To minimize the risk of hydroplaning during landing the pilot should ? [ Validation Marking ]
Question 89-1 : Make a 'positive' landing and apply maximum reverse thrust and brakes as quickly as possible use maximum reverse thrust and should start braking below the hydroplaning speed use normal landing braking and reverse technique postpone the landing until the risk of hydroplaning no longer exists
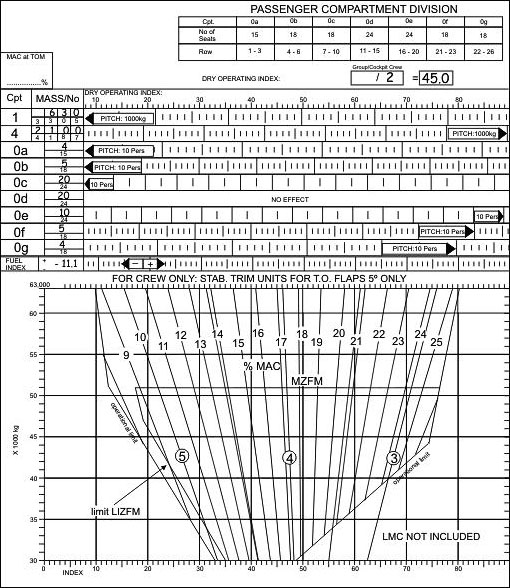
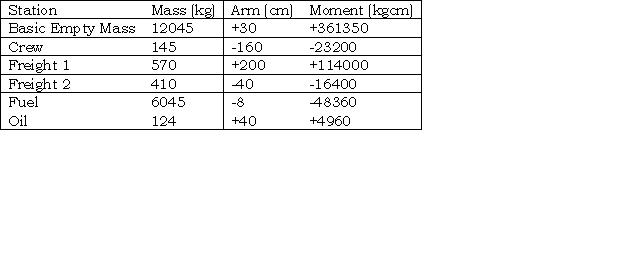
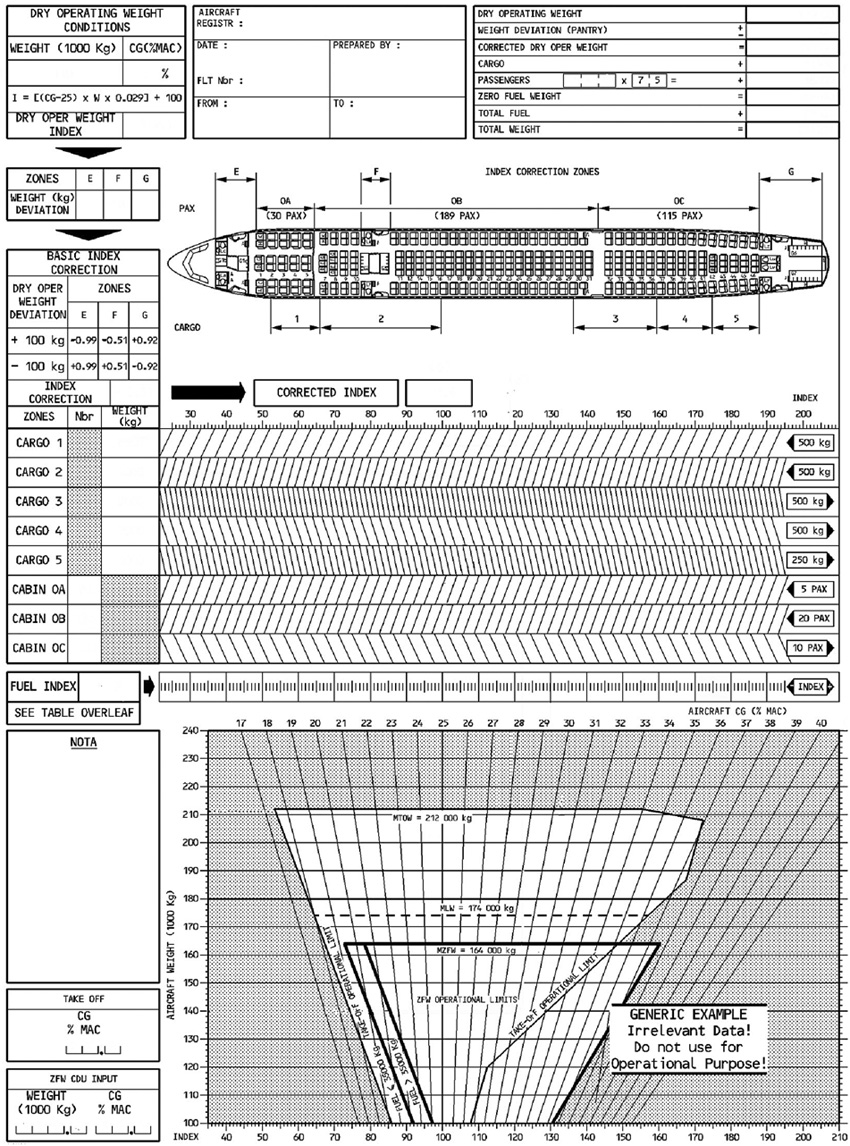
The stopway is an area which allows an increase only in the ?
