Given .pt = total pressure.ps = static pressure.pso = static pressure at sea ? [ Attestation AIM ]
Question 44-1 : Pt ps pt pso pt / ps pt pso / ps
 Pt - ps
Pt - ps Given .pt = total pressure.ps = static pressure.pso = static pressure at sea ?
Question 44-2 : Pt ps pt pso pt pso / pso pt ps / ps
 Pt - ps
Pt - ps Given .pt total pressure.ps static pressure.pd dynamic pressure.the airspeed ?
Question 44-3 : Pd ps pt pt pd pd ps
 Pd.
Pd. If an aircraft maintaining a constant cas and flight level is flying from a ?
Question 44-4 : Tas increases tas decreases mach number increases mach number decreases
 Tas increases.
Tas increases. If an aircraft maintaining a constant cas and flight level is flying from a ?
Question 44-5 : Tas decreases tas increases mach number increases mach number decreases
 Tas decreases.
Tas decreases. If oat decreases when at a constant mach number ?
Question 44-6 : Tas decreases tas increases tas decreases only if the flight level remains constant tas remains constant only if the flight level remains constant
 Tas decreases.
Tas decreases. If oat decreases when at a constant tas ?
Question 44-7 : Mach number increases mach number decreases mach number remains constant the difference between surrounding conditions and isa must be known to deduce the mach number variation
 Mach number increases.
Mach number increases. If oat increases when at a constant mach number ?
Question 44-8 : Tas increases tas decreases tas decreases only if the flight level remains constant tas remains constant only if the flight level remains constant
 Tas increases.
Tas increases. If oat increases when at a constant tas ?
Question 44-9 : Mach number decreases mach number increases mach number remains constant the difference between surrounding conditions and isa must be known to deduce the mach number variation
 Mach number decreases.
Mach number decreases. During a climb at a constant calibrated airspeed cas below the tropopause in ?
Question 44-10 : Tas and mach number increase tas and mach number decrease tas increases and mach number decreases tas decreases and mach number increases
In standard atmosphere when descending at constant cas ?
Question 44-11 : Tas decreases tas remains constant tas increases tas first increases and then remains constant below the tropopause
 Tas decreases.
Tas decreases. In the absence of position and instrument errors cas is equal to ?
Question 44-12 : Ias eas tas ias and eas
In the absence of position and instrument errors ?
Question 44-13 : Ias = cas ias = eas cas = eas cas = tas
 Ias = cas.
Ias = cas. The compressibility correction to cas to give eas .1 may be positive .2 is ?
Question 44-14 : 2 3 2 4 1 3 1 4
 2, 3.
2, 3. True air speed tas is obtained from indicated air speed ias by correcting for ?
Question 44-15 : 1 2 3 4 3 4 1 2 1 3 4
 1, 2, 3, 4.
1, 2, 3, 4. Tas is ?
Question 44-16 : Eas corrected for density error eas corrected for compressibility error cas corrected for density error cas corrected for compressibility error
 Eas corrected for density error.
Eas corrected for density error. When climbing at a constant cas in a standard atmosphere .1 tas decreases .2 ?
Question 44-17 : 2 3 2 4 1 3 1 4
 2, 3.
2, 3. When climbing at a constant cas ?
Question 44-18 : Mach number increases mach number decreases mach number remains constant the difference between surrounding conditions and isa must be known to deduce the mach number variation
 Mach number increases.
Mach number increases. When descending at a constant cas in a standard atmosphere .1 tas increases .2 ?
Question 44-19 : 2 4 2 3 1 3 1 4
 2, 4.
2, 4. When descending at a constant cas ?
Question 44-20 : Mach number decreases mach number increases mach number remains constant the difference between surrounding conditions and isa must be known to deduce the mach number variation
 Mach number decreases.
Mach number decreases. When descending at a constant mach number ?
Question 44-21 : Cas increases cas decreases cas remains constant the difference between surrounding conditions and isa must be known to deduce the cas variation
 Cas increases.
Cas increases. When flying in cold air colder than standard atmosphere indicated altitude is ?
Question 44-22 : Higher than the true altitude the same as the true altitude lower than the true altitude equal to the standard altitude
 Higher than the true altitude.
Higher than the true altitude. When flying in cold air colder than standard atmosphere the altimeter will ?
Question 44-23 : Overestimate underestimate show the actual height above the sea level show the actual height above ground
 Overestimate.
Overestimate. When flying in warm air warmer than standard atmosphere indicated altitude is ?
Question 44-24 : Lower than the true altitude the same as the true altitude higher than the true altitude equal to the standard altitude
 Lower than the true altitude.
