Which of the following statements is correct ? [ Professional DGAC ]
Question 74-1 : A stopway means an area beyond the take off runway able to support the aeroplane during an aborted take off an underrun is an area beyond the runway end which can be used for an aborted take off a clearway is an area beyond the runway which can be used for an aborted take off if a clearway or a stopway is used the lift off point must be attainable at least at the end of the permanent runway surface
 A stopway means an area beyond the take-off runway, able to support the aeroplane during an aborted take-off.
A stopway means an area beyond the take-off runway, able to support the aeroplane during an aborted take-off. Which of the following is true with regard to vmca air minimum control speed ?
Question 74-2 : Straight flight can not be maintained below vmca when the critical engine has failed the aeroplane is uncontrollable below vmca the aeroplane will not gather the minimum required climb gradient vmca only applies to four engine aeroplanes
 Straight flight can not be maintained below vmca, when the critical engine has failed.
Straight flight can not be maintained below vmca, when the critical engine has failed. Which of the following will decrease v1 ?
Question 74-3 : Inoperative anti skid increased take off mass inoperative flight management system increased outside air temperature
Which of the following are to be taken into account for the runway in use for ?
Question 74-4 : Airport elevation runway slope outside air temperature pressure altitude and wind components airport elevation runway slope standard temperature standard pressure and wind components airport elevation runway slope standard temperature pressure altitude and wind components airport elevation runway slope outside air temperature standard pressure and wind components
 Airport elevation, runway slope, outside air temperature, pressure altitude and wind components.
Airport elevation, runway slope, outside air temperature, pressure altitude and wind components. Changing the take off flap setting from flap 15° to flap 5° will normally ?
Question 74-5 : A longer take off distance and a better climb a shorter take off distance and an equal climb a better climb and an equal take off distance a shorter take off distance and a better climb
In accordance with cs 25 the reference landing speed vref has the following ?
Question 74-6 : 23% 15% 20% 10%
 23%.
23%. In relation to the net take off flight path the required 35 ft vertical ?
Question 74-7 : The minimum vertical distance between the lowest part of the aeroplane and all obstacles within the obstacle domain based on pressure altitudes the height by which acceleration and flap retraction should be completed the height at which power is reduced to maximum climb thrust
 The minimum vertical distance between the lowest part of the aeroplane and all obstacles within the obstacle domain.
The minimum vertical distance between the lowest part of the aeroplane and all obstacles within the obstacle domain. At a given altitude when a turbojet aeroplane mass is increased by 5% assuming ?
Question 74-8 : 5% 7 5% 10% 2 5%
 5%.
5%. What will be the effect on an aeroplane's performance if aerodrome pressure ?
Question 74-9 : It will decrease the take off distance required it will increase the take off distance required it will increase the take off ground run it will increase the accelerate stop distance
 It will decrease the take-off distance required.
It will decrease the take-off distance required. What will be the influence on the aeroplane performance if aerodrome pressure ?
Question 74-10 : It will increase the take off distance it will decrease the take off distance it will increase the take off distance available it will decrease the take off run
 It will increase the take-off distance.
It will increase the take-off distance. Which of the following distances will increase if you increase v1 but vr ?
Question 74-11 : Accelerate stop distance take off distance all engine take off distance take off run
 Accelerate stop distance.
Accelerate stop distance. Which of the following answers is true ?
Question 74-12 : V1 is lower or equal to vr v1 is higher vlof v1 is higher vr v1 is lower vmcg
 V1 is lower or equal to vr.
V1 is lower or equal to vr. The length of a clearway may be included in ?
Question 74-13 : The take off distance available the accelerate stop distance available the take off run available the distance to reach v1
 The take-off distance available.
The take-off distance available. How does runway slope affect allowable take off mass assuming other factors ?
Question 74-14 : A downhill slope increases allowable take off mass an uphill slope increases the allowable take off mass allowable take off mass is not affected by runway slope a downhill slope decreases allowable take off mass
 A downhill slope increases allowable take-off mass.
A downhill slope increases allowable take-off mass. Provided all other parameters stay constant which of the following alternatives ?
