Part fcl .a pilot who holds a licence which prohibits the piloting of aircraft ? [ MCQ aircraft ]
Question 5-1 : A private pilot an examiner an instructor a flight instructor
Part fcl .a 'multi pilot aircraft' is ?
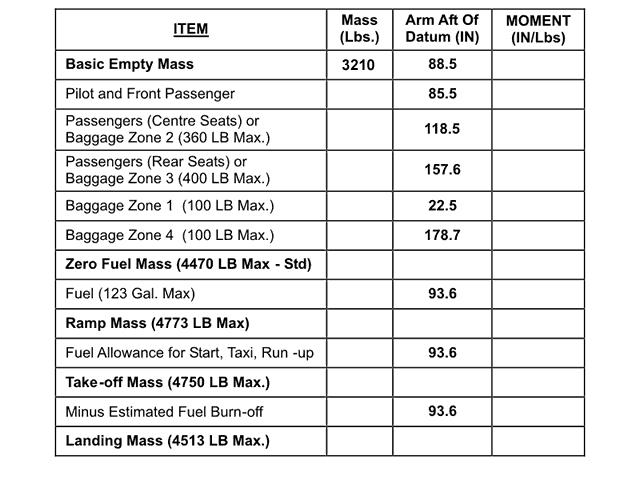
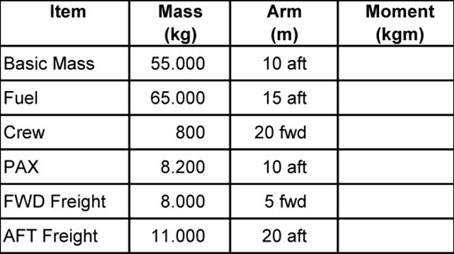
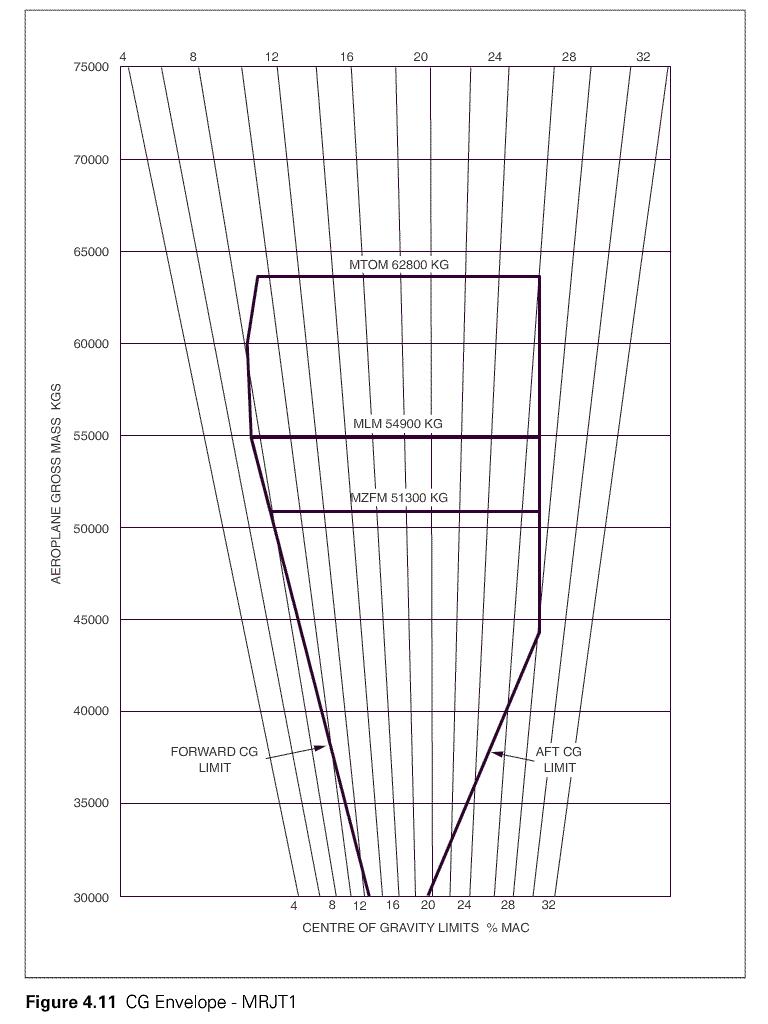
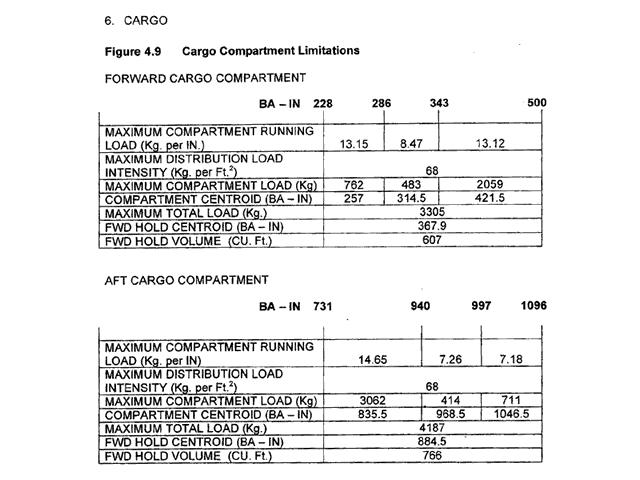
Question 5-2 : An aeroplanes certificated for operation with a minimum crew of at least two pilots a multi engines aircraft an aeroplanes requiring 2 pilots using multi crew cooperation an aircraft with dual flight controls
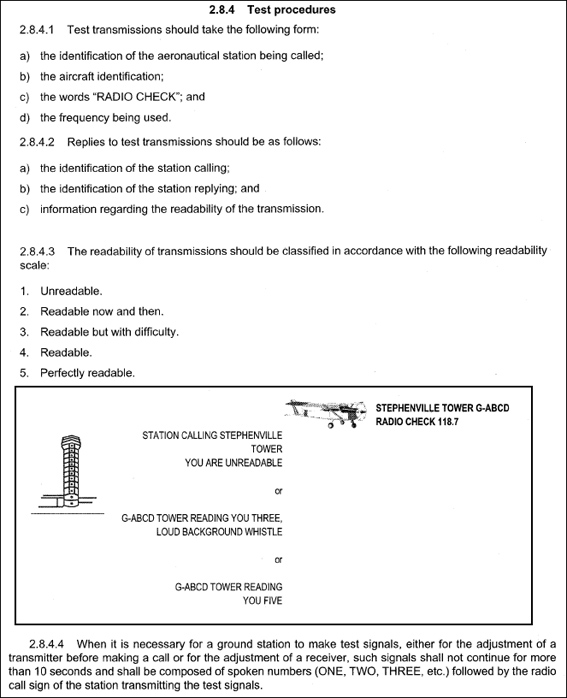 An aeroplanes certificated for operation with a minimum crew of at least two pilots.
An aeroplanes certificated for operation with a minimum crew of at least two pilots. Part fcl .the definition of a cross country flight is ?
Question 5-3 : A flight between a point of departure and a point of arrival following a preplanned route using standard navigation procedures a country flight prepared with standard navigation tools a non preplanned flight between two controlled airports a circular flight with the same point of departure and arrival
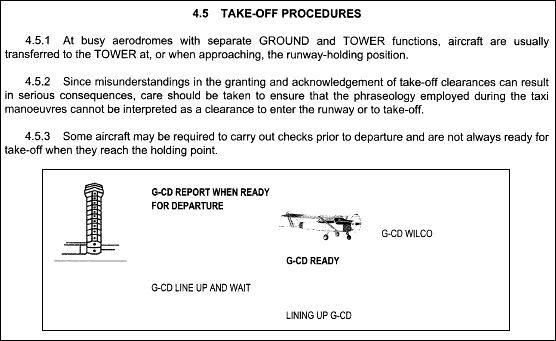 A flight between a point of departure and a point of arrival following a preplanned route, using standard navigation procedures.
