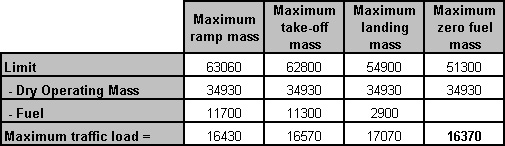
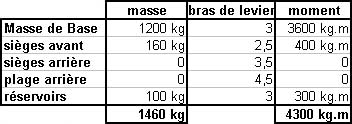
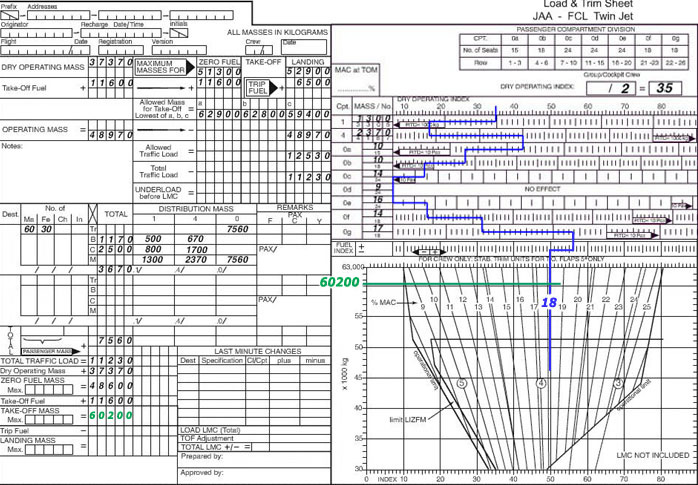
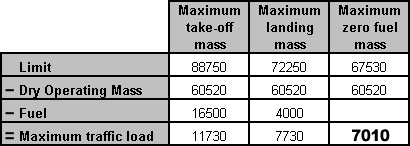
The cpdlc is a fans application which consists in ? [ Students VFR ]
Question 56-1 : Transmitting datalink formatted messages between the pilot and atc controller establishing air/ground connexion to verify if the datalink communication can be performed sending automatically aircraft surveillance data to the air traffic controller connecting the aircraft to the appropriate atc center
 Transmitting datalink formatted messages between the pilot and atc controller.
Transmitting datalink formatted messages between the pilot and atc controller. The ads is a fans application which consists in ?
Question 56-2 : Sending automatically aircraft surveillance data to the air traffic controller establishing automatic air/ground connexion to verify if the datalink communication can be performed connecting the aircraft to the appropriate atc center broadcasting aircraft position and intents to the other aircraft in the vicinity
 Sending automatically aircraft surveillance data to the air traffic controller.
Sending automatically aircraft surveillance data to the air traffic controller. In a datalink system the uplink communications consist in transmitting data ?
Question 56-3 : From the the ground to the aircraft from the aircraft to the ground from the flight deck to the cabin from the aircraft to the airline maintenance
 From the the ground to the aircraft.
From the the ground to the aircraft. In a datalink system the downlink communications consist in transmitting data ?
Question 56-4 : From the aircraft to the ground from the ground to the aircraft from the flight deck to the cabin from the airline maintenance to the aircraft
 From the aircraft to the ground.
From the aircraft to the ground. The ads is a fans application performed ?
Question 56-5 : Automatically without any crew action to define the set of data to downlink or the type of report contract manually the pilot has to define the set of data to downlink and the type of report contract semi automatically the pilot cannot define the set of data to downlink but can define the type of report contract semi automatically the pilot has to define the set of data to downlink but cannot define the type of report contract
 Automatically, without any crew action to define the set of data to downlink or the type of report contract.
Automatically, without any crew action to define the set of data to downlink or the type of report contract. When sent a mayday datalink message to the atc has the following effect on ads ?
Question 56-6 : The ads contract is switched to high periodic reporting rate no change to the current contract in process the ads current contract is stopped the ads current contract reporting rate is unchanged but includes more data
 The ads contract is switched to high periodic reporting rate.
The ads contract is switched to high periodic reporting rate. The characteristics of the satcom transmissions used for datalink ?
Question 56-7 : No line of sight limitation no variable quality of signals disturbed by ionospheric conditions no line of sight limitation variable quality of signals depending on ionospheric conditions line of sight limitation no variable quality of signals disturbed by ionospheric conditions line of sight limitation variable quality of signals depending on ionospheric conditions
The notification phase log on is a fans application which consists in ?
Question 56-8 : Associated datalink capability prior to operating any datalink communications with atc park stand to the airport pre flight controller to request the datalink pre departure clearance pdc aircraft position to the airport ground controller to request the datalink taxi clearance aircraft position to request the datalink clearance to enter an airspace
 Associated datalink capability, prior to operating any datalink communications with atc.