Question 74-15 : Decreased take off mass increased density increased flap setting increased outside air temperature decreased pressure altitude decreased flap setting decreased take off mass increased pressure altitude increased temperature increased pressure altitude increased outside air temperature increased take off mass
 Decreased take-off mass, increased density, increased flap setting.
Decreased take-off mass, increased density, increased flap setting. The effect of increasing the flap setting from zero to the recommended take off ?
Question 74-16 : Decreased tod required and increased field length limited tom increased tod required and decreased field length limited tom increased tod required and increased field length limited tom decreased tod required and decreased field length limited tom
 Decreased tod required and increased field length limited tom.
Decreased tod required and increased field length limited tom. How is vmca influenced by increasing pressure altitude ?
Question 74-17 : Vmca decreases with increasing pressure altitude vmca is not affected by pressure altitude vmca increases with increasing pressure altitude vmca decreases with pressure altitude higher than 4000 ft
 Vmca decreases with increasing pressure altitude.
Vmca decreases with increasing pressure altitude. Which one of the following is not affected by a tail wind ?
Question 74-18 : The climb limited take off mass the field limited take off mass the obstacle limited take off mass the take off run
Which statement is correct ?
Question 74-19 : Vr must not be less than 1 05 vmca and not less than v1 vr must not be less than 1 05 vmca and not less than 1 1 v1 vr must not be less than vmca and not less than 1 05 v1 vr must not be less than 1 1 vmca and not less than v1
 Vr must not be less than 1.05 vmca and not less than v1.
Vr must not be less than 1.05 vmca and not less than v1. Which of the following represents the minimum for v1 ?
Question 74-20 : Vmcg vlof vmu vr
 Vmcg.
Vmcg. In the event of engine failure below v1 the first action to be taken by the ?
Question 74-21 : Reduce the engine thrust deploy airbrakes or spoilers reverse engine thrust apply wheel brakes
 Reduce the engine thrust.
Reduce the engine thrust. If the antiskid system is inoperative which of the following statements is true ?
Question 74-22 : The accelerate stop distance increases the accelerate stop distance decreases it has no effect on the accelerate stop distance take off with anti skid inoperative is never permitted
 The accelerate stop distance increases.
The accelerate stop distance increases. Other factors remaining constant and not limiting how does increasing pressure ?
Question 74-23 : Allowable take off mass decreases allowable take off mass increases there is no effect on allowable take off mass allowable take off mass remains uninfluenced up to 5000 ft pressure altitude
 Allowable take-off mass decreases.
Allowable take-off mass decreases. If there is a tail wind the climb limited tom take off mass will ?
Question 74-24 : Not be affected increase decrease increase in the flaps extended case
 Not be affected.
Not be affected. Which of the following sets of factors will increase the climb limited tom ?
Question 74-25 : Low flap setting low pressure altitude low oat high flap setting low pressure altitude low oat low flap setting high pressure altitude high oat low flap setting high pressure altitude low oat
 Low flap setting, low pressure altitude, low oat.
Low flap setting, low pressure altitude, low oat. The requirements with regard to take off flight path and the climb segments are ?
Question 74-26 : The failure of the critical engine on a multi engines aeroplane the failure of any engine on a multi engine aeroplane two engine aeroplane the failure of two engines on a multi engine aeroplane
 The failure of the critical engine on a multi-engines aeroplane.
The failure of the critical engine on a multi-engines aeroplane. A head wind will ?
Question 74-27 : Increase the climb flight path angle increase the angle of climb increase the rate of climb shorten the time of climb
 Increase the climb flight path angle.
Increase the climb flight path angle. Assuming that the required lift exists which forces determine an aeroplane's ?
Question 74-28 : Weight drag and thrust weight and drag only thrust and drag only weight and thrust only
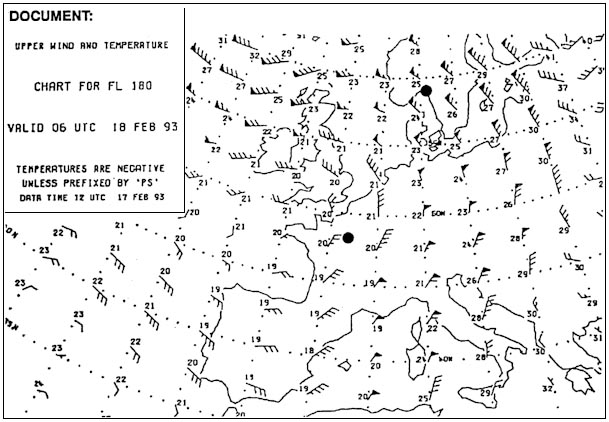 Weight, drag and thrust.
