The alignment time of a strapdown inertial system takes longer time when the ? [ Teaching aircraft ]
Question 51-1 : At a high latitude at a high longitude close to the equator at a location where the magnetic variation is greater than 15 degrees
 At a high latitude.
At a high latitude. An inertial navigation system ?
Question 51-2 : Can operate as stand alone equipment without any interface with other navigation equipments can only operate when interfacing with the gps equipment can only operate when interfacing with the radionavigation equipments can only operate when communicating with ground installations
 Can operate as stand alone equipment without any interface with other navigation equipments.
Can operate as stand alone equipment without any interface with other navigation equipments. In an inertial navigation system the principle used to obtain the change in ?
Question 51-3 : Single integration of acceleration according to time double integration of acceleration according to time single integration of position according to time double integration of position according to time
 Single integration of acceleration according to time.
Single integration of acceleration according to time. The characteristics of the earth which are being used during the alignment of ?
Question 51-4 : Earth rotation and gravity earth magnetic field and earth rotation longitude and gravity earth rotation and longitude
 Earth rotation and gravity.
Earth rotation and gravity. In a strapdown inertial system the accelerations are measured in a trihedron ?
Question 51-5 : Aircraft's trihedron pitch roll and yaw axis earth's trihedron longitude latitude absolute space earth's trihedron x y z
 Aircraft's trihedron (pitch, roll and yaw axis).
Aircraft's trihedron (pitch, roll and yaw axis). In a stabilised platform inertial system the accelerations are measured in a ?
Question 51-6 : Free from the aircraft trihedron fixed in absolute space merged with the aircraft's triehedron merged with only two axis of the aircraft trihedron the roll axis and the pitch axis
 Free from the aircraft trihedron.
Free from the aircraft trihedron. On the ins control panel the rotary knob can be selected to off nav or att ?
Question 51-7 : Nav is the normal system setting the att position is the back up position in case of failure of the navigation function nav is the normal system setting the off position is the back up position in case of failure of the navigation function att is the normal system setting att is the normal system setting the nav position inhibits the attitude data
 Nav is the normal system setting; the att position is the back up position in case of failure of the navigation function.
Nav is the normal system setting; the att position is the back up position in case of failure of the navigation function. The position data lat long computed by an irs can be used by the ?
Question 51-8 : Fms ils receiver adc tcas
 Fms.
Fms. The accuracy of the altitude computed by a stand alone inertial system ?
Question 51-9 : Decreases exponentially with flight time is bounded decreases proportionally with flight time is poor at the beginning of the flight
 Decreases exponentially with flight time.
Decreases exponentially with flight time. The output data of an irs include .1 present position lat long .2 tas.3 ?
Question 51-10 : 1 3 4 1 2 3 1 2 4 2 3 4
 1, 3, 4.
1, 3, 4. The drift of the gyroscopes of a stand alone inertial system ?
Question 51-11 : Is the main error source is not an error source induces a position error that decreases along the flight induces a bounded position error
 Is the main error source.
Is the main error source. Considering a stabilised platform inertial system this platform .1 can be ?
Question 51-12 : 1 3 1 2 2 3
 1, 3.
1, 3. Comparing the radio navigation system and the inertial navigation system .1 ?
Question 51-13 : 1 3 1 2 2 3
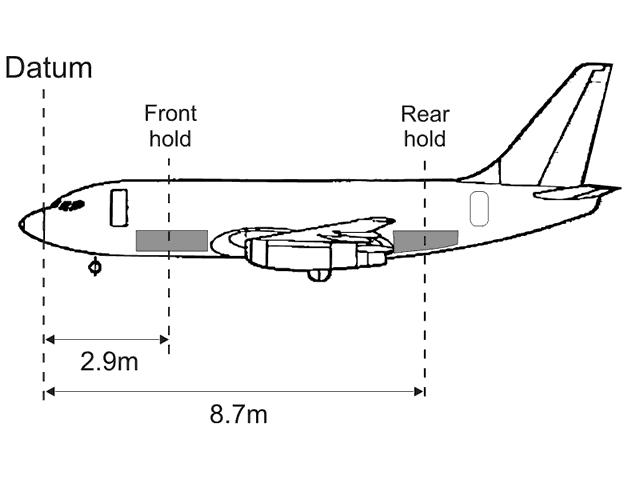 1, 3.
