During a descent at a constant mach number below the tropopause in isa ? [ Free airport ]
Question 45-1 : Cas and tas increase cas increases and tas decreases cas and tas decrease cas decreases and tas increases
 Cas and tas increase.
Cas and tas increase. During a descent at a constant ias below the tropopause in isa conditions ?
Question 45-2 : Mach number and tas decrease mach number and tas increase mach number increases and tas decreases mach number decreases and tas increases
 Mach number and tas decrease.
Mach number and tas decrease. During a descent at a constant calibrated airspeed cas below the tropopause in ?
Question 45-3 : Mach number and tas decrease mach number and tas increase mach number decreases and tas increases mach number increases and tas decreases
 Mach number and tas decrease.
Mach number and tas decrease. During a climb at a constant mach number below the tropopause in isa conditions ?
Question 45-4 : Ias and tas decrease ias increases and tas decreases ias decreases and tas increases ias and tas increase
 Ias and tas decrease.
Ias and tas decrease. If the pitot tube ices up during a flight the affected equipment s is are .1 ?
Question 45-5 : 3 1 2 3 1 3 1
 3.
3. If during a descent . the pneumatic altimeter reading is constant. the ?
Question 45-6 : The static ports are completely blocked the total pressure head is completely blocked there is a leakage in the static pressure line the antenna of the radio altimeter is completely iced up
 The static ports are completely blocked.
The static ports are completely blocked. For tas calculations the adc uses the following parameters .1 sat .2 tat .3 ?
Question 45-7 : 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 3 4 1 3 4
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. If the pitot tube becomes blocked during a descent the airspeed indicator ?
Question 45-8 : Under reads over reads under reads or over reads depending on the air density indicates a constant speed
 Under-reads.
Under-reads. Given .pt total pressure.ps static pressure.pd dynamic pressure.the altimeter ?
Question 45-9 : Ps ps pt pd pd ps
 Ps.
Ps. A pitot tube covered by ice which blocks the ram air inlet will affect the ?
Question 45-10 : Airspeed indicator altimeter vertical speed indicator airspeed indicator altimeter and vertical speed indicator
A dynamic pressure measurement circuit is constituted of the following pressure ?
Question 45-11 : Total pressure and static pressure static pressure only total pressure only total pressure and standard pressure
 Total pressure and static pressure.
Total pressure and static pressure. The qnh is by definition the value of the ?
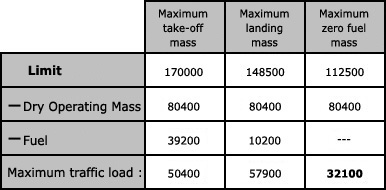
Question 45-12 : Altimeter setting so that the altimeter on the apron of the aerodrome for which it is given reads the elevation atmospheric pressure at the sea level of the location for which it is given altimeter setting so that the altimeter on the apron of the aerodrome for which it is given reads zero atmospheric pressure at the level of the ground overflown by the aircraft
The purpose of the vibrating device of an altimeter is to ?
Question 45-13 : Reduce the effect of friction in the linkages inform the crew of a failure of the instrument allow damping of the measurement in the unit reduce the pressure error
 Reduce the effect of friction in the linkages.
Reduce the effect of friction in the linkages. When climbing at a constant mach number ?
Question 45-14 : Cas decreases cas increases cas remains constant difference between surrounding conditions and isa must be known to deduce the cas variation
 Cas decreases.
Cas decreases. When descending at a constant cas ?
Question 45-15 : Eas increases eas decreases eas remains constant eas does not depend on altitude
 Eas increases.
Eas increases. When climbing at a constant mach number through an isothermal layer the cas ?
Question 45-16 : Decreases increases remains constant decreases if oat is lower than the standard temperature increases if higher
 Decreases.
Decreases. When climbing at a constant cas ?
Question 45-17 : Eas decreases eas increases eas remains constant eas does not depend on altitude
 Eas decreases.
Eas decreases. Vfe is the maximum speed ?
Question 45-18 : With the flaps extended for each approved flap position with the flaps extended in the landing position at which the flaps can be operated in turbulence with the flaps extended in the take off position
 With the flaps extended for each approved flap position.
With the flaps extended for each approved flap position. Tas is ?
Question 45-19 : Ias corrected for instrument position compressibility and density errors ias corrected for compressibility and density errors only cas corrected for instrument position compressibility and density errors cas corrected for instrument compressibility and density errors
 Ias corrected for instrument, position, compressibility and density errors.
Ias corrected for instrument, position, compressibility and density errors. Tas is ?
Question 45-20 : Cas corrected for compressibility and density errors cas corrected for density error only eas corrected for compressibility error only cas corrected for compressibility error only
 Cas corrected for compressibility and density errors.
Cas corrected for compressibility and density errors. Assuming the flight level and mach number remain constant when the oat increases ?
