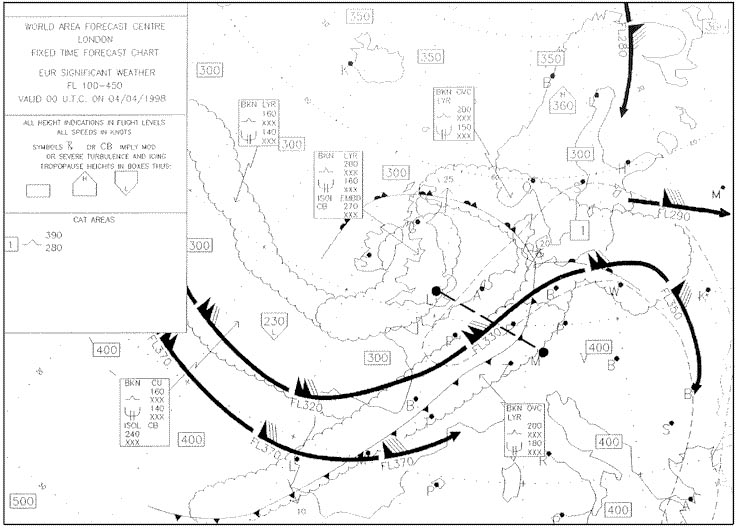
When in flight the needle of a needle and ball indicator is on the right and ? [ Quiz landing ]
Question 49-1 : Turning right with not enough bank turning right with too much bank turning left with not enough bank turning left with too much bank
 Turning right with not enough bank
Turning right with not enough bank When in flight the needle of a needle and ball indicator is on the left and the ?
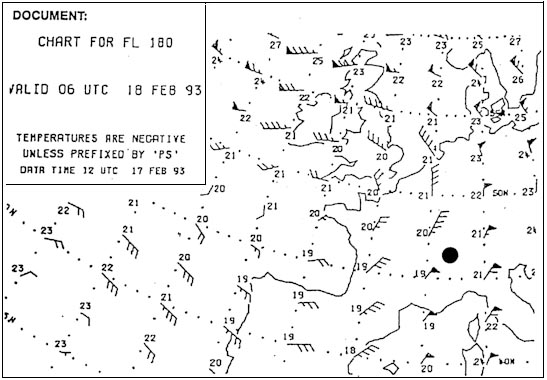
Question 49-2 : Turning left with not enough bank turning left with too much bank turning right with not enough bank turning right with too much bank
 Turning left with not enough bank
Turning left with not enough bank A stand by horizon or emergency attitude indicator ?
Question 49-3 : Contains its own separate gyro is automatically connected to the primary vertical gyro if the alternator fails is fully independent of external energy resources in an emergency situation only works of there is a complete electrical failure
 Contains its own separate gyro
Contains its own separate gyro In the building principle of a gyroscope the best efficiency is obtained ?
Question 49-4 : On the periphery and with a high rotational speed close to the axis and with a high rotational speed on the periphery and with a low rotational speed close to the axis and with a low rotational speed
 On the periphery and with a high rotational speed.
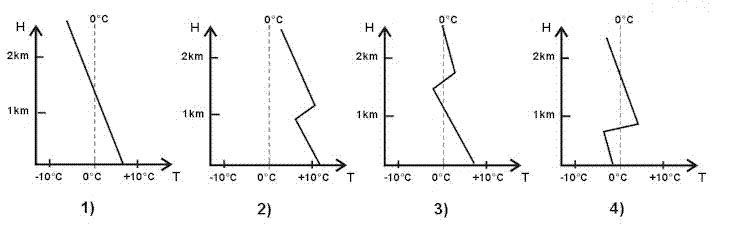
On the periphery and with a high rotational speed. The diagram representing a left turn with insufficient rudder is . 1045 ?
Question 49-5 : 4 3 1 2
 4.
4. The maximum directional gyro error due to the earth rotation is ?
Question 49-6 : 15°/hour 90°/hour 180°/hour 5°/hour
 15°/hour.
15°/hour. Heading information given by a gyro platform is given by a gyro at ?