1, 3. An inertial reference and navigation system is a 'strapdown' system when ?
Question 51-14 : The gyroscopes and the accelerometers are fixed regarding to the aircraft's body axes co ordinate system only the gyroscopes and not the accelerometers are fixed regarding to the aircraft's body axes co ordinate system the gyroscope and the accelerometers are mounted on a stabilised patform only the gyroscopes and not the accelerometers are mounted on a stabilised platform
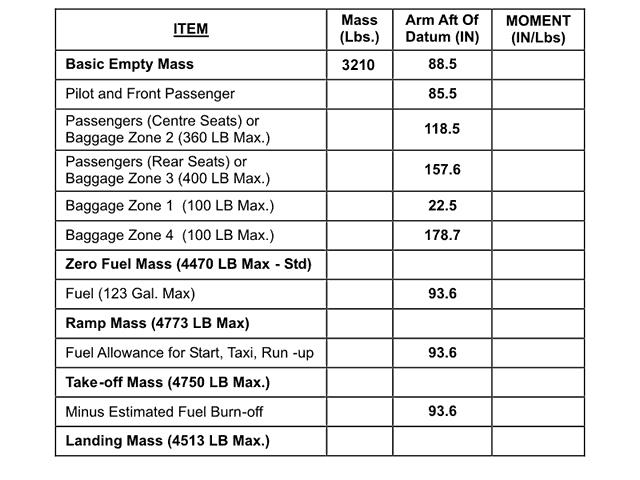 The gyroscopes and the accelerometers are fixed regarding to the aircraft's body axes co-ordinate system.
The gyroscopes and the accelerometers are fixed regarding to the aircraft's body axes co-ordinate system. If the navigation function of an ins is inoperative and the control rotary ?
Question 51-15 : Attitude and heading position only position and attitude attitude and ground speed
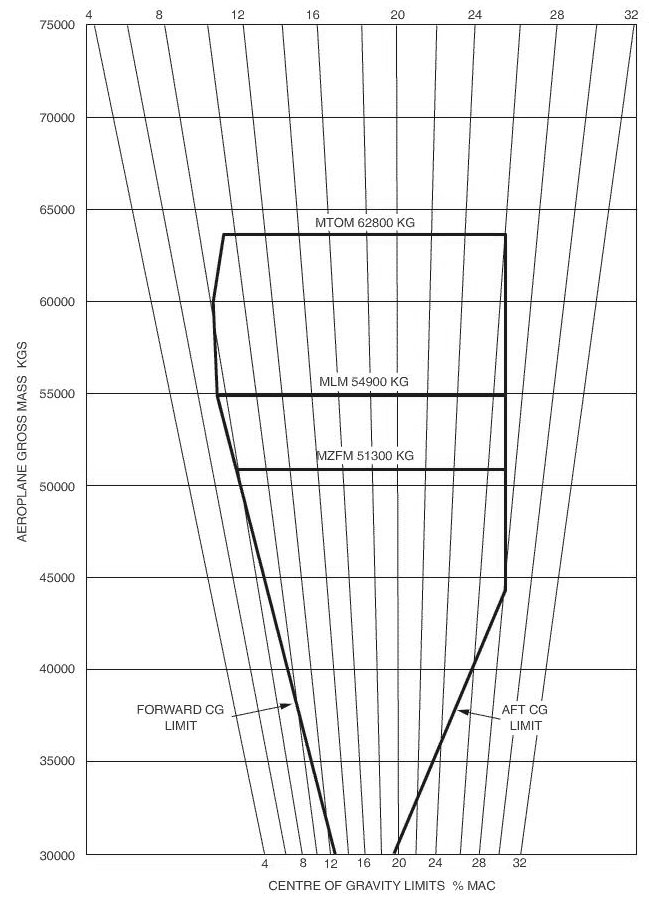 Attitude and heading.
Attitude and heading. The alignment of a strapdown inertial system consists in ?
