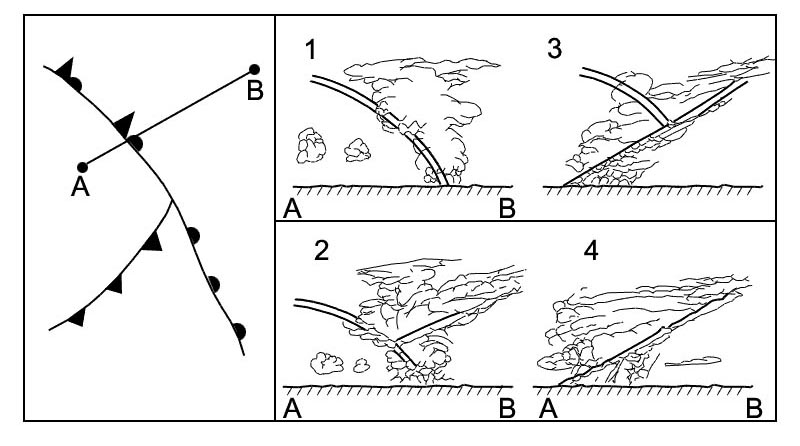
Which of the following diagrams correctly shows the movement of the power ? [ Exercise lift off ]
Question 75-1 : Figure d figure a figure b figure c
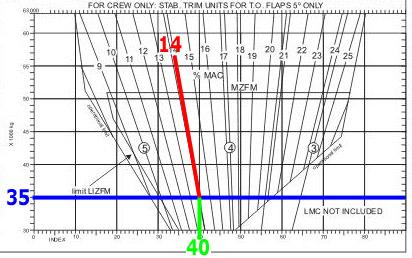 Figure d.
Figure d. In a steady descending flight descent angle gamma equilibrium of forces acting ?
Question 75-2 : T + w sin gamma = d t w sin gamma = d t d = w sin gamma t + d = w sin gamma
 T + w sin gamma = d
T + w sin gamma = d An aeroplane executes a steady glide at the speed for minimum glide angle if ?
Question 75-3 : Increases / increases / decreases decreases / constant / decreases increases / increases / constant increases / constant / increases
 Increases / increases / decreases.
Increases / increases / decreases. An aeroplane is in a power off glide at speed for minimum glide angle if the ?
Question 75-4 : Decreases increases remains the same may increase or decrease depending on the type of aeroplane
 Decreases.
Decreases. Which of the following combinations basically has an effect on the angle of ?
Question 75-5 : Configuration and angle of attack mass and altitude altitude and configuration configuration and mass
 Configuration and angle of attack.
Configuration and angle of attack. Two identical aeroplanes at different masses are descending at idle thrust ?
Question 75-6 : At a given angle of attack both the vertical and the forward speed are greater for the heavier aeroplane there is no difference between the descent characteristics of the two aeroplanes at a given angle of attack the heavier aeroplane will always glide further than the lighter aeroplane at a given angle of attack the lighter aeroplane will always glide further than the heavier aeroplane
 At a given angle of attack, both the vertical and the forward speed are greater for the heavier aeroplane.
At a given angle of attack, both the vertical and the forward speed are greater for the heavier aeroplane. Compared with still air the effect a headwind has on the values of the maximum ?
Question 75-7 : The maximum range speed increases and the maximum gradient climb speed is not affected the maximum range speed decreases and the maximum gradient climb speed increases the maximum range speed decreases and the maximum gradient climb speed decreases the maximum range speed decreases and the maximum gradient climb speed is not affected
 The maximum range speed increases and the maximum gradient climb speed is not affected.
The maximum range speed increases and the maximum gradient climb speed is not affected. The maximum speed in horizontal flight occurs when ?
Question 75-8 : The maximum thrust is equal to the total drag the thrust is equal to the maximum drag the thrust is equal to minimum drag the thrust does not increase further with increasing speed
 The maximum thrust is equal to the total drag.
