The function of the swirl vanes round the fuel nozzles is to .1 increase air ? [ Exercise Manual ]
Question 35-1 : 2 3 1 2 1 2 3 1 only
 2, 3.
2, 3. The take off of a jet aeroplane may be performed with 'reduced thrust' in order ?
Question 35-2 : Reduce maintenance costs save fuel reduce take off noise reduce the risk of engine failure during take off
 Reduce maintenance costs.
Reduce maintenance costs. In an ignition system during a normal start of a gas turbine engine igniter ?
Question 35-3 : Should commence prior to fuel entering the combustion chamber should commence after fuel has entered the combustion chamber should commence prior to starter motor engagement to prevent a hot start commences upon starter motor engagement and is deactivated at a rotor speed of approximately 15% below idle rpm
 Should commence prior to fuel entering the combustion chamber.
Should commence prior to fuel entering the combustion chamber. A gas turbine engine is run at ground idle for a period of time prior to ?
Question 35-4 : Prevent seizure of the rotor blades in their seals prevent vapour lock in the fuel control and/or fuel lines prevent seizure of the engine bearings allow the engine oil to cool
 Prevent seizure of the rotor blades in their seals.
Prevent seizure of the rotor blades in their seals. The purpose of variable by pass valves in a high bypass turbofan engine between ?
Question 35-5 : Prevent fan stall and lp compressor stall during engine start and low rotor speeds provide sufficient air to the hp compressor during engine start prevent fan surge at high rotor speeds high rpm prevent hp compressor stall during engine start
 Prevent fan stall and lp compressor stall during engine start and low rotor speeds.
Prevent fan stall and lp compressor stall during engine start and low rotor speeds. If a gas turbine engine fuel/oil heat exchanger is located downstream of the hp ?
Question 35-6 : Rise rise and the fuel nozzles eventually to become clogged fall fall and the oil jets eventually to become clogged
 Rise.
Rise. The compressor pressure ratio of an axial flow compressor is primarily ?
Question 35-7 : Number of stages rotor diameter compressor inlet temperature design value compressor inlet pressure design value
 Number of stages.
Number of stages. In a theoretical gas turbine cycle combustion takes place at constant ?
Question 35-8 : Pressure energy temperature volume
 Pressure.
Pressure. When a gas turbine engine accelerates from idle to take off thrust and the ?
Question 35-9 : A compressor stall stagnation supersonic airflow at the compressor blade trailing edges a compressor blade airflow angle of attack that is too small
 A compressor stall.
A compressor stall. Which of the following parameters remains constant in a divergent subsonic gas ?
Question 35-10 : Total temperature static pressure dynamic pressure static temperature
 Total temperature.
Total temperature. The most favourable conditions to apply the flexible take off procedure are .1 ?
Question 35-11 : 2 4 5 1 3 5 2 3 6 2 4 6
 2, 4, 5.
2, 4, 5. Assuming the jet pipe is not choked the equation to calculate jet engine thrust ?
Question 35-12 : T = m vj vv t = m vv vj t = m vv + vj t = mvj
 T = m(vj - vv)
T = m(vj - vv) Given . p0 = static ambient pressure .t0 = static ambient temperature.m = air ?
Question 35-13 : T = m vj vv + a pj p0 t = m vv vj + a t j t0 t = m vv vj + a pj p0 t = m vj vv + a tj t0
 T = m(vj -vv ) + a(pj - p0).
T = m(vj -vv ) + a(pj - p0). The axial compressor of a gas turbine engine usually has more stages than its ?
Question 35-14 : The power output of a turbine stage is higher than the power consumption of a compressor stage the compressor consumes much more power than the turbine bleed air is taken from the compressor turbine speed is much higher than compressor speed
 The power output of a turbine stage is higher than the power consumption of a compressor stage.
The power output of a turbine stage is higher than the power consumption of a compressor stage. On a fadec gas turbine engine during normal flight the power for the fadec's ?
Question 35-15 : The fadec power source s on the engine the aircraft battery the aircraft generator the apu generator
 The fadec power source(s) on the engine.
The fadec power source(s) on the engine. In a gas turbine combustion chamber ?
Question 35-16 : Secondary air is required for cooling of the inner casing the gas pressure increases in an axial downstream direction the axial velocity of the gas stream is greatest behind the swirl vanes the gas temperature is highest at the chamber outlet
 Secondary air is required for cooling of the inner casing.
