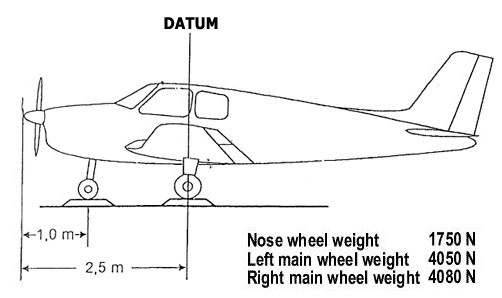
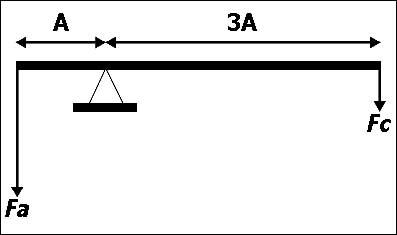
A 5 m long plank is on a pivot located at 3 m of the left side a user applies a ? [ Session helipad ]
Question 73-1 : 900 n 1500 n 600 n 1800 n
 900 n.
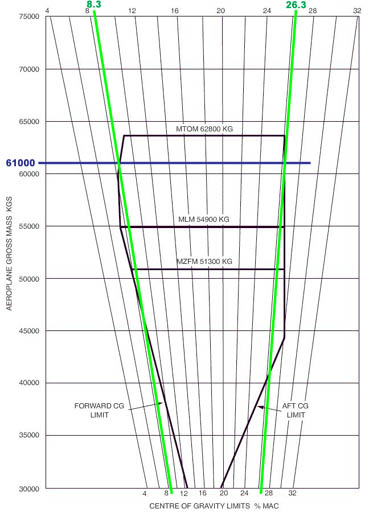
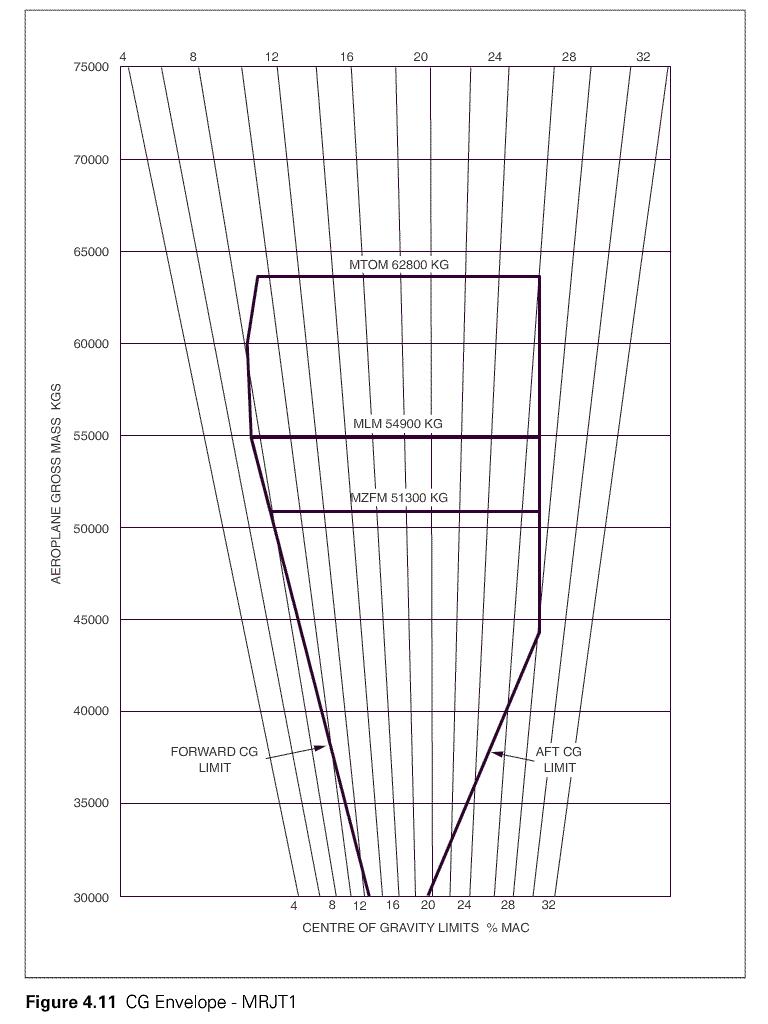
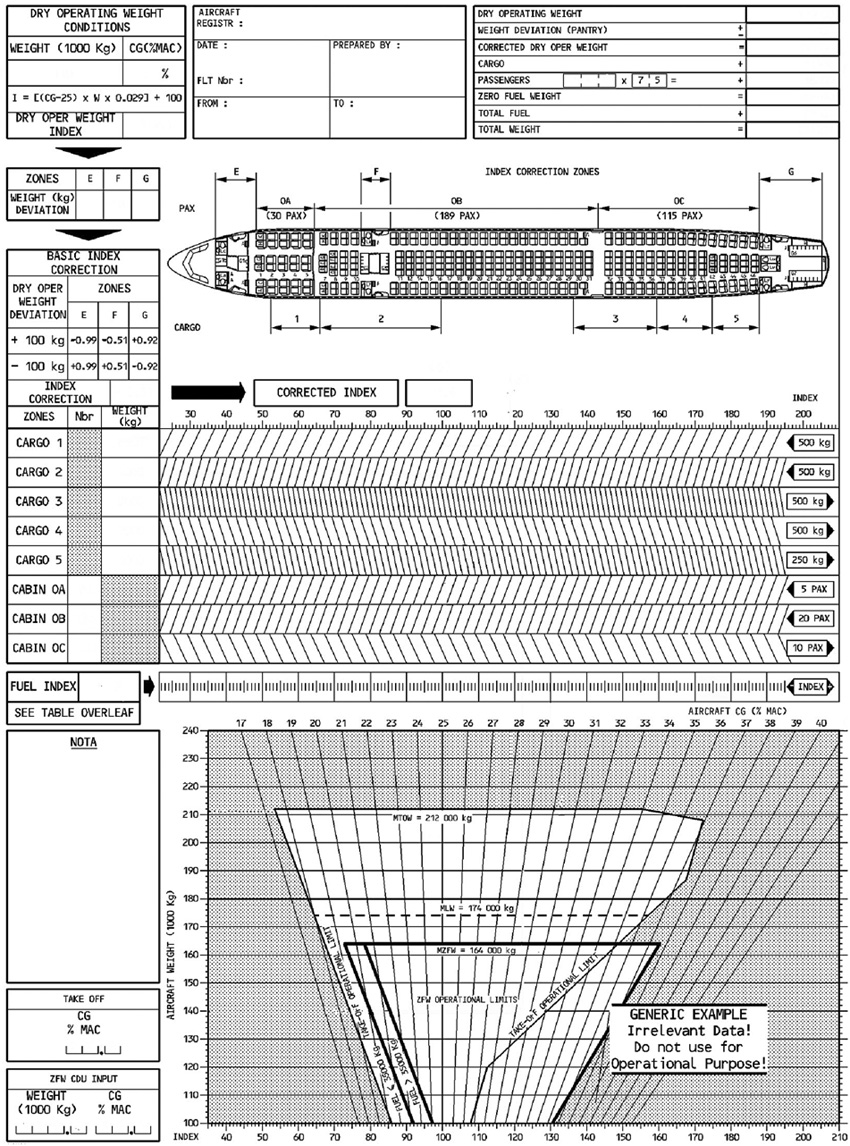
900 n. Refer to figure 031 52 .what is the forward cg limit and what is the aft cg ?
Question 73-2 : 87 3 and 94 6 86 4 and 94 2 82 and 94 5 87 2 and 94 2
 87.3 and 94.6.
87.3 and 94.6. Refer to figure 031 46 .how much fuel could be loaded at reference station 4 ?
Question 73-3 : 806 l 1171 l 487 l 324 l
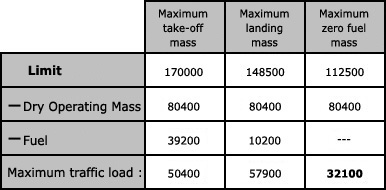
Length of the mean aerodynamic chord 1 m.moment arm of the forward cargo 0 50 ?
Question 73-4 : 110 kg 183 kg 165 kg 104 kg
 110 kg.
110 kg. For the transport aeroplane the moment balance arm for the forward hold ?