The maximum thrust is equal to the total drag. With respect to the optimum altitude which of the following statements is ?
Question 75-9 : An aeroplane sometimes flies above or below the optimum altitude because optimum altitude increases continuously during flight an aeroplane always flies below the optimum altitude because mach buffet might occur an aeroplane always flies at the optimum altitude because this is economically seen as the most attractive altitude an aeroplane flies most of the time above the optimum altitude because this yields the most economic result
 An aeroplane sometimes flies above or below the optimum altitude because optimum altitude increases continuously during flight.
An aeroplane sometimes flies above or below the optimum altitude because optimum altitude increases continuously during flight. How does the lift coefficient for maximum range vary with altitude . no ?
Question 75-10 : The lift coefficient is independent of altitude the lift coefficient decreases with increasing altitude the lift coefficient increases with increasing altitude only at low speeds the lift coefficient decreases with increasing altitude
 The lift coefficient is independent of altitude.
The lift coefficient is independent of altitude. The speed for maximum lift/drag ratio will result in ?
Question 75-11 : The maximum range for a propeller driven aeroplane the maximum endurance for a propeller driven aeroplane the maximum range for a jet aeroplane the maximum angle of climb for a propeller driven aeroplane
 The maximum range for a propeller driven aeroplane.
The maximum range for a propeller driven aeroplane. Which of the following provides maximum obstacle clearance during climb ?
Question 75-12 : The speed for maximum climb angle vx 1 2vs the speed for maximum rate of climb the speed at which the flaps may be selected one position further up
 The speed for maximum climb angle vx.
The speed for maximum climb angle vx. Which of the following factors will lead to an increase of ground distance ?
Question 75-13 : Tailwind decrease of aircraft mass increase of aircraft mass headwind
 Tailwind.
Tailwind. Which of the following factors leads to the maximum flight time of a glide ?
Question 75-14 : Low mass high mass headwind tailwind
 Low mass.
Low mass. When v1 has to be reduced because of a wet runway the one engine out obstacle ?
Question 75-15 : Decreases / remains constant increases / increases remains constant / remains constant decreases / decreases
 Decreases / remains constant.
Decreases / remains constant. Which statement concerning the inclusion of a clearway in take off calculation ?
Question 75-16 : The field length limited take off mass will increase the usable length of the clearway is not limited v1 is increased v1 remains constant
 The field length limited take-off mass will increase.
The field length limited take-off mass will increase. Which of the following factors favours the selection of a low flap setting for ?
Question 75-17 : High field elevation distant obstacles in the climb out path long runway and a high ambient temperature low field elevation close in obstacles in the climb out path long runway and a high ambient temperature high field elevation no obstacles in the climb out path low ambient temperature and short runway low field elevation no obstacles in the climb out path short runway and a low ambient temperature
 High field elevation, distant obstacles in the climb-out path, long runway and a high ambient temperature.
High field elevation, distant obstacles in the climb-out path, long runway and a high ambient temperature. How is v2 affected if t/o flaps 20° is chosen instead of t/o flaps 10° ?
Question 75-18 : V2 decreases if not restricted by vmca v2 has the same value in both cases v2 increases in proportion to the angle at which the flaps are set v2 has no connection with t/o flap setting as it is a function of runway length only
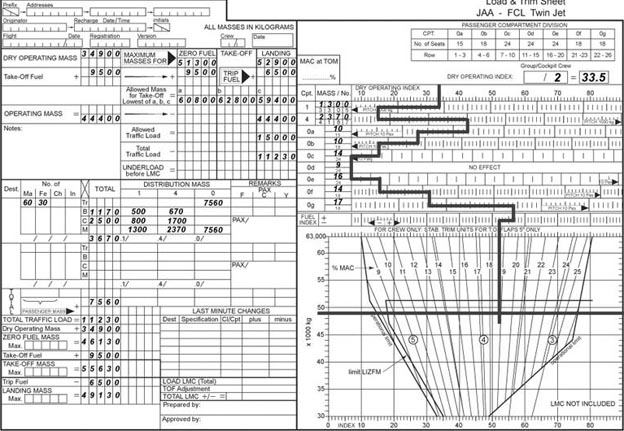
During the flight preparation the climb limited take off mass tom is found to ?
