Regarding a jet engine .i the maximum thrust increases as the pressure ? [ Report OACI ]
Question 33-1 : I is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is incorrect.
I is correct, ii is incorrect. One of the advantages of an annular combustion chamber is ?
Question 33-2 : A reduced thermal stress on the turbine that fewer igniters are required a higher structural strength a simpler assembly
 A reduced thermal stress on the turbine.
A reduced thermal stress on the turbine. The correct order of decreasing freezing points of the three mentioned fuels is ?
Question 33-3 : Jet a jet a 1 jet b jet b jet a 1 jet a jet a 1 jet a jet b jet b jet a jet a 1
 Jet a, jet a-1, jet b.
Jet a, jet a-1, jet b. Labyrinth seals in the lubrication system of a gas turbine engine are designed ?
Question 33-4 : Not completely tight allowing some movement between rotating and static parts not completely tight allowing only some radial movement between rotating and static parts completely tight allowing no movement between rotating and static parts completely tight allowing some axial movement between rotating and static parts
 Not completely tight, allowing some movement between rotating and static parts.
Not completely tight, allowing some movement between rotating and static parts. Regarding a jet engine .i the maximum thrust decreases as the pressure altitude ?
Question 33-5 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. The characteristics of an axial compressor are .1 a low pressure ratio by ?
Question 33-6 : 1 3 1 4 2 3 3 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-7 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-8 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-9 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. A flat rated turbofan engine has a constant maximum rated thrust level ?
Question 33-10 : Up to a specific oat up to a specific pressure altitude above a specific oat above a specific pressure altitude
 Up to a specific oat.
Up to a specific oat. Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-11 : I is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is incorrect.
I is correct, ii is incorrect. Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-12 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-13 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-14 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Which statement is correct about the flow in a divergent jet engine inlet .i ?
Question 33-15 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-16 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Which of the following statements is correct about the flow in a divergent ?
Question 33-17 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Both gas turbine and piston engines use a cycle made up of induction ?
Question 33-18 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. A twin spool engine with an inlet air mass flow of 220 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 33-19 : 0 1 1 1 10
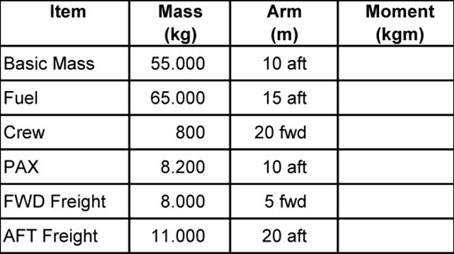 0.
0. A turbofan engine with an inlet air mass flow of 200 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 33-20 : 9 10 5 11
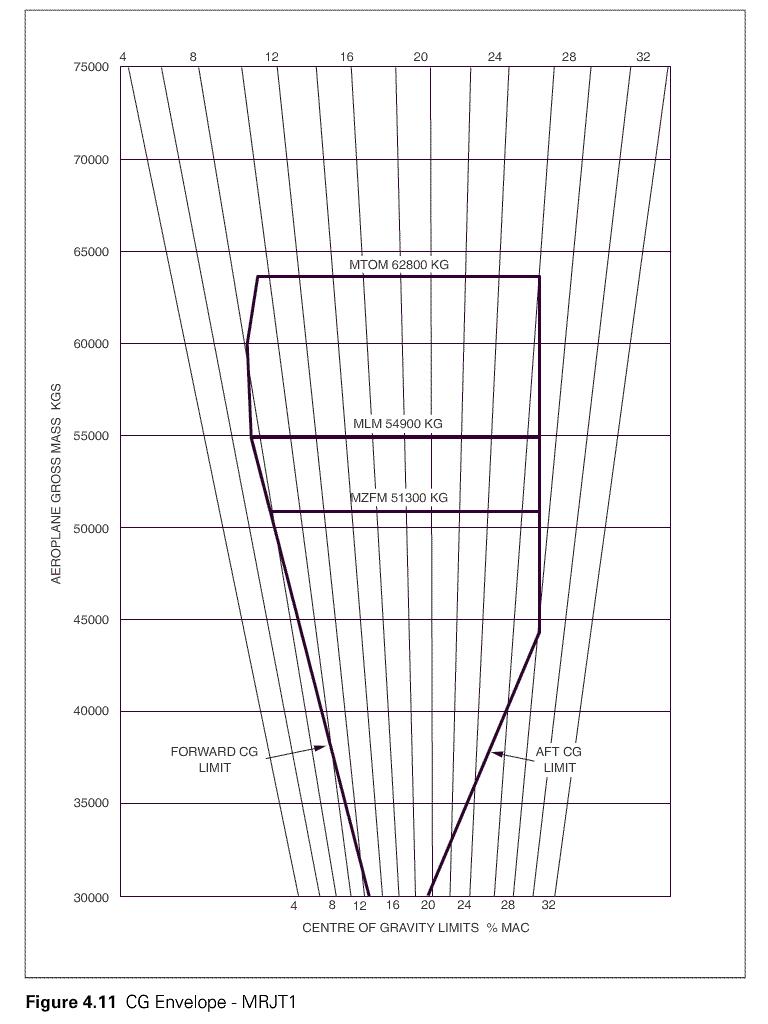 9.