Question 49-7 : 2 degrees of freedom in the horizontal axis 1 degree of freedom in the horizontal axis l degree of freedom in the vertical axis 2 degrees of freedom in the vertical axis
 2 degrees-of-freedom in the horizontal axis.
2 degrees-of-freedom in the horizontal axis. Among the systematic errors of the 'directional gyro' the error due to the ?
Question 49-8 : 10 5°/hour to the right 15°/hour to the right 7 5°/hour to the right 7 5°/hour to the left
 10.5°/hour to the right.
10.5°/hour to the right. A turn indicator is an instrument which indicates rate of turn rate of turn ?
Question 49-9 : 1 and 2 1 and 3 2 and 3 1 2 and 3
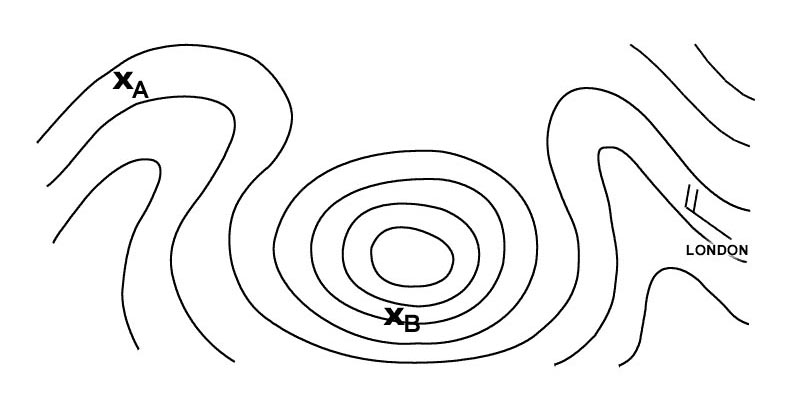
The diagram which shows a 40° left bank and 15° nose down attitude is number ?
Question 49-10 : 1 2 3 4
 1.
1. The heading read on the dial of a directional gyro is subject to errors one of ?
Question 49-11 : Is dependent on the ground speed of the aircraft its true track and the latitude of the flight is in spite of this insignificant and may be neglected is at its greatest value when the aircraft follows a meridional track shows itself by an apparent rotation of the horizontal axis of the gyroscope which seems to turn at 15° per hour to the right in the northern hemisphere
A gravity erector system is used to correct the errors on ?
Question 49-12 : An artificial horizon a directional gyro a turn indicator a gyromagnetic compass
 An artificial horizon.
An artificial horizon. During a deceleration phase at constant attitude the control system of an air ?
Question 49-13 : Nose down attitude nose up attitude constant attitude nose up followed by a nose down attitude
 Nose down attitude.
Nose down attitude. In a directional gyro gimballing errors are due to ?
Question 49-14 : A banked attitude an apparent weight and an apparent vertical the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field the aircraft's movement over the earth
 A banked attitude.
A banked attitude. Parallax error is ?
Question 49-15 : A reading error due to temperature effect due to pressure effect due to the effect of aircraft accelerations
 A reading error.
A reading error. The apparent wander of a directional gyro is 15°/h ?
Question 49-16 : At the north pole at the latitude 30° at the latitude 45° at the equator
 At the north pole
At the north pole The artificial horizon uses a gyroscope with . note the degree s of freedom of ?
Question 49-17 : Two degrees of freedom and its rotor spin axis is continuously maintained to local vertical by an automatic erecting system two degrees of freedom and its rotor spin axis is continuously maintained in the horizontal plane by an automatic erecting system one degree of freedom and its rotor spin axis is continuously maintained in the horizontal plane by an automatic erecting system one degree of freedom and its rotor spin axis is continuously maintained to local vertical by an automatic erecting system
 Two degrees of freedom, and its rotor spin axis is continuously maintained to local vertical by an automatic erecting system.
Two degrees of freedom, and its rotor spin axis is continuously maintained to local vertical by an automatic erecting system. The inertia of a gyroscope is greater when its rotation speed is ?
Question 49-18 : Higher and the mass of the spinning wheel is located further from the axis of rotation higher and the mass of the spinning wheel is closer to the axis of rotation lower and the mass of the spinning wheel is located further from the axis of rotation lower and the mass of the spinning wheel is closer to the axis of rotation
 Higher and the mass of the spinning wheel is located further from the axis of rotation.
