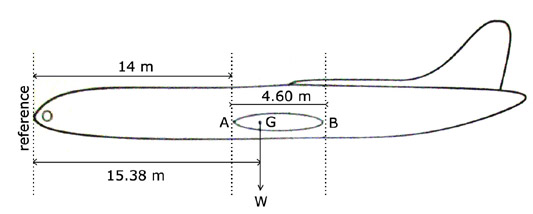
Which statement regarding the relationship between traffic load and range is ? [ Study Manual ]
Question 78-1 : The traffic load can be limited by the desired range the maximum zero fuel mass limits the maximum quantity of fuel the maximum landing mass is basically equal to the maximum zero fuel mass the maximum traffic load is not limited by the reserve fuel quantity
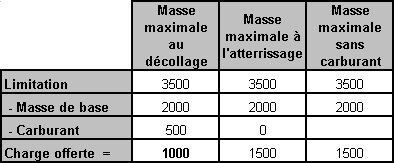 The traffic load can be limited by the desired range.
The traffic load can be limited by the desired range. Which statement regarding v1 is correct ?
Question 78-2 : Vr may not be lower than v1 v1 may not be higher than vmcg when determining v1 reverse thrust may only be used on the remaining symmetric engines the correction for up slope on the balanced v1 is negative
An increase in atmospheric pressure has among other things the following ?
Question 78-3 : A reduced landing distance and improved go around performance an increased landing distance and degraded go around performance an increased landing distance and improved go around performance a reduced landing distance and degraded go around performance
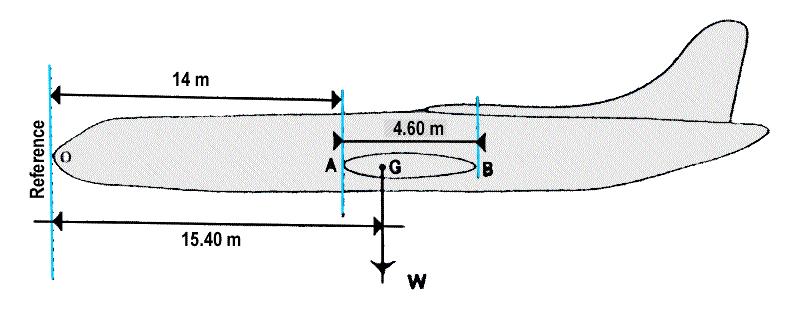 A reduced landing distance and improved go-around performance.
A reduced landing distance and improved go-around performance. A decrease in atmospheric pressure has among other things the following ?
Question 78-4 : An increased take off distance and degraded initial climb performance a reduced take off distance and improved initial climb performance an increased take off distance and improved initial climb performance a reduced take off distance and degraded initial climb performance
An increase in atmospheric pressure has among other things the following ?
Question 78-5 : A reduced take off distance and improved initial climb performance an increases take off distance and degraded initial climb performance an increased take off distance and improved initial climb performance a reduced take off distance and degraded initial climb performance
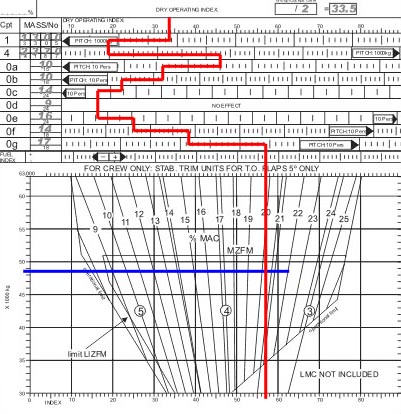 A reduced take-off distance and improved initial climb performance.
A reduced take-off distance and improved initial climb performance. The take off distance of an aircraft is 600m in standard atmosphere no wind at ?