Question 89-2 : Accelerate stop distance available take off run available take off distance available landing distance available
 Accelerate-stop distance available.
Accelerate-stop distance available. Vr cannot be lower than ?
Question 89-3 : V1 and 105% of vmca 105% of v1 and vmca 1 2 vs for twin and three engine jet aeroplane 1 15 vs for turbo prop with three or more engines
 V1 and 105% of vmca.
V1 and 105% of vmca. The one engine out take off run is the distance between the brake release point ?
Question 89-4 : The middle of the segment between vlof point and 35 ft point the lift off point the point where v2 is reached the point half way between v1 and v2
 The middle of the segment between vlof point and 35 ft point.
The middle of the segment between vlof point and 35 ft point. The decision speed at take off v1 is the calibrated airspeed ?
Question 89-5 : Below which take off must be rejected if an engine failure is recognized above which take off should be continued at which the take off must be rejected below which the take off must be continued at which the failure of the critical engine is expected to occur
 Below which take-off must be rejected if an engine failure is recognized, above which take-off should be continued.
Below which take-off must be rejected if an engine failure is recognized, above which take-off should be continued. Regarding unaccelerated horizontal flight minimum drag is ?
Question 89-6 : Proportional to aircraft mass a function of the pressure altitude a function of the density altitude independent of the aircraft mass
 Proportional to aircraft mass.
Proportional to aircraft mass. If the aircraft mass in a horizontal unaccelerated flight decreases ?
Question 89-7 : The minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag decreases the minimum drag increases and the ias for minimum drag decreases the minimum drag increases and the ias for minimum drag increases the minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag increases
 The minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag decreases.
The minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag decreases. Density altitude is the ?
Question 89-8 : Pressure altitude corrected for 'non standard' temperature altitude reference to the standard datum plane altitude read directly from the altimeter height above the surface
 Pressure altitude corrected for 'non standard' temperature.
Pressure altitude corrected for 'non standard' temperature. The density altitude ?
Question 89-9 : Is used to determine the aeroplane performance is equal to the pressure altitude is used to establish minimum clearance of 2 000 feet over mountains is used to calculate the fl above the transition altitude
 Is used to determine the aeroplane performance.
Is used to determine the aeroplane performance. Which of the following combinations adversely affects take off and initial ?
Question 89-10 : High temperature and high relative humidity low temperature and high relative humidity high temperature and low relative humidity low temperature and low relative humidity
 High temperature and high relative humidity.
High temperature and high relative humidity. What effect has a downhill slope on the take off speeds the slope ?
Question 89-11 : Decreases the take off speed v1 decreases the tas for take off increases the ias for take off has no effect on the take off speed v1
 Decreases the take-off speed v1.
Decreases the take-off speed v1. During climb to the cruising level a headwind component ?
Question 89-12 : Decreases the ground distance flown during that climb increases the amount of fuel for the climb increases the climb time decreases the climb time
 Decreases the ground distance flown during that climb.
Decreases the ground distance flown during that climb. What affect has a tailwind on the maximum endurance speed ?
Question 89-13 : No affect tailwind only effects holding speed the ias will be increased the ias will be decreased
 No affect.
