The take off distance available is ? [ Quiz topography ]
Question 77-1 : The length of the take off run available plus the length of the clearway available the runway length minus stopway the runway length plus half of the clearway the total runway length without clearway even if this one exists
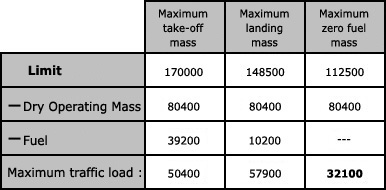 The length of the take-off run available plus the length of the clearway available.
The length of the take-off run available plus the length of the clearway available. The result of a higher flap setting up to the optimum at take off is ?
Question 77-2 : A shorter ground roll an increased acceleration a higher v1 a longer take off run
How is wind considered in the take off performance data of the aeroplane ?
Question 77-3 : Not more than 50% of a headwind and not less than 150% of the tailwind unfactored headwind and tailwind components are used not more than 80% headwind and not less than 125% tailwind since take offs with tailwind are not permitted only headwinds are considered
 Not more than 50% of a headwind and not less than 150% of the tailwind.
Not more than 50% of a headwind and not less than 150% of the tailwind. A higher pressure altitude at isa temperature ?
Question 77-4 : Decreases the field length limited take off mass decreases the take off distance increases the climb limited take off mass has no influence on the allowed take off mass
A higher outside air temperature oat ?
Question 77-5 : Decreases the brake energy limited take off mass increases the field length limited take off mass increases the climb limited take off mass decreases the take off distance
 Decreases the brake energy limited take-off mass.
Decreases the brake energy limited take-off mass. The take off distance required increases ?
Question 77-6 : Due to slush on the runway due to downhill slope because of the smaller angle of attack due to head wind because of the drag augmentation due to lower gross mass at take off
 Due to slush on the runway.
Due to slush on the runway. Due to standing water on the runway the field length limited take off mass will ?
Question 77-7 : Lower higher unaffected only higher for three and four engine aeroplanes
 Lower.
Lower. On a dry runway the accelerate stop distance is increased ?
Question 77-8 : By uphill slope by headwind by low outside air temperature by a lower take off mass because the aeroplane accelerates faster to v1
 By uphill slope.
By uphill slope. Uphill slope ?
Question 77-9 : Increases the take off distance more than the accelerate stop distance decreases the accelerate stop distance only decreases the take off distance only increases the allowed take off mass
 Increases the take-off distance more than the accelerate stop distance.
Increases the take-off distance more than the accelerate stop distance. V2 has to be equal to or higher than ?
Question 77-10 : 1 1 vmca 1 15 vmcg 1 1 vso 1 15 vr
 1.1 vmca.
1.1 vmca. V1 has to be ?
Question 77-11 : Equal to or higher than vmcg equal to or higher than vmca higher than vr equal to or higher than v2
 Equal to or higher than vmcg.
Equal to or higher than vmcg. Under which condition should you fly considerably lower 4 000 ft or more than ?
Question 77-12 : If at the lower altitude either considerably less headwind or considerably more tailwind can be expected if the maximum altitude is below the optimum altitude if at the lower altitude there is a greater headwind if at the lower altitude there is less tailwind
 If at the lower altitude either considerably less headwind or considerably more tailwind can be expected.
If at the lower altitude either considerably less headwind or considerably more tailwind can be expected. Which statement is correct for a descent without engine thrust at maximum lift ?
Question 77-13 : The higher the gross mass the greater is the speed for descent the higher the gross mass the lower is the speed for descent the higher the average temperature oat the lower is the speed for descent the mass of an aeroplane does not have any effect on the speed for descent
 The higher the gross mass the greater is the speed for descent.
The higher the gross mass the greater is the speed for descent. The maximum mass for landing could be limited by ?
