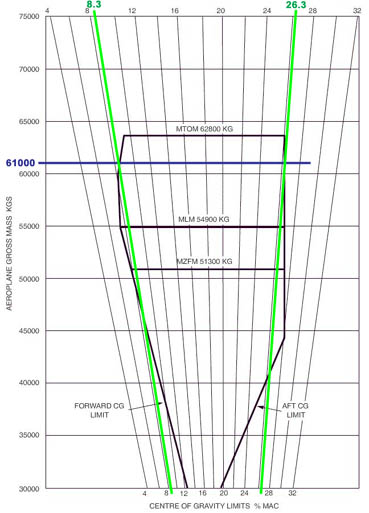
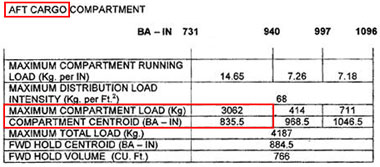
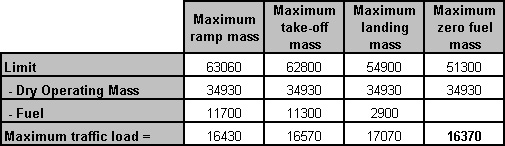
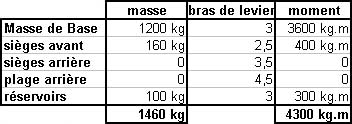
Omnidirectional departure normally allow departure in any direction if any ? [ Question security ]
Question 8-1 : Bearings and distances flying speed and time to reach the restriction gps coordinates latitude and longitude of the relevant point
 Bearings and distances.
Bearings and distances. Unless otherwise published or instructed by atc all turns after initial entry ?
Question 8-2 : To the right to the left at pilot's discretion it depends upon the inbound holding track
 To the right.
To the right. Altimeter pressure settings provided to aircraft shall be rounded ?
Question 8-3 : Down to the next hectopascal down to the next half hectopascal up to the next half hectopascal up to the next hectopascal
 Down to the next hectopascal.
Down to the next hectopascal. For the construction of precision approaches which is the operationally ?
Question 8-4 : 3° 2 5% 3% 5°
 3°.
3°. In an instrument approach procedures what is the name of segment connecting ?
Question 8-5 : Intermediate segment missed approach segment arrival segment secondary segment
 Intermediate segment.
Intermediate segment. The fixes connecting the arrival segment and final approach fix or point are ?
Question 8-6 : Iaf and if if and mapt faf/fap and mapt iaf and mapt
 Iaf and if.
Iaf and if. When should the flight crew shall be provided with the transition level ?
Question 8-7 : Before beginning the initial approach to an aerodrome before take off before top of descent before fl100
 Before beginning the initial approach to an aerodrome.
Before beginning the initial approach to an aerodrome. Approach segments .in an instrument approach procedures during the intermediate ?
Question 8-8 : The aircraft speed and configuration should be adjusted to prepare the aircraft for final approach alignment and descent for landing are made the aircraft is manoeuvring to enter the initial approach segment the aircraft leaves the en route structure to enter approach segment
 The aircraft speed and configuration should be adjusted to prepare the aircraft for final approach.
The aircraft speed and configuration should be adjusted to prepare the aircraft for final approach. Approach segments .in an instrument approach procedures during the initial ?
Question 8-9 : The aircraft leaves the en route structure and is manoeuvring to enter the intermediate approach.segment the aircraft speed and configuration should be adjusted to prepare the aircraft for final approach alignment and descent for landing are made the aircraft speed is adjusted to 1 2 stall speed
 The aircraft leaves the en-route structure and is manoeuvring to enter the intermediate approachxsxsegment.
The aircraft leaves the en-route structure and is manoeuvring to enter the intermediate approachxsxsegment. A control zone shall extend laterally to at least ?
Question 8-10 : 5 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned in the direction from which approaches may be made 10 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned in the direction from which approaches may be made 15 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned in the direction from which approaches may be made 20 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned in the direction from which approaches may be made
 5 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned in the direction from which approaches may be made.
5 nm from the centre of the aerodrome or aerodromes concerned in the direction from which approaches may be made. A controlled airspace extending upwards from a specified limit above the earth ?
Question 8-11 : Control area control zone advisory airspace flight information region
 Control area.
