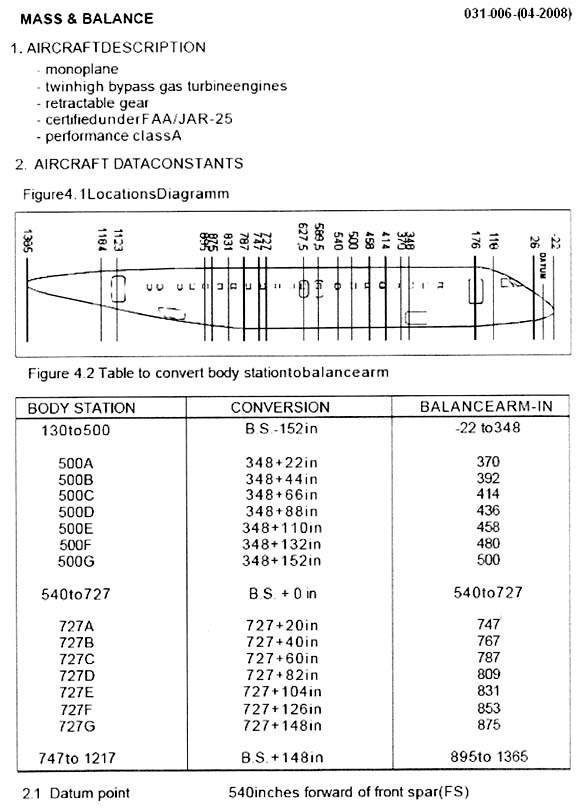
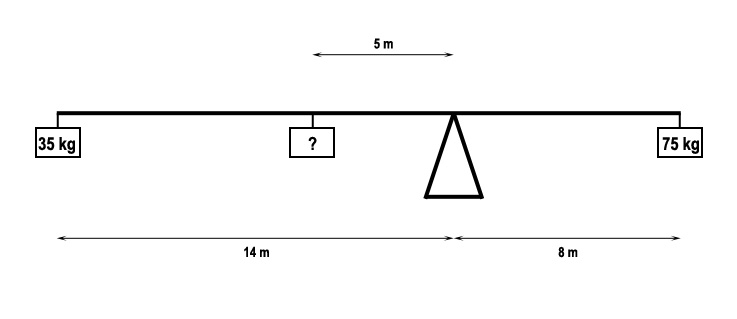
For the following see saw to be in balance . 236 ? [ Multiple protocol ]
Question 71-1 : Fb = a x fa / b fb = a + fa / b fb = a x b / fa fb = b x fa / a
 Fb = a x fa / b
Fb = a x fa / b For the following see saw to be in balance . 237 ?
Question 71-2 : Fc = fa / 3 fc = 3fa fc = fa / 3a fc = 3 / fa
 Fc = fa / 3
Fc = fa / 3 For the following boom to be in balance . 238 ?
Question 71-3 : B = fa x a / fb b = fb x a / fa b = fa x a / fb b = fb + a / fa
 B = fa x a / fb
B = fa x a / fb For the following boom to be in balance . 239 ?
Question 71-4 : A = b x fb / fa a = b + fb / fa a = b x fa / fb a = b fa + fb
 A = b x fb / fa
A = b x fb / fa A tri wheel aircraft has its datum 25 inches aft of the nose wheel and 180 ?
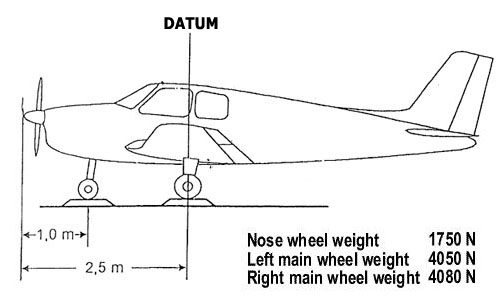
Question 71-5 : 6925 lbs and 201 2 inches from the nose wheel of the aircraft 6925 lbs and 176 3 inches from the nose wheel of the aircraft 3525 lbs and 172 7 inches from the datum 3525 lbs and 201 2 inches from the datum
 6925 lbs and 201.2 inches from the nose wheel of the aircraft.