Question 77-14 : The climb requirements with one engine inoperative in the approach configuration the climb requirements with one engine inoperative in the landing configuration the climb requirements with all engines in the approach configuration the climb requirements with all engines in the landing configuration but with gear up
 The climb requirements with one engine inoperative in the approach configuration.
The climb requirements with one engine inoperative in the approach configuration. On a long distance flight the gross mass decreases continuously as a ?
Question 77-15 : The specific range and the optimum altitude increases the speed must be increased to compensate the lower mass the specific range increases and the optimum altitude decreases the specific range decreases and the optimum altitude increases
 The specific range and the optimum altitude increases.
The specific range and the optimum altitude increases. With one or two engines inoperative the best specific range at high altitudes ?
Question 77-16 : Reduced improved not affected first improved and later reduced
 Reduced.
Reduced. In unaccelerated climb ?
Question 77-17 : Thrust equals drag plus the downhill component of the gross weight in the flight path direction lift is greater than the gross weight lift equals weight plus the vertical component of the drag thrust equals drag plus the uphill component of the gross weight in the flight path direction
The rate of climb is approximately equal to ?
Question 77-18 : The still air gradient multiplied by the tas the still air gradient divided by the tas the angle of climb multiplied by the tas the angle of climb divided by the tas
 The still-air gradient multiplied by the tas.
The still-air gradient multiplied by the tas. If the thrust available exceeds the thrust required for level flight ?
Question 77-19 : The aeroplane accelerates if the altitude is maintained the aeroplane descends if the airspeed is maintained the aeroplane decelerates if it is in the region of reversed command the aeroplane decelerates if the altitude is maintained
Any acceleration in climb with a constant power setting ?
Question 77-20 : Decreases the rate of climb and the angle of climb improves the climb gradient if the airspeed is below vx improves the rate of climb if the airspeed is below vy decreases rate of climb and increases angle of climb
 Decreases the rate of climb and the angle of climb.
Decreases the rate of climb and the angle of climb. As long as an aeroplane is in a steady climb ?
Question 77-21 : Vx is always less than vy vx may be greater or less than vy depending on altitude vx is always greater than vy vy is always greater than vmo
 Vx is always less than vy.
Vx is always less than vy. The best rate of climb at a constant gross mass ?
Question 77-22 : Decreases with increasing altitude since the thrust available decreases due to the lower air density increases with increasing altitude since the drag decreases due to the lower air density increases with increasing altitude due to the higher true airspeed is independent of altitude
 Decreases with increasing altitude since the thrust available decreases due to the lower air density.
Decreases with increasing altitude since the thrust available decreases due to the lower air density. The 'climb gradient' is defined as the ratio of ?
Question 77-23 : The increase of altitude to horizontal air distance expressed as a percentage the increase of altitude to distance over ground expressed as a percentage true airspeed to rate of climb rate of climb to true airspeed
 The increase of altitude to horizontal air distance expressed as a percentage.
The increase of altitude to horizontal air distance expressed as a percentage. Higher gross mass at the same altitude decreases the gradient and the rate of ?
Question 77-24 : Vy and vx are increased vx is increased and vy is decreased vy and vx are not affected by a higher gross mass vy and vx are decreased
 Vy and vx are increased.
Vy and vx are increased. A higher outside air temperature ?
Question 77-25 : Reduces the angle and the rate of climb increases the angle of climb but decreases the rate of climb does not have any noticeable effect on climb performance reduces the angle of climb but increases the rate of climb
 Reduces the angle and the rate of climb.
Reduces the angle and the rate of climb. When compared to still air conditions a constant headwind component ?
Question 77-26 : Increases the angle of flight path during climb increases the best rate of climb decreases the angle of climb increases the maximum endurance
 Increases the angle of flight path during climb.
Increases the angle of flight path during climb. The speed v1 is defined as ?
Question 77-27 : Take off decision speed take off climb speed speed for best angle of climb engine failure speed
 Take-off decision speed.
Take-off decision speed. The speed vlo is defined as ?
