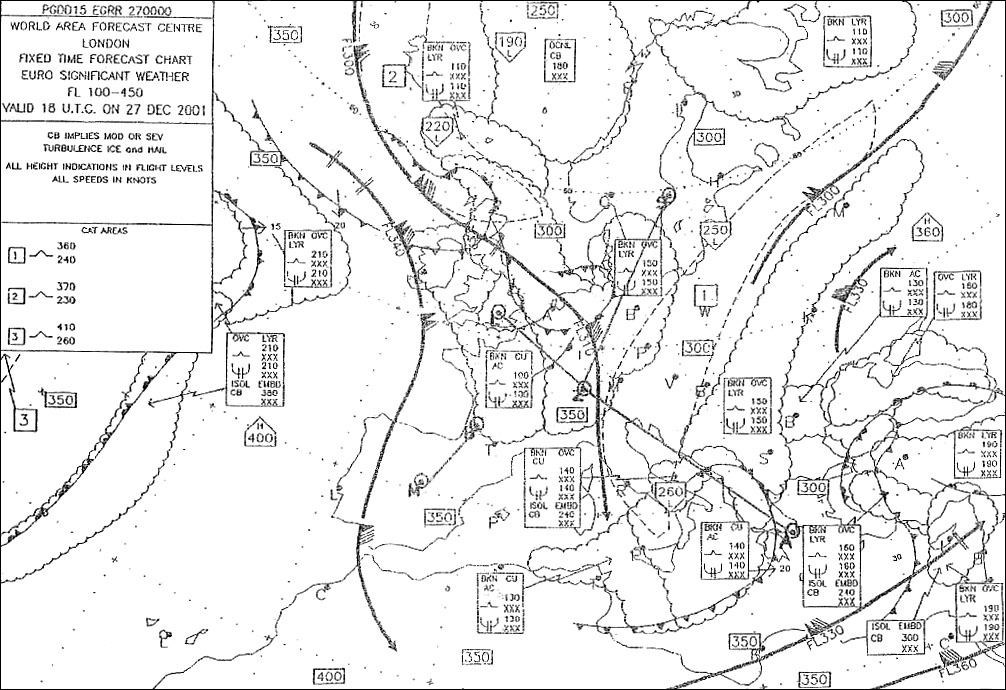
The flight crew of a turbojet aeroplane prepares a flight using the following ? [ Exam pilot ]
Question 90-1 : 34 430 kg 30 440 kg 32 480 kg 28 720 kg
The purpose of the decision point procedure is ?
Question 90-2 : To reduce the minimum required fuel and therefore be able to increase the traffic load to reduce the landing weight and thus reduce the structural stress on the aircraft to increase the safety of the flight to increase the amount of extra fuel
 To reduce the minimum required fuel and therefore be able to increase the traffic load.
To reduce the minimum required fuel and therefore be able to increase the traffic load. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 7 2.for the purpose ?
Question 90-3 : M/kias 74/330 lrc m/kias 74/290 m/kias 70/280
 M/kias .74/330
M/kias .74/330 Using the power setting table for the single engine aeroplane determine the ?
Question 90-4 : 134 kt and 55 7 lbs/h 131 kt and 56 9 lbs/h 125 kt and 55 7 lbs/h 136 kt and 56 9 lbs/h
 134 kt and 55.7 lbs/h.
134 kt and 55.7 lbs/h. For turbojet engine driven aeroplane given .taxi fuel 600 kg.fuel flow for ?
Question 90-5 : 77 800 kg 76 100 kg 80 500 kg 79 200 kg
 77 800 kg.
77 800 kg. The following apply .temperature isa +15°c.brake release mass 62000 kg.trip ?
Question 90-6 : 13500 kg 13000 kg 13200 kg 13800 kg
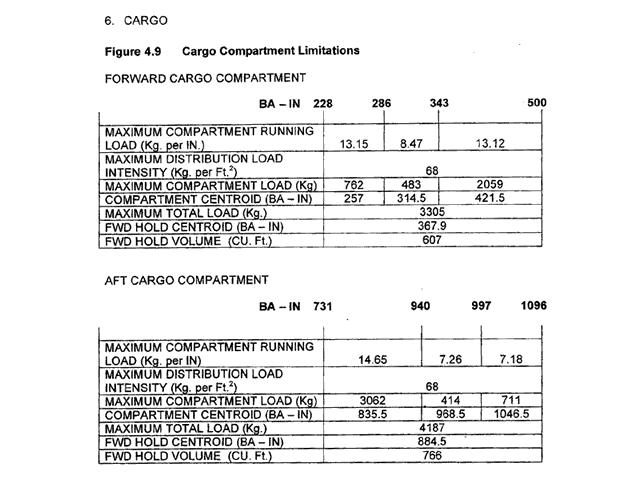 13500 kg.