Associated datalink capability, prior to operating any datalink communications with atc. Comparing the media used to transmit datalink communications the appropriate ?
Question 56-9 : Hf datalink vhf datalink satcom satcom hf datalink vhf datalink hf datalink satcom vhf datalink satcom vhf datalink hf datalink
The notification phase log on is a fans application which consists in ?
Question 56-10 : Establishing air/ground connection to verify if the datalink communication can be performed sending automatically aircraft surveillance data to the ats facility requesting to transfer datalink communication to the next atc center on the route transmitting datalink messages between the pilot and atc controller
 Establishing air/ground connection to verify if the datalink communication can be performed.
Establishing air/ground connection to verify if the datalink communication can be performed. The uplink datalink message 'at position climb to altitude and maintain' is ?
Question 56-11 : Cpdlc application ads application afn application taws application
 Cpdlc application.
Cpdlc application. The uplink datalink messages 'climb to reach altitude by time' means ?
Question 56-12 : A climb is to commence at a rate such that the specified level is reached at or before the specified time a climb is to commence at or before the specified time a climb is to commence at or after the specified time a climb is to commence at a rate such that the specified level is reached at or after the specified time
 A climb is to commence at a rate such that the specified level is reached at or before the specified time.
A climb is to commence at a rate such that the specified level is reached at or before the specified time. The uplink datalink message 'at time climb to and maintain altitude means ?
Question 56-13 : At the specified time a climb to the specified altitude is to be started and the specified altitude is to be maintained a climb is to commence at or before the specified time a climb is to commence at or after the specified time a climb is to commence at a rate such that the specified level is reached at or after the specified time
 At the specified time a climb to the specified altitude is to be started and the specified altitude is to be maintained.
At the specified time a climb to the specified altitude is to be started and the specified altitude is to be maintained. The fans concept involves implementation of datalink systems for use in .1 ?
Question 56-14 : 1 2 3 1 1 3 2 3
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. Acars systems consist of ?
Question 56-15 : On board units and ground units ground units on board units gpws units
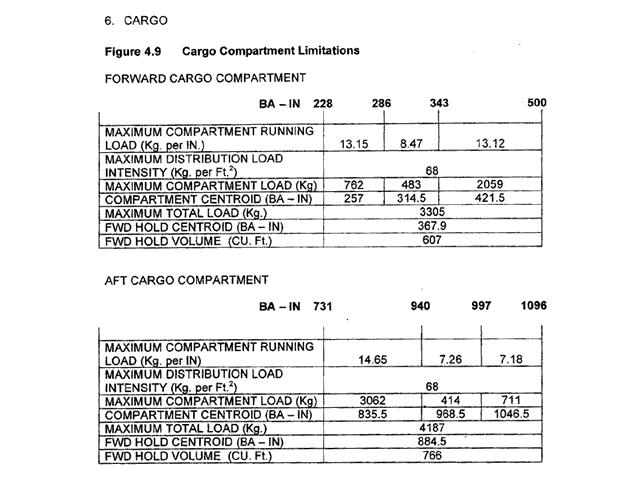 On-board units and ground units.
On-board units and ground units. The uplink datalink message 'expect cruise climb at time means ?
Question 56-16 : A climb instruction should be received to initiate the cruise climb at the specified time a climb to the given cruise altitude is to be terminated at the specified time a climb to the given cruise altitude is to be initiated at the specified time a climb instruction should be received to end the cruise climb at the specified time
 A climb instruction should be received to initiate the cruise climb at the specified time.
A climb instruction should be received to initiate the cruise climb at the specified time. The datalink communication message check stuck microphone frequency refers to ?
Question 56-17 : The atc to the pilot to check microphone buttons due to a continuous transmission detected on the frequency the atc to the pilot to transmit blind the atc to the pilot to revert to the voice communication by pushing and holding a few seconds the mike button the pilot to the atc to solve a continuous transmission issue with the voice frequency
 The atc to the pilot to check microphone buttons due to a continuous transmission detected on the frequency.
The atc to the pilot to check microphone buttons due to a continuous transmission detected on the frequency. The fms provides the following functions .1 fuel management.2 lateral flight ?
Question 56-18 : 1 2 4 1 2 3 2 3 3 4
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. The fms provides the following functions .1 aircraft position computation .2 ?
Question 56-19 : 1 3 4 2 3 4 1 2 3 1 2 4
 1, 3, 4.
1, 3, 4. The fms overfly function consists in ?
