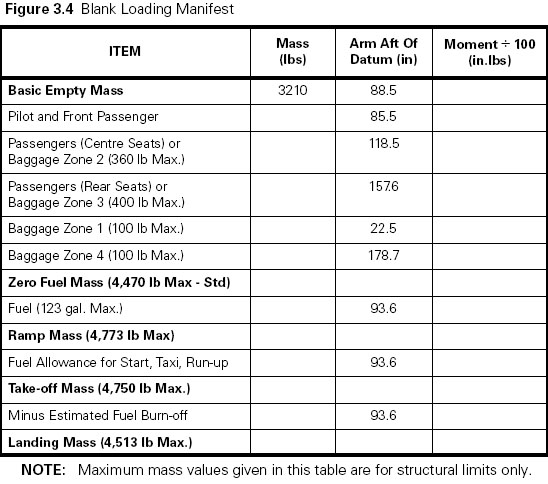
Assume an initial condition at a high cruise altitude with a constant speed ? [ Students VFR ]
Question 30-1 : The manifold absolute pressure map value may exceed the maximum allowed value the power of the engine will decrease the blade angle may reach the full fine limit the manifold absolute pressure map value will stay constant
 The manifold absolute pressure (map) value may exceed the maximum allowed value.
The manifold absolute pressure (map) value may exceed the maximum allowed value. If the engine with a fixed pitch propeller is detonating during climb out after ?
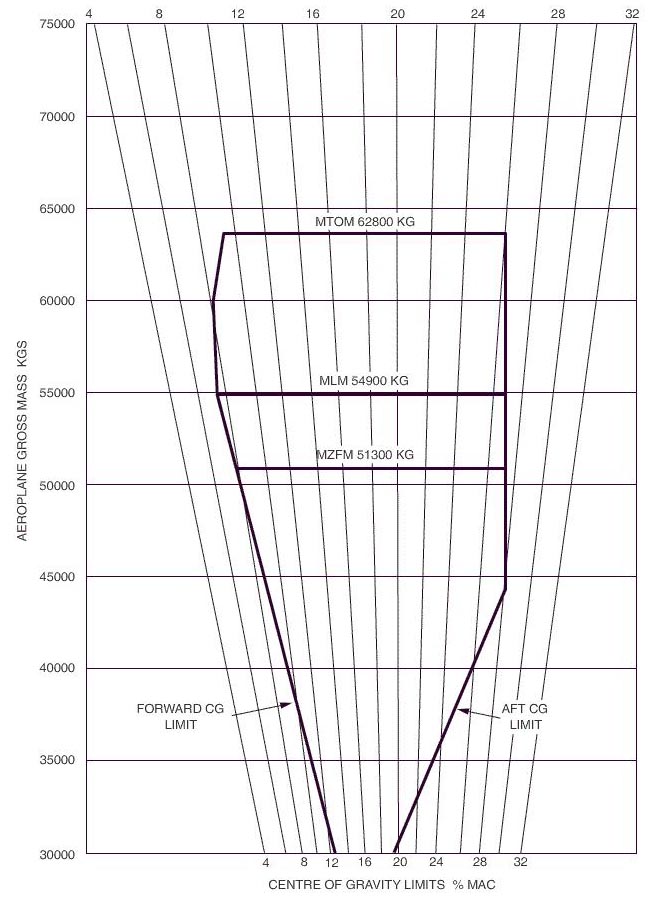
Question 30-2 : Reduce the throttle increase the rate of climb lean the mixture apply carburettor heat
 Reduce the throttle.
Reduce the throttle. If when the magneto selector switch is set to the off position a piston engine ?