A flight between a point of departure and a point of arrival following a preplanned route, using standard navigation procedures. Icao annex 1 definitions.'an authorization entered on or associated with a ?
Question 5-4 : A rating a requirement a skill an assessment
A signalman will ask the pilot to apply parking brakes by the following signals ?
Question 5-5 : Raise arm and hand with fingers extended horizontally in front of body then clench fist arms down palms facing inwards moving arms from extended position inwards horizontally moving his hands fingers extended palms towards ground crossing arms extended above his head
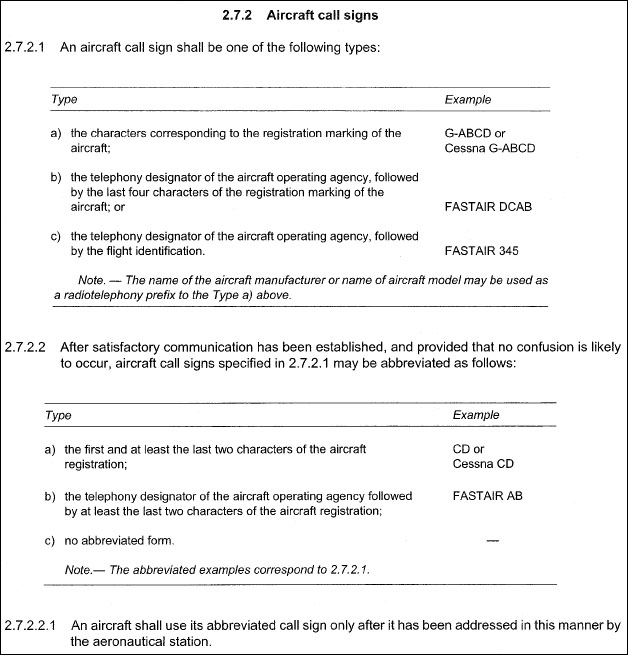 Raise arm and hand, with fingers extended, horizontally in front of body, then clench fist.
Raise arm and hand, with fingers extended, horizontally in front of body, then clench fist. Aircraft 'a' with an atc clearance is flying in vmc conditions within a control ?
Question 5-6 : Aircraft 'b' if 'a' is on its left aircraft 'b' regardless of the direction 'a' is approaching aircraft 'a' regardless of the direction which 'b' is approaching aircraft 'a' if 'b' is on its right
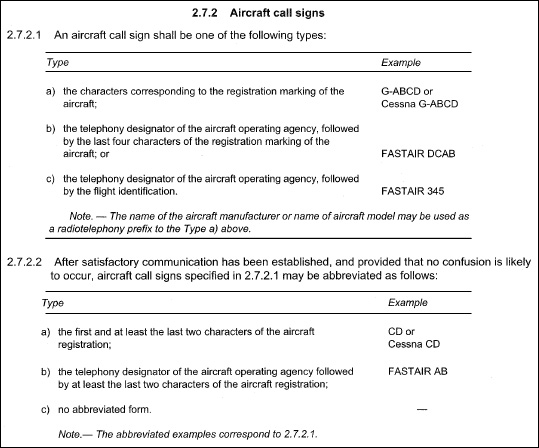 Aircraft 'b' if 'a' is on its left.
Aircraft 'b' if 'a' is on its left. Which fl can be used to perform a ifr flight on a magnetic track of 070° in ?
Question 5-7 : Fl 330 fl 280 fl 350 fl 310
 Fl 330.
Fl 330. Upon intercepting the assigned radial the controller advises you that you are ?
Question 5-8 : You are to assume responsibility for your own navigation radar services are terminated and you will be responsible for position reports you are to contact the centre at the next reporting point you are still in radar contact but must make position reports
 You are to assume responsibility for your own navigation.
You are to assume responsibility for your own navigation. An aircraft shall display if so equipped an anti collision light ?
Question 5-9 : To attract attention to the aircraft during start up at night during night flight only at night when aircraft is being towed
 To attract attention to the aircraft.
To attract attention to the aircraft. Anti collision lights aircraft equipped with red anticollision lights may ?