6925 lbs and 201.2 inches from the nose wheel of the aircraft. The mass of an aircraft is 1950 kg .if 450 kg is added to a cargo hold 1 75 ?
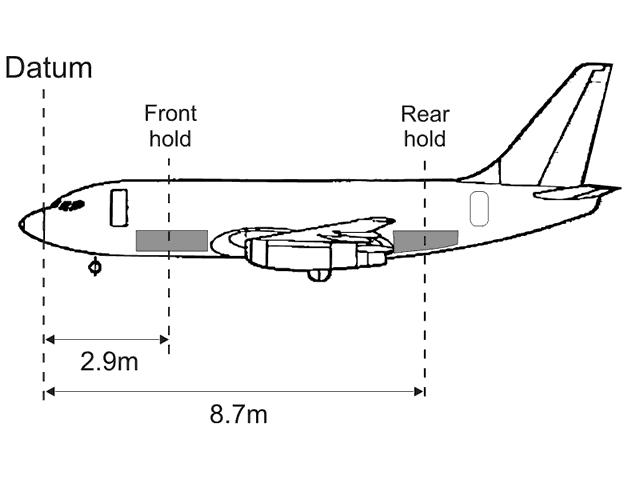
Question 71-6 : 33 cm 40 cm 30 cm 34 cm
 33 cm.
33 cm. If nose wheel moves aft during gear retraction how will this movement affect ?
Question 71-7 : It will cause the cg to move aft it will not affect the cg location it will cause the cg to move forward the cg location will change but the direction cannot be told the information given
 It will cause the cg to move aft.
It will cause the cg to move aft. Where is the centre of gravity of the aeroplane in the diagram . 185 ?
Question 71-8 : 26 57 cm forward of datum 32 29 cm forward of datum 26 57 cm aft of datum 32 29 cm aft of datum
 26.57 cm forward of datum.
26.57 cm forward of datum. Given .total mass 2900 kg.cg location station 115.aft cg limit station 116.the ?
Question 71-9 : 207 kg 317 kg 140 kg 14 kg
 207 kg.
207 kg. Given .total mass 7500 kg.centre of gravity cg location station 80 5.aft cg ?
Question 71-10 : 62 5 kg 73 5 kg 68 9 kg 65 8 kg
 62.5 kg.
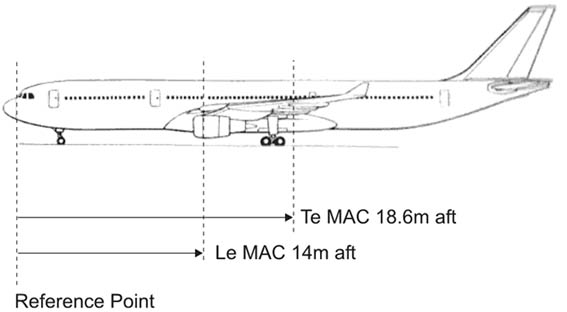
62.5 kg. A jet aeroplane with the geometrical characteristics shown in the appendix has ?
Question 71-11 : 27 5 % 35 5 % 30 4 % 16 9 %
 27.5 %.
27.5 %. The total mass of an aeroplane is 9000 kg the centre of gravity cg position is ?
Question 71-12 : 300 kg 30 kg 196 kg 900 kg
 300 kg.
300 kg. Assume .aircraft actual mass 4750 kg.centre of gravity at station 115 8.what ?
Question 71-13 : Station 117 69 station 118 33 station 120 22 station 118 25
 Station 117.69
Station 117.69 Given .aircraft mass 36000 kg.centre of gravity cg is located at station 17 ?
Question 71-14 : It moves aft by 0 31 m it moves forward by 0 157 m it moves aft by 3 22 m it moves aft by 0 157 m
 It moves aft by 0.31 m.
It moves aft by 0.31 m. Given the following information calculate the loaded centre of gravity cg . 197 ?
Question 71-15 : 56 53 cm aft datum 56 35 cm aft datum 60 16 cm aft datum 53 35 cm aft datum
 56.53 cm aft datum.
56.53 cm aft datum. Given are the following information at take off .given that the flight time is ?
Question 71-16 : 61 28 cm aft of datum 61 29 cm aft of datum 61 26 cm aft of datum 61 27 cm aft of datum
 61.28 cm aft of datum.