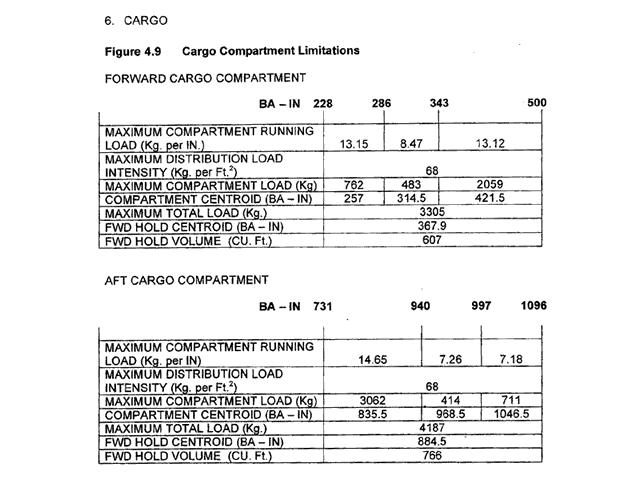
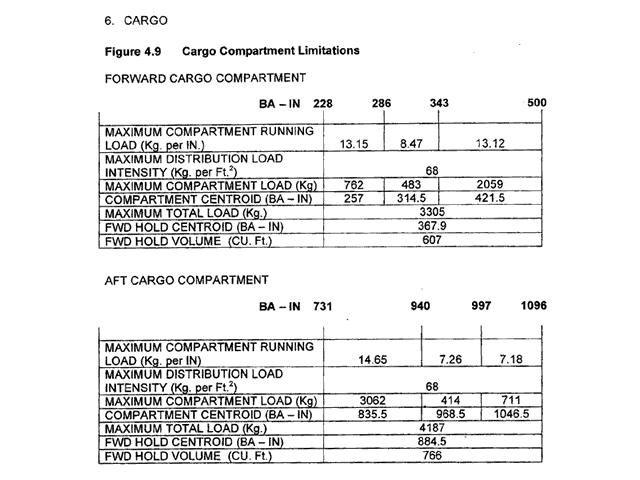
Question 30-3 : On a magneto the grounding wire is broken there is a carbon deposit on the spark plugs electrodes there are local hot points in the engine probably due to overheating of the cylinder heads a wire from the magneto is in contact with a metallic part of the engine
 On a magneto, the grounding wire is broken.
On a magneto, the grounding wire is broken. Ignition occurs in each cylinder of a four stroke engine tdc = top dead centre ?
Question 30-4 : Before tdc at each second crankshaft revolution before tdc at each crankshaft revolution behind tdc at each crankshaft revolution behind tdc at each second crankshaft revolution
 Before tdc at each second crankshaft revolution.
Before tdc at each second crankshaft revolution. The lubricating system of an air cooled piston engine is used to ?
Question 30-5 : Reduce internal friction and provide cooling keep the engine warm to operate the fuel control unit operate constant speed propellers
 Reduce internal friction and provide cooling.
Reduce internal friction and provide cooling. The first indication of carburettor icing in aeroplanes equipped with constant ?
Question 30-6 : Decrease in manifold pressure decrease in rpm rough running engine followed by an increase in manifold pressure rough running engine followed by loss in rpm
 Decrease in manifold pressure.
Decrease in manifold pressure. The mixture control for a carburettor achieves its control by ?
Question 30-7 : Varying the fuel supply to the main discharge tube moves the butterfly valve through a separate linkage to the main throttle control altering the depression on the main discharge tube varying the air supply to the main discharge tube
 Varying the fuel supply to the main discharge tube.
Varying the fuel supply to the main discharge tube. The mechanism to change the propeller blade angle of a small piston engine ?
Question 30-8 : Hydraulically by engine oil hydraulically by hydraulic fluid manually by the pilot by aerodynamic forces
 Hydraulically by engine oil.
Hydraulically by engine oil. The use of too low an octane fuel may cause ?
Question 30-9 : Detonation higher manifold pressure a cooling effect on cylinders vapour locking
 Detonation.
Detonation. Which one of the following factors would be most likely to increase the ?