Question 5-10 : On the ground when the engines are running outside the daylight period in flight but not on the ground when being towed while taxiing but not when being towed outside the daylight period at engine start during the daylight period this procedure is not applicable
 On the ground when the engines are running.
On the ground when the engines are running. The final authority as to the disposition of the aircraft has the ?
Question 5-11 : Pilot in command aircraft owner operator atc controller whenever the aircraft is flying in controlled airspace
 Pilot-in-command.
Pilot-in-command. Avoidance of collisions .an aircraft taxiing on the manoeuvring area of an ?
Question 5-12 : Aircraft taking off or about to take off other vehicles or pedestrians all vehicles on the taxiways except the 'follow me' vehicle larger heavier aircraft
 Aircraft taking off or about to take off.
Aircraft taking off or about to take off. Avoidance of collisions .the highest priority for landing has ?
Question 5-13 : An aircraft that is compelled to land emergency landing a military aircraft an aircraft on a diplomatic flight head of state an air ambulance carrying a very sick person needing immediate medical attention
 An aircraft that is compelled to land (emergency landing).
An aircraft that is compelled to land (emergency landing). Deviation from flight plan .pilots of controlled flights are requested to ?
Question 5-14 : 5% 3% 2% 4%
 5%.
5%. Except when a clearance is obtained from an atc unit a vfr flight cannot enter ?
Question 5-15 : 1500 ft or visibility is less than 5 km 1000 ft or visibility is less than 8 km 2000 ft or visibility is less than 5 km 1000 ft or visibility is less than 5 km
 1500 ft or visibility is less than 5 km.
1500 ft or visibility is less than 5 km. Flight plan inadvertent track changes .in the event that a controlled flight ?
Question 5-16 : Adjust the heading of aircraft to regain track as soon as practicable climb or descent by 500 ft inform the appropriate ats unit maintain vmc wait for instructions from the appropriate ats unit notify the appropriate ats unit immediately notifying the new track and to comply with instructions from ats
 Adjust the heading of aircraft to regain track as soon as practicable.
Adjust the heading of aircraft to regain track as soon as practicable. Flight plan .for flights in accordance with ifr within advisory airspace a ?
Question 5-17 : Shall be submitted changes to the flight plan have to be reported shall be submitted there is no obligation to report changes does not have to be submitted may be submitted at the pilots discretion in case a flight plan is submitted all changes shall be reported as soon as practicable to the appropriate ats unit
 Shall be submitted. changes to the flight plan have to be reported.
Shall be submitted. changes to the flight plan have to be reported. Icao annex 2 definitions .who is charged with the safe conduct of a flight ?
Question 5-18 : The pilot in command the atc controller whenever the aircraft is flying in controlled airspace the aircraft owner the airline operator
 The pilot-in-command.
The pilot-in-command. If no icao identifier has been attributed to an alternate airport box 16 of a ?
Question 5-19 : Write zzzz in box 16 and indicate in box 18 additional information altn/followed by the name of the airport write xxxx in box 16 and indicate in box 18 additional information altn/followed by the name of the airport write xxxx in box 16 and indicate in box 18 additional information degt/followed by the name of the airport write zzzz in box 16 and indicate in box 18 additional information degt/followed by the name of the airport
 Write zzzz in box 16 and indicate in box 18 (additional information) altn/followed by the name of the airport.
Write zzzz in box 16 and indicate in box 18 (additional information) altn/followed by the name of the airport. If radio communication is established during an interception but communications ?
Question 5-20 : Descend descend for landing let down you land
If radio contact with the intercepting aircraft is established but ?
Question 5-21 : Can not not possible unable to comply can not comply
 Can not
Can not In the event of a delay of a controlled flight the submitted flight plan should ?
Question 5-22 : 30 minutes of the estimated time off blocks 30 minutes of the estimated time of departure 60 minutes of the estimated time off blocks 60 minutes of the estimated time of departure
In the event that a controlled flight inadvertently deviates from its current ?