Control area. A controlled airspace extending upwards from the surface of the earth to a ?
Question 8-12 : Control zone control area air traffic zone advisory airspace
 Control zone.
Control zone. Which is the content of section 2 of air report airep ?
Question 8-13 : Estimated time of arrival eta endurance estimated elapse time eet endurance present position estimated time of arrival eta estimated time over fir boundary endurance
 Estimated time of arrival (eta), endurance.
Estimated time of arrival (eta), endurance. A lower limit of a control area shall be established at a height above the ?
Question 8-14 : 200 metres 300 metres 150 metres 500 metres
 200 metres.
200 metres. A minimum vertical separation shall be provided until aircraft are established ?
Question 8-15 : 300 m 1000 ft 200 m 660 ft 150 m 500 ft 100 m 330 ft
 300 m (1000 ft).
300 m (1000 ft). A 'rnav' distance based separation minimum may be used at the time the level is ?
Question 8-16 : 80 nm 50 nm 20 nm 60 nm
 80 nm.
80 nm. A separation minimum shall be applied between a light or medium aircraft and a ?
Question 8-17 : Less than 760 m 760 m less than 730 m 730 m
 Less than 760 m.
Less than 760 m. A so called 'visual approach' can be performed ?
Question 8-18 : During ifr flights if there is permanent sight on the movement area and the underlying ground during ifr and vfr flights in vmc during ifr flights if the cloudbase is 1000 ft more than the appropriate da or mda for that procedure as in above but in addition there should be a visibility of 5 5 km or more
 During ifr flights, if there is permanent sight on the movement area and the underlying ground.
During ifr flights, if there is permanent sight on the movement area and the underlying ground. A special air report comprises a number of sections in section i the pilot ?
Question 8-19 : A position report including aircraft identification height position and time weather noted flight identification and weather noted urgent messages
A strayed aircraft is ?
Question 8-20 : An aircraft which has deviated significantly from its intended track or which reports that it is lost only that aircraft which has deviated significantly its intended track only that aircraft which reports that it is lost an aircraft in a given area but whose identity has not been established
 An aircraft which has deviated significantly from its intended track or which reports that it is lost
An aircraft which has deviated significantly from its intended track or which reports that it is lost A vfr flight when flying inside an ats airspace classified as b has to maintain ?
Question 8-21 : 5 km below 3050 m 10 000 ft ams 1 500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds 5 km visibility 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds 5 km below 3050 m 10 000 ft amsl and clear of clouds 8 km below 3050 m 10 000 ft amsl 1 500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds
A vfr flight when flying inside an ats airspace classified as c has to maintain ?
Question 8-22 : 8 km at or above 3050 m 10000 ft amsl 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds 5 km at or above 3050 m 10000 ft amsl 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds 5 nm at or above 3050 m 10000 ft amsl 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds 8 km at or above 3050 m 10000 ft amsl and clear of clouds
 8 km at or above 3050 m (10000 ft) amsl 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds.
8 km at or above 3050 m (10000 ft) amsl 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds. According to international agreements wind direction shall be adjusted to the ?
Question 8-23 : Before landing and take off when the local variation exceeds 10° east or 10° west in upper wind forecast for areas north of lat 60° north or 60° south when an aircraft on the request by a meteorological watch office mwo or at specified points transmits a pirep
 Before landing and take-off.
Before landing and take-off. Aerodrome control service priority for landing .if an aircraft enters the ?
Question 8-24 : It shall be permitted to land if its actions indicate that it so desires it shall not be permitted to land it shall not be permitted to land unless it becomes evident that the aircraft is in a state of emergency it shall only be permitted to land after having received proper authorisation from the aerodrome authority
 It shall be permitted to land if its actions indicate that it so desires.
It shall be permitted to land if its actions indicate that it so desires. Air traffic control service is provided for the purpose of ?
Question 8-25 : Preventing collisions between aircraft between aircraft and obstacles on the manoeuvring area and expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of air traffic preventing collisions between controlled air traffic and expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of air traffic avoiding collisions between all aircraft and maintaining an orderly flow of air traffic applying separation between aircraft and expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of air traffic
 Preventing collisions between aircraft, between aircraft and obstacles on the manoeuvring area and expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of air traffic.
Preventing collisions between aircraft, between aircraft and obstacles on the manoeuvring area and expediting and maintaining an orderly flow of air traffic. Air traffic service unit means ?