Higher and the mass of the spinning wheel is located further from the axis of rotation. The rate of turn indicator uses a gyroscope . .1 the spinning wheel axis of ?
Question 49-19 : 2 4 3 4 1 5 3 5
 2, 4.
2, 4. The latitude at which the apparent wander of a directional gyro is equal to 0 is ?
Question 49-20 : The equator latitude 30° latitude 45° the north pole
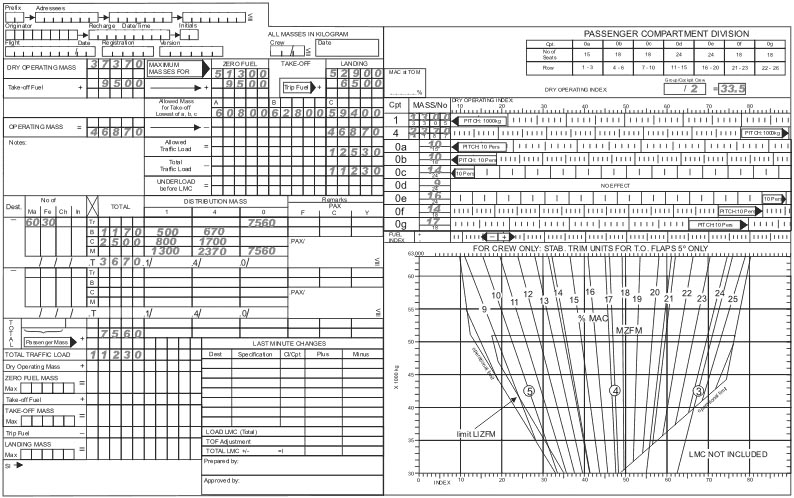 The equator.
The equator. The gyroscope used in an attitude indicator has a spin axis which is ?
Question 49-21 : Vertical horizontal perpendicular to the longitudinal axis horizontal parallel to the longitudinal axis horizontal perpendicular to the yaw axis
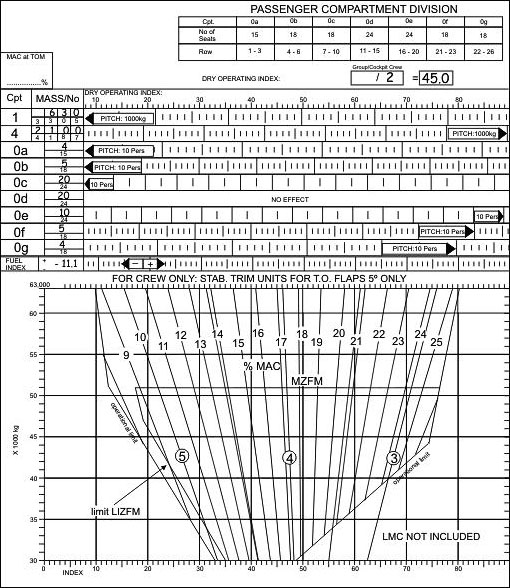 Vertical.
Vertical. For an aircraft flying a true track of 360° between the 5°s and 5°n ?
Question 49-22 : Approximately 0°/hour +5°/hour 5°/hour 15°/hour
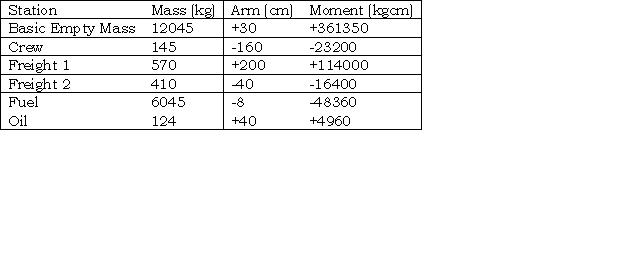 Approximately 0°/hour
Approximately 0°/hour A rate gyro is used in a .1 directional gyro indicator.2 turn co ordinator.3 ?
