On a large aeroplane the input data of the stall warning system are .1 angle ? [ Diploma registration ]
Question 63-1 : 1 4 1 2 4 2 3 4 1 2
 1, 4
1, 4 Concerning the tcas ii .1 neither advisory nor traffic display is provided for ?
Question 63-2 : 1 2 3 1 2 1 3 2 3
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. The aural alert associated with the mode 5 excessive deviation below glideslope ?
Question 63-3 : 'glideslope' 'caution glideslope' 'too low glideslope' 'monitor glideslope'
 'glideslope'.
'glideslope'. The aural alert associated with the mode 1 excessive descent rate of the gpws is ?
Question 63-4 : 'sink rate' 'don't sink' 'too low terrain' 'terrain'
 'sink rate'.
'sink rate'. The aural alert associated with the mode 3 altitude loss after take off or go ?
Question 63-5 : 'don't sink' 'sinkrate' 'too low terrain' 'terrain'
 'don't sink'.
'don't sink'. The aural alert associated with the mode 2 excessive terrain closure rate of ?
Question 63-6 : 'terrain' 'sinkrate' 'don't sink' 'climb'
 'terrain'.
'terrain'. The radio altimeter supplies data to the following system s .1 altitude alert ?
Question 63-7 : 2 3 4 1 4 3 3 4
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. The input data to the gpws originate from the .1 transponder.2 angle of ?
Question 63-8 : 4 1 4 2 3 4
 4.
4. The main function s of a tcas is to .1 alert the crew to ground proximity.2 ?
Question 63-9 : 2 1 3 1 2 3 4 2 4
 2.
2. The aural alert s associated with the mode 1 excessive descent rate of the gpws ?
Question 63-10 : 3 4 2 4 1 2
 3, 4.
3, 4. The aural alert s associated with the mode 3 altitude loss after take off or go ?
Question 63-11 : 1 2 2 4 3 4
 1.
1. The aural alert s associated with the mode 5 excessive deviation below ?
Question 63-12 : 3 2 2 4 1
 3.
3. A tcas resolution advisory ra voice message 'climb climb now' repeated twice ?
Question 63-13 : After a 'descend' ra when a reversal in the vertical manoeuvre sense is required after a 'climb' ra when the climb vertical rate is too weak each time a 'climb' ra is announced by a voice message when cleared of conflict and below the cruise altitude
 After a 'descend' ra when a reversal in the vertical manoeuvre sense is required.
After a 'descend' ra when a reversal in the vertical manoeuvre sense is required. When comparing a tcas traffic advisory ta and a resolution advisory ra which ?
Question 63-14 : A ta indicates the relative position of the intruding traffic an ra provides a vertical traffic avoidance manoeuvre an ra indicates the relative position of the intruding traffic a ta provides a vertical traffic avoidance manoeuvre a ta provides the display of the traffic on the navigation display and the red arc on the vertical speed indicator an ra provides the voice alerts an ra generates the intruders colour codes on the navigation display according to the threat a ta manages the other tcas functions
 A ta indicates the relative position of the intruding traffic; an ra provides a vertical traffic avoidance manoeuvre.
A ta indicates the relative position of the intruding traffic; an ra provides a vertical traffic avoidance manoeuvre. On a large aeroplane and according to the cs 25 207 when the speed is reduced ?
Question 63-15 : At a speed exceeding the stall speed by not less than 5 kt or 5% cas whichever is greater at a speed exceeding the stall speed by not less than 10 kt or 10% cas exactly at the stall speed at the stall speed +/ 5% cas
 At a speed exceeding the stall speed by not less than 5 kt or 5% cas, whichever is greater.
At a speed exceeding the stall speed by not less than 5 kt or 5% cas, whichever is greater. If a tcas resolution advisory ra requires an immediate descent while at the ?
Question 63-16 : Follow the tcas ra and inform the atc comply with the atc request consider both requests and remain at the same level start a climb first and then follow the tcas ra
 Follow the tcas ra and inform the atc.
Follow the tcas ra and inform the atc. Your aircraft and an intruding traffic are tcas ii equipped .your tcas can ?
Question 63-17 : Coordinated resolution advisories coordinated traffic advisories resolution advisories coordinated with the atc instructions traffic advisories coordinated with the atc instructions
 Coordinated resolution advisories.
Coordinated resolution advisories. Which of these statements about the activation of the take off warning when a ?
Question 63-18 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Which of these statements about the activation of the take off warning when a ?
Question 63-19 : I is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is correct, ii is incorrect.
I is correct, ii is incorrect. Which of these statements about the activation of the take off warning when a ?
Question 63-20 : I is incorrect ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is correct.
I is incorrect, ii is correct. The stick pusher is a part of the ?
Question 63-21 : Stall protection system automatic flight control system afcs flight envelope protection fep system stall warning system sws
The egpws ?
Question 63-22 : Is an enhanced gpws which has a its own world terrain database is an enhanced gpws which warns the crew if the airplane is not in the appropriate configuration for take off is an enhanced gpws which is able to provide resolution advisories in the lateral plane has nothing to do with the gpws
 Is an enhanced gpws which has a its own world terrain database.