Question 30-10 : Using too lean a fuel/air mixture the use of a fuel with a high octane rating as compared to the use of one with a low octane rating using an engine with a low compression ratio slightly retarding the ignition timing
 Using too lean a fuel/air mixture.
Using too lean a fuel/air mixture. Vents in oil tanks are primarily to ?
Question 30-11 : Prevent excessive pressure from building up in tank prevent overthrow allow for expansion of hot oil eliminate foaming
 Prevent excessive pressure from building up in tank.
Prevent excessive pressure from building up in tank. The cylinder head and oil temperatures may exceed their normal operating ranges ?
Question 30-12 : A lower octane rating than specified for the engine is used a higher octane rating than specified for the engine is used the engine is operated at a higher than normal oil pressure the engine is operated at a too rich mixture
 A lower octane rating than specified for the engine is used.
A lower octane rating than specified for the engine is used. When starting the engine or when the engine is running at idle rpm on the ?
Question 30-13 : Rich to make starting possible and to cool the engine sufficiently when idling rich because the choke valve is closed rich because carburettor heat is switched on weak to prevent the engine consuming too much fuel
 Rich, to make starting possible and to cool the engine sufficiently when idling.
Rich, to make starting possible and to cool the engine sufficiently when idling. The cylinder head and oil temperature gauges are to exceed the normal operating ?
Question 30-14 : Uses fuel that has a rating lower than specified for the engine operates with the mixture control set too rich uses fuel that has a rating higher than specified for the engine operating with higher than normal oil pressure
The lubricating system of an aircraft engine is used to ?
Question 30-15 : Aid in dissipation of heat keep the engine warm operate ground adjustable propellers prevent inter crystalline corrosion
 Aid in dissipation of heat
Aid in dissipation of heat On design purpose the relationship between the fuel octane rating and the ?
Question 30-16 : The higher the octane rating is the higher the maximum compression ratio is the lower the octane rating is the higher the maximum compression ratio is the higher the octane rating is the lower the maximum compression ratio is the maximum compression ratio is independent of the octane rating
A magnetic plug in an engine oil system can be used to ?
Question 30-17 : Collect ferrous particles collect carbon found in the oil collect static electricity prevent metallic particles from entering the oil system
 Collect ferrous particles.
Collect ferrous particles. Once the engine has started ignition systems of piston engines are ?
Question 30-18 : Independent of the electrical system of the aircraft dependent on the battery dependent on the dc generator dependent on the ac generator
 Independent of the electrical system of the aircraft.
Independent of the electrical system of the aircraft. The blade angle of a propeller is the angle between the ?
Question 30-19 : Reference chord line and the propeller plane of rotation reference chord line and the relative airflow reference chord line and the propeller axis of rotation plane of rotation and the relative airflow
 Reference chord line and the propeller plane of rotation.
Reference chord line and the propeller plane of rotation. In very cold weather a slightly higher than normal engine oil pressure during ?
Question 30-20 : Is acceptable if it decreases after startup is unacceptable and requires the engine to be shut down is unacceptable but does not require the engine to be shut down requires an oil change
 Is acceptable, if it decreases after startup.
Is acceptable, if it decreases after startup. Assuming the same swept volume and no turbo charger diesel engines compared to ?
Question 30-21 : Produce less maximum power output operate at higher exhaust gas temperatures show a higher fuel flow at the same power output produce a higher maximum power output
 Produce less maximum power output.
Produce less maximum power output. The operating principle of magnetos in a piston engine ignition system consists ?
Question 30-22 : Breaking the primary circuit in order to induce a low amperage high voltage current which is distributed to the spark plugs obtaining a high amperage low voltage current in order to generate the spark accumulating in a capacitor a low voltage current from the battery and inducing it as a high voltage current at the moment the spark is generated creating a brief high intensity magnetic field that will be sent through the distributor at the appropriate time
 Breaking the primary circuit in order to induce a low amperage, high voltage current, which is distributed to the spark plugs.
