The parameter that determines the relationship between eas and tas is ? [ Test maintenance ]
Question 52-1 : Density altitude pressure altitude oat mach number
 Density altitude.
Density altitude. With cas and pressure altitude we can deduce ?
Question 52-2 : Eas tas eas and tas nothing
 Eas.
Eas. Speed of sound is proportional to ?
Question 52-3 : The square root of the absolute temperature the square root of the tas the square of the absolute temperature the square of the tas
 The square root of the absolute temperature.
The square root of the absolute temperature. The total air temperature tat is ?
Question 52-4 : The temperature resulting from the aircraft motion in the air the static air temperature sat multiplied by the recovery factor the impact air temperature measured by the pitot probe the average temperature resulting from the temperature measure of the pitot and tat probes
 The temperature resulting from the aircraft motion in the air.
The temperature resulting from the aircraft motion in the air. During a climb if the total pressure head is rapidly clogged up by ice the ?
Question 52-5 : The static pressure decreases implying an increasing ias the static pressure decreases implying a decreasing ias the ias remains also constant the static pressure increases implying a decreasing ias
 The static pressure decreases, implying an increasing ias.
The static pressure decreases, implying an increasing ias. The static air temperature sat is ?
Question 52-6 : The ambient outside air temperature the temperature resulting from the aircraft motion in the air the outside air temperature measured by the pitot probe the tat divided by the recovery factor
 The ambient outside air temperature.
The ambient outside air temperature. The limits of the green scale of an airspeed indicator are ?
Question 52-7 : Vs1 and vno vs1 and vmo vs0 and vne vs1 and vne
 Vs1 and vno.
Vs1 and vno. Concerning the pitot and static system the static pressure error varies ?
Question 52-8 : 2 and 3 1 2 and 3 1 and 3 1 and 2
The alternate static source is used ?
Question 52-9 : When the static ports become blocked when the drain holes freeze to compensate the static pressure error to compensate the hysteresis of the aneroid capsule
 When the static ports become blocked.
When the static ports become blocked. The machmeter is subject to position error this error varies according to .1 ?
Question 52-10 : 1 3 1 2 3 3 1
The data output from the adc are .1 barometric altitude.2 mach number.3 cas.4 ?
Question 52-11 : 1 2 3 4 5 1 4 2 3 4 1 3 5
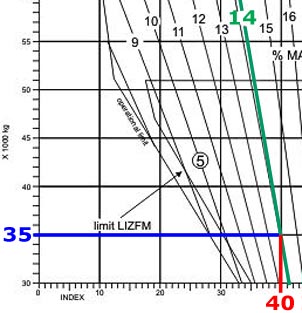 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5. An aeroplane is cruising at fl 60 with a tas of 100 kt in standard atmosphere ?
Question 52-12 : 1 2 3 2 3 1 2 1 3
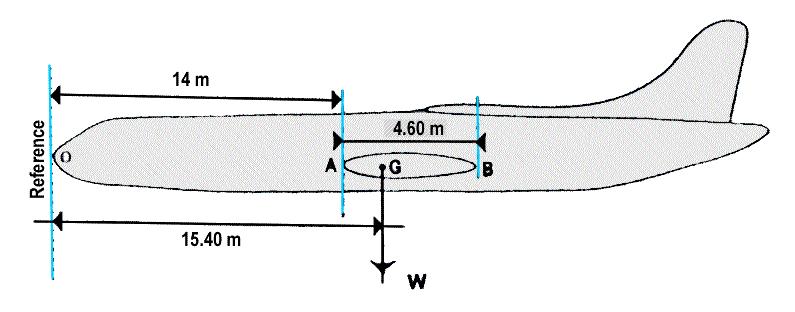 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. The tas is obtained from the cas by correcting for the following errors .1 ?