No affect. During climb with all engines the altitude where the rate of climb reduces to ?
Question 89-14 : Service ceiling absolute ceiling thrust ceiling aerodynamic ceiling
The maximum rate of climb that can be maintained at the absolute ceiling is ?
Question 89-15 : 0 ft/min 125 ft/min 500 ft/min 100 ft/min
 0 ft/min.
0 ft/min. A twin engine aeroplane is flying at the minimum control speed with take off ?
Question 89-16 : Straight flight straight flight and altitude heading altitude and a positive rate of climb of 100 ft/min altitude
The speed v2 is ?
Question 89-17 : The take off safety speed that speed at which the pic should decide to continue or not the take off in the case of an engine failure the lowest airspeed required to retract flaps without stall problems the lowest safety airspeed at which the aeroplane is under control with aerodynamic surfaces in the case of an engine failure
 The take-off safety speed.
The take-off safety speed. Which take off speed is affected by the presence or absence of stopway and/or ?
Question 89-18 : V1 v2 vmcg vmca
 V1.
V1. Maximum and minimum values of v1 are limited by ?
Question 89-19 : Vr and vmcg v2 and vmca vr and vmca v2 and vmcg
 Vr and vmcg.
Vr and vmcg. Take off run is defined as the ?
Question 89-20 : Horizontal distance along the take off path from the start of the take off to a point equidistant between the point at which vlof is reached and the point at which the aeroplane is 35 ft above the take off surface distance to v1 and stop assuming an engine failure at v1 distance to 35 feet with an engine failure at v1 or 115% all engine distance to 35 feet distance from brake release to v2
 Horizontal distance along the take-off path from the start of the take-off to a point equidistant between the point at which vlof is reached and the point at which the aeroplane is 35 ft above the take-off surface.
Horizontal distance along the take-off path from the start of the take-off to a point equidistant between the point at which vlof is reached and the point at which the aeroplane is 35 ft above the take-off surface. The minimum value of v2 must exceed vmc by ?
Question 89-21 : 10% 15% 20% 30%
 10%.
10%. Which of the following is true according to the relevant regulations for turbo ?
Question 89-22 : Maximum landing distance at the destination aerodrome and at any alternate aerodrome is 0 7 x lda landing distance available maximum landing distance at destination is 0 95 x lda landing distance available maximum take off run is 0 5 x runway maximum use of clearway is 1 5 x runway
 Maximum landing distance at the destination aerodrome and at any alternate aerodrome is 0.7 x lda (landing distance available).
Maximum landing distance at the destination aerodrome and at any alternate aerodrome is 0.7 x lda (landing distance available). For take off obstacle clearance calculations obstacles may be avoided ?
Question 89-23 : By banking not more than 15° between 50 ft and 400 ft above the runway elevation by banking as much as needed if aeroplane is more than 50 ft above runway elevation only by using standard turns by standard turns but only after passing 1500 ft
 By banking not more than 15° between 50 ft and 400 ft above the runway elevation.
By banking not more than 15° between 50 ft and 400 ft above the runway elevation. The speed vr ?
Question 89-24 : Is the speed at which rotation to the lift off angle of attack is initiated must be higher than v2 must be higher than vlof must be equal to or lower than v1
 Is the speed at which rotation to the lift-off angle of attack is initiated.
Is the speed at which rotation to the lift-off angle of attack is initiated. If the take off mass of an aeroplane is brake energy limited a higher uphill ?
Question 89-25 : Increase the maximum mass for take off decrease the maximum mass for take off have no effect on the maximum mass for take off decrease the required take off distance
 Increase the maximum mass for take-off.
Increase the maximum mass for take-off. If the take off mass of an aeroplane is tyre speed limited downhill slope would ?
Question 89-26 : Have no effect on the maximum mass for take off decrease the maximum mass for take off increase the maximum mass for take off increase the required take off distance
 Have no effect on the maximum mass for take-off.
Have no effect on the maximum mass for take-off. The take off mass could be limited by ?
Question 89-27 : The take off distance available toda the maximum brake energy and the climb gradient with one engine inoperative the take off distance available toda only the maximum brake energy only the climb gradient with one engine inoperative only
 The take-off distance available (toda), the maximum brake energy and the climb gradient with one engine inoperative.
