The loading for a flight is shown in the loadsheet with the following data ? [ Mandatory landing ]
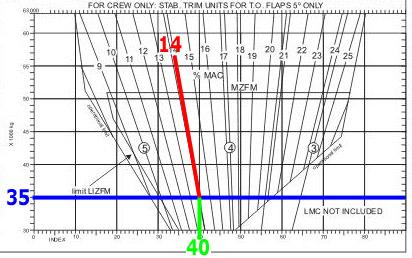
Question 67-1 : Landing cg is out of limits at 10 17 m aft of datum landing cg is out of limits at 11 97 m aft of datum take off cg is out of limits at 10 17 m aft of datum take off cg is out of limits at 12 34 m aft of datum
 Landing cg is out of limits at 10.17 m aft of datum.
Landing cg is out of limits at 10.17 m aft of datum. Given an aeroplane with .maximum structural landing mass 68000 kg.maximum zero ?
Question 67-2 : 75000 kg and 17200 kg 75000 kg and 20000 kg 77200 kg and 19400 kg 77200 kg and 22200 kg
 75000 kg and 17200 kg.
75000 kg and 17200 kg. Dry operating mass is the mass of the aircraft less ?
Question 67-3 : Usable fuel and traffic load usable fuel traffic load potable water and lavatory chemicals usable fuel potable water and lavatory chemicals
 Usable fuel and traffic load.
Usable fuel and traffic load. The total mass of the aircraft including crew crew baggage plus catering and ?
Question 67-4 : Dry operating mass zero fuel mass landing mass maximum zero fuel mass
 Dry operating mass.
Dry operating mass. The responsibility for determination of the mass of 'operating items' and 'crew ?
Question 67-5 : The operator the commander the authority of the state of registration the person compiling the weighing schedule
 The operator.
The operator. The dry operating mass is the total mass of the aircraft ready for a specific ?
Question 67-6 : Usable fuel and traffic load the traffic load useful fuel crew and crew baggage
 Usable fuel and traffic load.
Usable fuel and traffic load. The take off mass of an aeroplane is 66700 kg which includes a traffic load of ?
Question 67-7 : 42000 kg 56200 kg 41455 kg 42545 kg
 42000 kg.
42000 kg. The maximum certificated taxi or ramp mass is that mass to which an aircraft ?
Question 67-8 : A fixed value which is listed in the flight manual a value which varies with airfield temperature and altitude corrections are listed in the flight manual a value which varies only with airfield altitude standard corrections are listed in the flight manual a value which is only affected by the outside air temperature corrections are calculated from data given in the flight manual
 A fixed value which is listed in the flight manual.
A fixed value which is listed in the flight manual. The maximum mass to which an aeroplane may be loaded prior to engine start is ?
Question 67-9 : Maximum certificated taxi ramp mass maximum regulated taxi ramp mass maximum certificated take off mass maximum regulated take off mass
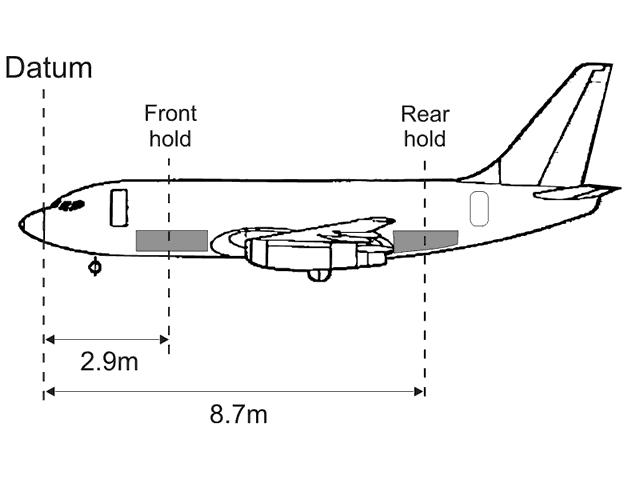 Maximum certificated taxi (ramp) mass.
Maximum certificated taxi (ramp) mass. The zero fuel mass and the dry operating mass ?
