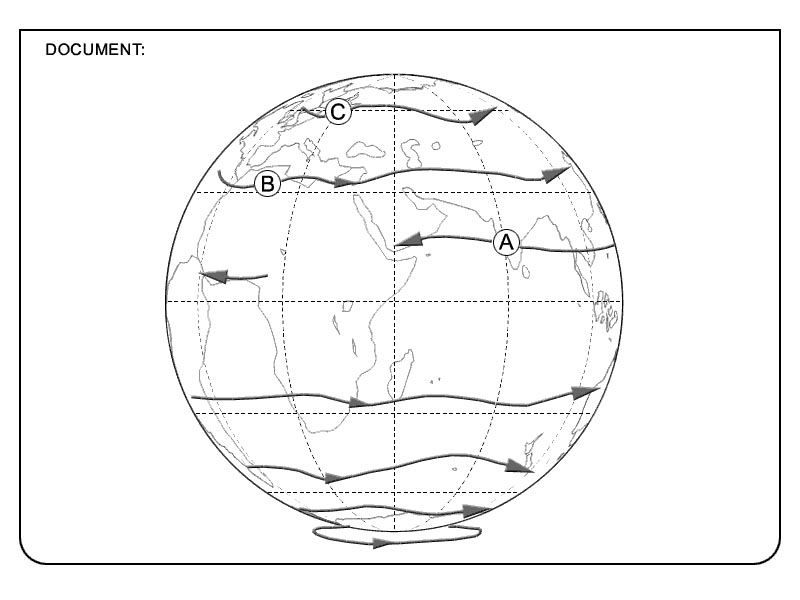
A passenger oxygen mask is ? [ Path visibility ]
Question 38-1 : A continuous flow mask and in principle should not be used if there is smoke in the cabin an on demand type mask and in principle should not be used if there is smoke in the cabin a continuous flow mask and must be used if there is smoke in the cabin an on demand type mask and must be used if there is smoke in the cabin
 A continuous flow mask and in principle should not be used if there is smoke in the cabin.
A continuous flow mask and in principle should not be used if there is smoke in the cabin. A smoke hood is a device covering ?
Question 38-2 : The whole head and with a continuous oxygen flow the whole head and with an oxygen flow only on demand only the nose and the mouth and with an oxygen/air mix only the nose and the mouth and with a continuous oxygen flow
 The whole head and with a continuous oxygen flow.
The whole head and with a continuous oxygen flow. Regarding the chemical oxygen generator to enable the oxygen to flow the ?
Question 38-3 : Firmly pull the mask towards his face operate the relevant switch in his armrest firmly pull the door compartment of the oxygen mask storage turn the oxygen valve to open
 Firmly pull the mask towards his face.
Firmly pull the mask towards his face. Fixed oxygen systems in pressurised aeroplanes are used to provide oxygen .1 ?
Question 38-4 : 1 4 1 2 4 3 2 3
 1, 4.
1, 4. When using an emergency oxygen mask a pilot is able to ?
Question 38-5 : Both transmit and receive receive only transmit only neither transmit or receive
 Both transmit and receive
Both transmit and receive A smoke mask is a ?
Question 38-6 : Mask with flow on request and covers the whole face continuous flow mask and covers the whole face mask with flow on request and covers only the nose and the mouth continuous flow mask and covers only the nose and the mouth
 Mask with flow on request and covers the whole face.
Mask with flow on request and covers the whole face. Which of these statements about chemical oxygen generators are correct or ?
Question 38-7 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Which of these statements about chemical oxygen generators are correct or ?
Question 38-8 : I is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is correct
 I is correct, ii is incorrect.
I is correct, ii is incorrect. Which of these statements about chemical oxygen generators are correct or ?
Question 38-9 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which of these statements about chemical oxygen generators are correct or ?
Question 38-10 : I is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is incorrect, ii is correct.
I is incorrect, ii is correct. The advantages of a chemical oxygen source for the passenger cabin are . 1 ?
Question 38-11 : 1 2 4 and 6 1 2 3 4 5 and 6 2 3 and 5 1 3 4 and 5
 1, 2, 4 and 6
1, 2, 4 and 6 The disadvantages of a chemical oxygen source for the passenger cabin are . 1 a ?