The take-off distance available (toda), the maximum brake energy and the climb gradient with one engine inoperative. The climb limited take off mass can be increased by ?
Question 89-28 : A lower flap setting for take off and selecting a higher v2 selecting a lower v1 selecting a lower v2 selecting a lower vr
 A lower flap setting for take-off and selecting a higher v2.
A lower flap setting for take-off and selecting a higher v2. In the event that the take off mass is obstacle limited and the take off flight ?
Question 89-29 : 15 degrees up to height of 400 ft 10 degrees up to a height of 400 ft 20 degrees up to a height of 400 ft 25 degrees up to a height of 400 ft
 15 degrees up to height of 400 ft.
15 degrees up to height of 400 ft. Which speed provides maximum obstacle clearance during climb ?
Question 89-30 : The speed for which the ratio between rate of climb and forward speed is maximum v2 + 10 kt the speed for maximum rate of climb v2
 The speed for which the ratio between rate of climb and forward speed is maximum.
The speed for which the ratio between rate of climb and forward speed is maximum. The take off mass of an aeroplane is restricted by the climb limit what would ?
Question 89-31 : None the effect would vary depending upon the height of any obstacle within the net take off flight path the climb limited take off mass would increase the climb limited take off mass would decrease
 None.
None. If other factors are unchanged the fuel mileage nautical miles per kg is ?
Question 89-32 : Lower with a forward centre of gravity position independent from the centre of gravity position lower with an aft centre of gravity position higher with a forward centre of gravity position
 Lower with a forward centre of gravity position.
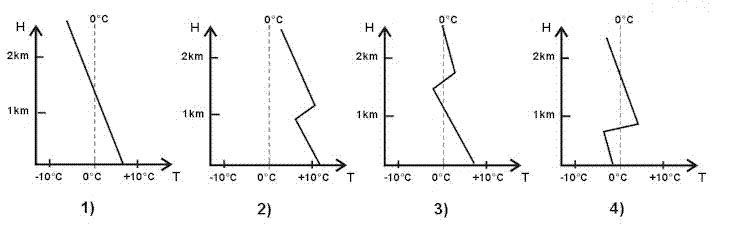
Lower with a forward centre of gravity position. Considering a rate of climb diagram rate of climb versus tas for an aeroplane ?
Question 89-33 : Diagram a diagram b diagram c diagramd
 Diagram a.
Diagram a. What is the effect of increased mass on the performance of a gliding aeroplane ?
Question 89-34 : The speed for best angle of descent increases there is no effect the gliding angle decreases the lift/drag ratio decreases
 The speed for best angle of descent increases.
The speed for best angle of descent increases. Which force compensates the weight in unaccelerated straight and level flight ?
Question 89-35 : The lift the thrust the drag the resultant from lift and drag
 The lift.
The lift. In which of the flight conditions listed below is the thrust required equal to ?
Question 89-36 : In level flight with constant ias in accelerated level flight in a climb with constant ias in a descent with constant tas
 In level flight with constant ias.
In level flight with constant ias. The load factor in a turn in level flight with constant tas depends on ?
Question 89-37 : The bank angle only the radius of the turn and the bank angle the true airspeed and the bank angle the radius of the turn and the weight of the aeroplane
 The bank angle only.
The bank angle only. The induced drag of an aeroplane ?
Question 89-38 : Decreases with increasing airspeed decreases with increasing gross weight is independent of the airspeed increases with increasing airspeed
 Decreases with increasing airspeed.
Decreases with increasing airspeed. The induced drag of an aeroplane at constant mass in un accelerated level ?
Question 89-39 : The lowest achievable speed in a given configuration vs1 vmo va
 The lowest achievable speed in a given configuration.
The lowest achievable speed in a given configuration. The point where drag coefficient/lift coefficient is a minimum is ?
Question 89-40 : The lowest point of the drag curve the point where a tangent from the origin touches the drag curve at stalling speed vs on the 'back side' of the drag curve
 The lowest point of the drag curve.
The lowest point of the drag curve. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
3519 Free Training Exam
