At constant fuel flow if engine compressor air is bled off for engine anti ? [ Questionnaire LAPL ]
Question 32-1 : Will rise will be unchanged will fall may rise or fall depending on which stage of the compressor is used for the bleed and the rpm of the engine at the moment of selection
 Will rise.
Will rise. A hung abortive start of a gas turbine engine may be caused by ?
Question 32-2 : A too low pneumatic starter pressure compressor surging the starter cutting out early in the starting sequence before the engine has accelerated to the required rpm for ignition failure of the fuel to ignite in the starting sequence after the engine has been accelerated to the required rpm by the starter
 A too low pneumatic starter pressure.
A too low pneumatic starter pressure. A reverse thrust alert on the flight deck occurs when .1 the reverser doors ?
Question 32-3 : 1 3 2 4 1 4 2 3
 1, 3.
1, 3. In a single spool gas turbine engine the compressor rpm is ?
Question 32-4 : The same as turbine rpm independent of turbine rpm greater than turbine rpm less than turbine rpm
 The same as turbine rpm.
The same as turbine rpm. The primary reason for a limitation being imposed on the temperature of the gas ?
Question 32-5 : Ensure that the maximum acceptable temperature at the turbine blades is not exceeded ensure that the maximum acceptable temperature within the combustion chamber is not exceeded prevent damage to the combustion chamber from overheating prevent damage to the jet pipe from overheating
 Ensure that the maximum acceptable temperature at the turbine blades is not exceeded.
Ensure that the maximum acceptable temperature at the turbine blades is not exceeded. One of the purposes of the bleed valves fitted to axial flow compressors is to ?
Question 32-6 : Reduce the tendency to compressor stall enable an external air supply to spin up the compressor for engine starting spill compressor air should the engine overspeed thus controlling the speed control the acceleration time of the engine
 Reduce the tendency to compressor stall.
Reduce the tendency to compressor stall. A modern auxiliary power unit apu is designed to provide power for ground ?
Question 32-7 : Air conditioning and electrical services either air conditioning or electrical services but never both at the same time air conditioning and electrical services on the ground electrical and hydraulic back up services in the air air conditioning and thrust in the event of engine failure
 Air conditioning and electrical services.
Air conditioning and electrical services. The disadvantages of axial flow compressors compared to centrifugal flow ?
Question 32-8 : 1 and 3 1 and 2 2 and 4 2 and 3
 1 and 3.
1 and 3. A stage in an axial compressor ?
Question 32-9 : Consists of a rotor disc followed by a ring of stator blades has a compression ratio in the order of 2 1 consists of a ring of stator blades followed by a rotor disc has a compression ration in the order of 0 8
 Consists of a rotor disc followed by a ring of stator blades.
Consists of a rotor disc followed by a ring of stator blades. In a turbo jet the purpose of the turbine is to ?
Question 32-10 : Drive the compressor by using part of the energy from the exhaust gases clear the burnt gases the expansion of which provide the thrust compress the air in order to provide a better charge of the combustion chamber drive devices like pumps regulator generator
 Drive the compressor by using part of the energy from the exhaust gases.
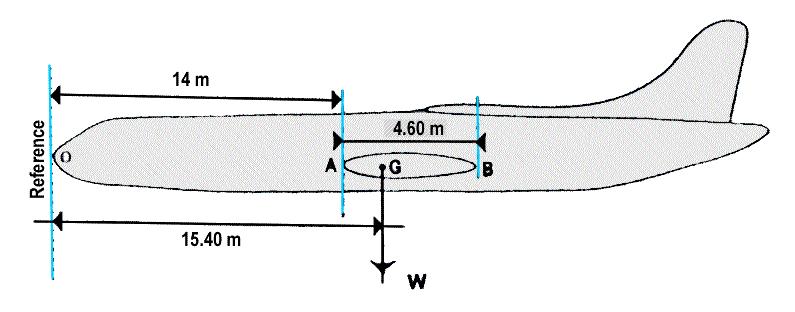
Drive the compressor by using part of the energy from the exhaust gases. The gas turbine illustrated is of the following type . 916 ?
Question 32-11 : Free turbine and centrifugal compressor free turbine and axial compressor single shaft turbine and centrifugal compressor single shaft turbine and axial compressor
 Free turbine and centrifugal compressor.
Free turbine and centrifugal compressor. The control of free turbine engines on turboprops is accomplished by . a ?