Question 67-10 : Differ by the value of the traffic load mass are the same value differ by the sum of the mass of usable fuel plus traffic load mass differ by the mass of usable fuel
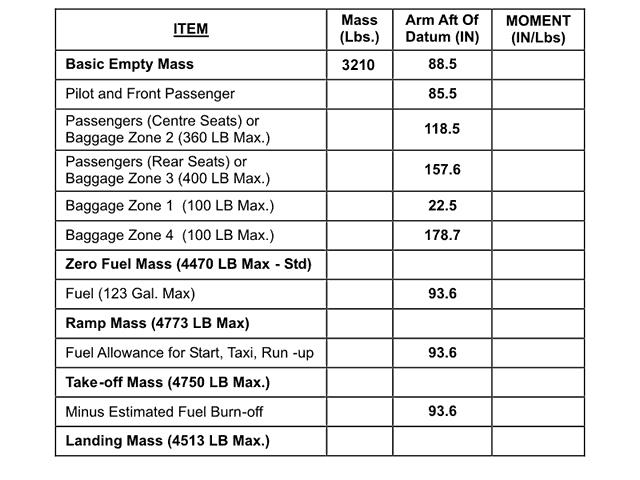 Differ by the value of the traffic load mass.
Differ by the value of the traffic load mass. A revenue flight is planned for the transport aeroplane take off mass is not ?
Question 67-11 : 4530 kg 5400 kg 6350 kg 3185 kg
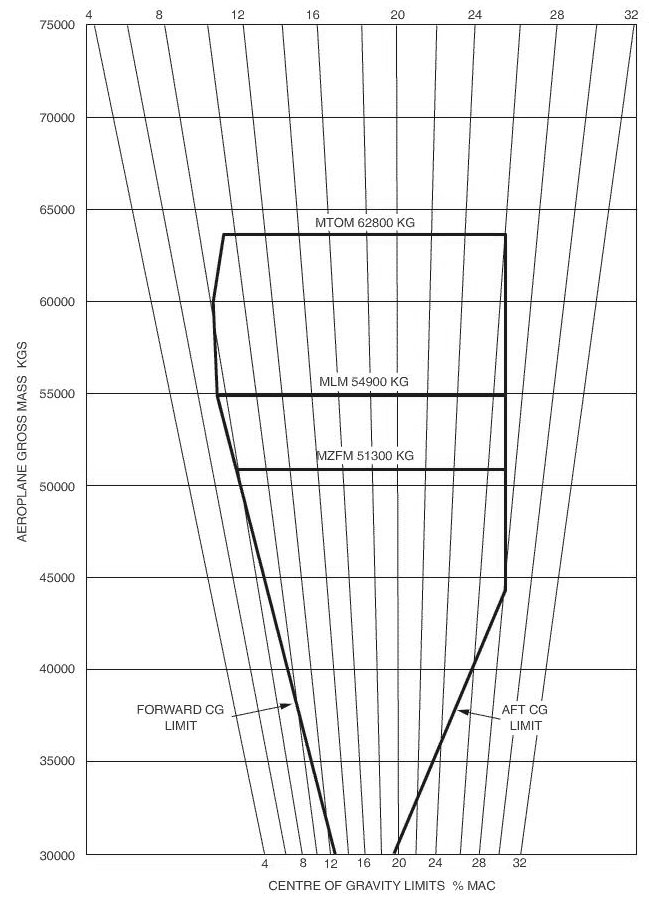 4530 kg.
4530 kg. The empty mass of an aeroplane is given as 44800 kg .operational items ?
Question 67-12 : 18400 kg 20700 kg 23000 kg 19460 kg
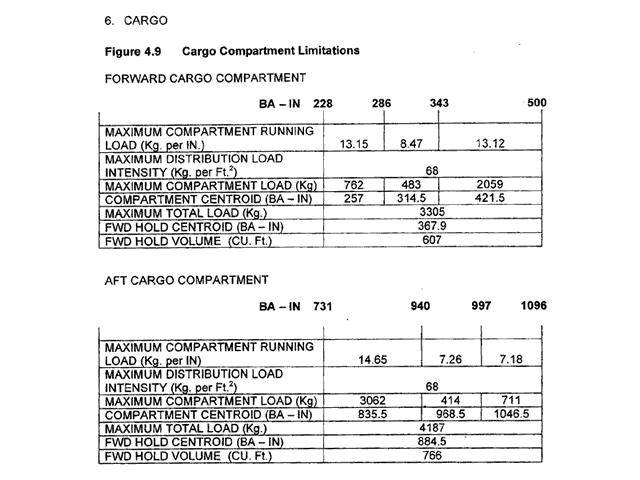 18400 kg.