Question 73-5 : 367 9 inches 257 inches 314 5 inches 421 5 inches
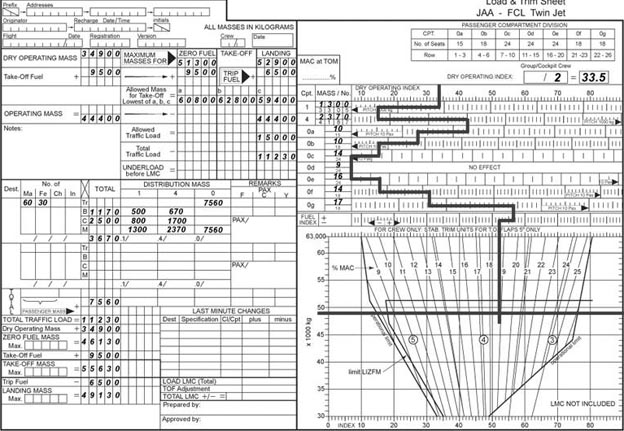
Referring to the loading manual for the transport aeroplane the maximum load ?
Question 73-6 : 68 kg per square foot 150 kg per square foot 68 lbs per square metre 68 kg per square meter
 68 kg per square foot.
68 kg per square foot. The maximum intensity floor loading for an aeroplane is given in the flight ?
Question 73-7 : 416 kg 1015 6 kg 41 6 kg 101 6 kg
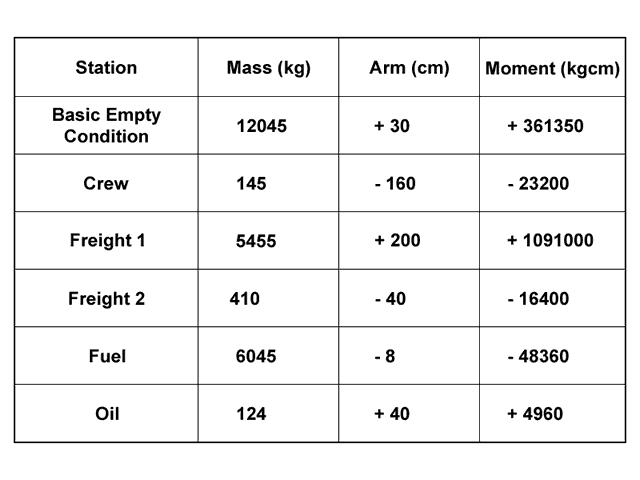 416 kg
416 kg A pallet having a freight platform which measures 200 cm x 250 cm has a total ?
Question 73-8 : 285 5 kg may be added 158 3 kg must be off loaded 28 5 kg must be off loaded 28 5 kg may be added
 285.5 kg may be added.
285.5 kg may be added. From the loading manual for the jet transport aeroplane the maximum floor ?
Question 73-9 : 68 kg per square foot 150 kg per square foot 3305 kg in forward compartment and 4187 kg in aft compartment 7288 kg in forward compartment and 9232 kg in aft compartment
 68 kg per square foot.
68 kg per square foot. From the loading manual for the transport aeroplane the aft cargo compartment ?
Question 73-10 : 4187 kg 9232 kg 1568 kg 3062 kg
 4187 kg.
4187 kg. From the loading manual for the transport aeroplane the maximum load that can ?
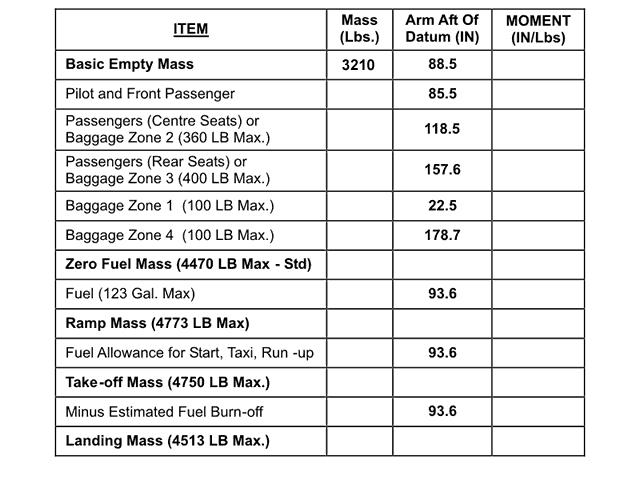
Question 73-11 : 835 5 inches is 3062 kg 421 5 inches is 2059 lbs 421 5 inches is 4541 kg 835 5 inches is 6752 kg
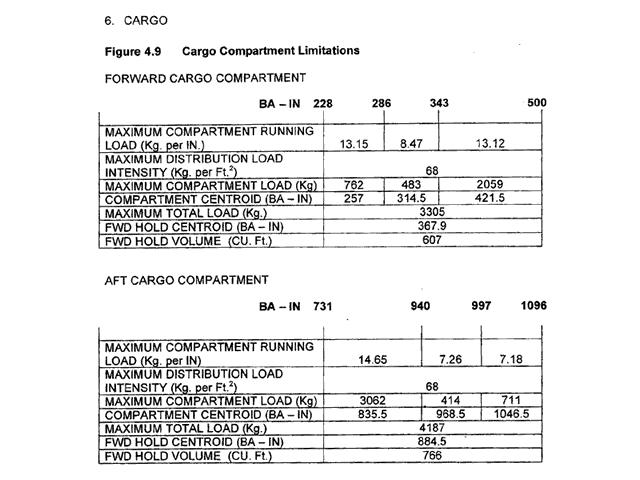 835.5 inches is 3062 kg.