Question 49-23 : 2 1 2 3 1 1 2
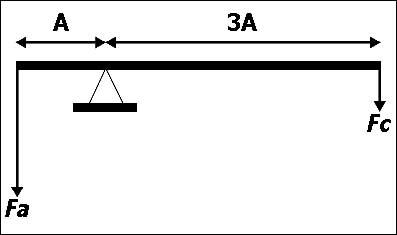 2.
2. A directional gyro consists of a .nb the degree s of freedom of a gyro does not ?
Question 49-24 : 2 degrees of freedom horizontal axis gyro 2 degrees of freedom vertical axis gyro 1 degrees of freedom horizontal axis gyro 1 degrees of freedom vertical axis gyro
The spin axis of the turn indicator gyro is aligned along the ?
Question 49-25 : Lateral axis of the aircraft longitudinal axis of the aircraft vertical axis of the aircraft longitudinal axis of flight
 Lateral axis of the aircraft.
Lateral axis of the aircraft. The properties of a gyroscope are .1 rigidity in space .2 rigidity on earth ?
Question 49-26 : 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 4
The rate of turn given by the rate of turn indicator is valid ?
Question 49-27 : For the airspeed range defined during the calibration of the instrument for all airspeeds with flaps retracted only for the cruising speed
 For the airspeed range defined during the calibration of the instrument.
For the airspeed range defined during the calibration of the instrument. Without any external action the axis of a free gyroscope is fixed with ?
Question 49-28 : Space the earth the aircraft the apparent vertical
 Space.
Space. Due to the rotation of the earth the apparent drift of a horizontal free ?
Question 49-29 : 11° per hour to the right 15° per hour to the left 2° per hour to the right 7° per hour to the left
 11° per hour to the right.
11° per hour to the right. Due to the rotation of the earth the apparent drift of a horizontal free ?
Question 49-30 : 7 5° per hour to the left 15° per hour to the right 2° per hour to the left 11° per hour to the right
 7.5° per hour to the left.
7.5° per hour to the left. Due to the rotation of the earth the apparent drift of a horizontal free ?
Question 49-31 : 7 5° per hour to the right 15° per hour to the left 2° per hour to the right 11° per hour to the left
 7.5° per hour to the right.
7.5° per hour to the right. A free gyro has the axis of the spinning rotor horizontal and aligned with the ?
Question 49-32 : 13°/h to the right 7 5°/h to the left 7 5°/h to the right 13°/h to the left
 13°/h to the right.
13°/h to the right. For a directional gyro the system which detects the local vertical supplies ?
Question 49-33 : A levelling erection torque motor a nozzle integral with the outer gimbal ring a torque motor on the sensitive axis two torque motors arranged horizontally
 A levelling erection torque motor.
A levelling erection torque motor. A directional gyro is corrected for an apparent drift due to the earth's ?
Question 49-34 : 5°/h to the left 2 5°/h to the right 5°/h to the right 2 5°/h to the left
 5°/h to the left.
5°/h to the left. A control system consisting of four pendulous vanes is used in ?
Question 49-35 : An air driven artificial horizon a directional gyro indicator a strap down inertial system a gyromagnetic indicator
 An air driven artificial horizon.
An air driven artificial horizon. Considering an air driven artificial horizon when an airplane accelerates ?
Question 49-36 : A false nose up indication a false nose down indication a correct and constant pitch indication a right or left wing down indication depending on the runway direction
 A false nose-up indication.
A false nose-up indication. Considering an air driven artificial horizon when an airplane decelerates on ?
Question 49-37 : A false nose down indication a false nose up indication a correct and constant pitch indication a right or left wing down indication depending on the runway direction
 A false nose-down indication.
A false nose-down indication. Concerning the directional gyro the apparent drift rate due to the earth's ?
Question 49-38 : Latitude longitude latitude and longitude magnetic longitude
 Latitude.
Latitude. The spin axis of the turn indicator gyroscope is parallel to the ?
Question 49-39 : Pitch axis roll axis yaw axis longitudinal axis
 Pitch axis.
Pitch axis. Parallax error is due to ?
Question 49-40 : A reading under an oblique angle temperature pressure aircraft accelerations
 A reading under an oblique angle.
A reading under an oblique angle. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1919 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 49