Question 32-12 : 1 5 and 6 1 3 and 5 3 4 and 6 2 4 and 5
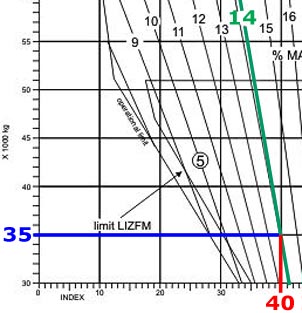
 1, 5 and 6.
1, 5 and 6. The static thrust of a turbo jet at the selection of full power .1 equals the ?
Question 32-13 : 1 and 3 4 only 1 and 2 2 and 3
The purpose of a compressor bleed valve is to prevent surging ?
Question 32-14 : At low compressor rpm generated by foreign object ingestion of the first compressor stages with altitude
 At low compressor rpm.
At low compressor rpm. Severe compressor stall can be indicated amongst others by ?
Question 32-15 : A rise in turbine gas temperature tgt and a change in vibration level an increase in engine pressure ratio epr and a decrease in tgt and fuel flow a decrease in tgt and a change in vibration level a rise in tgt and an increase in fuel flow
In a gas turbine engine compressor blades which are not rigidly fixed in ?
Question 32-16 : The resultant of aerodynamic and centrifugal forces thermal expansion blade creep oil pressure
 The resultant of aerodynamic and centrifugal forces.
The resultant of aerodynamic and centrifugal forces. The characteristics of a centrifugal compressor are .1 a high pressure ratio ?
Question 32-17 : 1 and 2 1 and 4 2 and 3 3 and 4
 1 and 2.
1 and 2. The diffuser in a centrifugal compressor is a device in which the ?
Question 32-18 : Pressure rises and velocity falls pressure rises at a constant velocity velocity pressure and temperature rise velocity rises and pressure falls
 Pressure rises and velocity falls.
Pressure rises and velocity falls. The thrust reversers of jet engines may use clamshell doors in order to ?
Question 32-19 : Change the direction of the exhaust gas stream stop the flow of the exhaust gas stream reduce the pressure of the exhaust gas stream by diffusing it to atmosphere absorb any surge in engine thrust
 Change the direction of the exhaust gas stream.
Change the direction of the exhaust gas stream. By pass turbine engines are mainly used in commercial aviation because ?
Question 32-20 : At high subsonic airspeeds they have a better propulsive efficiency than propeller or straight jet engines they produce less noise they are lighter than straight jet engines twin spool or triple spool jet engines require a high by pass ratio
 At high subsonic airspeeds they have a better propulsive efficiency than propeller or straight jet engines.
At high subsonic airspeeds they have a better propulsive efficiency than propeller or straight jet engines. Engine auxiliary gearboxes ?
Question 32-21 : Provide the drives for a wide variety of services and may even provide for the support of the engine in the airframe always provide drives for fuel pumps oil pumps speed sensing and torque sensing never provide a torque sensing facility are driven by the output from the free power turbine
 Provide the drives for a wide variety of services and may even provide for the support of the engine in the airframe.
Provide the drives for a wide variety of services and may even provide for the support of the engine in the airframe. The greatest risk created by a free turbine overspeed is ?
Question 32-22 : Bursting of the free turbine disk a surge of the gas generator creep of the turbine blades an engine overtemperature
 Bursting of the free turbine disk.
Bursting of the free turbine disk. The thermal efficiency of a gas turbine engine will increase with a ?
Question 32-23 : Decrease in ambient air temperature increase in ambient air temperature increase in humidity decrease in ambient air pressure
 Decrease in ambient air temperature.
Decrease in ambient air temperature. Creep of turbine blades is caused by ?
Question 32-24 : High blade temperature whilst under centrifugal loading prolonged idling at low rpm bending stresses set up by gas pressure static imbalance of the blades
 High blade temperature whilst under centrifugal loading.
High blade temperature whilst under centrifugal loading. By pass ratio in a turbine engine is the ratio of the ?
Question 32-25 : Cold air mass flow to the hot air mass flow speed of the combusted air to the speed of the by pass air intake air pressure to the turbine delivery air pressure tertiary air mass flow to the primary air mass flow
 Cold air mass flow to the hot air mass flow.
Cold air mass flow to the hot air mass flow. On landing and prior to shut down a gas turbine engine should be run at 'ground ?