Weight, drag and thrust. How does the best angle of climb and best rate of climb vary with increasing ?
Question 74-29 : Both decrease best angle of climb decreases while best rate of climb increases best angle of climb increases while best rate of climb decreases both increase
 Both decrease.
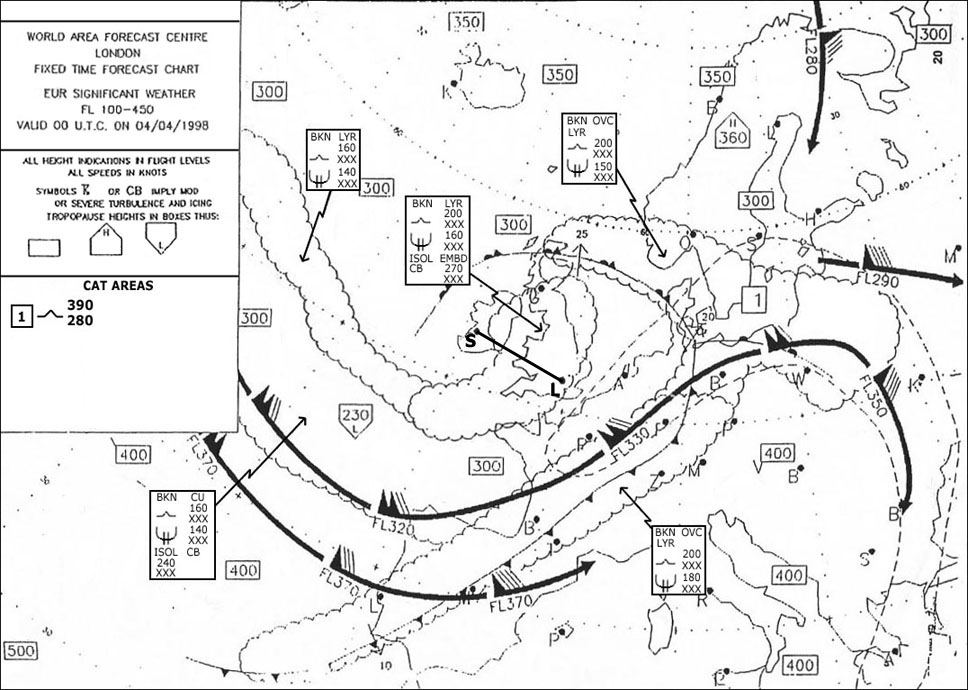
Both decrease. An operator shall ensure that the net take off flight path clears all obstacles ?
Question 74-30 : 90 m + 0 125 d 0 125 d 90 m + 1 125 d 90 m + d / 0 125
 90 m + 0.125 d.
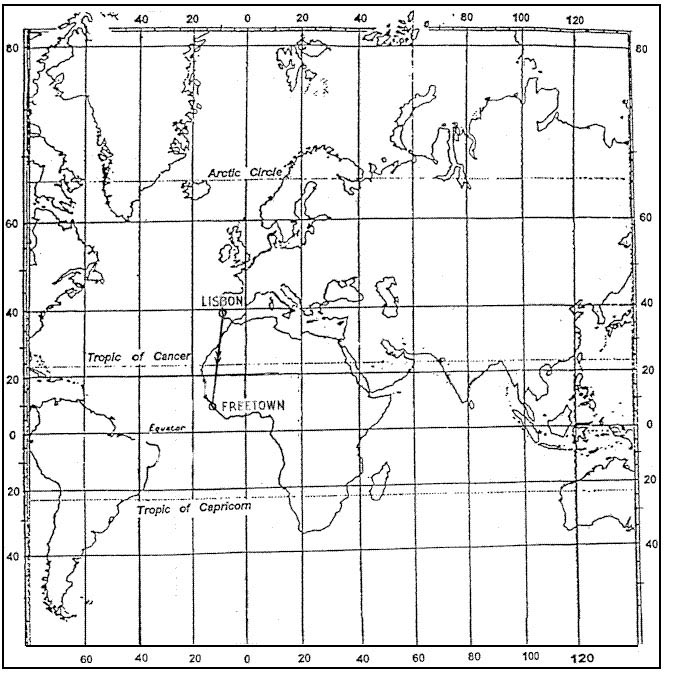
90 m + 0.125 d. What is the effect of tail wind on the time to climb to a given altitude ?