Question 5-23 : The tas varies by plus or minus 5% of the tas notified in the flight plan of an emergency it is a deviation from the track the estimated time is in error by more than 10 minutes
 The tas varies by plus or minus 5% of the tas notified in the flight plan.
The tas varies by plus or minus 5% of the tas notified in the flight plan. Interception.an aircraft equipped with ssr transponder which is intercepted by ?
Question 5-24 : Code 7700 code 7600 code 7500 code 7000
 Code 7700.
Code 7700. Interception day or night .which manoeuvre will be executed by an intercepting ?
Question 5-25 : An abrupt break away manoeuvre from the intercepted aircraft consisting of a climbing turn of 90 degrees or more without crossing the line of flight of the intercepted aircraft rocking aircraft twice in front of the intercepting aircraft after acknowledgement by intercepted aircraft a slow level turn normally to the left circling the intercepted aircraft in a counter clockwise pattern for aeroplanes in a clockwise pattern for helicopter rocking aircraft and flashing navigational lights at regular intervals
 An abrupt break-away manoeuvre from the intercepted aircraft consisting of a climbing turn of 90 degrees or more without crossing the line of flight of the intercepted aircraft.
An abrupt break-away manoeuvre from the intercepted aircraft consisting of a climbing turn of 90 degrees or more without crossing the line of flight of the intercepted aircraft. Interception .if any instructions received by radio from any sources conflict ?
Question 5-26 : Follow the instructions of the intercepting aircraft and request immediate clarification ignore the signals of the intercepting aircraft and request instructions from the appropriate ats unit ignore the signals of the intercepting aircraft and continue in accordance with the last clearance received select transponder mode a squawk 7600 fly holding patterns until having received instructions from the appropriate ats unit
 Follow the instructions of the intercepting aircraft and request immediate clarification.
Follow the instructions of the intercepting aircraft and request immediate clarification. Raise hand just above shoulder height with open palm ensuring eye contact with ?
Question 5-27 : Set brakes start engines chocks removed release brakes
 Set brakes.
Set brakes. Special vfr flights may the authorized to operate locally within a control zone ?
Question 5-28 : E airspace c d and e airspaces d and e airspaces d airspace
 E airspace.
E airspace. The planned cruising speed for the first leg or all of the cruising portion of ?
Question 5-29 : True air speed tas estimated ground speed g/s indicated air speed ias true air speed at 65% power
 True air speed (tas).
True air speed (tas). The vmc minima for a vfr flight inside an ats airspace classified as b is ?
Question 5-30 : 8 km visibility when at or above 3050 m 10000 ft amsl and 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds 8 km visibility when at or above 3050 m 10000 ft amsl and clear of clouds 5 nm visibility below 3050 m 100000 ft amsl clear of clouds 5 nm visibility when below 3050 m 10000 ft amsl 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from cloud
 8 km visibility when at or above 3050 m (10000 ft) amsl, and 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds.
8 km visibility when at or above 3050 m (10000 ft) amsl, and 1500 m horizontal and 300 m vertical from clouds. Visual signals .in flight in the aerodrome pattern the pilot of an aircraft ?
Question 5-31 : Aerodrome unsafe do not land return for landing and clearances to land and to taxi will be given in due course give way to other aircraft notwithstanding any previous instructions do not land for the time being
 Aerodrome unsafe, do not land.
Aerodrome unsafe, do not land. Visual flight rules .an aircraft operating in accordance with vfr above the sea ?
Question 5-32 : A distance from cloud of 1500 m horizontally and 1000 ft vertically and a flight visibility of 5 km a distance from cloud of 1000 m horizontally and 1000 ft vertically and a flight visibility of 8 km a distance from cloud of 1500 m horizontally and 1000 ft vertically and a flight visibility of 5 km clear of cloud and with the surface in sight visibility 8 km
 A distance from cloud of 1500 m horizontally and 1000 ft vertically and a flight visibility of 5 km.
A distance from cloud of 1500 m horizontally and 1000 ft vertically and a flight visibility of 5 km. Visual flight rules .except when a clearance is obtained from an atc unit vfr ?