Question 56-20 : Manually selecting a flight plan waypoint to fly over when sequencing it instead of flying by at the transition manually selecting a flight plan to fly over each of the waypoints at the transitions along the route selecting the secondary flight plan making it active to fly over the legs manually selecting a flight plan waypoint to hold over for a selected time
 Manually selecting a flight plan waypoint to fly over when sequencing it instead of flying by at the transition.
Manually selecting a flight plan waypoint to fly over when sequencing it instead of flying by at the transition. The 'fms' navigation database processing should include the following check s ?
Question 56-21 : At each phase of the process from the reception of each supplier's data to the distribution and loading of the formatted database at the reception of each supplier's data and after the assembly of those data collected at the end of the fms formatting phase of all of the data collected and assembled at the loading phase into the fms the check is performed by the fms
 At each phase of the process, from the reception of each supplier's data to the distribution and loading of the formatted database.
At each phase of the process, from the reception of each supplier's data to the distribution and loading of the formatted database. The most common sensors interfacing a fms to compute the aircraft position ?
Question 56-22 : 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 4 1 4
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. The most common sensors interfacing a fms to compute the aircraft position ?
Question 56-23 : 1 2 4 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 1 3
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. The most common sensors interfacing a fms to compute the aircraft position ?
Question 56-24 : 1 3 1 2 3 2 3 1 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. The most common sensors interfacing a fms to compute the aircraft position ?
Question 56-25 : 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 1 3 4
 1, 2.
1, 2. The fms provides the following functions .1 radio tuning.2 fuel management.3 ?
Question 56-26 : 1 2 3 3 4 2 3 4 1 2 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. Concerning the fms flight management system the cost index is determined by ?
Question 56-27 : Aircraft operating cost by fuel cost fuel cost by aircraft operating cost aircraft cruise speed by fuel cost fuel cost by aircraft cruise speed
 Aircraft operating cost by fuel cost.
Aircraft operating cost by fuel cost. Concerning the fms flight management system entering a high cost index results ?
Question 56-28 : High airspeed and high fuel trip maximum range airspeed minimum trip fuel minimum airspeed
 High airspeed and high fuel trip.
High airspeed and high fuel trip. Concerning the fms flight management system entering a cost index of zero ?
Question 56-29 : Maximum range airspeed maximum cruising airspeed minimum range airspeed minimum airspeed
 Maximum range airspeed.
Maximum range airspeed. The fms is approved for localizer approaches ?
Question 56-30 : If the localizer signals are used by the fms if the gps only is used as navigation sensor if the gps and dmes only are used as combined navigation sensors if the dmes only are used as navigation sensors
 If the localizer signals are used by the fms.
If the localizer signals are used by the fms. Concerning the fms flight management system entering a cost index of zero ?
Question 56-31 : Results in minimum trip fuel results in maximum trip fuel does not influence fuel consumption modifies only cruising airspeed
 Results in minimum trip fuel.
Results in minimum trip fuel. The fms is approved to provide guidance for the following approaches .1 rnav ?
Question 56-32 : 1 3 2 4 1 3 4 1 2
 1, 3.
1, 3. The fms is approved to provide guidance for the following approaches .1 rnav ?
Question 56-33 : 1 4 2 3 1 2 4 1 3 4
 1, 4.
1, 4. The fms is approved to provide guidance for the following approaches ?
Question 56-34 : Non precision approaches non precision approaches and ils cat i precision approaches only non precision and precision approaches precision approaches limited to cat ii
 Non precision approaches.
Non precision approaches. The fms navigation database includes the following data .1 obstacles.2 ?
Question 56-35 : 2 3 5 1 2 3 1 3 5 1 2 4
 2, 3, 5.
2, 3, 5. The purpose of the fms temperature compensation function is ?
Question 56-36 : To provide compensated altitudes for temperatures different from standard atmosphere along the vertical approach profile to provide compensated temperatures at the waypoints along the vertical approach profile to provide the destination airport air temperature to provide the destination airport or runway elevation
 To provide compensated altitudes for temperatures different from standard atmosphere along the vertical approach profile.
To provide compensated altitudes for temperatures different from standard atmosphere along the vertical approach profile. The fms provides the following functions .1 lateral and vertical flight plan ?
Question 56-37 : 1 3 1 2 3 1 3 4 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. Concerning the fms the parameters used to work out the vertical flight profile ?
Question 56-38 : 1 2 3 1 2 3 5 1 2 5 3 4 5
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. Components of the fms are .1 cdu control and display unit .2 database.3 fmc ?
Question 56-39 : 1 2 3 1 2 4 5 1 3 3 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. The fms provides the following functions .1 vertical flight plan management .2 ?
Question 56-40 : 1 2 3 1 2 4 2 3 4 1 3 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2199 Free Training Exam