Lower than the true altitude. Which of the following statements are correct for an aeroplane cruising at fl ?
Question 44-25 : 1 2 and 3 are all correct 2 and 3 are correct 1 and 2 are correct 1 and 3 are correct
 1, 2 and 3 are all correct.
1, 2 and 3 are all correct. With eas and density altitude we can deduce ?
Question 44-26 : Tas cas cas and tas ias
 Tas.
Tas. With eas and pressure altitude zp we can deduce ?
Question 44-27 : Cas tas cas and tas ias
 Cas.
Cas. During a climb the total pressure probe of the airspeed indicator becomes ?
Question 44-28 : Decreases until reaching the stall speed increases until reaching vmo decreases by 1% per 600 ft increases by 1% per 600 ft
 Decreases until reaching the stall speed.
Decreases until reaching the stall speed. With constant weight and configuration an aircraft always takes off at the same ?
Question 44-29 : Equivalent airspeed ground speed true airspeed indicated airspeed
 Equivalent airspeed.
Equivalent airspeed. An airspeed indicator includes a capsule inside this capsule is ?
Question 44-30 : Total pressure and outside is static pressure static pressure and outside is dynamic pressure dynamic pressure and outside is static pressure a very low residual pressure and outside is static pressure
 Total pressure and outside is static pressure.
Total pressure and outside is static pressure. An aircraft is equipped with one altimeter that is compensated for position ?
Question 44-31 : The greater the speed the greater the error between the two altimeters the greater the speed the lower the error between the two altimeters the lower the speed the greater the error between the two altimeters the error between the two altimeters does not depend on the speed
 The greater the speed, the greater the error between the two altimeters.
The greater the speed, the greater the error between the two altimeters. An aneroid capsule .1 measures differential pressure.2 measures absolute ?
Question 44-32 : 2 3 1 3 2 4 1 4
 2, 3.
2, 3. An altimeter contains one or more aneroid capsules inside these capsules is ?
Question 44-33 : A very low residual pressure and outside is static pressure static pressure and outside is dynamic pressure dynamic pressure and outside is static pressure static pressure and outside a very low residual pressure