Question 8-26 : Air traffic control units flight information centres or air services reporting offices air traffic control units and flight information centres air traffic control units and air services reporting offices flight information centres and air services reporting offices
 Air traffic control units, flight information centres or air services reporting offices.
Air traffic control units, flight information centres or air services reporting offices. Air traffic services unit clocks and other time recording devices shall be ?
Question 8-27 : 30 seconds of utc at all times 15 seconds of utc at all times 10 seconds of utc at all times 1 minute of utc at all times
 30 seconds of utc at all times.
30 seconds of utc at all times. Aircraft flying along the same track may be separated by dme distances from the ?
Question 8-28 : 10 nm 15 nm 20 nm 12 nm
 10 nm.
10 nm. Airspace classification services.during a 'visual approach' in controlled ?
Question 8-29 : Atc will provide separation with other traffic atc will provide separation only between flights under ifr atc will provide separation with arriving but not with departing traffic pilots are responsible for separation with arriving and departing aircraft
 Atc will provide separation with other traffic.
Atc will provide separation with other traffic. Altimeter setting change during climb .on flights in accordance with ifr the ?
Question 8-30 : Transition altitude transition level transition layer level specified by atc
 Transition altitude.
Transition altitude. The transition level ?
Question 8-31 : Shall be the lowest flight level available for use above the transition altitude shall be the highest available flight level below the transition altitude that has been established is published for the aerodrome in the section enr of the aip is calculated and declared for an approach by the pilot in command
 Shall be the lowest flight level available for use above the transition altitude.
Shall be the lowest flight level available for use above the transition altitude. Altimeter setting procedures transition altitude .the transition altitude of ?
Question 8-32 : 3000 ft 2500 ft 1500 ft 1000 ft
 3000 ft.
3000 ft. Altimeter setting procedures transition layer .unless instructed otherwise by ?
Question 8-33 : Altitude in a descent altitude in a climb flight level in a descent either altitude or flight level in a climb
 Altitude in a descent.
Altitude in a descent. Altimeter setting procedures transition level .the vertical position of an ?
Question 8-34 : As flight level according pilot's choice as altitude as height
 As flight level.
As flight level. The transition level ?
Question 8-35 : Will be passed to aircraft by ats units is published on the approach and landing chart for each aerodrome is calculated by the pilot in command is published and updated in the notam
 Will be passed to aircraft by ats units.
Will be passed to aircraft by ats units. An air traffic control unit ?
Question 8-36 : May ask an aircraft to temporarily change its call sign for safety reasons when there is a risk of confusion between two or more similar call signs may require to change the call sign for safety reasons when there is a risk of confusion between two or more similar call signs providing the aircraft is on a repetitive flight plan must not ask an aircraft to change its call sign may not ask an aircraft to change its call sign after accepting the flight plan
 May ask an aircraft to temporarily change its call sign for safety reasons when there is a risk of confusion between two or more similar call signs.
May ask an aircraft to temporarily change its call sign for safety reasons when there is a risk of confusion between two or more similar call signs. An aircraft in climb or descent is considered to have crossed a level when the ?
Question 8-37 : More than 300 ft more than 100 ft 1000 ft more than 500 ft
 More than 300 ft.
More than 300 ft. An aircraft intercepted by another aircraft shall immediately attempt to ?
Question 8-38 : 121 5 mhz 243 mhz 121 5 mhz 125 5 mhz 121 5 mhz 282 8 mhz 243 mhz 125 5 mhz
 121.5 mhz - 243 mhz
121.5 mhz - 243 mhz Outside rvsm airspace an aircraft is considered to be maintaining its assigned ?
Question 8-39 : +/ 300 ft of the assigned level +/ 500 ft of the assigned level +/ 200 ft of the assigned level +/ 250 ft of the assigned level
 +/- 300 ft of the assigned level.
+/- 300 ft of the assigned level. An aircraft is considered to overtake another if it approaches the other ?
Question 8-40 : 70 degrees with the plane of symmetry of the latter 50 degrees with the plane of symmetry of the latter 60 degrees with the plane of symmetry of the latter 80 degrees with the plane of symmetry of the latter
 70 degrees with the plane of symmetry of the latter.
70 degrees with the plane of symmetry of the latter. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
279 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 8