Question 52-13 : 2 4 2 4 1 2 3 4
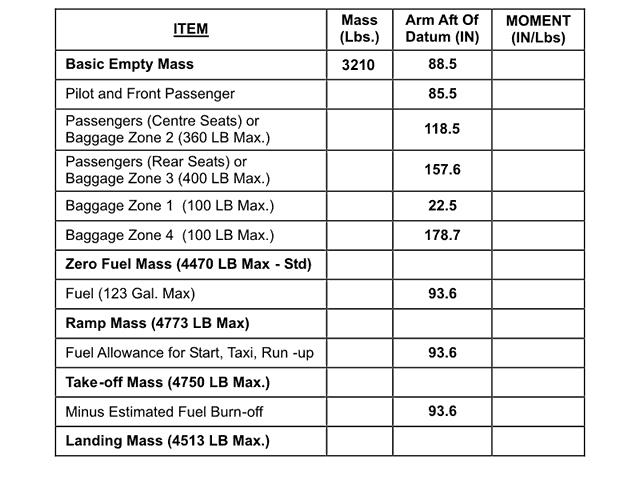 2, 4.
2, 4. The cas is obtained from ias by correcting for the following errors .1 ?
Question 52-14 : 1 3 3 1 3 4 2 3 4
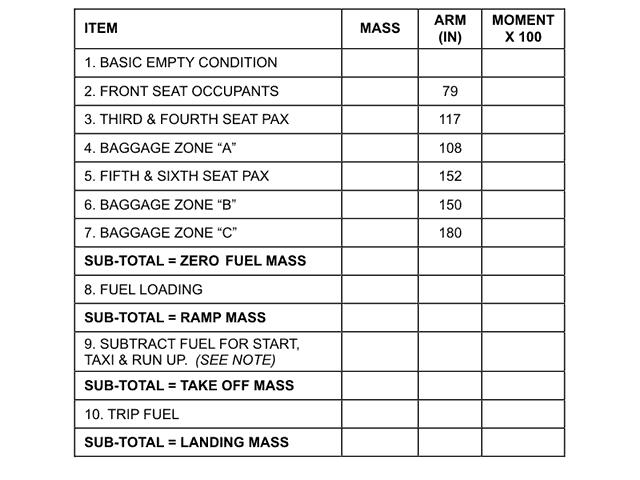 1, 3.
1, 3. The eas is obtained from the cas by correcting for the following errors .1 ?
Question 52-15 : 2 4 2 4 1 2 3 4
 2
2 If the static ports are completely clogged up by ice during a climb the ?
Question 52-16 : Zero a descent if the outside static pressure is less than the pressure in the instrument's gauge a constant rate of climb even if the aircraft is levelling out an increasing rate of climb if the ambient static pressure decreases
 Zero.
Zero. Eas is equal to ?
Question 52-17 : Cas corrected for compressibility error cas corrected for density error tas corrected for compressibility error tas corrected for compressibility and density errors
 Cas corrected for compressibility error.
Cas corrected for compressibility error. During a climb at a constant mach number below the tropopause in standard ?
Question 52-18 : Cas and tas decrease cas increases and tas decreases cas decreases and tas increases cas and tas increase
 Cas and tas decrease.
Cas and tas decrease. When climbing at a constant cas through an isothermal layer the mach number ?
Question 52-19 : Increases decreases remains constant decreases if oat is lower than the standard temperature
 Increases.
Increases. If the pilot increases the reference pressure using the sub scale setting knob ?
Question 52-20 : Increases decreases decreases if qnh > 1013 hpa decreases if qnh < 1013 hpa
 Increases.
Increases. The alternate static source of a light non pressurized aircraft is located in ?
Question 52-21 : Lower than ambient pressure due to aerodynamic suction higher than ambient pressure due to aerodynamic suction higher than ambient pressure if qnh is greater than 1013 hpa lower than ambient pressure if qnh is greater than 1013 hpa
 Lower than ambient pressure due to aerodynamic suction.
Lower than ambient pressure due to aerodynamic suction. Eas can be obtained from the following data ?
Question 52-22 : Cas and pressure altitude ias and density altitude tas and pressure altitude cas and density altitude
 Cas and pressure altitude.
Cas and pressure altitude. Cas is equal to ?
Question 52-23 : Ias corrected for position and instrument errors ias corrected for compressibility error eas corrected for density error eas corrected for compressibility and density errors
 Ias corrected for position and instrument errors.
Ias corrected for position and instrument errors. Eas is equal to ?