835.5 inches is 3062 kg. An aeroplane whose specific data is shown in the annex has a planned take off ?
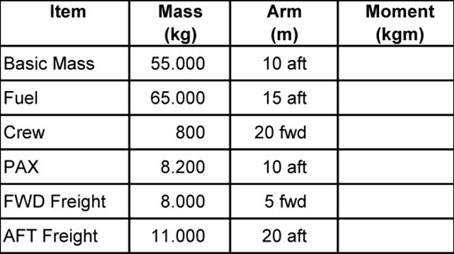
Question 73-12 : Front cargo 3 740 kg rear cargo 6 760 kg front cargo 9 260 kg rear cargo 1 240 kg front cargo 6 760 kg rear cargo 3 740 kg front cargo 4 550 kg rear cargo 5 950 kg
 Front cargo: 3 740 kg, rear cargo: 6 760 kg
Front cargo: 3 740 kg, rear cargo: 6 760 kg The floor limit of an aircraft cargo hold is 5 000 n/m2 .it is planned to load ?
Question 73-13 : 80 kg 800 kg 32 kg 320 kg
 80 kg.
80 kg. The floor of the main cargo hold is limited to 4000 n/m2 .it is planned to load ?
Question 73-14 : 100 kg 1000 kg 500 kg 5000 kg
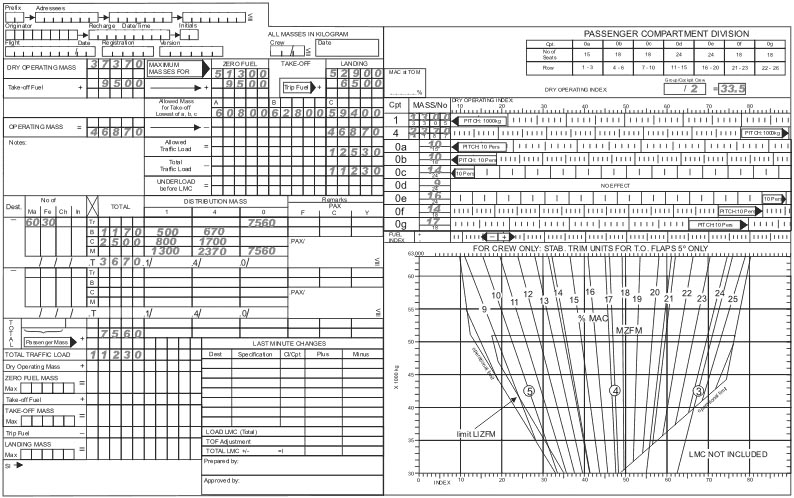 100 kg.
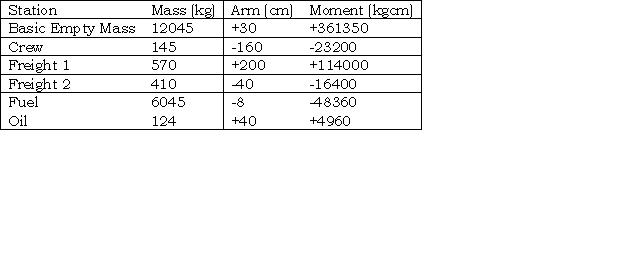
100 kg. Given . actual mass 116 500 lbs. original cg station 435 0. compartment a ?