Question 78-6 : 755 m 715 m 555 m 685 m
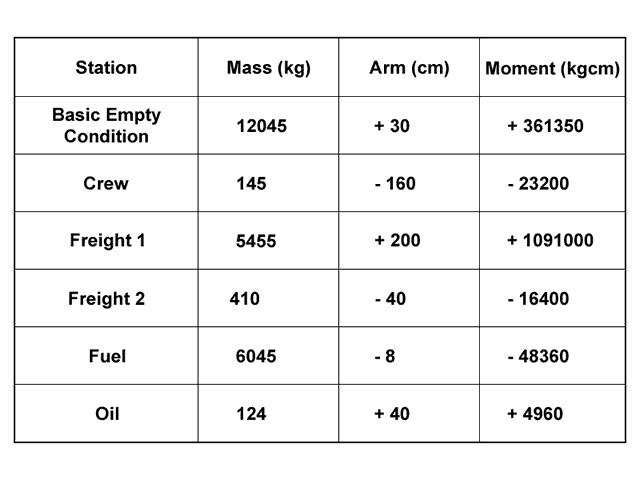 755 m.
755 m. An aircraft has two certified landing flaps positions 25° and 35° .if a pilot ?
Question 78-7 : A reduced landing distance and degraded go around performance a reduced landing distance and better go around performance an increased landing distance and degraded go around performance an increased landing distance and better go around performance
 A reduced landing distance and degraded go-around performance.
A reduced landing distance and degraded go-around performance. A runway is contaminated by a 0 5 cm layer of wet snow the take off distance in ?
Question 78-8 : Increased unchanged decreased very significantly decreased
 Increased.
Increased. With an true airspeed of 194 kt and a vertical speed of 1000 ft/min the climb ?
Question 78-9 : 5 1% 3 5% 5 4% 4 5%
 5.1%.
5.1%. If the airworthiness documents do not specify a correction for landing on a wet ?
Question 78-10 : 15% 5% 10% 20%
 15%.
15%. What percentages of the head wind and tail wind component are taken into ?
Question 78-11 : 50% head wind and 150% tail wind 100% head wind and 100% tail wind 50% head wind and 100% tail wind 150% head wind and 50% tail wind
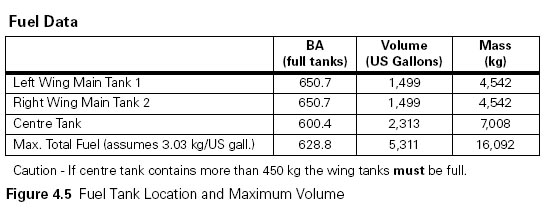 50% head wind and 150% tail wind.
50% head wind and 150% tail wind. If all other parameters remain constant what is the influence of mass on the ?
Question 78-12 : The roc speed increases with increasing mass the roc speed decreases with increasing mass the roc is affected by the mass but not the roc speed the roc and the roc speed are independent of the mass
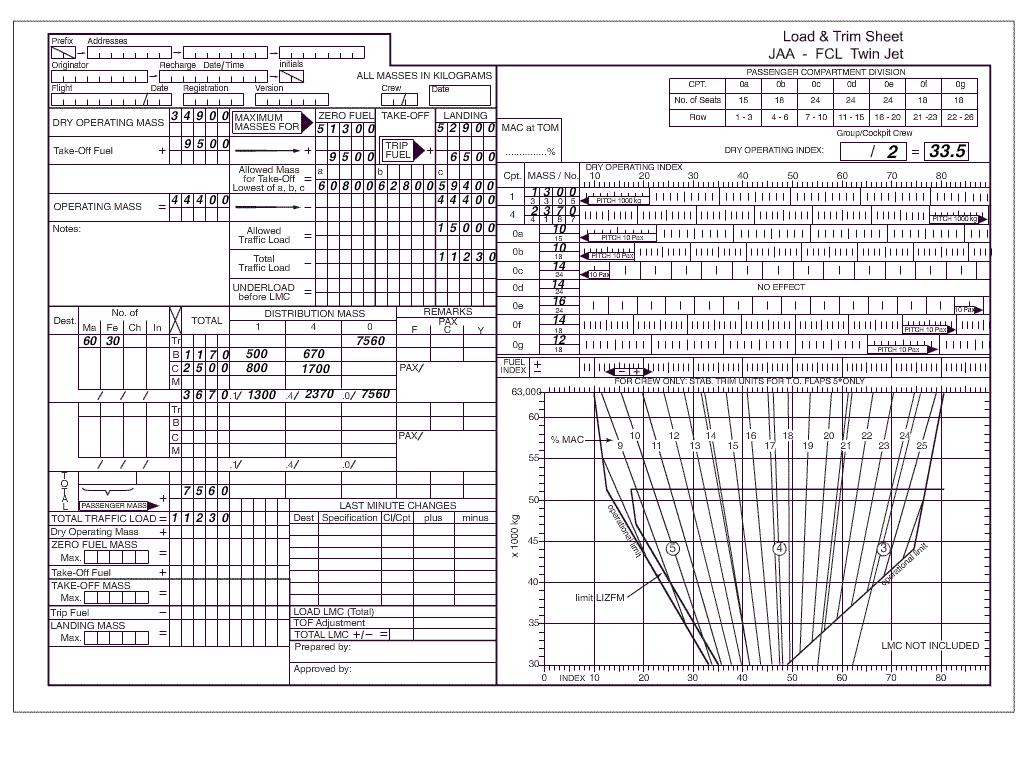 The roc speed increases with increasing mass.