Secondary air is required for cooling of the inner casing. If there is a single input data failure on a fadec gas turbine engine ?
Question 35-17 : The engine continues to operate normally the engine stops the engine is set at a fail safe thrust the electronic engine control unit uses a constant data value for computation
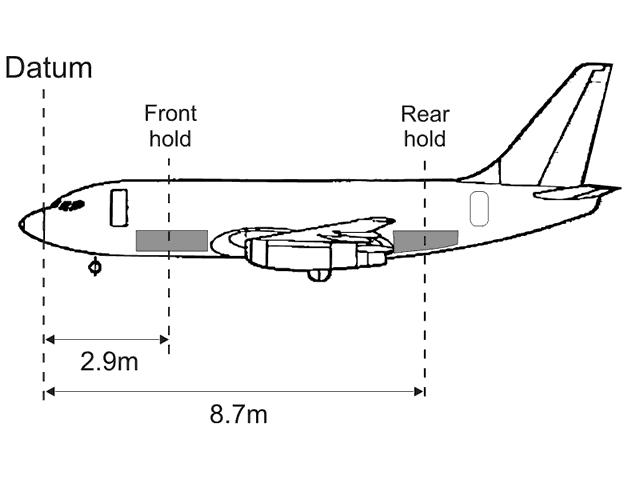 The engine continues to operate normally.
The engine continues to operate normally. Concerning the fuel system high pressure shut off valve hpsov of a gas turbine ?
Question 35-18 : Ignition is activated before fuel is delivered by the hpsov to the fuel nozzles the hpsov is located between the hp fuel pump and the fuel control unit manual hpsov control from the cockpit is not possible with fadec equipped engines the hpsov is mounted in the wing front spar near the pylon
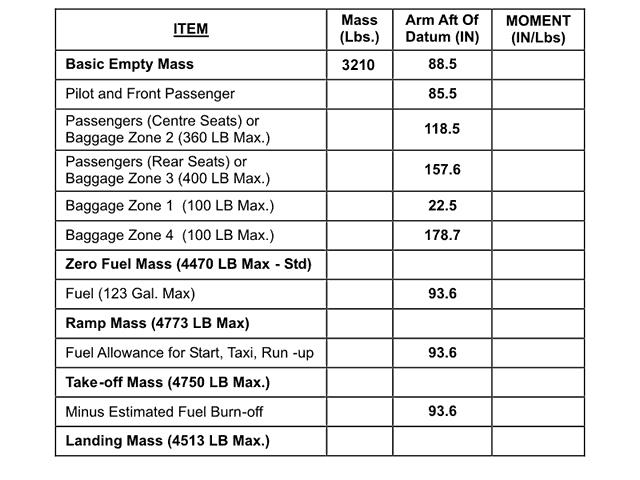 Ignition is activated before fuel is delivered by the hpsov to the fuel nozzles.
Ignition is activated before fuel is delivered by the hpsov to the fuel nozzles. Derated or reduced take offs save engine life primarily due to ?
Question 35-19 : Reduced low cycle fatigue damage the maximum oil temperature not being exceeded reduced corrosion of the hp turbine blades reduced creep damage due to higher egt levels during take off
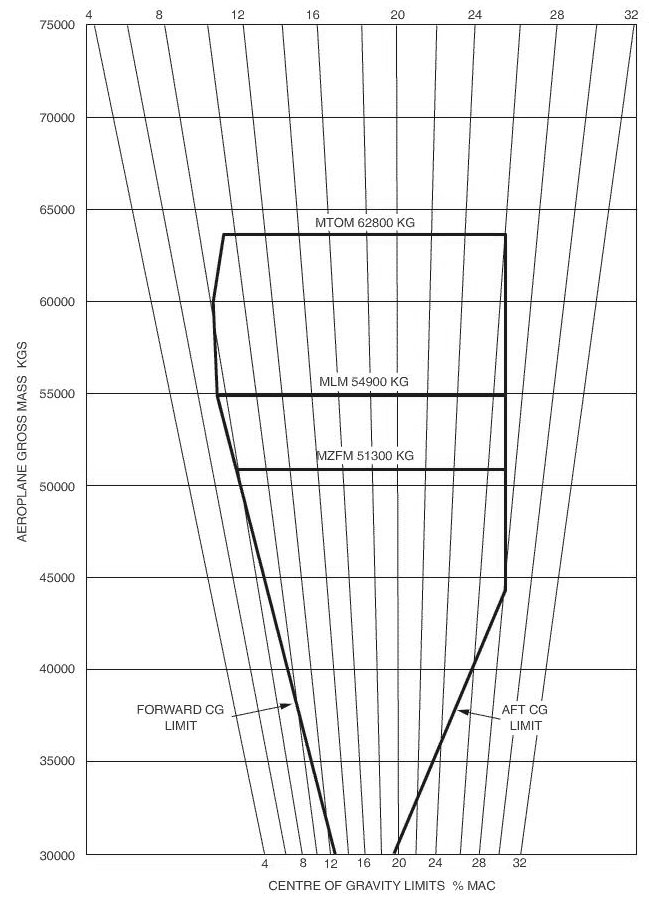 Reduced low cycle fatigue damage.