Question 5-33 : Ceiling is less than 1500 ft or the ground visibility is less than 5 km ceiling is less than 1000 ft or the ground visibility is less than 5 km ceiling is less than 2000 ft or the ground visibility is less than 5 km ceiling is less than 1000 ft or the ground visibility is less than 8 km
 Ceiling is less than 1500 ft or the ground visibility is less than 5 km.
Ceiling is less than 1500 ft or the ground visibility is less than 5 km. Visual signals .in flight the pilot of an aircraft observes a series of ?
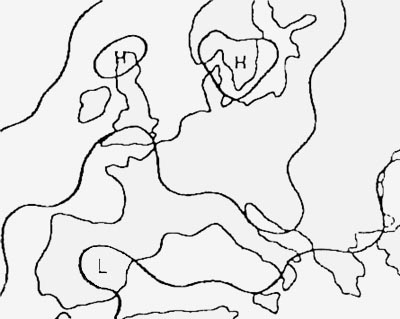
Question 5-34 : The unauthorised aircraft is flying in or about to enter a restricted prohibited or danger area and the aircraft is to take such remedial action as may be necessary the aerodrome nearby you have chosen for landing is unsafe do not attempt to land proceed to your alternate notwithstanding any previous instructions stay in the circuit do not land for the time being give way to other aircraft and continue circling
 The unauthorised aircraft is flying in or about to enter a restricted, prohibited or danger area and the aircraft is to take such remedial action as may be necessary.
The unauthorised aircraft is flying in or about to enter a restricted, prohibited or danger area and the aircraft is to take such remedial action as may be necessary. When two aircraft are approaching head on or approximately so and there is a ?
Question 5-35 : Alter its heading to the right alter its heading to the left descent climb
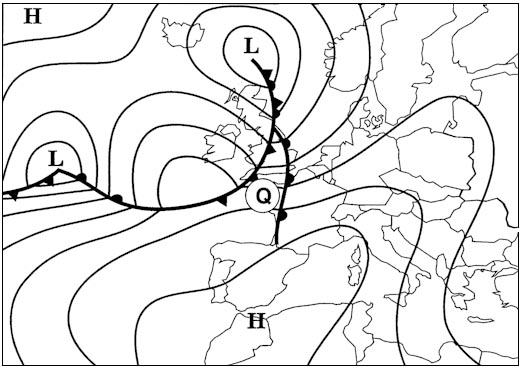
Whenever unlawful interference with an aircraft is suspected and where ?
Question 5-36 : Setting the ssr decoder to mode a code 7500 and thereafter to code 7700 setting the ssr decoder to mode a 7500 then to standby and thereafter to code 7700 setting the ssr decoder to mode a 7700 then to standby and thereafter to code 7500 setting the ssr decoder to mode a code 7000 and thereafter to code 7500
 Setting the ssr decoder to mode a code 7500 and thereafter to code 7700.
Setting the ssr decoder to mode a code 7500 and thereafter to code 7700. While taxiing an aircraft receives from the airport controller the following ?
Question 5-37 : May continue to taxy towards the take off area is cleared for take off must stop must return to its point of departure
While taxying an aircraft receives the following light signal from the control ?
Question 5-38 : Must vacate the landing area in use may continue to taxi to the take off area must stop must return to its point of departure
 Must vacate the landing area in use.
Must vacate the landing area in use. Whilst flying in an aerodrome's traffic circuit an aircraft receives a series ?
Question 5-39 : Must come back to land and the landing clearance will be sent in due time must give way to another aircraft is cleared to land must land immediately and clear the landing area
 Must come back to land and the landing clearance will be sent in due time.
Must come back to land and the landing clearance will be sent in due time. Vfr flights shall not be operated above ?
Question 5-40 : Fl 195 fl 165 fl 205 fl 145
 Fl 195.
Fl 195. Free SCHOOL Account.
You are a training organization and you want to create an unlimited number of accounts for your students in order to follow their progress.
Nothing could be simpler! To offer this unique service to your students and advise them precisely according to their progress, read the page SCHOOL Account.
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
159 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 5