Question 51-16 : Measuring the earth rotation and local gravitation to position the reference trihedron positionning the accelerometers positioning the gyroscopes and accelerometers relative to the fuselage axis positioning the platform relative to the local vertical and true north
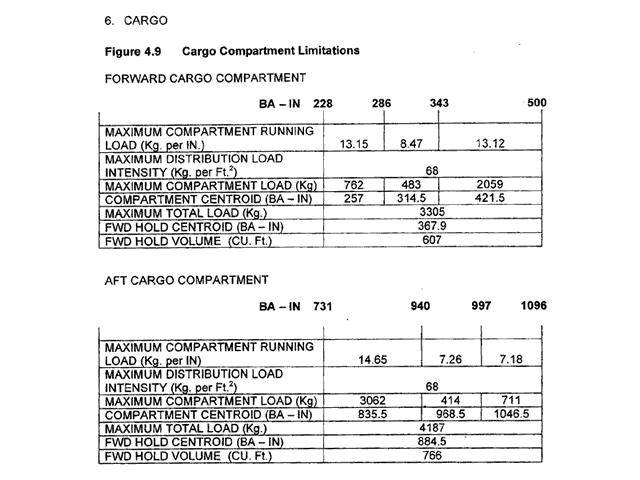 Measuring the earth rotation and local gravitation to position the reference trihedron.
Measuring the earth rotation and local gravitation to position the reference trihedron. The position error of a stand alone inertial system ?
Question 51-17 : Increases along the time remains constant is sinusoidal increases up to 2 nm due to the drift error of the gyroscopes then stabilizes
 Increases along the time.
Increases along the time. The position error of a stand alone inertial system is ?
Question 51-18 : Small a few minutes after initialisation and increases along the flight small and constant along the flight large a few minutes after initialisation and reduces along the flight constant along the flight with an accuracy depending on the accuracy of the accelerometers
 Small a few minutes after initialisation and increases along the flight.
Small a few minutes after initialisation and increases along the flight. The output data of an irs include .1 present position lat long .2 altitude.3 ?
Question 51-19 : 1 3 4 1 2 3 1 4 1 2 3 4
 1, 3, 4.
1, 3, 4. The attitude data computed by an irs can be used by the ?
Question 51-20 : Auto pilot system tcas gpws stall warning system
 Auto pilot system.
Auto pilot system. If the position data lat long is no longer computed an irs the affected system ?
Question 51-21 : The fms the adc and the tcas the fms and the tcas the tcas
 The fms.
The fms. The energy required to operate a strapdown inertial system is supplied by ?
Question 51-22 : The electrical system the bleed air system the hydraulic system a dedicated pneumatic system
 The electrical system.
The electrical system. When the rotary knob on the ins control panel is set to 'nav' mode it is ?
Question 51-23 : The normal operating mode allowing use of all the functions of the system the navigation mode allowing use of all the functions of the system except attitude the alignment function in flight the navigation mode allowing use of all the functions of the system except heading
 The normal operating mode allowing use of all the functions of the system.
The normal operating mode allowing use of all the functions of the system. The alignment of a gyro stabilized inertial platform consists in positionning ?
Question 51-24 : The vertical axis and true north the pitch axis only the pitch and roll axis the roll axis only
In an inertial navigation system a tas input ?
Question 51-25 : Required to provide a wind direction and velocity read out not required required for polar navigation required for the automatic flight control system afcs to compute a heading according to track
 Required to provide a wind direction and velocity read out.
Required to provide a wind direction and velocity read out. The platform of an inertial navigation system ins is maintained at right angles ?
Question 51-26 : Aircraft manoeuvres earth rotation transport wander and coriolis gyroscopic inertia earth rotation and real drift vertical velocities earth precession centrifugal forces and transport drift movement in the yawing plane secondary precession and pendulous oscillation
 Aircraft manoeuvres, earth rotation, transport wander and coriolis.
Aircraft manoeuvres, earth rotation, transport wander and coriolis. In an inertial navigation system ins ground speed gs is calculated ?
Question 51-27 : By integrating measured acceleration from tas and w/v from air data computer adc from tas and w/v from rnav data by integrating gyro precession in n/s and e/w directions respectively
 By integrating measured acceleration.
By integrating measured acceleration. During the initial alignment of an inertial navigation system ins the equipment ?
