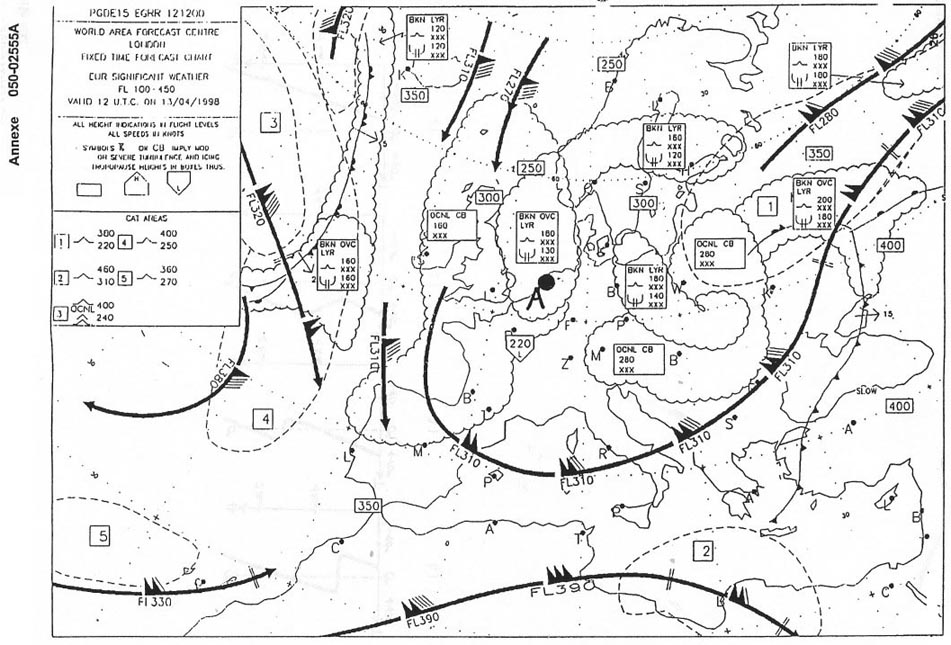
When climbing at a constant cas in standard atmosphere ? [ Understand DGAC ]
Question 47-1 : Tas increases tas decreases tas remains constant tas first decreases then remains constant above the tropopause
 Tas increases.
Tas increases. The compressibility error must be taken into account only for aeroplane with ?
Question 47-2 : Tas greater than approximately 200 kt tas greater than approximately 100 km/h mach number greater than 0 8 mach number greater or equal to 1
 Tas greater than approximately 200 kt.
Tas greater than approximately 200 kt. An aeroplane is flying at fl300 and mach number 0 76 .the indicated total air ?
Question 47-3 : Standard standard +26°c standard 26°c standard +10°c
 Standard.
Standard. The alternate static source of a light non pressurized aeroplane is located in ?
Question 47-4 : Tends to over read tends to under read indicates zero is blocked
 Tends to over-read.
Tends to over-read. The alternate static source of a light non pressurized aeroplane is located in ?
Question 47-5 : The airspeed indicator tends to over read the airspeed indicator tends to under read the airspeed indicator indicates a consistent decreasing speed it has no influence on airspeed indicator reading
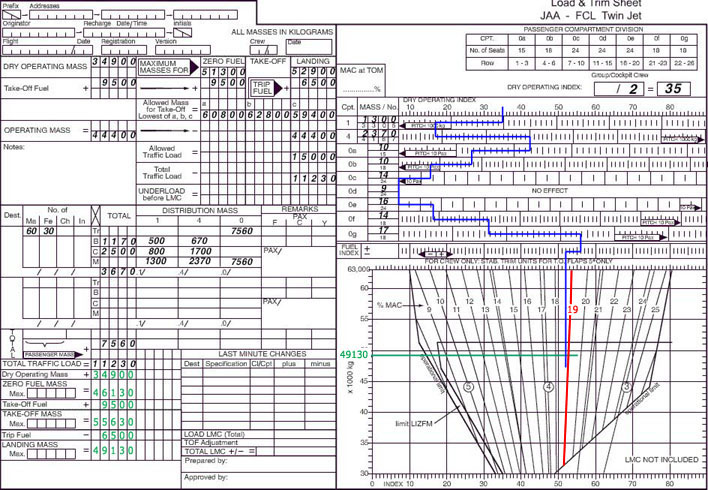 The airspeed indicator tends to over-read.
The airspeed indicator tends to over-read. An airplane is flying at fl140 with a cas of 260 kt in standard conditions the ?