9. A turbofan engine with an inlet air mass flow of 220 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 33-21 : 10 11 1 1 12
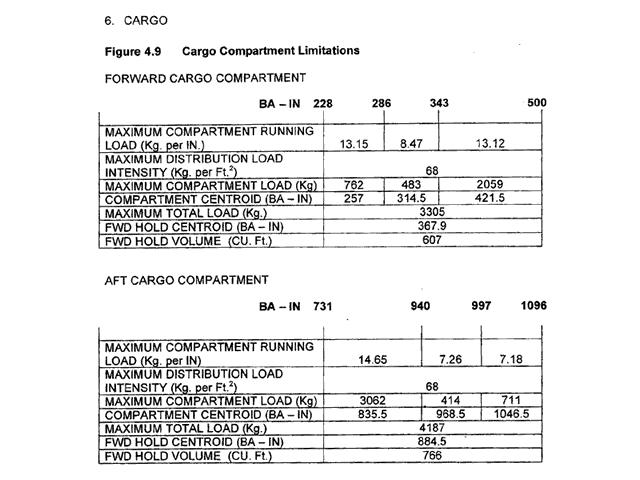 10.
10. A turbofan engine with a bypass air mass flow of 200 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 33-22 : 10 11 1 1 9
 10.
10. A turbofan engine with an inlet air mass flow of 220 kg/s and a bypass mass ?
Question 33-23 : 10 11 1 1 9
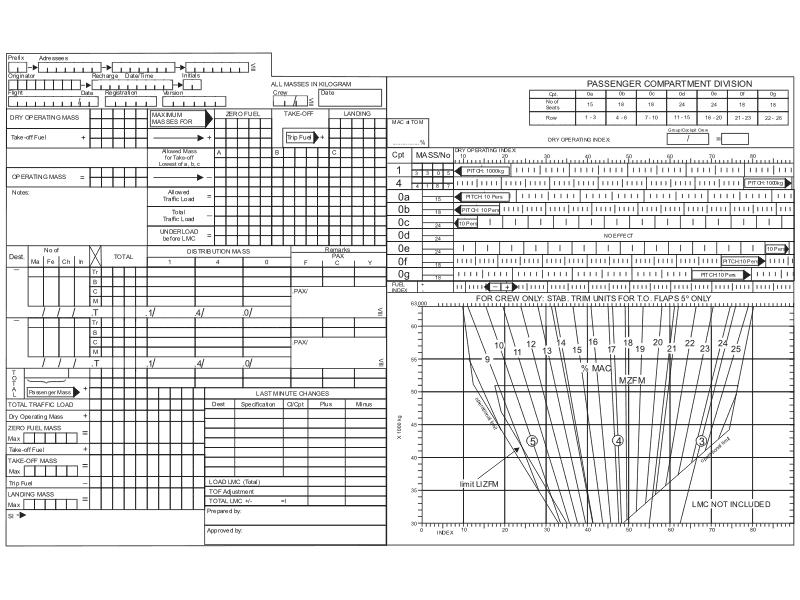 10.