Question 51-28 : Will not accept a 10° error in initial latitude but will accept a 10° error in initial longitude will accept a 10° error in initial latitude but will not accept a 10° error in initial longitude will not accept a 10° error in initial latitude or initial longitude will accept a 10° error in initial latitude and initial longitude
 Will not accept a 10° error in initial latitude but will accept a 10° error in initial longitude.
Will not accept a 10° error in initial latitude but will accept a 10° error in initial longitude. The average value for the position error of the ins inertial navigation systems ?
Question 51-29 : 0 5 to 2 nm/h 2 to 5 nm/h 10 to 12 nm/h 6 to 8 nm/h
 0.5 to 2 nm/h.
0.5 to 2 nm/h. The output data of an irs are .1 true track.2 mach number.3 present position ?
Question 51-30 : 1 3 4 5 3 2 5 1 2 3 4
 1, 3, 4, 5.
1, 3, 4, 5. After alignment of the stable platform of an inertial navigation system ins ?
Question 51-31 : Acceleration north/south and east/west true heading and attitude latitude longitude and attitude acceleration north/south and east/west and true heading latitude longitude and true heading
 Acceleration north/south and east/west, true heading and attitude.
Acceleration north/south and east/west, true heading and attitude. In an inertial reference system accelerations are measured in relation to ?
Question 51-32 : Aircraft axis wgs84 earth coordinates the direction of true north local vertical at the aircraft position
 Aircraft axis.
Aircraft axis. The full alignment of the stable platform of an inertial navigation system ins ?
Question 51-33 : Is only possible on the ground when the aircraft is at a complete stop may be carried out on the ground or when in straight and level flight may be carried out at any time so long as an accurate position is inserted into the system may be carried out during any phase of flight
 Is only possible on the ground when the aircraft is at a complete stop.
Is only possible on the ground when the aircraft is at a complete stop. Which of the following statements concerning the aircraft positions indicated ?
Question 51-34 : The positions are likely to differ because they are calculated from different sources the positions will only differ if one of the systems has been decoupled because of a detected malfunction the positions will only differ if an error has been made when inputting the present position at the departure airport the positions will be the same because they are an average of three different positions
 The positions are likely to differ because they are calculated from different sources.
The positions are likely to differ because they are calculated from different sources. A pilot accidentally turning off the irs in flight and then turns it back on a ?
Question 51-35 : It can only be used for attitude reference everything returns to normal and is usable the irs is usable in nav mode after a position update no useful information can be obtained from the irs
 It can only be used for attitude reference.
It can only be used for attitude reference. Concerning the operation of an ins/irs the nav mode must be selected ?
Question 51-36 : Prior to movement of the aircraft off the gate when the alignment procedure is commenced on the runway just prior to take off prior to the loading of passengers and/or freight
 Prior to movement of the aircraft off the gate.
Prior to movement of the aircraft off the gate. The data that needs to be inserted into an inertial reference system in order ?
Question 51-37 : Aircraft position in latitude and longitude the position of an in range dme airport icao identifier aircraft heading
 Aircraft position in latitude and longitude.
Aircraft position in latitude and longitude. Which of the following statements concerning the loss of alignment by an ?
Question 51-38 : The navigation mode including present position and ground speed outputs is inoperative for the remainder of the flight it is not usable in any mode and must be shut down for the rest of the flight the mode selector has to be rotated to att then back through align to nav in order to obtain an in flight realignment the irs has to be coupled to the remaining serviceable system and a realignment carried out in flight
 The navigation mode, including present position and ground speed outputs, is inoperative for the remainder of the flight.
The navigation mode, including present position and ground speed outputs, is inoperative for the remainder of the flight. Mode 'localizer arm' active on flight director means ?
Question 51-39 : System is armed for localizer approach and coupling will occur upon capturing centre line localizer alarm making localizer approach not authorized coupling has occurred and system provides control data to capture the centreline localizer is armed and coupling will occur when flag warning disappears
 System is armed for localizer approach and coupling will occur upon capturing centre line.
System is armed for localizer approach and coupling will occur upon capturing centre line. A closed loop control system in which a small power input controls a much ?
Question 51-40 : A servomechanism an amplifier a feedback control circuit an autopilot
 A servomechanism.
A servomechanism. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1999 Free Training Exam