Question 47-6 : 0 51 0 53 0 41 0 43
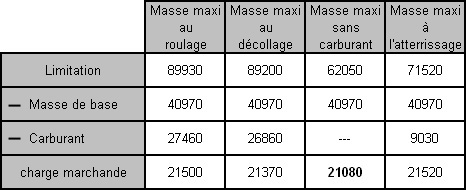 0.51
0.51 An aeroplane is flying at fl300 with a tas of 470 kt in standard conditions the ?
Question 47-7 : 0 8 0 82 0 83 0 53
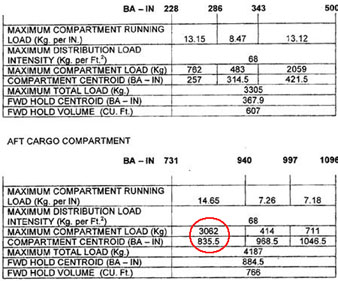 0.8
0.8 During a climb at a constant cas below the tropopause in standard atmosphere ?
Question 47-8 : The mach number increases and the speed of sound decreases the mach number decreases and the speed of sound increases the mach number and the speed of sound increase the mach number and the speed of sound decrease
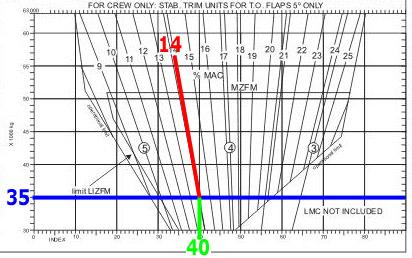 The mach number increases and the speed of sound decreases.
The mach number increases and the speed of sound decreases. A servo assisted altimeter is more accurate than a simple altimeter because the ?
Question 47-9 : The capsules are detected by a very sensitive electro magnetic pick off the pointers are detected by a very sensitive electro magnetic pick off the capsules are inhibited the capsules are not taken into account
 The capsules are detected by a very sensitive electro-magnetic pick-off.
The capsules are detected by a very sensitive electro-magnetic pick-off. An aeroplane is flying at fl100 and mach number 0 76 the indicated total air ?
Question 47-10 : 44°c 54°c 41°c 51°c
 -44°c.
-44°c. Concerning the pitot and static system the position error varies with .1 ?
Question 47-11 : 2 3 1 3 1 2 3 1 2
 2, 3.
2, 3. An aeroplane is flying at fl 320 and mach number 0 79 .the oat is 53°c ?
Question 47-12 : 27°c standard 34°c 10°c
 -27°c.
-27°c. Which of these statements is true ?
Question 47-13 : The probes used for sat measurements have a recovery factor of 0 75 to 0 90 while the probes used for tat measurements have a recovery factor of around 1 00 the probes used for sat measurements have a recovery factor of around 1 00 the probes used for tat measurements are directly connected to the temperature indicator instruments the probes used for sat measurements have a recovery factor ranging from 75 to 90 percent
 The probes used for sat measurements have a recovery factor of 0.75 to 0.90, while the probes used for tat measurements have a recovery factor of around 1.00.
The probes used for sat measurements have a recovery factor of 0.75 to 0.90, while the probes used for tat measurements have a recovery factor of around 1.00. An aeroplane is in a steady descend the auto throttle maintains a constant mach ?
Question 47-14 : Increases decreases remains constant decreases if the static temperature is lower than the standard temperature increases if higher
 Increases.
Increases. In a gyromagnetic compass the direction of the earth's magnetic field is given ?
Question 47-15 : Flux valve adc direct indicating compass directional gyro
 Flux valve.
Flux valve. The magnetic heading can be derived from the true heading by means of a ?
Question 47-16 : Map showing the isogonal lines map showing the isoclinic lines deviation correction curve compass swinging curve
 Map showing the isogonal lines.
Map showing the isogonal lines. The fields affecting a magnetic compass originate from .1 magnetic masses .2 ?
Question 47-17 : 1 2 4 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 3 4
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. The input signal of the amplifier of the gyromagnetic compass resetting device ?
Question 47-18 : Error detector flux valve directional gyro unit directional gyro erection device
 Error detector.
Error detector. In the gyromagnetic compass the heading information from the flux valve is sent ?
Question 47-19 : Error detector erector system heading indicator amplifier
 Error detector.
Error detector. The gyromagnetic compass torque motor ?
Question 47-20 : Causes the directional gyro unit to precess causes the heading indicator to precess feeds the error detector system is fed by the flux valve
 Causes the directional gyro unit to precess.
Causes the directional gyro unit to precess. A pilot wishes to turn left on to a southerly heading with 20° bank at a ?
Question 47-21 : 160° 200° 170° 190°
 160°.
160°. A pilot wishes to turn left on to a northerly heading with 10° bank at a ?
Question 47-22 : 030° 355° 330° 015°
 030°
030° A gyromagnetic compass is a system which always consists of . 1 a horizontal ?
Question 47-23 : 1 3 4 5 1 4 2 3 5 2 3
 1, 3, 4, 5.
1, 3, 4, 5. In a gyromagnetic compass the flux valve feeds the ?
Question 47-24 : Error detector erecting system heading indicator amplifier
 Error detector.