13500 kg. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 3 1c. for a flight ?
Question 90-7 : A 17600 kg b 6 hr 50 min a 16200 kg b 6 hr 20 min a 17000 kg b 6 hr 10 min a 20000 kg b 7hr 00 min
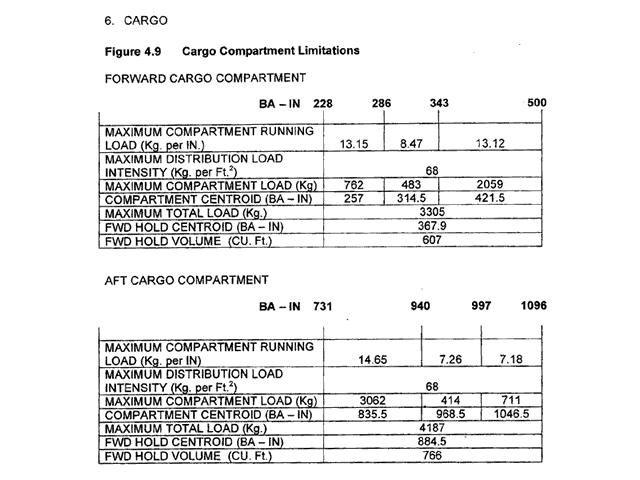 (a) 17600 kg (b) 6 hr 50 min.
(a) 17600 kg (b) 6 hr 50 min. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 3 5. for a flight of ?
Question 90-8 : A 18100 kg b 7hr 20 min a 15800 kg b 6hr 00 min a 21800 kg b 9hr 25 min a 19000 kg b 7hr 45min
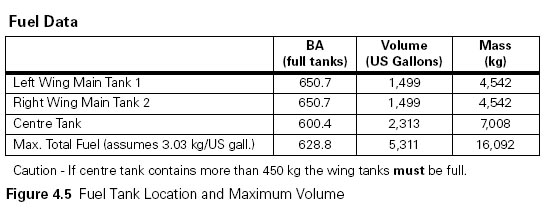 (a) 18100 kg (b) 7hr 20 min
(a) 18100 kg (b) 7hr 20 min Mark the correct statement .if a decision point procedure is applied for flight ?
Question 90-9 : The trip fuel to the destination aerodrome is to be calculated via the decision point the trip fuel to the destination aerodrome is to be calculated via the suitable enroute alternate a destination alternate is not required the fuel calculation is based on a contingency fuel from departure aerodrome to the decision point
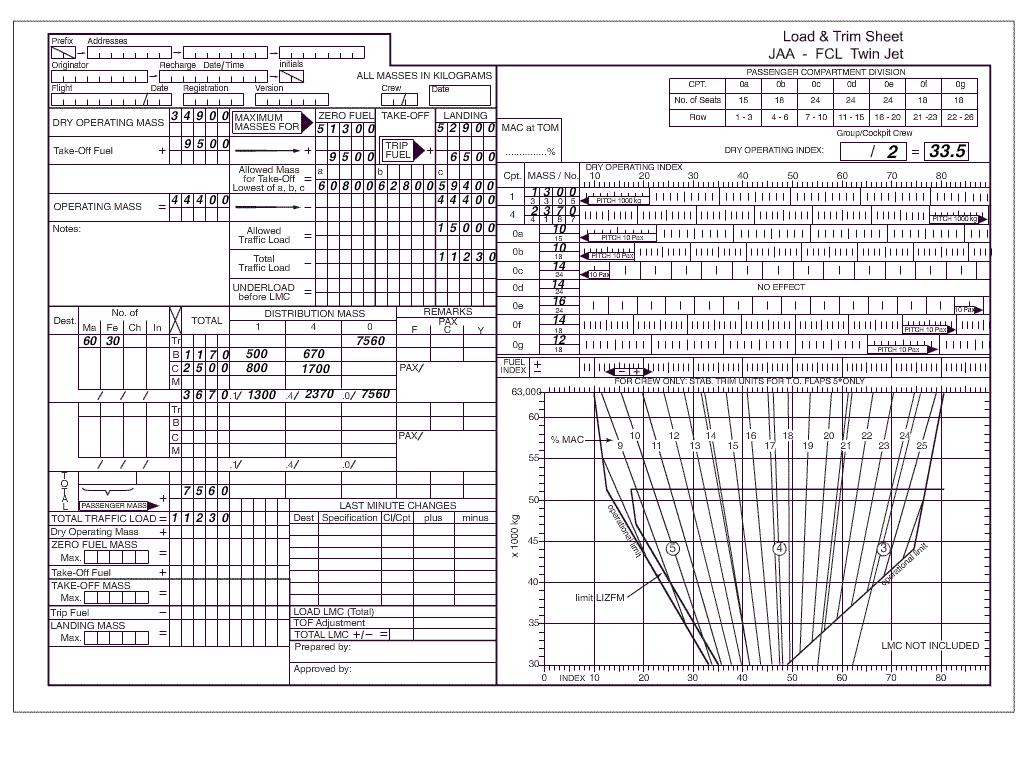 The trip fuel to the destination aerodrome is to be calculated via the decision point.