18400 kg. The maximum zero fuel mass is a structural limiting mass it is made up of the ?
Question 67-13 : Traffic load traffic load unuseable fuel and crew standard mass unuseable and crew standard mass traffic load and crew standard mass
 Traffic load.
Traffic load. The take off mass of an aeroplane is 141000 kg .total fuel on board is 63000 kg ?
Question 67-14 : 79000 kg 78000 kg 93000 kg 65200 kg
 79000 kg.
79000 kg. 'standard mass' as used in the computation of passenger load establish the mass ?
Question 67-15 : 35 kg irrespective of age provided they occupy a seat 35 kg only if they are over 2 years old and occupy a seat 35 kg for children over 2 years occupying a seat and 10 kg for infants less than 2 years not occupying a seat 35 kg for children over 2 years occupying a seat and 10 kg for infants less than 2 years occupying a seat
 35 kg irrespective of age provided they occupy a seat.
35 kg irrespective of age provided they occupy a seat. The maximum certificated take off mass is ?
Question 67-16 : A structural limit which may not be exceeded for any take off a take off limiting mass which is affected by the aerodrome altitude and temperature a take off limiting mass which is governed by the gradient of climb after reaching v2 limited by the runway take off distance available it is tabulated in the flight manual
 A structural limit which may not be exceeded for any take-off.
A structural limit which may not be exceeded for any take-off. For a particular aeroplane the structural maximum mass without any fuel on ?
Question 67-17 : A fixed value which is stated in the aeroplane operating manual a variable value which is governed by the pcn and acn a variable value which is governed by the traffic load carried a fixed value which will limit the amount of fuel carried
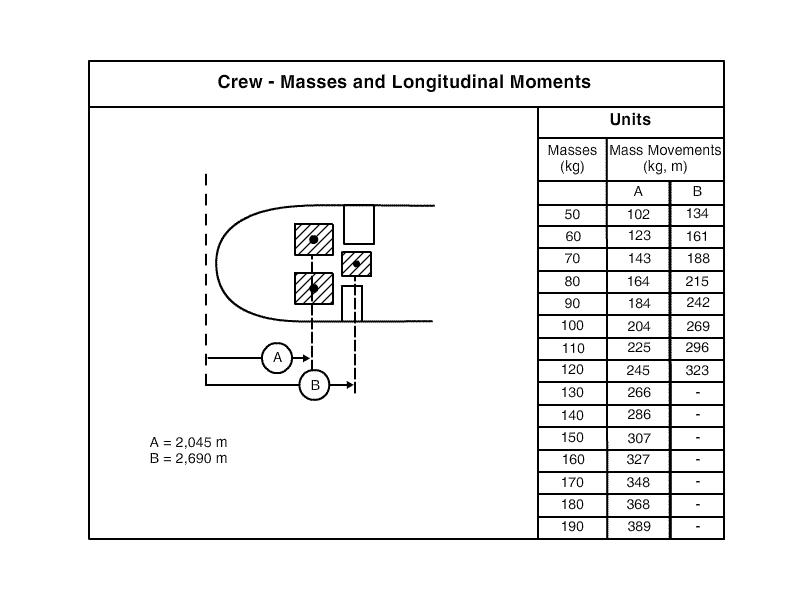 A fixed value which is stated in the aeroplane operating manual.
A fixed value which is stated in the aeroplane operating manual. On an aeroplane with a seating capacity of more than 30 it is decided to use ?