The roc speed increases with increasing mass. What is the equation for the climb gradient expressed in percentage during ?
Question 78-13 : Climb gradient = thrust drag /weight x 100 climb gradient = thrust + drag /lift x 100 climb gradient = thrust mass /lift x 100 climb gradient = lift/weight x 100
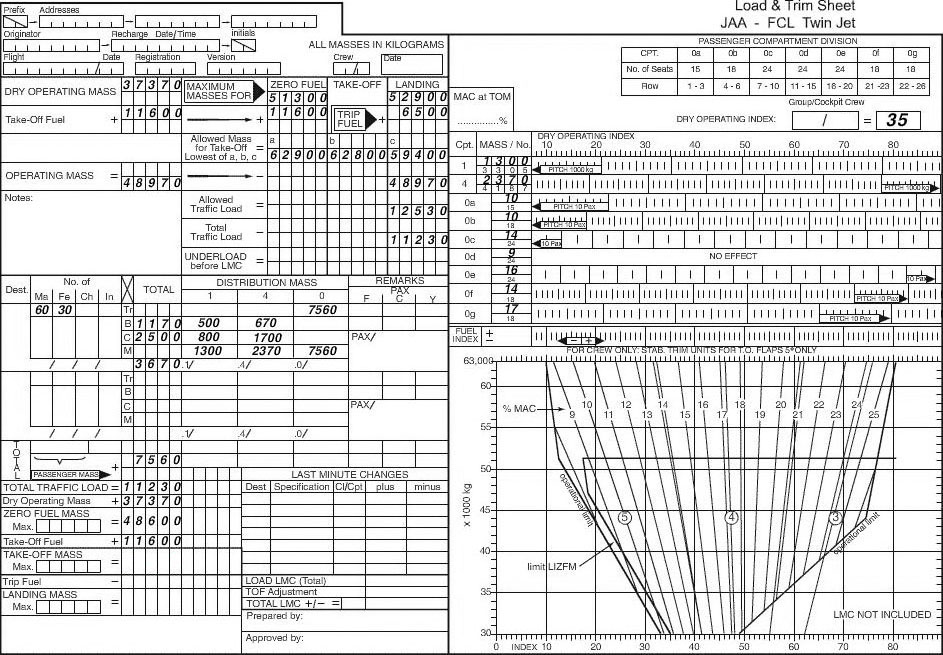 Climb gradient = ((thrust - drag)/weight) x 100
Climb gradient = ((thrust - drag)/weight) x 100 The take off runway performance requirements for transport category aeroplanes ?
Question 78-14 : Failure of the critical engine or all engines operating whichever requirement gives the greater distance all engines operating only one engine inoperative only failure of the critical engine only
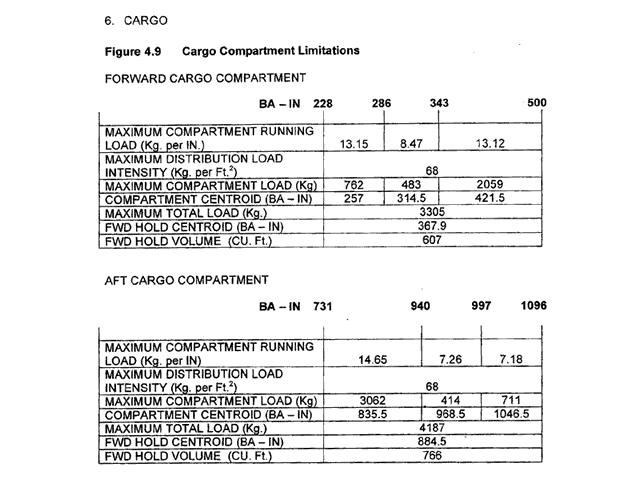 Failure of the critical engine or all engines operating whichever requirement gives the greater distance.