Question 52-24 : Ias corrected for position instrument and compressibility errors ias corrected for compressibility error cas corrected for density error tas corrected for compressibility error
 Ias corrected for position, instrument and compressibility errors.
Ias corrected for position, instrument and compressibility errors. The altimeter is subject to static pressure error this error results from ?
Question 52-25 : Incorrect pressure sensing caused by disturbed airflow around the static ports imperfect elasticity of the aneroid capsules frictions inside the instrument cabin pressure slightly lower than outside air pressure due to airflow over the fuselage
 Incorrect pressure sensing caused by disturbed airflow around the static ports.
Incorrect pressure sensing caused by disturbed airflow around the static ports. The machmeter is subject to position error this error results from ?
Question 52-26 : Incorrect pressure sensing caused by disturbed airflow around the pitot tube and/or static ports incorrect altimeter setting imperfect elasticity of the capsules non standard atmospheric conditions
 Incorrect pressure sensing caused by disturbed airflow around the pitot tube and/or static ports.
Incorrect pressure sensing caused by disturbed airflow around the pitot tube and/or static ports. The eas is obtained from the ias by correcting for the following errors .1 ?
Question 52-27 : 1 2 4 1 2 3 1 2 1 2 3 4
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. When descending at a constant cas through an isothermal layer the mach number ?
Question 52-28 : Decreases increases remains constant increases if oat is lower than the standard temperature decreases if higher
 Decreases.
Decreases. In standard atmosphere at sea level the eas is ?
Question 52-29 : Equal to the tas independent of the tas higher than the tas lower than the tas
 Equal to the tas.
Equal to the tas. The alternate static source of a light non pressurized aircraft is located in ?
Question 52-30 : Indicate a momentary climb indicate a slight momentary descent indicate a high rate of descent be blocked
 Indicate a momentary climb.
Indicate a momentary climb. Concerning the pitot and static system the static pressure error ?
Question 52-31 : Is caused by disturbed airflow around the static ports is a direct effect of heating of the static ports affects the alternate static port only is a direct effect of a blockage of the static port
 Is caused by disturbed airflow around the static ports.
Is caused by disturbed airflow around the static ports. The output data from the adc are used by .1 transponder.2 efis.3 automatic ?
Question 52-32 : 1 2 3 1 2 1 3 2 3
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. Maintaining cas and flight level constant a fall in ambient temperature results ?
Question 52-33 : Lower tas because air density increases lower tas because air density decreases higher tas because air density increases higher tas because air density decreases
 Lower tas because air density increases.
Lower tas because air density increases. If oat increases whilst maintaining a constant cas and flight level ?
Question 52-34 : Mach number remains constant mach number decreases tas remains constant tas decreases
 Mach number remains constant.
Mach number remains constant. If oat decreases whilst maintaining a constant cas and flight level ?
Question 52-35 : Mach number remains constant mach number increases tas remains constant tas increases
 Mach number remains constant.
Mach number remains constant. The adc uses the following parameters as input data ?
Question 52-36 : Static pressure total pressure tat mach number baro altitude cas tas baro altitude tat total pressure static pressure tat egt
 Static pressure, total pressure, tat.
Static pressure, total pressure, tat. The total pressure head comprises a mast which moves its port to a distance ?
Question 52-37 : To locate it outside the boundary layer not to disturb the aerodynamic flow around the aircraft it is protected from icing it is easily accessible during maintenance checks
 To locate it outside the boundary layer.
To locate it outside the boundary layer. In case of static blockage the airspeed indicator ?
Question 52-38 : Under reads in climb and over reads in descent over reads in climb and under reads in descent over reads in climb only under reads in descent only
 Under-reads in climb and over-reads in descent.
Under-reads in climb and over-reads in descent. The machmeter is subject to position error this error concerns ?
Question 52-39 : Pitot tubes and static ports pitot tubes only static ports only alternate static sources only
 Pitot tubes and static ports.
Pitot tubes and static ports. Given .pt total pressure.ps static pressure.pd dynamic pressure.the airspeed ?
Question 52-40 : Pt ps ps pt pd ps pt pd
 Pt - ps
Pt - ps ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
2039 Free Training Exam