Question 75-19 : By selecting a higher flap setting by selecting a higher v2 by selecting a lower v2 by selecting a lower flap setting
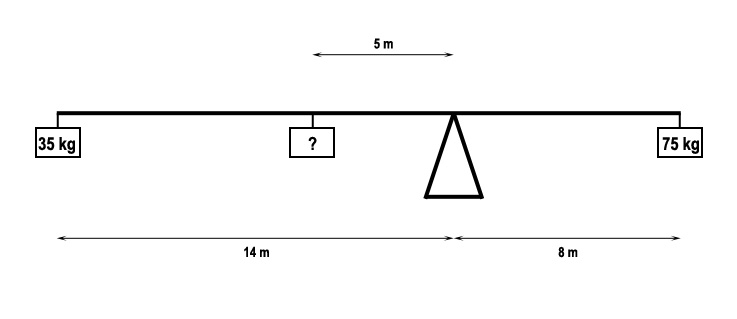 By selecting a higher flap setting.
By selecting a higher flap setting. If on a particular flight the value of v1 used on take off exceeds the correct ?
Question 75-20 : The accelerate/stop distance will exceed the accelerate/stop distance available the one engine inoperative take off distance may exceed the take off distance available v2 may be too high so that climb performance decreases it may lead to over rotation
 The accelerate/stop distance will exceed the accelerate/stop distance available.
The accelerate/stop distance will exceed the accelerate/stop distance available. Which is the correct sequence of speeds during take off ?
Question 75-21 : Vmcg v1 vr v2 v1 vmcg vr v2 v1 vr vmcg v2 v1 vr v2 vmca
 Vmcg, v1, vr, v2.
Vmcg, v1, vr, v2. Regarding the obstacle limited take off mass which of the following statements ?
Question 75-22 : A take off in the direction of an obstacle is also permitted in tail wind condition wind speed plays no role when calculating this particular mass the obstacle limited mass can never be lower than the climb limited take off mass the maximum bank angle which can be used is 10°
 A take-off in the direction of an obstacle is also permitted in tail wind condition.
A take-off in the direction of an obstacle is also permitted in tail wind condition. When an aircraft takes off with the mass limited by the toda ?
Question 75-23 : The actual take off mass equals the field length limited take off mass the distance from brake release to v1 will be equal to the distance from v1 to the 35 feet point the 'balanced take off distance' equals 115% of the 'all engine take off distance' the end of the runway will be cleared by 35 feet following an engine failure at v1
 The actual take-off mass equals the field length limited take-off mass.
The actual take-off mass equals the field length limited take-off mass. For a take off from a contaminated runway which of the following statements is ?
Question 75-24 : The performance data for take off must be determined in general by means of calculation only a few values are verified by flight tests the greater the depth of contamination at constant take off mass the more v1 has to be decreased to compensate for decreasing friction dry snow is not considered to affect the take off performance a slush covered runway must be cleared before take off even if the performance data for contaminated runway is available
 The performance data for take-off must be determined in general by means of calculation, only a few values are verified by flight tests.
The performance data for take-off must be determined in general by means of calculation, only a few values are verified by flight tests. To minimize the risk of hydroplaning during landing the pilot should ?
Question 75-25 : Make a 'positive' landing and apply maximum reverse thrust and brakes as quickly as possible use maximum reverse thrust and should start braking below the hydroplaning speed use normal landing braking and reverse technique postpone the landing until the risk of hydroplaning no longer exists
 Make a 'positive' landing and apply maximum reverse thrust and brakes as quickly as possible.
Make a 'positive' landing and apply maximum reverse thrust and brakes as quickly as possible. The stopway is an area which allows an increase only in the ?