10. The throttle lever angle tla information of a fadec controlled gas turbine ?
Question 33-24 : To the electronic engine control unit by a direct electrical wiring connection to the hydro mechanical main engine control via cables and pulleys to a single dedicated channel of the fadec
 To the electronic engine control unit by a direct electrical wiring connection.
To the electronic engine control unit by a direct electrical wiring connection. A twin spool engine with a bypass mass flow of 250 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 33-25 : 1 2 0 0 5
 1.
1. Which of the following statements regarding variable inlet guide vanes vigvs ?
Question 33-26 : Vigvs are located at the front of the hp compressor and together with the vsvs control compressor airflow vigvs are located in the front of the fan and control both fan and compressor air flow vsvs are used in the compressor only and are used to increase pressure ratio vigvs prevent lp compressor stall and vsvs prevent hp compressor stall if vigvs move towards the open position vsvs move towards the closed position
 Vigvs are located at the front of the hp compressor and, together with the vsvs, control compressor airflow.
Vigvs are located at the front of the hp compressor and, together with the vsvs, control compressor airflow. A turbofan engine with an inlet air mass flow of 300 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 33-27 : 5 6 1 7
 5.
5. A turbofan engine with a bypass mass flow of 250 kg/s and a hp compressor mass ?
Question 33-28 : 5 6 1 4
A turbofan engine with an inlet air mass flow of 300 kg/s and a bypass mass ?
Question 33-29 : 5 6 1 2
 5.
5. A turbofan engine with a bypass mass flow of 888 kg/s and a hp compressor mass ?
Question 33-30 : 8 9 1 12 7
Bleeding air from the hp compressor of a turbofan whilst maintaining thrust ?
Question 33-31 : Egt and fuel flow hp compressor discharge pressure and n2 n2 and fuel flow egt and n1
 Egt and fuel flow.
Egt and fuel flow. A twin spool engine with an inlet air mass flow of 500 kg/s and a bypass mass ?
Question 33-32 : 1 2 0 3
 1.
1. Compressor stall is due to ?
Question 33-33 : An excessively high angle of attack of the rotor blades an excessively low angle of attack of the rotor blades an excessively high axial velocity an inadequate fuel flow
 An excessively high angle of attack of the rotor blades.
An excessively high angle of attack of the rotor blades. A turbofan engine with an inlet air mass flow of 1000 kg/s and a hp compressor ?
Question 33-34 : 8 01 9 01 1 12 10 01
 8.01.
8.01. Which of these statements about an reaction turbine are correct or incorrect .i ?
Question 33-35 : I is correct ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is incorrect.
I is correct, ii is incorrect. The electronic engine control of a fadec gas turbine engine checks ?
Question 33-36 : All input and output data active channel input and output data only input data only output data only
 All input and output data.
All input and output data. Jet engine total efficiency indicates the efficiency at which ?
Question 33-37 : Chemical power in the fuel is transformed into propulsive power t x v chemical power in the fuel is transformed into an increase of jet kinetic energy per second the increase of jet kinetic energy is transformed into propulsive energy potential energy in the jet is transformed into propulsive energy
 Chemical power in the fuel is transformed into propulsive power (t x v).
Chemical power in the fuel is transformed into propulsive power (t x v). Which statement is correct for a gas turbine engine with a constant speed ?
Question 33-38 : I is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. The fadec of a gas turbine engine consists of ?
Question 33-39 : An electronic engine control unit and its peripherals fuel metering actuators electrical wiring sensors an electronic engine control unit only all electronic engine control units installed on the aircraft an electronic engine control unit and the engine display units in the cockpit
 An electronic engine control unit and its peripherals (fuel metering, actuators, electrical wiring, sensors).
An electronic engine control unit and its peripherals (fuel metering, actuators, electrical wiring, sensors). The bypass ratio .i is the ratio of inlet air mass flow to exhaust air mass ?
Question 33-40 : I is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is correct.
I is incorrect, ii is correct. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1279 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 33