Is an enhanced gpws which has a its own world terrain database. The stall warning computer of a large aeroplane uses the following data .1 ?
Question 63-23 : 2 3 1 2 1 2 3 1 3
 2, 3.
2, 3. When a tcas is operating a failure of the active transponder will cause the ?
Question 63-24 : No longer operate normally operate in the traffic advisory ta mode only operate normally operate in the resolution advisory ra mode only
 No longer operate normally.
No longer operate normally. The stall warning system of a large aeroplane includes .1 an angle of attack ?
Question 63-25 : 1 2 4 1 2 3 1 3 2 4
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. The gpws receives data from the following systems .1 landing gear and flaps ?
Question 63-26 : 1 3 1 2 3 4 3 4 1 2
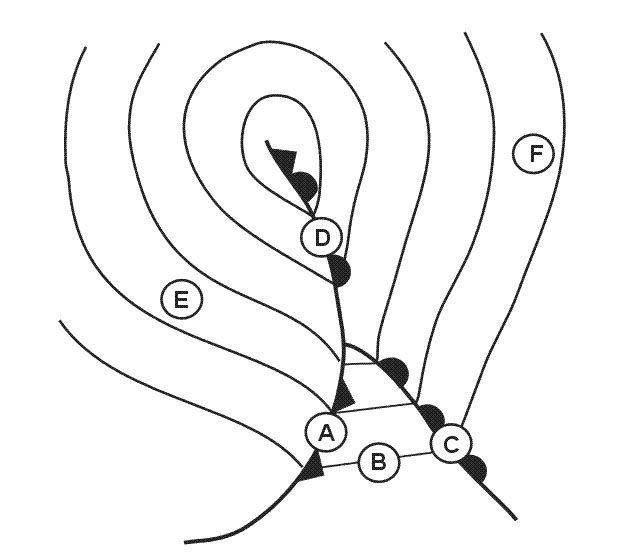 1, 3.
1, 3. For compatibility between the different components of a flight warning system ?
Question 63-27 : Stall windshear gpws tcas stall tcas gpws windshear tcas stall windshear gpws gpws stall tcas windshear
 Stall, windshear, gpws, tcas.
Stall, windshear, gpws, tcas. When a tcas resolution advisory ra climb instruction is generated the required ?
Question 63-28 : Does not take into account the stall margin takes into account a 1 3 vs stall margin always takes into account the stall margin takes into account a 1 1 vs stall margin
 Does not take into account the stall margin.
Does not take into account the stall margin. The aural alert s associated with the mode 4 of the gpws unsafe terrain ?
Question 63-29 : 1 2 3 1 2 2 2 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. When enhanced gpws egpws terrain is displayed if the computed aircraft position ?
Question 63-30 : The terrain display will diverge from the real terrain environment around the aircraft position the egpws will perform a correction of position thus the terrain display accuracy won't be degraded the egpws will fail the terrain display function and the terrain will be removed from the navigation display the egpws has its own position sensors thus the terrain display accuracy won't be degraded
 The terrain display will diverge from the real terrain environment around the aircraft position.
The terrain display will diverge from the real terrain environment around the aircraft position. With a tcas ii when a corrective resolution is generated ?
Question 63-31 : The vertical speed must be effectively modified without delay the heading must be effectively modified without delay the ias must be effectively modified without delay no action is required vertical speed heading and ias can remained unchanged
 The vertical speed must be effectively modified without delay.
The vertical speed must be effectively modified without delay. At high angles of attack and according to the type of aeroplane the stall ?
Question 63-32 : 2 1 2 1 3 1 2 3
 2.
2. To stop the warning generated by the overspeed warning system the pilot may .1 ?
Question 63-33 : 3 1 2 3 1 3 2 3
 3.
3. To warn the flight crew an overspeed warning system can use .1 an aural ?
Question 63-34 : 1 1 2 2 1 2 3
 1.
1. When a tcas resolution advisory ra is generated the required vertical speed ?
Question 63-35 : Is displayed on the vsi shows a red arc on the vsi as your target rate of climb/ descent is vocally announced takes account of a stall margin
 Is displayed on the vsi.
Is displayed on the vsi. A tcas generates traffic advisory ta or resolution advisory ra according to ?
Question 63-36 : Time speed distance flight level
 Time.
Time. For an aircraft efis equipped . 1 the nd displays flight director command bars. ?
Question 63-37 : 2 2 4 1 3 1 4
 2.
2. The primary flight display pfd displays information dedicated to ?
Question 63-38 : Piloting weather situation engines and alarms systems
 Piloting.
Piloting. According to cs 25 section 3 concerning the electronic display systems the ?
Question 63-39 : Armed mode engaged mode warning caution
 Armed mode.
Armed mode. According to cs25 concerning the electronic display systems the colour ?
Question 63-40 : Green white magenta amber
 Green.
Green. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2479 Free Training Exam