Question 75-26 : Accelerate stop distance available take off run available take off distance available landing distance available
 Accelerate-stop distance available.
Accelerate-stop distance available. Vr cannot be lower than ?
Question 75-27 : V1 and 105% of vmca 105% of v1 and vmca 1 2 vs for twin and three engine jet aeroplane 1 15 vs for turbo prop with three or more engines
 V1 and 105% of vmca.
V1 and 105% of vmca. The one engine out take off run is the distance between the brake release point ?
Question 75-28 : The middle of the segment between vlof point and 35 ft point the lift off point the point where v2 is reached the point half way between v1 and v2
 The middle of the segment between vlof point and 35 ft point.
The middle of the segment between vlof point and 35 ft point. The decision speed at take off v1 is the calibrated airspeed ?
Question 75-29 : Below which take off must be rejected if an engine failure is recognized above which take off should be continued at which the take off must be rejected below which the take off must be continued at which the failure of the critical engine is expected to occur
 Below which take-off must be rejected if an engine failure is recognized, above which take-off should be continued.
Below which take-off must be rejected if an engine failure is recognized, above which take-off should be continued. Regarding unaccelerated horizontal flight minimum drag is ?
Question 75-30 : Proportional to aircraft mass a function of the pressure altitude a function of the density altitude independent of the aircraft mass
 Proportional to aircraft mass.
Proportional to aircraft mass. If the aircraft mass in a horizontal unaccelerated flight decreases ?
Question 75-31 : The minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag decreases the minimum drag increases and the ias for minimum drag decreases the minimum drag increases and the ias for minimum drag increases the minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag increases
 The minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag decreases.
The minimum drag decreases and the ias for minimum drag decreases. Density altitude is the ?
Question 75-32 : Pressure altitude corrected for 'non standard' temperature altitude reference to the standard datum plane altitude read directly from the altimeter height above the surface
 Pressure altitude corrected for 'non standard' temperature.
Pressure altitude corrected for 'non standard' temperature. The density altitude ?
Question 75-33 : Is used to determine the aeroplane performance is equal to the pressure altitude is used to establish minimum clearance of 2 000 feet over mountains is used to calculate the fl above the transition altitude
 Is used to determine the aeroplane performance.
Is used to determine the aeroplane performance. Which of the following combinations adversely affects take off and initial ?
Question 75-34 : High temperature and high relative humidity low temperature and high relative humidity high temperature and low relative humidity low temperature and low relative humidity
 High temperature and high relative humidity.
High temperature and high relative humidity. What effect has a downhill slope on the take off speeds the slope ?
Question 75-35 : Decreases the take off speed v1 decreases the tas for take off increases the ias for take off has no effect on the take off speed v1
 Decreases the take-off speed v1.
Decreases the take-off speed v1. During climb to the cruising level a headwind component ?
Question 75-36 : Decreases the ground distance flown during that climb increases the amount of fuel for the climb increases the climb time decreases the climb time
 Decreases the ground distance flown during that climb.
Decreases the ground distance flown during that climb. What affect has a tailwind on the maximum endurance speed ?
Question 75-37 : No affect tailwind only effects holding speed the ias will be increased the ias will be decreased
 No affect.
No affect. During climb with all engines the altitude where the rate of climb reduces to ?
Question 75-38 : Service ceiling absolute ceiling thrust ceiling aerodynamic ceiling
 Service ceiling.
Service ceiling. The maximum rate of climb that can be maintained at the absolute ceiling is ?
Question 75-39 : 0 ft/min 125 ft/min 500 ft/min 100 ft/min
 0 ft/min.
0 ft/min. A twin engine aeroplane is flying at the minimum control speed with take off ?
Question 75-40 : Straight flight straight flight and altitude heading altitude and a positive rate of climb of 100 ft/min altitude
 Straight flight.
Straight flight. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2959 Free Training Exam