61.28 cm aft of datum. Given that the total mass of an aircraft is 112000 kg with a centre of gravity ?
Question 71-17 : 29344 kg 16529 kg 8680 kg 43120 kg
 29344 kg.
29344 kg. The total mass of an aeroplane is 145000 kg and the centre of gravity limits ?
Question 71-18 : 7500 kg 35000 kg 62500 kg 3500 kg
 7500 kg.
7500 kg. With respect to multi engine piston powered aeroplane determine the block fuel ?
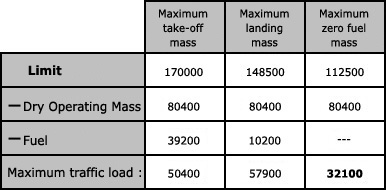
Question 71-19 : 56160 9360 433906 30888
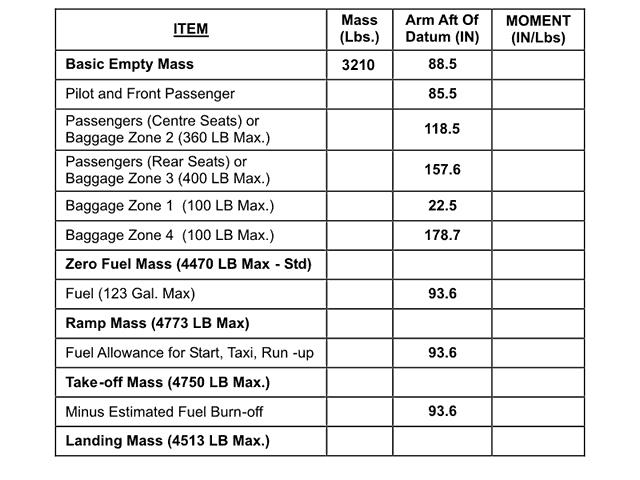
With respect to a multi engine piston powered aeroplane determine the total ?
Question 71-20 : 401338 lbs in 432221 lbs in 433906 lbs in 377746 lbs in
 401338 lbs.in
401338 lbs.in Determine the cg location at take off in the following conditions .basic empty ?
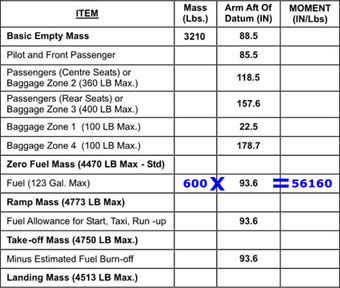
Question 71-21 : 91 92 inches aft of datum 91 84 inches aft of datum 91 69 inches aft of datum 93 60 inches aft of datum
 91.92 inches aft of datum.
91.92 inches aft of datum. With respect to a single engine piston powered aeroplane determine the zero ?
Question 71-22 : 2548 8 6675 2496 3 2311 8
 2548,8.
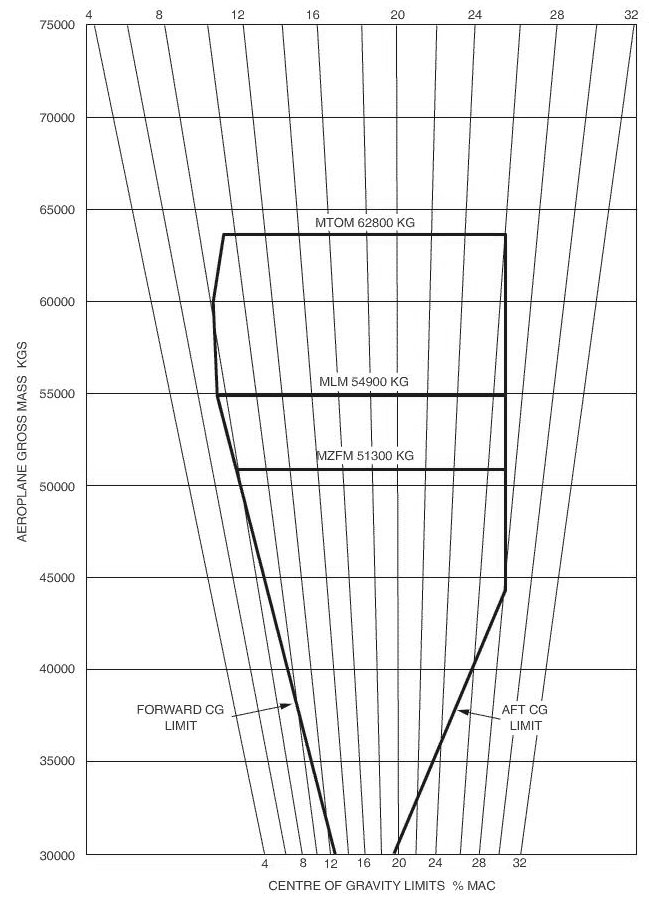
2548,8. The aeroplane has a mass of 51 000 kg in the cruise the range of safe cg ?