Question 67-18 : 84 kg 88 kg 76 kg 83 kg
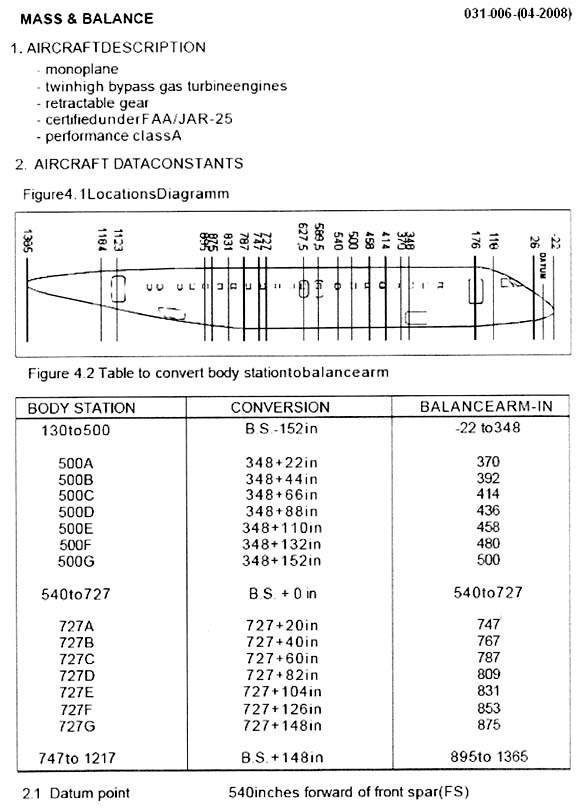 84 kg.
84 kg. The standard mass for a child is ?
Question 67-19 : 35 kg for all flights 35 kg for holiday charters and 38 kg for all other flights 38 kg for all flights 30 kg for holiday charters and 35 kg for all other flights
 35 kg for all flights.
35 kg for all flights. On an aeroplane with 20 or more seats engaged on an inter continental flight ?