The trip fuel to the destination aerodrome is to be calculated via the decision point. An aeroplane has the following masses .estimated landing weight 50 000 kg.trip ?
Question 90-10 : 4 300 kg 6 185 kg 9 000 kg 6 400 kg
 4 300 kg.
4 300 kg. In a flight plan when the destination aerodrome is a and the alternate ?
Question 90-11 : 30 minutes holding 1 500 feet above aerodrome b 30 minutes holding 2 000 feet above aerodrome b 15 minutes holding 2 000 feet above aerodrome a 30 minutes holding 1 500 feet above aerodrome a
 30 minutes holding 1,500 feet above aerodrome b
30 minutes holding 1,500 feet above aerodrome b A jet aeroplane has a cruising fuel consumption of 4060 kg/h and 3690 kg/h ?
Question 90-12 : 8120 kg 7380 kg 1845 kg 3500 kg
 8120 kg.
8120 kg. Given .fuel density = 0 78 kg/l .dry operating mass = 33500 kg .traffic load = ?
Question 90-13 : 17 350 kg 22 100 kg 17 550 kg 21 900 kg
 17 350 kg.
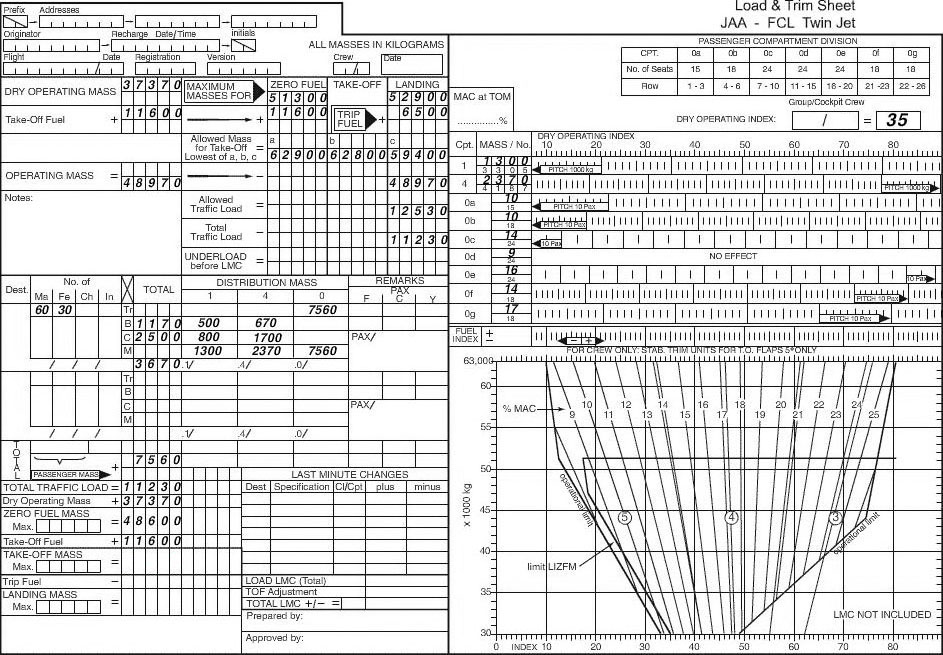
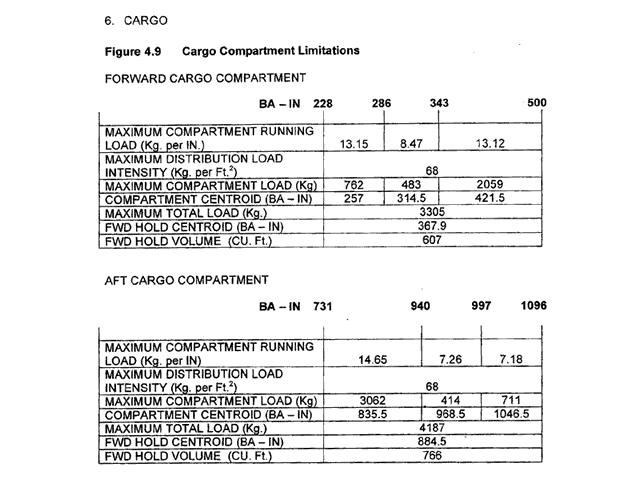
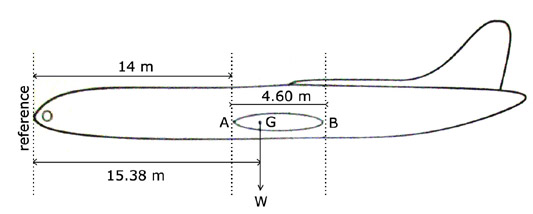
17 350 kg. Planning an ifr flight from paris to london for the twin jet aeroplane ?
Question 90-14 : 1000 kg 1500 lbs 1100 kg 1000 lbs
Provided that flight conditions on the leg gamma to delta remain unchanged and ?
Question 90-15 : 4475 kg 4745 kg 4635 kg 4250 kg
 4475 kg.
4475 kg. The required time for final reserve fuel for turbojet aeroplane is ?
Question 90-16 : 30 minutes 45 minutes 60 minutes variable with wind velocity
 30 minutes.
30 minutes. A flight has to be made with a single engine aeroplane .for the fuel ?
Question 90-17 : 276 lbs 265 lbs 208 lbs 250 lbs
 276 lbs.
276 lbs. See flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 5 2 and 4 5 3 1.given .distance c d ?
Question 90-18 : 14 500 kg 14 200 kg 17 800 kg 17 500 kg
 14 500 kg.
14 500 kg. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 5 4.planning an ifr ?
Question 90-19 : 273 kg 320 kg 210 kg 263 kg
 273 kg.
273 kg. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 paragraph 2 1 and figure 4 ?
Question 90-20 : Fmp 4% fmp 0% fmp 1% fmp 10%
 Fmp 4%