Question 71-23 : Forward limit 4% aft limit 29 7% mac forward limit 5% aft limit 29 7% mac forward limit 4% aft limit 29 2% mac forward limit 5% aft limit 29 5% mac
 Forward limit 4% aft limit 29.7% mac.
Forward limit 4% aft limit 29.7% mac. Considering the annex attached to the 50 000 kg mass determine the displacement ?
Question 71-24 : The centre of gravity move back from 4% to 5% mac the centre of gravity move forward from 4% to 5% mac the centre of gravity move back from 5% to 4% mac the centre of gravity move forward from 5% to 4% mac
 The centre of gravity move back from 4% to 5% mac.
The centre of gravity move back from 4% to 5% mac. Using the weight and balance graph provided in the appendix determine the range ?
Question 71-25 : From 5% to 29 2% mac from 5% to 29 5% mac from 4% to 29 5% mac if flaps and landing gear are retracted from 4% to 29 2% mac if flaps and landing gear are retracted
 From 5% to 29.2% mac.
From 5% to 29.2% mac. Prior to departure an aircraft is loaded with 16500 litres of fuel at a fuel ?
Question 71-26 : Lighter than anticipated and the calculated safety speeds will be too high lighter than anticipated and the calculated safety speeds will be too low heavier than anticipated and the calculated safety speeds will be too high heavier than anticipated and the calculated safety speeds will be too low
 Lighter than anticipated and the calculated safety speeds will be too high.
Lighter than anticipated and the calculated safety speeds will be too high. An additional baggage container is loaded into the aft cargo compartment but is ?
Question 71-27 : Will give reduced safety margins will not be achieved will be greater than required are unaffected but v1 will be increased
 Will give reduced safety margins.
Will give reduced safety margins. Fuel loaded onto an aeroplane is 15400 kg but is erroneously entered into the ?
Question 71-28 : Speed at which the airplane will leave the ground will be higher than expected v1 will be increased v1 will be reached sooner than expected the aeroplane will rotate much earlier than expected
 Speed at which the airplane will leave the ground will be higher than expected.
Speed at which the airplane will leave the ground will be higher than expected. Which of the following is unlikely to have any effect on the position of the ?
Question 71-29 : Changing the tailplane horizontal stabiliser incidence angle lowering the landing gear movement of cabin attendants going about their normal duties normal consumption of fuel for a swept wing aeroplane
 Changing the tailplane (horizontal stabiliser) incidence angle.
Changing the tailplane (horizontal stabiliser) incidence angle. Which of the following is unlikely to have any effect on the position of the ?
Question 71-30 : Changing the tailplane horizontal stabiliser incidence angle lowering the landing gear movement of cabin attendants going about their normal duties normal consumption of fuel for a swept wing aeroplane
 Changing the tailplane (horizontal stabiliser) incidence angle.
Changing the tailplane (horizontal stabiliser) incidence angle. When the centre of gravity is at the forward limit an aeroplane will be ?
Question 71-31 : Extremely stable and will require excessive elevator control to change pitch extremely stable and require small elevator control to change pitch extremely unstable and require excessive elevator control to change pitch extremely unstable and require small elevator control to change pitch
 Extremely stable and will require excessive elevator control to change pitch.
Extremely stable and will require excessive elevator control to change pitch. A mass of 500 kg is loaded at a station which is located 10 metres behind the ?