Question 38-12 : 1 3 and 5 1 2 3 4 and 5 2 and 4 1 2 3 and 5
The advantages of a gaseous oxygen source compared with a chemical source for ?
Question 38-13 : 2 3 1 only 2 only 1 2
 2, 3.
2, 3. High frequency vibration usually emanates from ?
Question 38-14 : Transmission shafting the main rotor gearbox the engine or tail rotor the main rotor blades
The sand filter located at the air intake of a gas turbine engine ?
Question 38-15 : Reduces the efficiency of the air intake increases the efficiency of the air intake has no effect on the efficiency of the air intake has an effect on the efficiency of the compressor only
 Reduces the efficiency of the air intake.
Reduces the efficiency of the air intake. Warning lights associated with basic pitot/static heating systems in ?
Question 38-16 : Either the heating element or the power relay has failed the heating element has failed the power supply to the system has failed the heating system is on and the heater is cycling on/off
 Either the heating element or the power relay has failed.
Either the heating element or the power relay has failed. Helicopter engine bellmouth air intakes ?
Question 38-17 : May be heated by either hot oil electric mats or engine bleed air are always heated by engine bleed air from the engine compressor are always heated by electrically heated mats are not heated
 May be heated by either hot oil, electric mats or engine bleed air.
May be heated by either hot oil, electric mats or engine bleed air. Heating systems for helicopters may obtain hot air from the following sources ?
Question 38-18 : 1 3 2 3 2 1
 1, 3.
1, 3. Warning devices associated with air conditioning systems fitted in helicopters ?
Question 38-19 : A green system ''on'' information light and amber bleed air failure lights amber bleed air failure warning lights and red fire warnings for three wheel air cycle machine failure a green system serviceable light and an amber warning light an amber system ''on'' information light a green serviceable light and either a red or amber duct overpressure light
 A green system ''on'' information light and amber bleed air failure lights.
A green system ''on'' information light and amber bleed air failure lights. The most common type of starter used on a helicopter engine is ?
Question 38-20 : A d c starter/generator a d c starter motor an a c starter/generator an a c starter motor
 A d.c starter/generator.
A d.c starter/generator. The most common material used in the construction of gearbox casings is ?
Question 38-21 : Magnesium alloy aluminium alloy steel alloy titanium alloy
 Magnesium alloy.
Magnesium alloy. For a large helicopter ram air ventilation ?
Question 38-22 : May be provided throughout the cockpit and cabin through a series of ducts is provided to pilots only is ducted from the downwash of the main rotors to gasper ducts throughout the helicopter may be provided throughout the cabin from ducts in doors only
 May be provided throughout the cockpit and cabin through a series of ducts.
May be provided throughout the cockpit and cabin through a series of ducts. The throttle control may be interconnected with ?
Question 38-23 : The collective lever to increase power with increased pitch application the collective lever to decrease power with increased pitch application the yaw pedals to increase tail rotor speed for directional control inputs the cyclic stick to increase power for cyclic control inputs
 The collective lever, to increase power with increased pitch application.
The collective lever, to increase power with increased pitch application. The purpose of the primary stops in a flying control system is to ?
Question 38-24 : Restrict the movement of the controls within the correct range prevent damage to the system when the helicopter is parked in high winds act as a stop in case of vibration of the controls bring the main and tail rotors to rest as soon as possible after shut down
 Restrict the movement of the controls within the correct range.
Restrict the movement of the controls within the correct range. The ducted fan type tail rotor ?
Question 38-25 : Uses an aerofoil shaped duct creating thrust is chosen in design solely due to the safety reasons is mounted at the base of the fin allowing lighter supporting structure and to offset the fin to counter tail rotor drift is of simpler design and of a lower cost of manufacture than a traditional tail rotor
 Uses an aerofoil shaped duct creating thrust.
Uses an aerofoil shaped duct creating thrust. Friction controls are usually fitted to ?
Question 38-26 : Both collective and cyclic controls but only the collective friction is adjustable in flight both collective and cyclic controls which are adjustable in flight the collective control only the cyclic control only
 Both collective and cyclic controls, but only the collective friction is adjustable in flight.