Reduced low cycle fatigue damage. The diagram shown in annex represents a twin spool turbofan positions before ?
Question 35-20 : 1 and 2 1 and 8 2 and 3 5 and 8
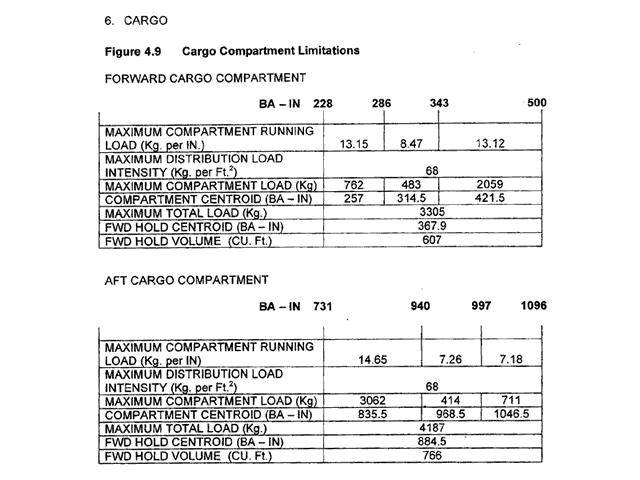 1 and 2.
1 and 2. What is the average compression ratio of a centrifugal compressor ?
Question 35-21 : 1 4 1 15 1 60 1 5 10
 1:4.
1:4. If engine compressor air is bled off for engine anti icing or a similar system ?
Question 35-22 : Will rise will be unchanged may rise or fall depending on which stage of the compressor is used for the bleed and the rpm of the engine at the moment of selection will fall
 Will rise.
Will rise. Increasing the frequency of variations in thrust setting during normal ?
Question 35-23 : Low cycle fatigue damage is more severe the egt limit would be exceeded more often fatigue due to vibration is more severe creep will be more severe
 Low cycle fatigue damage is more severe.
Low cycle fatigue damage is more severe. An axial compressor when operating below its design speed has ?
Question 35-24 : A tendency to stall in the front stages a tendency to stall in the rear stages a tendency to stall in the centre stages no tendency to stall
 A tendency to stall in the front stages.
A tendency to stall in the front stages. The compressor blades in a rotating gas turbine engine are held in position by ?
Question 35-25 : The mountings and the resultant of aerodynamic and centrifugal forces abradable seals and aerodynamic forces a centrifugal latch the mountings and thermal expansion only
 The mountings and the resultant of aerodynamic and centrifugal forces.
The mountings and the resultant of aerodynamic and centrifugal forces. Some gas turbine engines have multiple stages in the hp and lp turbines ?
Question 35-26 : Because one stage does not generate sufficient shaft power to facilitate balancing of the turbine assembly to help stabilise the pressure between the compressor and the turbine to reduce noise in the propelling nozzle
 Because one stage does not generate sufficient shaft power.
Because one stage does not generate sufficient shaft power. In which part of a gas turbine engine are high temperature requirements most ?
Question 35-27 : The combustion chamber and front part of the hp turbine the last part of the hp compressor and front part of the hp turbine the turbine and exhaust nozzle the combustion chamber and exhaust nozzle
 The combustion chamber and front part of the hp turbine.
The combustion chamber and front part of the hp turbine. A twin spool engine with an inlet air mass flow of 500 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 35-28 : 1 0 2 3
A 'fan' stage of a ducted fan turbine engine is driven by ?