Question 67-20 : 15 kg per passenger 13 kg per passenger 14 kg per passenger 11 kg per passenger
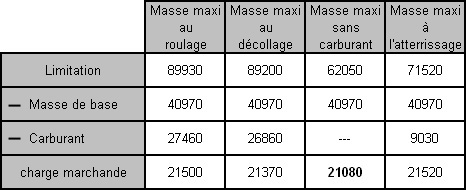
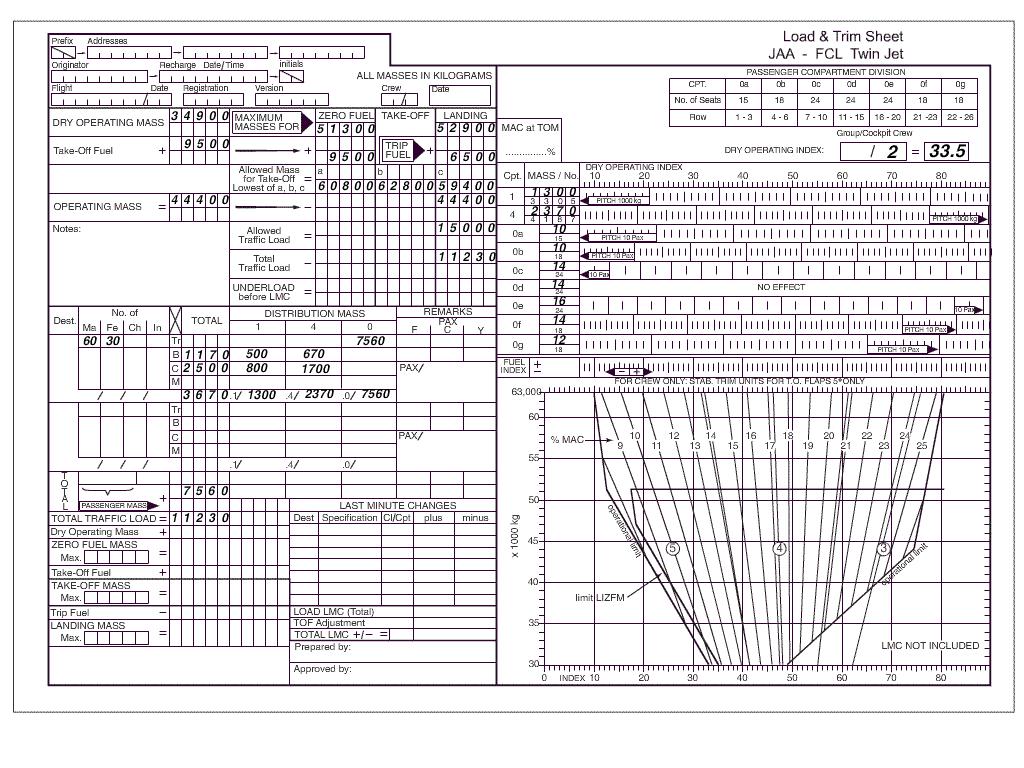
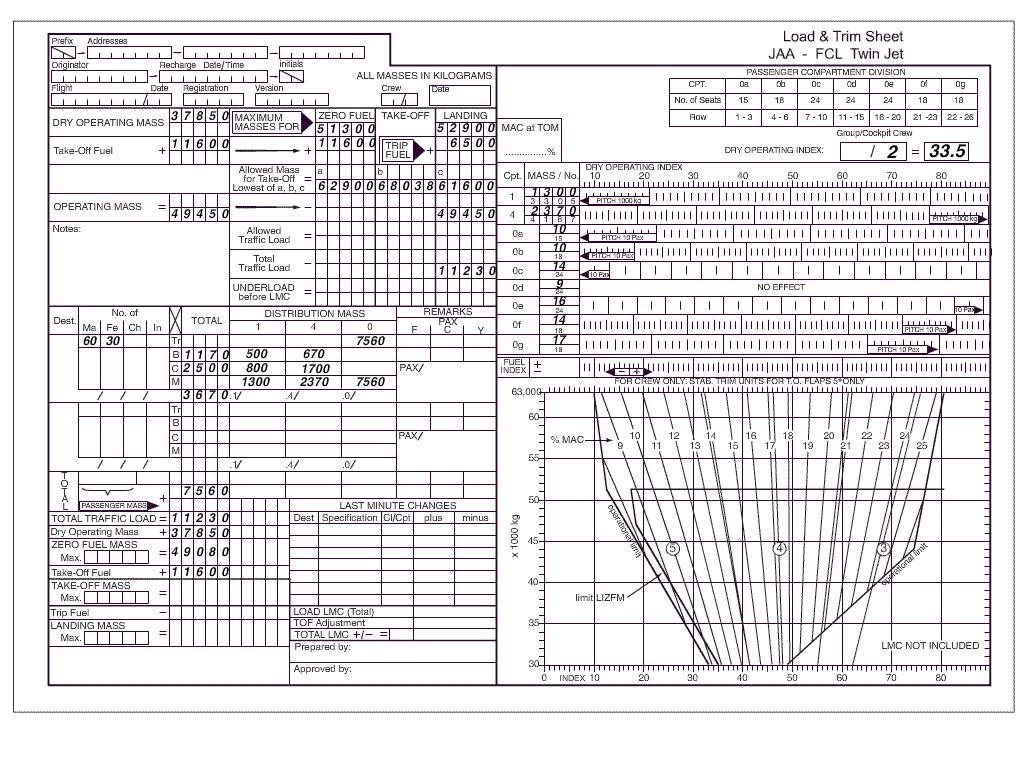
The following data applies to a planned flight .dry operating mass 34900 kg ?
Question 67-21 : 12700 kg 13230 kg 15200 kg 10730 kg
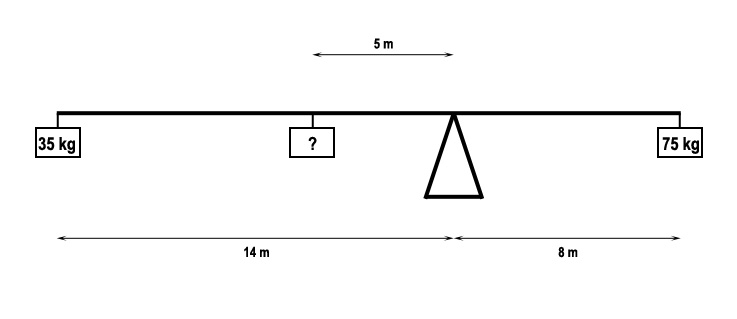 12700 kg.
12700 kg. In determining the dry operating mass of an aeroplane it is common practice to ?