Both collective and cyclic controls, but only the collective friction is adjustable in flight. Which of the following statements about the swash plate in a helicopter ?
Question 38-27 : To be able to move or to tilt the swash plate in all directions at least three separate servo units are needed helicopters with a so called artificial feel do not need a swash plate all helicopters are equipped with a swash plate another name for swash plate is spider arm
The main reason for fitting a rotor brake can be .1 to bring the rotor quickly ?
Question 38-28 : 1 3 3 4 1 3 4 2 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. Rotor brakes are often located ?
Question 38-29 : On the tail rotor drive shaft on the main rotor shaft on a separate drive shaft on the main rotor gear box within the main rotor gearbox
 On the tail rotor drive shaft.
On the tail rotor drive shaft. Rotor brake discs are manufactured from ?
Question 38-30 : Steel or carbon fibre alumicnium or steel steel or titanium boron aluminide or titanium
 Steel or carbon fibre.
Steel or carbon fibre. Wear rate of a control rod spherical bearing is ?
Question 38-31 : Exponential progressive constant unpredictable
 Exponential.
Exponential. The purpose of the fixed scissors is to ?
Question 38-32 : Resist the rotational force applied to the lower swashplate in a rotorhead system ensure the wheel remains correctly orientated to the oleo leg in a landing gear act as the lower jaw of the cable cut device on a hoist provide part of feedback mechanism in an auto pilot system
 Resist the rotational force applied to the lower swashplate in a rotorhead system.
Resist the rotational force applied to the lower swashplate in a rotorhead system. Tail rotors differ from most main rotors in that ?
Question 38-33 : The pitch changes from a negative angle setting to a positive angle setting the tail rotor rotates at a lower speed they always have few blades the lead/lag hinge is incorporated with the flapping hinge
 The pitch changes from a negative angle setting to a positive angle setting.
The pitch changes from a negative angle setting to a positive angle setting. Tail rotors differ from main rotors in that ?
Question 38-34 : They do not provide for blade pitch cyclic variation pitch remains constant throughout all flight regimes they rotate at a lower speed they always have fewer blades
 They do not provide for blade pitch cyclic variation.
They do not provide for blade pitch cyclic variation. Main rotor droop stops ?
Question 38-35 : Are inactive during flight move to prevent the rotor disc drooping excessively during turbulent conditions preventing damage to the tail cone in flight prevents rotor droop in flight by ensuring the engine provides additional power immediately when required by the rotor prevents engine power reducing below the requirements to sustain rotor rpm
 Are inactive during flight.
Are inactive during flight. An unshrouded tail rotor has ?
Question 38-36 : Equal pitch change to all blades different pitch change to each blade cyclic pitch control only rpm control independently of the main rotor
 Equal pitch change to all blades.
Equal pitch change to all blades. On the diagram the rotating blade pitch control is indicated by the letter . ?
Question 38-37 : D a b c
 D.
D. What is a typical characteristic of a fully articulated rotor system ?
Question 38-38 : The blades are free to flap drag and feather independently of one another the rotor head has flapping hinges only the blades have hinges for all movements the rotor head only has elastomeric hinges for all movements of the blades
 The blades are free to flap, drag and feather independently of one another.
The blades are free to flap, drag and feather independently of one another. Which of the following statements with respect to the rotor brake is correct ?
Question 38-39 : The rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a disc brake the rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a drum brake the rotor brake always slows down the drive shaft between the engine s and the main gear box a hydraulically actuated rotor brake is connected to the same hydraulic system as the flight controls in order to ensure the necessary reliability
 The rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a disc brake.
The rotor brake is nearly always implemented as a disc brake. A rotor is fully articulated when ?
Question 38-40 : The blades each have the possibility to flap drag and feather separately the rotor head has hinges for flapping as well as dragging the blades have been mounted flexibly with regard to flapping and dragging the rotor has more than two blades that have separate flapping and feathering hinges
 The blades each have the possibility to flap, drag and feather separately.
The blades each have the possibility to flap, drag and feather separately. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1479 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 38