Failure of the critical engine or all engines operating whichever requirement gives the greater distance. Which combination of answers of the following parameters give an increase or ?
Question 78-15 : 1 3 5 and 8 1 4 6 and 8 2 4 5 and 7 2 3 6 and 7
 1, 3, 5 and 8.
1, 3, 5 and 8. In certain conditions v2 can be limited by vmca ?
Question 78-16 : Low take off mass large flap extension low field elevation low take off mass small flap extension low field elevation high take off mass large flap extension low field elevation high take off mass small flap extension high field elevation
 Low take-off mass, large flap extension, low field elevation.
Low take-off mass, large flap extension, low field elevation. For turbo prop aeroplanes the required runway length at a destination airport is ?
Question 78-17 : The same as that required at an alternate airport less then that required at an alternate airport more than that required at an alternate airport 60% greater than that required at an alternate airport
If the actual landing mass is higher than planned ?
Question 78-18 : The landing distance will be longer the landing distance will be unaffected the approach path will be steeper the approach path will be steeper and threshold speed higher
 The landing distance will be longer.
The landing distance will be longer. Considering vr which statement is correct ?
Question 78-19 : Vr is the speed at which rotation should be initiated vr is the lowest climb speed after engine failure in case of engine failure below vr the take off should be aborted vr is the lowest speed for directional control in case of engine failure
 Vr is the speed at which rotation should be initiated.
Vr is the speed at which rotation should be initiated. Which statement regarding v1 is correct ?
Question 78-20 : V1 must not exceed vr v1 must not exceed vmcg when determining the v1 reverse thrust is only allowed to be taken into account on the remaining symmetric engines the v1 correction for up slope is negative
 V1 must not exceed vr.
V1 must not exceed vr. Which statement is correct ?
Question 78-21 : The climb limited take off mass depends on pressure altitude and outer air temperature the performance limited take off mass is the highest of field length limited take off mass climb limited take off mass obstacle limited take off mass the climb limited take off mass will increase if the headwind component increases the climb limited take off mass increases when a larger take off flap setting is used
 The climb limited take-off mass depends on pressure altitude and outer air temperature.
The climb limited take-off mass depends on pressure altitude and outer air temperature. Which statement is correct for a descent without engine thrust at maximum lift ?
Question 78-22 : A tailwind component increases the ground distance a headwind component increases the ground distance a tailwind component increases fuel and time to descent a tailwind component increases the time in the descent
 A tailwind component increases the ground distance.
A tailwind component increases the ground distance. Which one of the following statements is true concerning the effect of changes ?
Question 78-23 : A decrease will cause an increase of the climb gradient an increase will cause a decrease in take off distance required an increase will cause a decrease in the landing distance required a decrease will cause an increase in the take off ground run
 A decrease will cause an increase of the climb gradient.
A decrease will cause an increase of the climb gradient. Which of the following statements is correct ?
Question 78-24 : The climb limited take off mass is independent of the wind component the performance limited take off mass is independent of the wind component the accelerate stop distance required is independent of the runway condition the take off distance with one engine out is independent of the wind component
 The climb limited take-off mass is independent of the wind component.
The climb limited take-off mass is independent of the wind component. Which of the alternatives represents the correct relationship ?
Question 78-25 : Vmcg and v1 should not exceed vr vmca and v2 should not exceed v1 vmcl and v1 should not exceed vr v2 and v1 should not exceed vmcg
 Vmcg and v1 should not exceed vr.
Vmcg and v1 should not exceed vr. With all engines out a pilot wants to fly for maximum time therefore he has to ?
Question 78-26 : The minimum power required the critical mach number the minimum angle of descent the maximum lift
 The minimum power required.