Question 67-22 : Flight crew 85 kg cabin crew 75 kg each these are inclusive of a hand baggage allowance flight crew 85 kg cabin crew 75 kg each these do not include a hand baggage allowance flight crew male 88 kg female 75 kg cabin crew 75 kg each these include an allowance for hand baggage flight crew male 88 kg female 75 kg cabin crew 75 kg each these do not include an allowance for hand baggage
 Flight crew 85 kg, cabin crew 75 kg, each. these are inclusive of a hand baggage allowance.
Flight crew 85 kg, cabin crew 75 kg, each. these are inclusive of a hand baggage allowance. The medium range jet transport aeroplane is to operate a flight carrying the ?
Question 67-23 : 14470 kg 13655 kg 16080 kg 15815 kg
 14470 kg.
14470 kg. An aircraft is to depart from an airfield at a take off mass of 302550 kg .fuel ?
Question 67-24 : 141100 kg 19650 kg 121450 kg 39105 kg
 141100 kg.
141100 kg. Conversion of fuel volume to mass ?
Question 67-25 : May be done by using standard fuel density values as specified in the operations manual if the actual fuel density is not known may be done by using standard fuel density values as specified in easa air ops must be done by using actual measured fuel density values must be done using fuel density values of 0 79 for jet a1 and 0 76 for jet a2 as specified in easa air ops
 May be done by using standard fuel density values as specified in the operations manual, if the actual fuel density is not known.
May be done by using standard fuel density values as specified in the operations manual, if the actual fuel density is not known. Standard masses may be used for the computation of mass values for baggage if ?
Question 67-26 : Has 20 or more seats has 6 or more seats has 30 or more seats is carrying 30 or more passengers
 Has 20 or more seats.
Has 20 or more seats. A jet transport has the following structural limits . maximum ramp mass 63 060 ?
Question 67-27 : 16 370 kg 17 070 kg 16 570 kg 16 430 kg
 16 370 kg.
16 370 kg. A flight has been made from london to valencia carrying minimum fuel and ?
Question 67-28 : 14 331 kg 13 240 kg 16 770 kg 9 830 kg
 14 331 kg.
14 331 kg. The term 'useful load' as applied to a aircraft includes ?
Question 67-29 : Traffic load plus useable fuel the revenue earning portion of traffic load only traffic load only the revenue earning portion of traffic load plus useable fuel
 Traffic load plus useable fuel.
Traffic load plus useable fuel. An aeroplane is performance limited to a landing mass of 54230 kg .the dry ?
Question 67-30 : 29280 kg 17080 kg 12200 kg 10080 kg
 29280 kg.
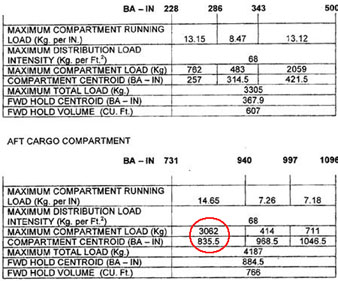
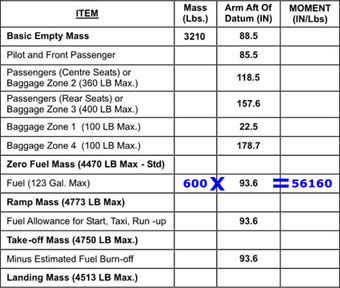
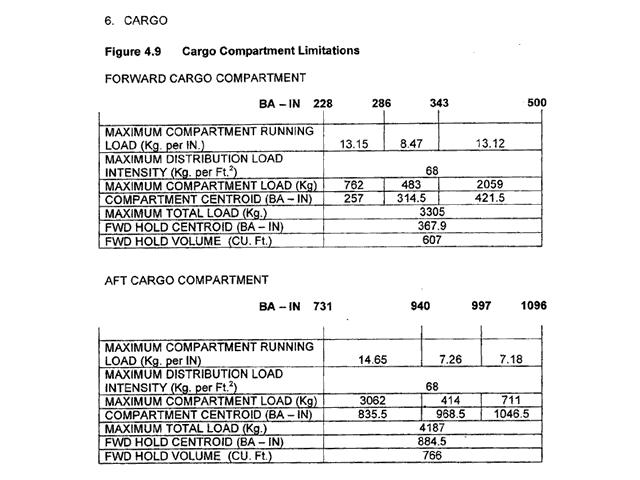
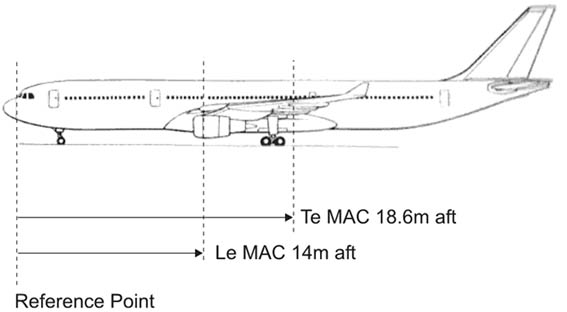
29280 kg. For the medium range transport aeroplane from the loading manual determine the ?