Question 77-28 : Landing gear operating speed design low operating speed long distance operating speed lift off speed
 Landing gear operating speed.
Landing gear operating speed. Vx is ?
Question 77-29 : The speed for best angle of climb the speed for best rate of climb the speed for best specific range the speed for best angle of flight path
 The speed for best angle of climb.
The speed for best angle of climb. The speed for best rate of climb is called ?
Question 77-30 : Vy vx v2 vo
 Vy.
Vy. The stalling speed or the minimum steady flight speed at which the aeroplane is ?
Question 77-31 : Vso vs1 vs vmc
 Vso.
Vso. The absolute ceiling ?
Question 77-32 : Is the altitude at which the rate of climb theoretically is zero can be reached only with minimum steady flight speed is the altitude at which the best climb gradient attainable is 5% is the altitude at which the aeroplane reaches a maximum rate of climb of 100 ft/min
 Is the altitude at which the rate of climb theoretically is zero.
Is the altitude at which the rate of climb theoretically is zero. The maximum operating altitude for a certain aeroplane with a pressurised cabin ?
Question 77-33 : Is the highest pressure altitude certified for normal operation is dependent on aerodynamic ceiling is dependent on the oat is only certified for four engine aeroplanes
 Is the highest pressure altitude certified for normal operation.
Is the highest pressure altitude certified for normal operation. The approach climb requirement has been established to ensure ?
Question 77-34 : Minimum climb gradient in case of a go around with one engine inoperative obstacle clearance in the approach area manoeuvrability in case of landing with one engine inoperative manoeuvrability during approach with full flaps and gear down all engines operating
 Minimum climb gradient in case of a go-around with one engine inoperative.
Minimum climb gradient in case of a go-around with one engine inoperative. Which statement relating to a take off from a wet runway is correct ?
Question 77-35 : A reduction of screen height is allowed in order to reduce weight penalties the use of a reduced vr is sufficient to maintain the same safety margins as for a dry runway in the case of a reverser inoperative the wet runway performance information can still be used screen height reduction cannot be applied because of the consequent reduction in obstacle clearance
 A reduction of screen height is allowed in order to reduce weight penalties.
A reduction of screen height is allowed in order to reduce weight penalties. Take off performance data for the ambient conditions show the following ?
Question 77-36 : 5° the obstacle limit is increased but the runway limit decreases 5° both limitations are increased 20° the obstacle limit is increased but the runway limit decreases 20° both limitations are increased
 5°, the obstacle limit is increased but the runway limit decreases.
5°, the obstacle limit is increased but the runway limit decreases. A climb gradient required is 3 3% for an aircraft maintaining 100 kt true ?
Question 77-37 : 330 ft/min 3 300 ft/min 3 30 m/s 33 0 m/s
 330 ft/min.
330 ft/min. An aircraft has two certified landing flaps positions 25° and 35° if a pilot ?
Question 77-38 : An increased landing distance and better go around performance a reduced landing distance and better go around performance an increased landing distance and degraded go around performance a reduced landing distance and degraded go around performance
 An increased landing distance and better go-around performance.
An increased landing distance and better go-around performance. The take off distance of an aircraft is 800m in standard atmosphere no wind at ?
Question 77-39 : 970 m 810 m 890 m 870 m
 970 m.
970 m. Is there any difference between the vertical speed versus forward speed curves ?
Question 77-40 : Yes the difference is that for a given angle of attack both the vertical and forward speeds of the heavier aeroplane will be larger no difference the difference is that the heavier aeroplane will always glide a greater distance the difference is that the lighter aeroplane will always glide a greater distance
 Yes, the difference is that for a given angle of attack both the vertical and forward speeds of the heavier aeroplane will be larger.
Yes, the difference is that for a given angle of attack both the vertical and forward speeds of the heavier aeroplane will be larger. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
3039 Free Training Exam