The minimum power required. Considering the take off decision speed v1 which of the following is correct ?
Question 78-27 : If an engine failure is recognized before reaching v1 the take off must be aborted v1 may not be less than v2min the minimum take off safety speed if an engine failure is recognized after reaching v1 the take off must be aborted v1 is sometimes greater than the rotation speed vr
 If an engine failure is recognized before reaching v1, the take-off must be aborted.
If an engine failure is recognized before reaching v1, the take-off must be aborted. The effect of a higher take off flap setting up to the maximum certified take ?
Question 78-28 : An increase of the field length limited take off mass but a decrease of the climb limited take off mass a decrease of both the field length limited take off mass and the climb limited take off mass a decrease of the field length limited take off mass but an increase of the climb limited take off mass an increase of both the field length limited take off mass and the climb limited take off mass
 An increase of the field length limited take-off mass but a decrease of the climb limited take-off mass.
An increase of the field length limited take-off mass but a decrease of the climb limited take-off mass. Which of the following statements is correct ?
Question 78-29 : A stopway is an area beyond the end of tora able to support the aeroplane mass during an abandoned take off a declared safe area is an area beyond the runway end which can be used for an abandoned take off a clearway is an area beyond the runway end which can be used for an abandoned take off if a clearway or a stopway is used in the take off calculations the lift off point may be beyond the end of tora
 A stopway is an area beyond the end of tora able to support the aeroplane mass during an abandoned take-off.
A stopway is an area beyond the end of tora able to support the aeroplane mass during an abandoned take-off. Besides lift the forces that determine the gradient of climb of an aeroplane are ?
Question 78-30 : Weight drag and thrust weight and drag only thrust and drag only weight and thrust only
 Weight, drag and thrust.
Weight, drag and thrust. What happens when flying at the 'backside of the power curve' ?
Question 78-31 : The speed is unstable the aeroplane will not stall the altitude cannot be maintained the elevator must be pulled to lower the nose
 The speed is unstable.
The speed is unstable. The effect that an increased outside air temperature has on the climb ?
Question 78-32 : Reduces both the climb gradient and the rate of climb increases the climb gradient and decreases the rate of climb does not affect the climb performance reduces the climb gradient and increases the rate of climb
 Reduces both the climb gradient and the rate of climb.
Reduces both the climb gradient and the rate of climb. A headwind component increasing with altitude as compared to zero wind ?
Question 78-33 : Has no effect on rate of climb does not have any effect on the angle of flight path during climb improves angle and rate of climb decreases angle and rate of climb
 Has no effect on rate of climb.
Has no effect on rate of climb. During a descent a headwind will ?
Question 78-34 : Increases the angle of the descent flight path increases the angle of descent increases the rate of descent increases the descent distance over ground
 Increases the angle of the descent flight path.
Increases the angle of the descent flight path. With an true airspeed of 194 kt and a vertical speed of 1000 ft/min the climb ?
Question 78-35 : 3° 3% 5° 8%
 3°.
3°. With regard to a jet aeroplane specific range is the ?
Question 78-36 : Tas divided by fuel flow fuel flow divided by tas unit of thrust per unit of fuel fuel flow per unit of thrust
 Tas divided by fuel flow.
Tas divided by fuel flow. Which of the following statements concerning tires is the major consideration ?
Question 78-37 : Rotation rate of the tyre and temperature tyre pressure and brake temperature rotation rate of the tyre and vmbe tyre pressure and temperature
 Rotation rate of the tyre and temperature.
Rotation rate of the tyre and temperature. What will increase the 'landing field length limited landing mass' when ?
Question 78-38 : A headwind a downslope a contaminated runway an increase in pressure altitude
 A headwind.
A headwind. When calculating approach speeds the minimum approach speed in the initial ?
Question 78-39 : 1 4 to 1 5 times vs1 2 times vs1 1 15 times vs0 1 05 times vat
 1.4 to 1.5 times vs1.
1.4 to 1.5 times vs1. You are approaching a wet runway in gusty conditions you should ?
Question 78-40 : Increase approach speed adopt a steeper approach path decrease approach speed increase landing speed
 Increase approach speed.
Increase approach speed. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
3079 Free Training Exam