Question 73-15 : 433 3 463 7 506 3 436 7
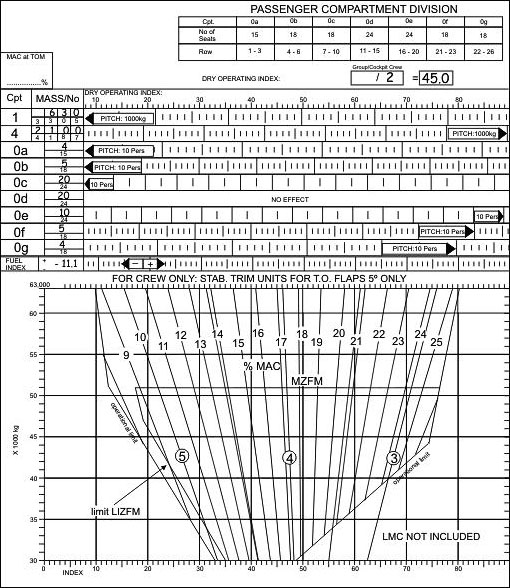 433.3
433.3 Pallet ground base 1 44 m² .the pallet is carried on two ground supports each ?
Question 73-16 : 351 kg 508 kg 175 kg 1054 kg
 351 kg.
351 kg. The maximum floor loading for a cargo compartment in an aircraft is given as ?
Question 73-17 : 40 cm by 200 cm 30 cm by 300 cm 30 cm by 200 cm 40 cm by 300 cm
 40 cm by 200 cm.
40 cm by 200 cm. Given the following data how much cargo must be moved from the forward hold to ?
Question 73-18 : 2760 kg 2904 kg 6000 kg 1467 kg
What is the maximum running load in the aft section of the forward lower ?
Question 73-19 : 13 12 kg/in 13 15 kg/in 14 65 kg/in 7 18 kg/in
 13.12 kg/in.
13.12 kg/in. Palletised cargo ?
Question 73-20 : Consists of different cargo box on pallets stored in the cargo holds can be loaded without specific loading equipment consists of passenger baggage on pallets stored in the cargo holds has fallen out of use due to the lack of protection
Bulk cargo ?
Question 73-21 : Can be loaded without specific loading equipment consists of different cargo box on pallets stored in the cargo holds consists of passenger baggage on pallets stored in the cargo holds has fallen out of use due to the lack of protection
 Can be loaded without specific loading equipment.
Can be loaded without specific loading equipment. Containerised cargo ?
Question 73-22 : Consists of baggage and cargo loaded into standard size containers stored in the cargo holds consists of different cargo box on pallets stored in the cargo holds can be loaded without specific loading equipment has fallen out of use due to the lack of protection
 Consists of baggage and cargo loaded into standard size containers stored in the cargo holds.
Consists of baggage and cargo loaded into standard size containers stored in the cargo holds. Bulk cargo ?
Question 73-23 : Consists of cargo box baggage loosely loaded in the cargo holds consists of different cargo box on pallets stored in the cargo holds consists of passenger baggage on pallets stored in the cargo holds has fallen out of use due to the lack of protection
 Consists of cargo (box, baggage) loosely loaded in the cargo holds.
Consists of cargo (box, baggage) loosely loaded in the cargo holds. Define the maximum load distribution ?
Question 73-24 : Load divided by smallest area mass per unit area load divided by largest area maximum admissible g force load
 Load divided by smallest area.
Load divided by smallest area. A pallet having a freight platform which measures 100 cm x 150 cm has a total ?
Question 73-25 : 20 kg may be added 140 kg must be off loaded 900 kg may be added 14 kg must be off loaded
 20 kg may be added.
20 kg may be added. A container that measure 1 42m² is to be loaded the maximum floor loading is ?
Question 73-26 : 1022 kg 507 kg 511 kg 720 kg
 1022 kg.
1022 kg. An aircraft has a mass of 5000 lbs and the cg is located at 80 inches aft of ?
Question 73-27 : 35 97 lbs 58 15 lbs 39 50 lbs 23 15 lbs
 35.97 lbs.
35.97 lbs. An aircraft has a loaded mass of 5500 lbs the cg is 22 inches aft of the datum ?
Question 73-28 : 23 9 inches 21 1 inches 26 3 inches 22 9 inches
 23.9 inches.