Question 71-32 : 80000 nm 30000 nm 50000 nm 130000 nm
 80000 nm.
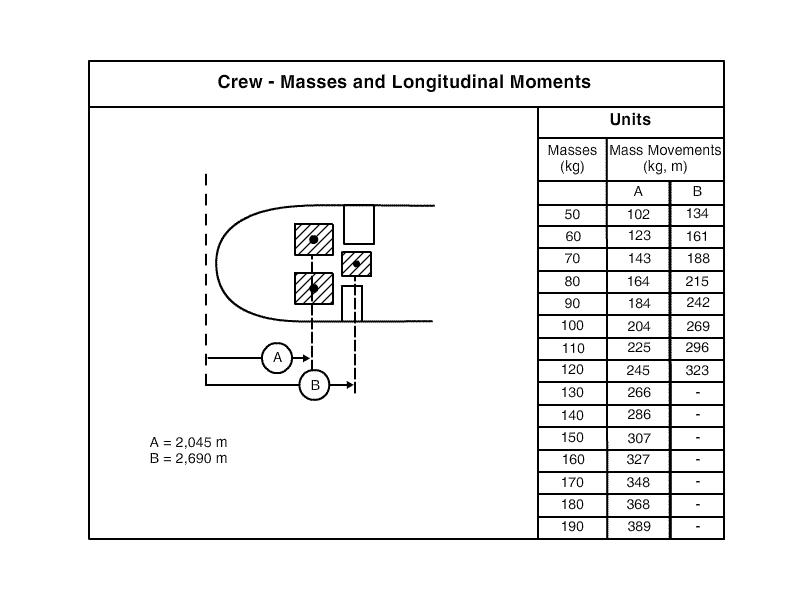
80000 nm. Without the crew the mass and longitudinal cg position of the aircraft are 6000 ?
Question 71-33 : 6270 kg and 4 594 m 6270 kg and 5 012 m 6270 kg and 4 61 m 6270 kg and 4 796 m
 6270 kg and 4.594 m.
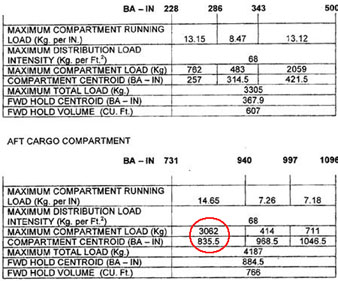
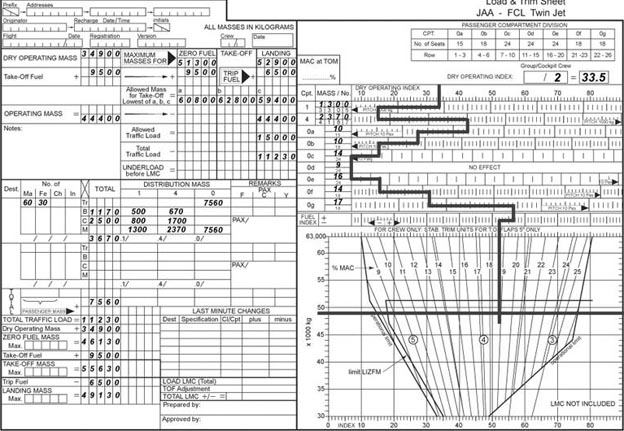
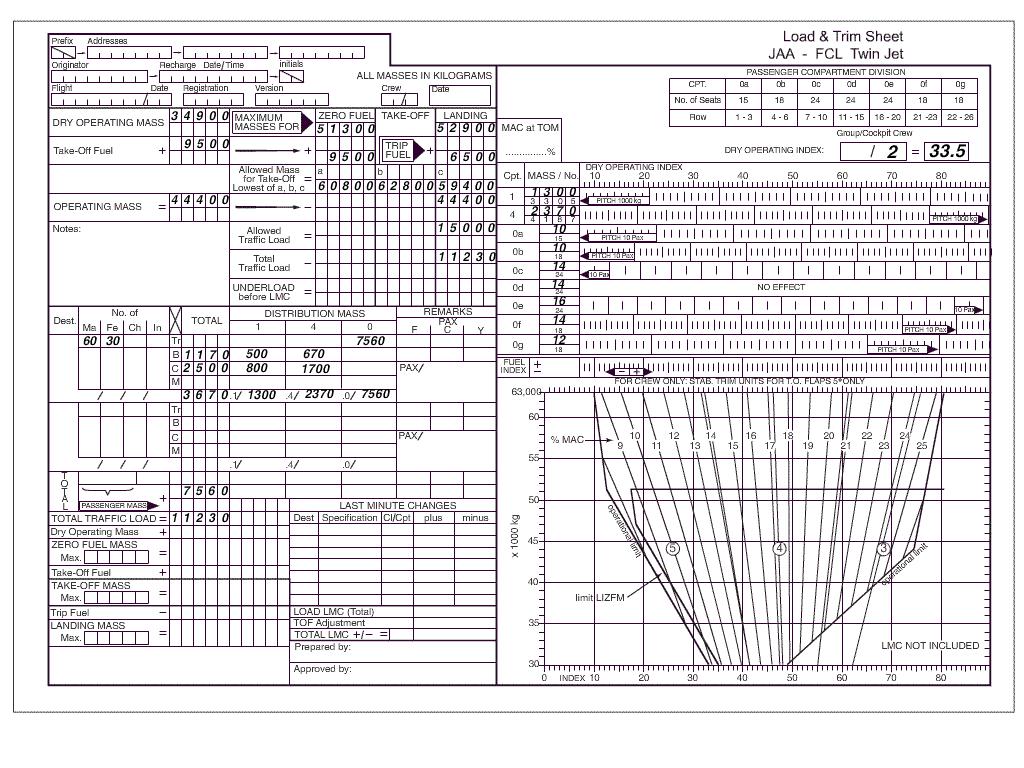