Question 45-21 : Ias remains constant and tas increases ias and tas decrease ias increases and tas decreases ias decreases and tas increases
 Ias remains constant and tas increases.
Ias remains constant and tas increases. Assuming the flight level and mach number remain constant when the oat decreases ?
Question 45-22 : Ias remains constant and tas decreases ias increases and tas decreases ias decreases and tas increases ias and tas increase
 Ias remains constant and tas decreases.
Ias remains constant and tas decreases. A vertical speed indicator measures the difference between ?
Question 45-23 : The instantaneous static pressure and the static pressure at a previous moment the total pressure and the static pressure the total instantaneous pressure and the total pressure at a previous moment the dynamic pressure and the static pressure
 The instantaneous static pressure and the static pressure at a previous moment.
The instantaneous static pressure and the static pressure at a previous moment. At flight level and mach number constant if oat increases the cas ?
Question 45-24 : Remains constant increases decreases decreases if oat is lower than standard temperature increases in the opposite case
 Remains constant.
Remains constant. A temperature sensor has a recovery factor of 0 95 the temperature measured is ?
Question 45-25 : Static air temperature sat + 95% of the ram rise ram air temperature rat + 95% of the ram rise 95% of the static air temperature sat 95% of the ram air temperature rat
A thermocouple type temperature sensing is composed of ?
Question 45-26 : Two dissimilar metals joined together at one end called hot junction or measure junction two identical metals joined together at one end called hot junction or measure junction two identical metals joined together at both ends called hot and cold junctions a single wire metal winding
 Two dissimilar metals joined together at one end (called hot junction or measure junction).
Two dissimilar metals joined together at one end (called hot junction or measure junction). At flight level and mach number constant if oat decreases the cas ?
Question 45-27 : Remains constant increases decreases decreases if oat is lower than standard temperature increases in the opposite case
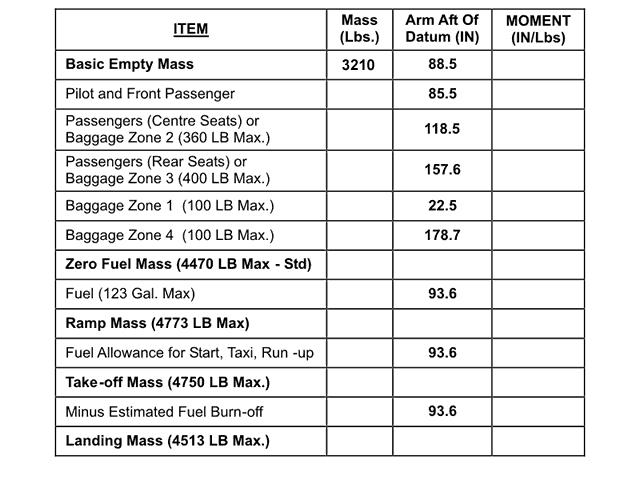
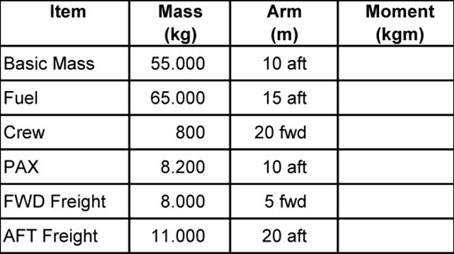
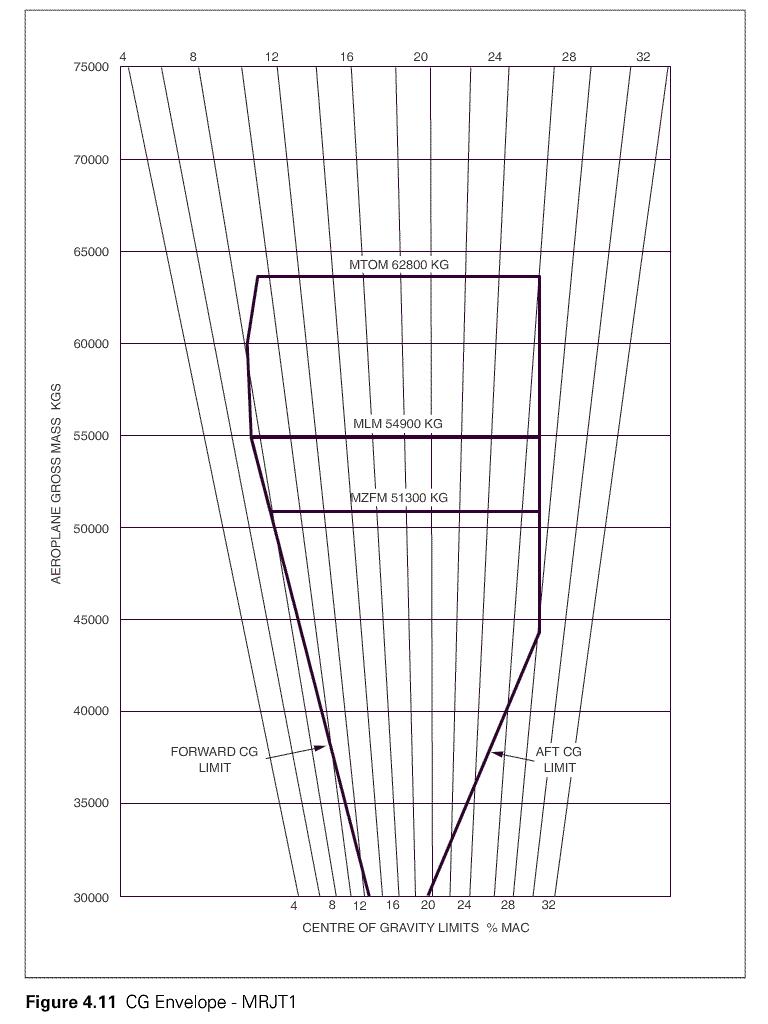
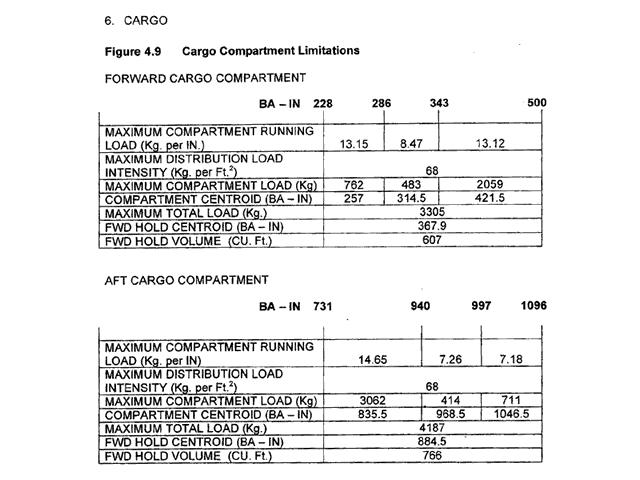
The altimeter of your aircraft indicates 15000 ft with a subscale setting of ?
Question 45-28 : 15000 ft 14640 ft 15360 ft 572 hpa
 15000 ft.
15000 ft. During a climb at a constant ias below the tropopause in isa conditions ?