Fmp 4% The final reserve fuel for aeroplanes with turbine engines is ?
Question 90-21 : Fuel to fly for 30 minutes at holding speed at 1500 ft 450 m above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions fuel to fly for 45 minutes at holding speed at 1500 ft 450 m above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions fuel to fly for 45 minutes at holding speed at 1000 ft 300 m above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions fuel to fly for 60 minutes at holding speed at 1500 ft 450 m above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions
 Fuel to fly for 30 minutes at holding speed at 1500 ft (450 m) above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions.
Fuel to fly for 30 minutes at holding speed at 1500 ft (450 m) above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions. The fuel burn of an aircraft turbine engine is 220 l/h with a fuel density of 0 ?
Question 90-22 : 235 l/h 206 l/h 220 l/h 176 l/h
 235 l/h.
235 l/h. At reference or see flight planning manual mep1 figure 3 1.a flight is to be ?
Question 90-23 : 6 us gallon 9 us gallon 12 us gallon 3 us gallon
 6 us gallon.
6 us gallon. When using decision point procedure you reduce the ?
Question 90-24 : Contingency fuel by adding contingency only from the burnoff between decision point and destination contingency fuel by adding contingency only from the burnoff between the decision airport and destination reserve fuel from 10% down to 5% holding fuel by 30%
 Contingency fuel by adding contingency only from the burnoff between decision point and destination.
Contingency fuel by adding contingency only from the burnoff between decision point and destination. A jet aeroplane is to fly from a to b the minimum final reserve fuel must allow ?
Question 90-25 : 30 minutes hold at 1500 ft above destination aerodrome elevation when no alternate is required 20 minutes hold over alternate airfield 30 minutes hold at 1500 ft above mean sea level 15 minutes hold at 1500 ft above destination aerodrome elevation
 30 minutes hold at 1500 ft above destination aerodrome elevation, when no alternate is required.