6270 kg and 4.594 m. Using the load and trim sheet for the mrjt1 aircraft which of the following is ?
Question 71-34 : 40 0 35 5 41 5 33 0
 40.0
40.0 Using the data given in the load and trim sheet determine which of the ?
Question 71-35 : 46130 kg and 17 8% 46130 kg and 20 8% 51300 kg and 20 8% 41300 kg and 17 8%
 46130 kg and 17.8%.
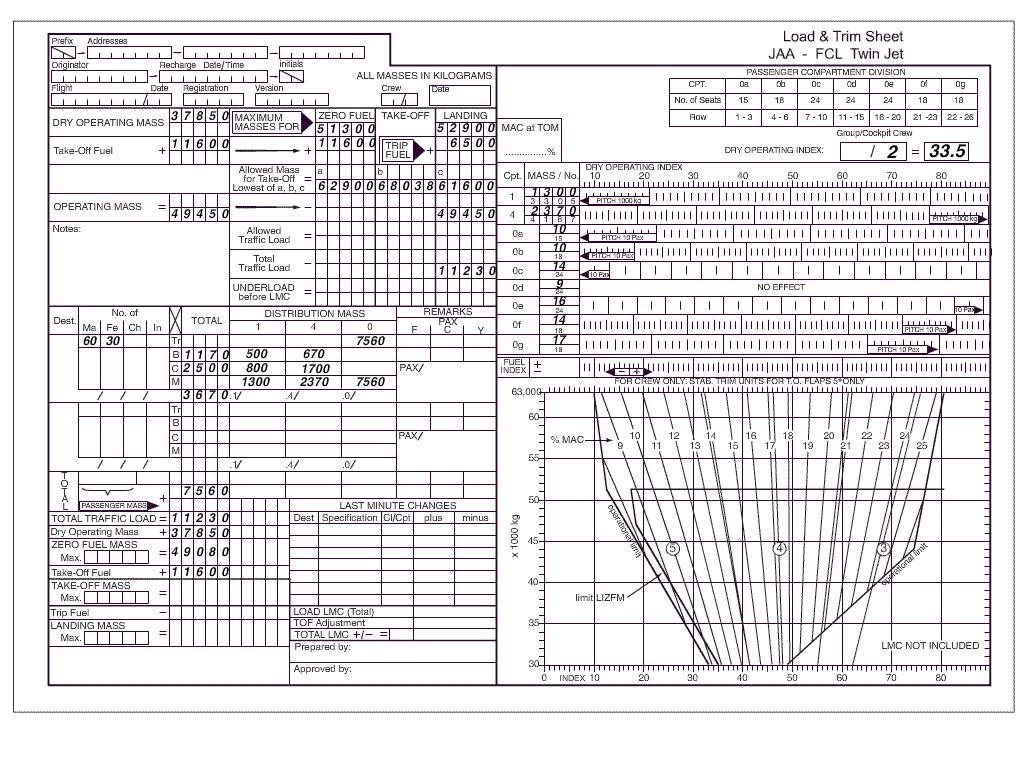
46130 kg and 17.8%. Using the data given in the load and trim sheet determine from the following ?