 A very low residual pressure and outside is static pressure.
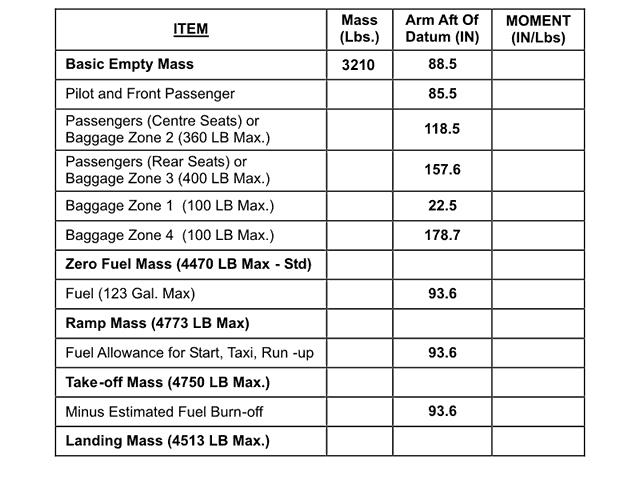
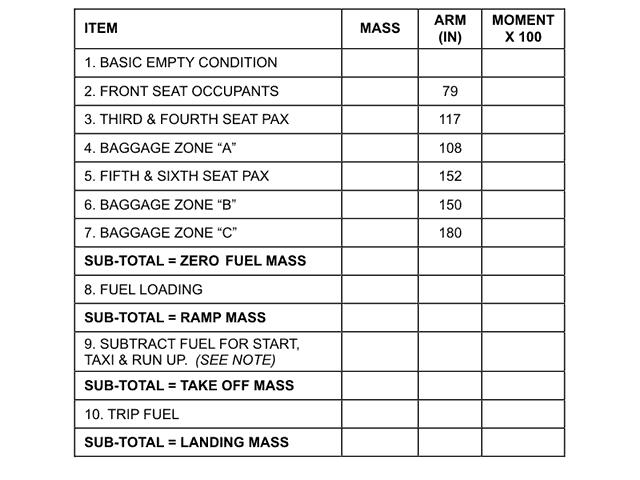
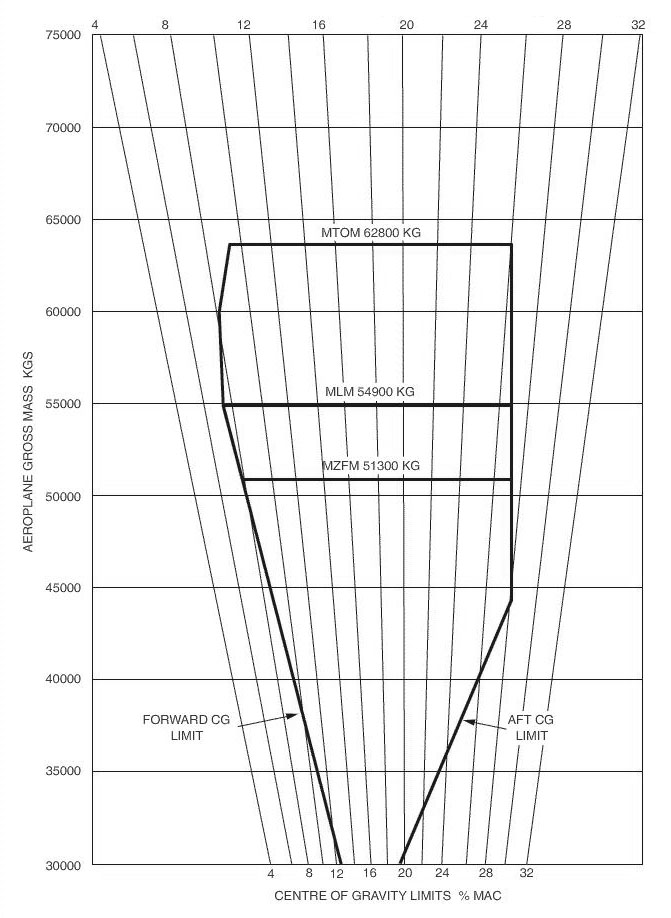
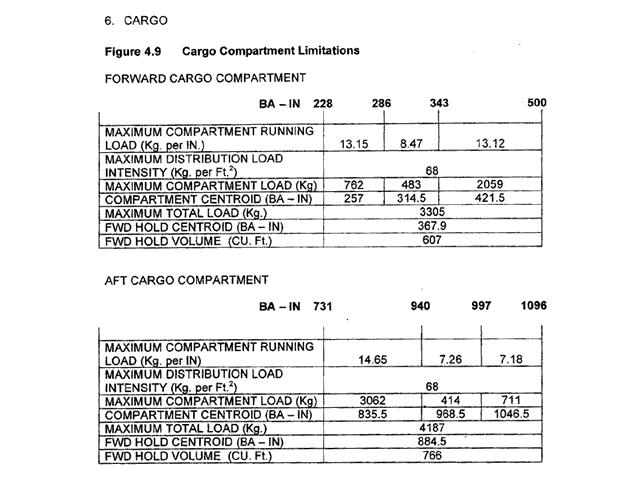
A very low residual pressure and outside is static pressure. The altimeter of your aircraft indicates 10000 ft with a subscale setting of ?
Question 44-34 : 10000 ft 10400 ft 9600 ft 697 hpa
 10000 ft.
10000 ft. The altimeter indicates true altitude ?
Question 44-35 : In isa conditions only when the temperature on the ground is +15 % with a lapse rate of 2 °c per 1000 feet and correct qnh is set when the temperature on the ground is +15 °c with a lapse rate of 2 °c per 1000 feet and correct qfe is set when pressure at mean sea level is 10135 25 hpa with a ground temperature of +15°c and a density equal to 1 225 kg/m3
 In isa conditions only.
In isa conditions only. Tas can be obtained from the following data ?
Question 44-36 : Eas and density altitude eas and pressure altitude cas and density altitude cas and pressure altitude
 Eas and density altitude.
Eas and density altitude. The maximum tas is obtained at ?
Question 44-37 : The flight level at which simultaneously cas = vmo and m = mmo the maximum flight level all the flight level s where cas =vmo all the flight level s where m =mmo
 The flight level at which simultaneously cas = vmo and m = mmo.
The flight level at which simultaneously cas = vmo and m = mmo. The input data of an adc are .1 oat .2 tat.3 static pressure .4 total ?
Question 44-38 : 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 3 4 1 2 4
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. Given .mach number m = 0 70.measured impact temperature = 48 °c.the recovery ?
Question 44-39 : 65 °c 45 °c 68 °c 51 °c
 -65 °c
-65 °c During a descent at a constant mach number below the tropopause in isa ?
Question 44-40 : Ias and tas increase ias and tas decrease ias increases and tas decreases ias decreases and tas increases
 Ias and tas increase.
Ias and tas increase. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1719 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 44