30 minutes hold at 1500 ft above destination aerodrome elevation, when no alternate is required. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 5 1. given brake ?
Question 90-26 : 1138 kg 1040 kg 1238 kg 1387 kg
 1138 kg
1138 kg At reference or see flight planning manual sep 1 figure 2 2 table 2 2 3.using ?
Question 90-27 : 160 kt and 69 3 lbs/h 158 kt and 74 4 lbs/h 160 kt and 71 1 lbs/h 159 kt and 71 7 lbs/h
 160 kt and 69.3 lbs/h.
160 kt and 69.3 lbs/h. At reference or see flight planning manual mep 1 figure 3 3.a flight has to be ?
Question 90-28 : 91 us gallons 76 us gallons 118 us gallons 86 us gallons
 91 us gallons.
91 us gallons. Integrated range' curves or tables are presented in the aeroplane operations ?
Question 90-29 : To determine the fuel consumption for a certain still air distance considering the decreasing fuel flow with decreasing mass to determine the flight time for a certain leg under consideration of temperature deviations to determine the still air distance for a wind components varying with altitude to determine the optimum speed considering the fuel cost as well as the time related cost of the aeroplane
 To determine the fuel consumption for a certain still air distance considering the decreasing fuel flow with decreasing mass.
To determine the fuel consumption for a certain still air distance considering the decreasing fuel flow with decreasing mass. At reference or see flight planning manual sep 1 figure 2 4 .using the range ?
Question 90-30 : 865 nm 739 nm 851 nm 911 nm
 865 nm.
865 nm. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 4. the final reserve ?
Question 90-31 : Pressure altitude aeroplane mass and flaps up with minimum drag airspeed pressure altitude aeroplane mass and flaps down with maximum range speed pressure altitude aeroplane mass and flaps up with maximum range speed pressure altitude aeroplane mass and flaps down with minimum drag airspeed
 Pressure altitude, aeroplane mass and flaps up with minimum drag airspeed
Pressure altitude, aeroplane mass and flaps up with minimum drag airspeed Finish the endurance/fuel calculation and determine atc endurance for a twin ?
Question 90-32 : Atc endurance 04 07 atc endurance 04 12 atc endurance 03 37 atc endurance 03 52
 Atc endurance: 04:07
Atc endurance: 04:07 Given .oat +5°c.during climb average head wind component 20 kt.take off from ?
Question 90-33 : 9 min 3 3 usg 10 min 3 6 usg 7 min 2 6 usg 9 min 2 7 usg
 9 min. 3,3 usg
9 min. 3,3 usg Maximum allowable take off mass 64 400 kg.maximum landing mass 56 200 ?
Question 90-34 : 11 100 kg 11 400 kg 14 400 kg 8 600 kg
 11 100 kg.
11 100 kg. At reference or use flight planning manual sep 1 table 2 2 3 .given .fl 70.oat ?
Question 90-35 : 12 35 gph tas 159 kt 73 90 gph tas 159 kt 12 35 gph tas 151 kt 11 95 gph tas 160 kt
 12.35 gph, tas: 159 kt.
12.35 gph, tas: 159 kt. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 5 3 1. given flight ?
Question 90-36 : 345 nam. 2000 kg 350 nam. 2000 kg 345 nam. 2100 kg 437 nam. 2100 kg
 345 namxsx 2000 kg
345 namxsx 2000 kg Planning a flight from paris charles de gaulle to london heathrow for a twin ?
Question 90-37 : 51 629 kg 55 765 kg 51 425 kg 52 265 kg
 51 629 kg.
51 629 kg. You are to determine the maximum fuel load which can be carried in the ?
Question 90-38 : 800 kg 1000 kg 700 kg 500 kg
 800 kg.
800 kg. At reference or see flight planning manual mrjt 1 figure 4 5 1.given .brake ?
Question 90-39 : 1700 kg 1650 kg 1750 kg 1800 kg
 1700 kg.
1700 kg. At reference or see flight planning manual sep 1 figure 2 1. given .take off ?
Question 90-40 : 22 min 6 7 gal 45 nam 24 min 7 7 gal 47 nam 16 5 min 4 9 gal 34 5 nam 23 min 7 7 gal 50 nam
 22 min, 6.7 gal, 45 nam
22 min, 6.7 gal, 45 nam ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
3559 Free Training Exam