Question 74-31 : The time to climb does not change the time to climb increases the time to climb decreases the effect on time to climb will depend on the aeroplane type
 The time to climb does not change.
The time to climb does not change. The angle of climb with flaps extended compared to that with flaps retracted ?
Question 74-32 : Smaller larger not change increase at moderate flap setting decrease at large flap setting
 Smaller.
Smaller. Vx and vy with take off flaps will be ?
Question 74-33 : Lower than that for clean configuration higher than that for clean configuration same as that for clean configuration changed so that vx increases and vy decreases compared to clean configuration
 Lower than that for clean configuration.
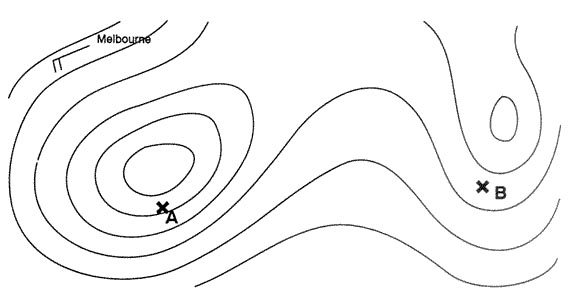
Lower than that for clean configuration. Other factors remaining constant how does increasing altitude affect vx and vy ?
Question 74-34 : Both will increase both will remain the same both will decrease vx will decrease and vy will increase
 Both will increase.
Both will increase. Considering tas for maximum range and maximum endurance other factors remaining ?
Question 74-35 : Both will increase with increasing altitude both will decrease with increasing altitude both will stay constant regardless of altitude tas for maximum range will increase with increased altitude while tas for maximum endurance will decrease with increased altitude
 Both will increase with increasing altitude.
Both will increase with increasing altitude. Given that .vef= critical engine failure speed.vmcg= ground minimum control ?
Question 74-36 : Vmcg is less than or equal to vef is less than v1 v2min is less than or equal to vef is less than or equal to vmu 1 05 vmca is less than or equal to vef is less than or equal to v1 1 05 vmcg is less than vefis less than or equal to vr
 Vmcg is less than or equal to vef is less than v1.
Vmcg is less than or equal to vef is less than v1. Given .vs= stalling speed.vmca= air minimum control speed.vmu= minimum unstick ?
Question 74-37 : Vs< vmca < v2 min v2 min < vmca < vmu vr < vmca < vlof vmu = vmca < v1
 Vs< vmca < v2 min
Vs< vmca < v2 min Regarding take off the take off decision speed v1 ?
Question 74-38 : Is the airspeed on the ground at which the pilot is assumed to have made a decision to continue or discontinue the take off is always equal to vef engine failure speed is an airspeed at which the aeroplane is airborne but below 35 ft and the pilot is assumed to have made a decision to continue or discontinue the take off is the airspeed of the aeroplane upon reaching 35 feet above the take off surface
 Is the airspeed on the ground at which the pilot is assumed to have made a decision to continue or discontinue the take-off.
Is the airspeed on the ground at which the pilot is assumed to have made a decision to continue or discontinue the take-off. An airport has a 3000 metres long runway and a 2000 metres clearway at each end ?
Question 74-39 : 4500 metres 6000 metres 4000 metres 5000 metres
 4500 metres.
4500 metres. The net flight path gradient after take off compared to the actual climb ?
Question 74-40 : Smaller larger equal depends on type of aircraft and may be smaller or larger respectively
 Smaller.
Smaller. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2919 Free Training Exam