Question 45-29 : The mach number and the true airspeed increase the mach number and the true airspeed decrease the mach number increases and the true airspeed decreases the mach number decreases and the true airspeed increases
 The mach number and the true airspeed increase.
The mach number and the true airspeed increase. The altimeter of your aircraft indicates 11000 ft with a subscale setting of ?
Question 45-30 : 11000 ft 11740 ft 10260 ft 670 hpa
 11000 ft.
11000 ft. The altimeter of your aircraft indicates 17000 ft with a subscale setting of ?
Question 45-31 : 17000 ft 17540 ft 16460 ft 527 hpa
 17000 ft.
17000 ft. The altimeter of your aircraft indicates 16000 ft with a subscale setting of ?
Question 45-32 : 16000 ft 14300 ft 17700 ft 549 hpa
 16000 ft.
16000 ft. An aeroplane is in a steady climb the auto throttle maintains a constant mach ?
Question 45-33 : Decreases increases remains constant decreases if the static temperature is lower than the standard temperature increases if higher
 Decreases.
Decreases. An angle of attack sensor may consist of .1 an inertial system computing the ?
Question 45-34 : 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 1 3
 2, 3.
2, 3. An airplane is in steady cruise at flight level 290 the auto throttle maintains ?
Question 45-35 : Remains constant increases decreases increases if the static temperature is higher than the standard temperature decreases if lower
 Remains constant.
Remains constant. In standard atmosphere when climbing at constant cas ?
Question 45-36 : Tas and mach number increase tas and mach number decrease tas increases and mach number decreases tas decreases and mach number increases
 Tas and mach number increase.
Tas and mach number increase. In a standard atmosphere and at the sea level the calibrated airspeed cas is ?
Question 45-37 : Equal to the true airspeed tas independent of the true airspeed tas higher than the true airspeed tas lower than the true airspeed tas
 Equal to the true airspeed (tas).
Equal to the true airspeed (tas). The parameter that determines the relationship between eas and tas is ?
Question 45-38 : Density altitude pressure altitude oat mach number
 Density altitude.
Density altitude. With cas and pressure altitude we can deduce ?
Question 45-39 : Eas tas eas and tas nothing
 Eas.
Eas. Speed of sound is proportional to ?
Question 45-40 : The square root of the absolute temperature the square root of the tas the square of the absolute temperature the square of the tas
 The square root of the absolute temperature.
The square root of the absolute temperature. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1759 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 45