Error detector. The operating principle of the vertical speed indicator vsi is based on the ?
Question 47-25 : Static pressure dynamic pressure total pressure kinetic pressure
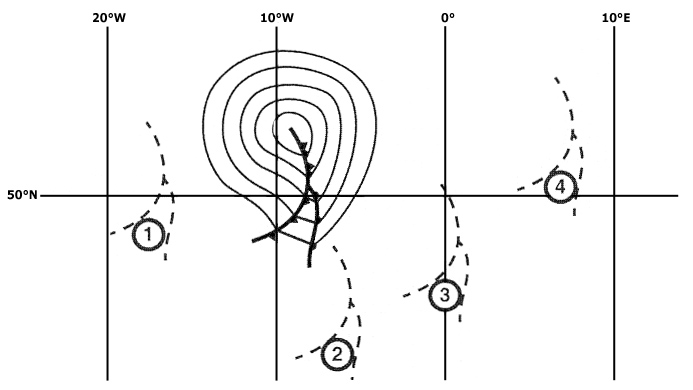
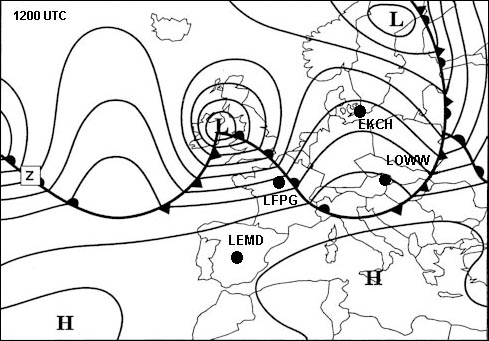
A pilot wishes to turn right through 90° on to north at rate 2 at latitude of ?
Question 47-26 : 330° 360° 030° 010°
 330°.
330°. An aircraft takes off on a runway with an alignment of 045° the compass is ?
Question 47-27 : A value below 045° 045° a value above 045° in the southern hemisphere a value above 045° in the northern hemisphere
 A value below 045°.
A value below 045°. In the northern hemisphere during deceleration following a landing in a ?
Question 47-28 : No apparent turn an apparent turn to the east an apparent turn to the west an apparent turn to the south
 No apparent turn.
No apparent turn. In the northern hemisphere during deceleration following a landing in a ?
Question 47-29 : No apparent turn an apparent turn to the east an apparent turn to the west an apparent turn to the north
 No apparent turn.
No apparent turn. During deceleration following a landing in a westerly direction a magnetic ?
Question 47-30 : An apparent turn to the south an apparent turn to the north no apparent turn no apparent turn only on northern latitudes
 An apparent turn to the south.
An apparent turn to the south. During deceleration following a landing in a westerly direction a magnetic ?
Question 47-31 : An apparent turn to the north an apparent turn to the south no apparent turn no apparent turn only on southern latitudes
 An apparent turn to the north.
An apparent turn to the north. During deceleration following a landing in an easterly direction a magnetic ?
Question 47-32 : An apparent turn to the south an apparent turn to the north no apparent turn no apparent turn only on northern latitudes
 An apparent turn to the south.
An apparent turn to the south. During deceleration following a landing in an easterly direction a magnetic ?
Question 47-33 : An apparent turn to the north an apparent turn to the south no apparent turn no apparent turn only on southern latitudes
 An apparent turn to the north.
An apparent turn to the north. About a magnetic compass ?
Question 47-34 : Turning error is due to the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field acceleration errors are due to the angle of dip acceleration errors are due to schuler oscillations errors of parallax are due to the oscillation of the compass rose
 Turning error is due to the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field.
Turning error is due to the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field. A pilot wishes to turn right on to a southerly heading with 20° bank at a ?
Question 47-35 : 200° 150° 170° 180°
 200°.
200°. The turning errors of a direct reading magnetic compass are ?
Question 47-36 : Maximum at the magnetic poles maximum at the magnetic equator minimum at a latitude of 45° minimum at the magnetic poles
 Maximum at the magnetic poles.
Maximum at the magnetic poles. A flux valve detects the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field .1 ?
Question 47-37 : 2 4 1 2 1 2 4 3 4
 2, 4.
2, 4. The direct reading magnetic compass is no more reliable when approaching . 1 ?
Question 47-38 : 1 1 2 3 1 2 1 3
 1
1 In the northern hemisphere during a take off run in a westerly direction a ?
Question 47-39 : An apparent turn to the north an apparent turn to the south no apparent turn an apparent turn to approximately the heading 255°
 An apparent turn to the north.
An apparent turn to the north. In the northern hemisphere during the take off run in an easterly direction a ?
Question 47-40 : An apparent turn to the north an apparent turn to the south no apparent turn an apparent turn to approximately the heading 100°
 An apparent turn to the north.
An apparent turn to the north. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1839 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 47