23.9 inches. The cg limits of an aircraft are from 83 inches to 93 inches aft of the datum ?
Question 73-29 : 55 38 lbs 74 96 lbs 82 09 lbs 22 49 lbs
 55.38 lbs.
55.38 lbs. An aircraft has three holds situated 10 inches 100 inches and 250 inches aft of ?
Question 73-30 : 500 kg 250 kg 400 kg 350 kg
 500 kg.
500 kg. A 5 kg mass is located at the end of a plank at 4m of the pivot on the other ?
Question 73-31 : 2 5 kg 10 kg 12 kg 3 kg
 2.5 kg.
2.5 kg. A 5m rope is attached around a pivot a man a user pulls a force of 400 newton ?
Question 73-32 : 400 n 800 n 600 n 200 n
 400 n.
400 n. A 3 m long plank is on a pivot located at 1m of the left side a user applies a ?
Question 73-33 : 200 n 400 n 600 n 800 n
 200 n.
200 n. Which pallet can be loaded in a hold whose maximum linear floor loading is 630 ?
Question 73-34 : 1 2 x 1 2m mass 700 kg 1 2 x 1 2m mass 760 kg 1 1 x 1 1m mass 700 kg 1 1 x 1 1m mass 760 kg
 1.2 x 1.2m, mass 700 kg.
1.2 x 1.2m, mass 700 kg. Which of the following statements about loading is correct ?
Question 73-35 : Containers can be connected directly to the aircraft and each container has its own manifest bulk cargo loading requires much less ground personal than the loading of containers live animals are never loaded as bulk cargo pallets are mainly used on small aircraft and are strapped down
 Containers can be connected directly to the aircraft and each container has its own manifest.
Containers can be connected directly to the aircraft and each container has its own manifest. Rush bags last minute baggage and cabin crew baggage is held in/on ?
Question 73-36 : Bulk cargo palletised cargo forbidden cargo containerized cargo
 Bulk cargo.
Bulk cargo. The maximum floor loading for a cargo compartment is given as 70 kg/m² .a ?
Question 73-37 : 1 8 m² 8 82 m² 0 48 m² 0 56 m²
 1.8 m².
1.8 m². Crew baggage is considered to be ?
Question 73-38 : Variable load palletized load containerized cargo load forbidden cargo load
 Variable load.
Variable load. Which of the following can be considered as bulk cargo ?
Question 73-39 : Baggage from late arrival passengers and crew hand baggage palletised cargo cargo on containers live animals
 Baggage from late arrival passengers and crew hand baggage.
Baggage from late arrival passengers and crew hand baggage. A jet aeroplane is climbing at constant mach number below the tropopause .which ?
Question 73-40 : Ias decreases and tas decreases ias increases and tas decreases ias increases and tas increases ias decreases and tas increases
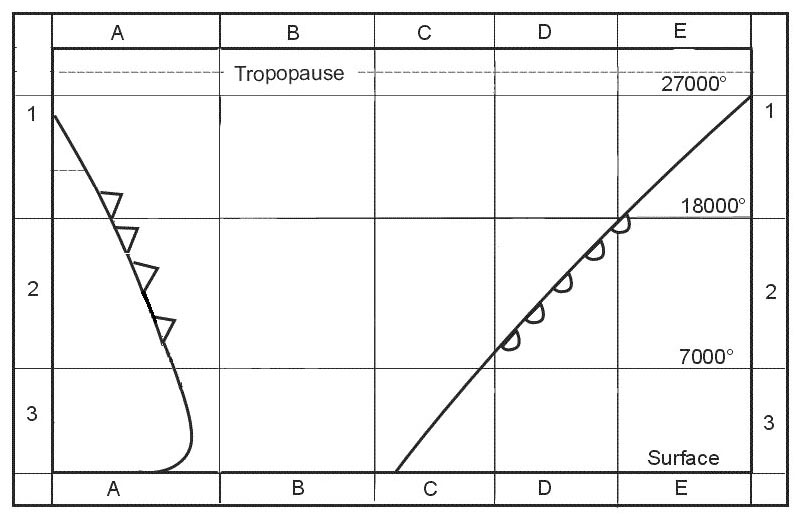 Ias decreases and tas decreases.
Ias decreases and tas decreases. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2879 Free Training Exam