Question 35-29 : The low pressure turbine airflow drawn across it by the high pressure compressor the high pressure compressor through reduction gearing the high pressure turbine
 The low pressure turbine.
The low pressure turbine. The oil supply to gas turbine engine bearings is maintained in the event of the ?
Question 35-30 : Differential pressure opening the bypass valve of the main oil filter the hp fuel pump the scavenge pumps a back up oil system
 Differential pressure opening the bypass valve of the main oil filter.
Differential pressure opening the bypass valve of the main oil filter. One of the purposes of compressor bleed valves is to ?
Question 35-31 : Decrease the airflow across the rear compressor stages whilst that across the early stages is increased limit the acceleration period of the engine increase the airflow across the rear compressor stages whilst that across the early stages is decreased decrease the load on the compressor when the engine is approaching maximum rpm
 Decrease the airflow across the rear compressor stages, whilst that across the early stages is increased.
Decrease the airflow across the rear compressor stages, whilst that across the early stages is increased. Turbine blade stages may be classed as either 'impulse' or 'reaction' in an ?
Question 35-32 : I drops ii remains constant i rises ii remains constant i remains constant ii drops i remains constant ii rises
 (i) drops (ii) remains constant
(i) drops (ii) remains constant One advantage of having three instead of two spools in some high bypass ?
Question 35-33 : Fewer variable stator vanes and variable inlet guide vanes are required to prevent compressor stall at low rotor speeds fewer variable stator vanes and variable inlet guide vanes are required to prevent compressor stall at high rotor speeds there is a lower fuel consumption due to a higher overall pressure ratio there is a lower fuel consumption and more thrust due to higher overall pressure ratio
 Fewer variable stator vanes and variable inlet guide vanes are required to prevent compressor stall at low rotor speeds.
Fewer variable stator vanes and variable inlet guide vanes are required to prevent compressor stall at low rotor speeds. The compressor surge effect during acceleration is prevented by the ?
Question 35-34 : Fuel control unit f c u variable setting type nozzle guide vanes surge bleed valves inlet guide vanes
 Fuel control unit (f.c.u.).
Fuel control unit (f.c.u.). Creep in a gas turbine engine is ?
Question 35-35 : The permanent increase in length of metal parts due to a combination of tensile stress and high temperatures over a prolonged period expansion of metal parts due to temperature increase the elastic increase in length of metal parts due to tensile stress and high temperatures crack formation in metal parts due to cyclic mechanical loads and high temperatures
 The permanent increase in length of metal parts due to a combination of tensile stress and high temperatures over a prolonged period.
The permanent increase in length of metal parts due to a combination of tensile stress and high temperatures over a prolonged period. About a twin spool compressor ?
Question 35-36 : The low pressure spool runs at a lower rpm than the high pressure spool both spools run at the same rpm the low pressure spool runs at a very high rpm thus preventing the onset of compressor stall when operating at very high rpm's the later stages within the high pressure spool will have a large negative angle of attack
 The low pressure spool runs at a lower rpm than the high pressure spool.
The low pressure spool runs at a lower rpm than the high pressure spool. In addition to providing 'customer' bleed for aeroplane systems air may be bled ?
Question 35-37 : At low rotor speed at high rotor speed and prevent stall at high rotor speed and recover from stall at high rotor speed
 At low rotor speed.
At low rotor speed. One reason to fit a tip shroud to a turbine blade is to ?
Question 35-38 : Increase turbine efficiency provide a seal for the cooling airflow prevent blade creep reduce turbine temperatures
 Increase turbine efficiency.
Increase turbine efficiency. The most important oil system instrument indication during gas turbine engine ?
Question 35-39 : Oil pressure oil temperature oil quantity oil filter clogged warning signal
 Oil pressure.
Oil pressure. Turbine blade stages may be classed as either 'impulse' or 'reaction' in an ?
Question 35-40 : The pressure drops across the stator blades and remains constant across the rotor blades the pressure rises across the stator blades and remains constant across the rotor blades the pressure remains constant across the stator blades and drops across the rotor blades the pressure remains constant across stator blades and rises across the rotor blades
 The pressure drops across the stator blades and remains constant across the rotor blades.
The pressure drops across the stator blades and remains constant across the rotor blades. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1359 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 35