Question 67-31 : 11348 litres 8850 litres 11646 litres 5674 litres
 11348 litres.
11348 litres. The flight preparation of a turbojet aeroplane provides the following data ?
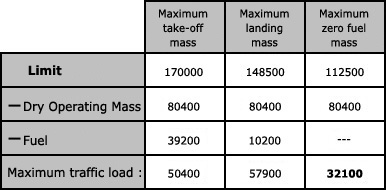
Question 67-32 : 54 000 kg 55 000 kg 55 500 kg 61 500 kg
 54 000 kg.
54 000 kg. The crew of a transport aeroplane prepares a flight using the following data . ?
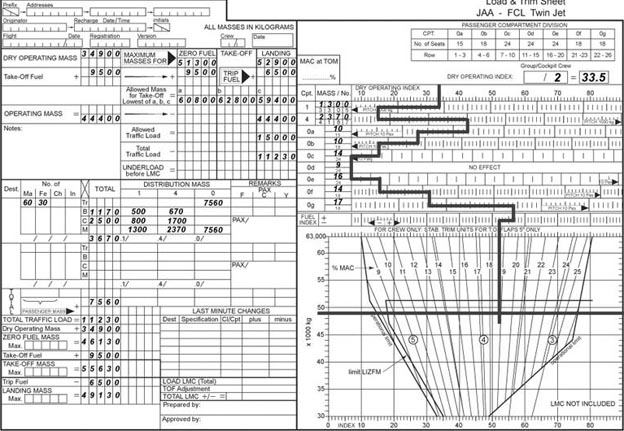
Question 67-33 : 32 100 kg 40 400 kg 32 900 kg 18 900 kg
 32 100 kg.
32 100 kg. The dry operating mass of an aircraft is 2000 kg .the maximum take off mass ?
Question 67-34 : 1000 kg 950 kg 1500 kg 1450 kg
 1000 kg.
1000 kg. The basic empty mass of an aircraft is 30000 kg the masses of the following ?
Question 67-35 : 30 665 kg 30 300 kg 38 300 kg 30 785 kg
 30 665 kg.
30 665 kg. By adding to the basic empty mass the following fixed necessary equipment for a ?
Question 67-36 : Dry operating mass take off mass zero fuel mass landing mass
 Dry operating mass.
Dry operating mass. An aircraft dry operating mass is 3000 kg the maximum take off landing and zero ?
Question 67-37 : 1600 kg 1550 kg 2200 kg 2150 kg
 1600 kg.
1600 kg. Given .maximum structural take off mass 8350 kg.maximum structural landing mass ?
Question 67-38 : 7000 kg 7780 kg 7790 kg 8350 kg
 7000 kg.
7000 kg. Given .zero fuel mass 6660 kg.trip fuel 990 kg.block fuel 1540 kg.taxi fuel 25 ?
Question 67-39 : 8175 kg 8200 kg 7210 kg 8110 kg
 8175 kg.
8175 kg. Given .zero fuel mass 4920 kg.trip fuel 880 kg.block fuel 1330 kg.taxi fuel 25 ?
Question 67-40 : 6225 kg 6250 kg 6810 kg 6360 kg
 6225 kg.
6225 kg. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2639 Free Training Exam