Question 32-26 : The core temperature to diminish the turbine blade temperature to reduce only the engine to be compressor washed cool oil flushing of bearings particularly those in the turbines
 The core temperature to diminish.
The core temperature to diminish. Both gas turbine and piston engines utilise a cycle of induction compression ?
Question 32-27 : I continuous ii constant pressure i continuous ii constant volume i intermittent ii constant pressure i intermittent ii constant volume
 (i) continuous (ii) constant pressure
(i) continuous (ii) constant pressure For a subsonic airflow in a divergent duct the ?
Question 32-28 : Pressure increases velocity decreases and temperature increases pressure decreases velocity increases and temperature increases pressure increases velocity decreases and temperature decreases pressure decreases velocity increases and temperature decreases
 Pressure increases, velocity decreases and temperature increases.
Pressure increases, velocity decreases and temperature increases. An engine pressure ratio epr can be defined as the ratio of ?
Question 32-29 : Jet pipe total pressure to compressor inlet total pressure jet pipe total pressure to combustion chamber pressure combustion chamber pressure to compressor inlet total pressure compressor outlet pressure to compressor inlet total pressure
 Jet pipe total pressure to compressor inlet total pressure.
Jet pipe total pressure to compressor inlet total pressure. For a fan jet engine the by pass ratio is the ?
Question 32-30 : Cold air mass flow divided by the hot air mass flow hot air mass flow divided by the cold air mass flow hot air mass flow divided by the fuel flow fuel flow divided by hot air mass flow
 Cold air mass flow divided by the hot air mass flow.
Cold air mass flow divided by the hot air mass flow. The by pass air in a by pass type gas turbine engine promotes lower specific ?
Question 32-31 : Decrease in exhaust gas flow average velocity and higher propulsive efficiency decrease in combustion chamber temperature and higher thermal efficiency increase in exhaust gas flow average velocity thus increasing engine pressure ratio increase in the mean jet temperature and increase in thermal efficiency
 Decrease in exhaust gas flow average velocity and higher propulsive efficiency.
Decrease in exhaust gas flow average velocity and higher propulsive efficiency. In the airflow through a single spool axial flow turbo jet engine the axial ?
Question 32-32 : On exit from the propelling nozzle as it leaves the compressor within the combustion chamber as it leaves the turbine
 On exit from the propelling nozzle.
On exit from the propelling nozzle. In a jet engine the propelling nozzle ?
Question 32-33 : Must be designed to obtain the correct balance of pressure and velocity to prevent flow separation reduces noise directs the hot gas stream onto the turbine at the optimum angle of attack decreases the velocity and increases the pressure in the jet pipe to provide greater thrust
 Must be designed to obtain the correct balance of pressure and velocity to prevent flow separation.
Must be designed to obtain the correct balance of pressure and velocity to prevent flow separation. In a multi spool turbofan engine the fan is driven by ?
Question 32-34 : The rearmost turbine the intermediate turbine the foremost turbine all three turbines since they are on a common shaft with the compressor
 The rearmost turbine.
The rearmost turbine. After air has passed through the compressor of a gas turbine engine the ?
Question 32-35 : Temperature will be higher than the inlet temperature velocity will be higher than the inlet velocity pressure will be the same as the inlet pressure velocity will be the same as the inlet velocity
 Temperature will be higher than the inlet temperature.
Temperature will be higher than the inlet temperature. To achieve reverse thrust on a turbine engine with a high by pass ratio ?
Question 32-36 : The fan flow is deflected the fan is stopped the direction of rotation of the fan is reversed the flow of hot stream air is reversed
 The fan flow is deflected.
The fan flow is deflected. An aircraft flying in conditions of continuous heavy rain and high ambient ?
Question 32-37 : Engine igniters airframe de icing only engine intake anti icing only both engine intake anti icing and airframe de icing
 Engine igniters.
Engine igniters. The engine type represented in the drawing is a . 951 ?
Question 32-38 : Twin spool turbofan single spool turbofan twin spool turbojet triple spool turbofan
 Twin-spool turbofan.
Twin-spool turbofan. When the combustion gases pass through a turbine the ?
Question 32-39 : Pressure drops pressure rises axial velocity decreases temperature increases
 Pressure drops.
Pressure drops. Regarding a jet engine .i the maximum thrust decreases as the pressure altitude ?
Question 32-40 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1239 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 32