Breaking the primary circuit in order to induce a low amperage, high voltage current, which is distributed to the spark plugs. In a four stroke piston engine the only 'driving' stroke is ?
Question 30-23 : Power induction compression exhaust
 Power.
Power. Excessive priming of a piston engine should be avoided because .1 it drains the ?
Question 30-24 : 2 3 4 1 2 4 1 3 4 1 2 3
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. Which one of the following factors would be most likely to increase the ?
Question 30-25 : High cylinder head temperature the use of a fuel with a high octane rating as compared to the use of one with a low octane rating using an engine with a low compression ratio slightly retarding the ignition timing
 High cylinder head temperature.
High cylinder head temperature. The octane rating of a fuel characterises the ?
Question 30-26 : Resistance to detonation fuel volatility quantity of heat generated by its combustion fuel electrical conductivity
 Resistance to detonation.
Resistance to detonation. Both gas turbine and piston engines use a cycle made up of induction ?
Question 30-27 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. When tas increases the blade angle of a constant speed propeller will rpm and ?
Question 30-28 : Increase decrease first decrease and after a short time increase to its previous value remain constant
 Increase.
Increase. With an aircraft fitted with a fixed pitch propeller during flight at normal ?
Question 30-29 : Loss of approximately 100 rpm an additional load on the other magneto excessive vibration the engine to overheat
Both gas turbine and piston engines use a cycle made up of induction ?
Question 30-30 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. When excessively leaning the mixture for a better fuel economy but still on the ?
Question 30-31 : Cylinder head and exhaust gas temperature engine rpm oil temperature manifold pressure
 Cylinder head and exhaust gas temperature.
Cylinder head and exhaust gas temperature. Both gas turbine and piston engines use a cycle made up of induction ?
Question 30-32 : I is incorrect ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is incorrect, ii is correct.
I is incorrect, ii is correct. Given the following statements about diesel engines .1 power is set by the ?
Question 30-33 : 2 3 4 1 2 3 1 3 5 2 4 5
 2, 3, 4.
2, 3, 4. Diesel engines compared to petrol engines have ?
Question 30-34 : A higher compression ratio a lower compression ratio the same compression ratio a variable compression ratio
 A higher compression ratio.
A higher compression ratio. The power output of a diesel engine without a turbo charger is regulated by ?
Question 30-35 : Fuel flow only airflow only fuel flow and airflow mixture
 Fuel flow only .
Fuel flow only . The ignition system of a running piston engine receives electrical energy from ?
Question 30-36 : Rotating permanent magnets batteries generators capacitors
 Rotating permanent magnets.
Rotating permanent magnets. The purpose of magnetic chip detectors is to ?
Question 30-37 : Warn of impending failure increase lubricating oil adhesion to main surfaces remove large items of debris from the system perform the function of a micron filter
 Warn of impending failure.
Warn of impending failure. Apart from flight into known icing conditions the intake system of a diesel ?
Question 30-38 : Is never heated because a diesel engine is a injection engine needs to be heated to prevent ice on the air filter needs to be heated at low power settings due to vaporisation heat is never heated because diesel engines operate at very high temperatures
 Is never heated because a diesel engine is a injection engine.
Is never heated because a diesel engine is a injection engine. The thermal efficiency of a diesel engine is higher than that of a petrol ?
Question 30-39 : The compression ratio is much higher the calorific value of the fuel is higher the egt is higher the air mass flow through the engine is higher
 The compression ratio is much higher.
The compression ratio is much higher. Given the following statements about diesel engines .1 power is regulated by ?
Question 30-40 : 2 3 5 1 2 3 1 3 5 2 4 5
 2, 3, 5.
2, 3, 5. Explore our services.
Browse these pages to learn more about our services dedicated to exam and easa certification exam. Discover our tool, our team, our answers to your frequently asked questions and the advantages of our solution adapted to your learning needs.
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
1159 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 30