Question 71-36 : 17 5% 20 3% 22 6% 20 1%
 17.5%.
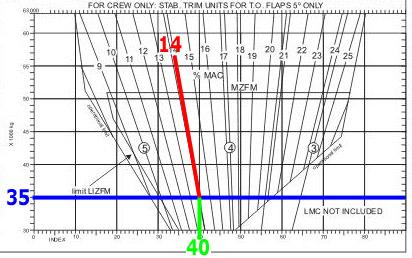
17.5%. Using the data given at the appendix to this question if the fuel index ?
Question 71-37 : 49130 kg and 19% 52900 kg and 21 6% 49130 kg and 21 8% 52900kg and 19%
 49130 kg and 19%.
49130 kg and 19%. Using the data given at the appendix determine which of the following correctly ?
Question 71-38 : 48600 kg and 57 0 51300 kg and 57 0 46300 kg and 20 5 35100 kg and 20 5
 48600 kg and 57.0.
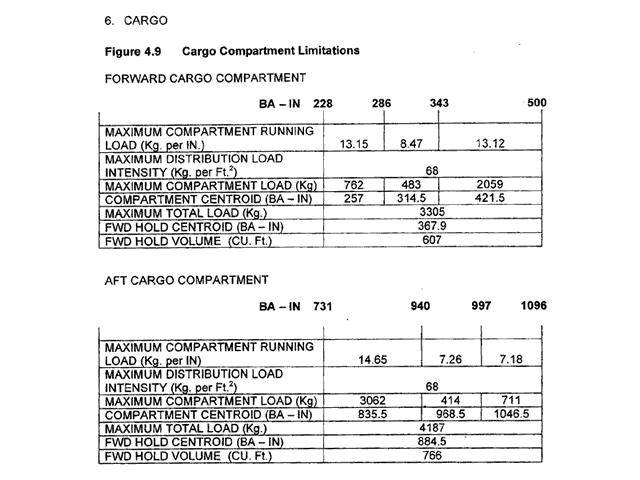
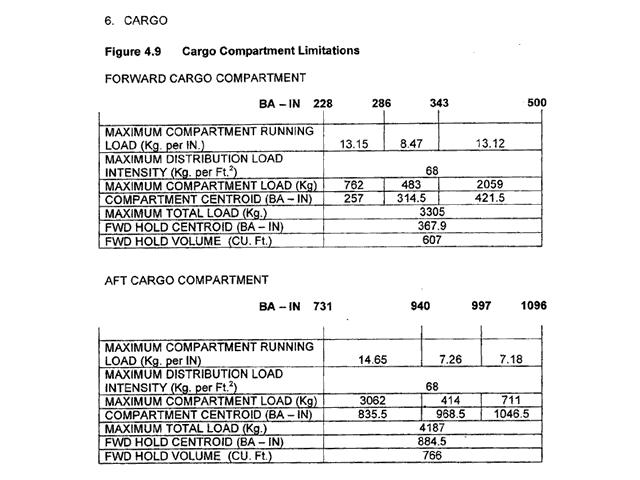
48600 kg and 57.0. For this question use annex ecqb 031 mb 02 v2015 03 .from the data given at the ?
Question 71-39 : 18% 19% 15% 14%
 18%.
18%. From the data contained in the attached appendix the maximum allowable take off ?
Question 71-40 : 61600 kg and 12150 kg 68038 kg and 18588 kg 66770 kg and 17320 kg 60425 kg and 10975 kg
 61600 kg and 12150 kg.
61600 kg and 12150 kg. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2799 Free Training Exam
