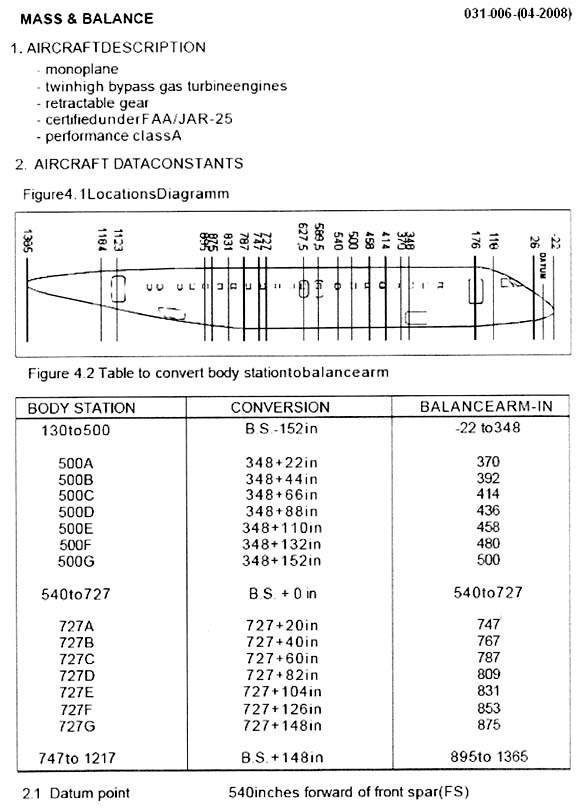
Whilst in level cruising flight an aeroplane with a pressurised cabin ? [ Support Airworthiness ]
Question 23-1 : The differential pressure will rise to its maximum value thus causing the safety relief valves to open a descent must be initiated to prevent the oxygen masks dropping when the cabin altitude reaches 14000 ft the aircraft has to climb to a higher flight level in order to reduce the cabin altitude to its initial value the crew has to intermittently cut off the incoming air flow in order to maintain a zero cabin altitude
 The differential pressure will rise to its maximum value, thus causing the safety relief valves to open.
The differential pressure will rise to its maximum value, thus causing the safety relief valves to open. At reference in a pressurized aircraft whose cabin altitude is 8000 ft a crack ?
Question 23-2 : Fl 230 fl 180 fl 280 fl 340
 Fl 230.
Fl 230. The pressurisation system of an aeroplane ?
Question 23-3 : Has the capability to maintain a cabin pressure higher than ambient pressure only pressurises the flight deck area will maintain a zero cabin differential pressure at all altitudes will maintain a sea level cabin altitude at all altitudes
 Has the capability to maintain a cabin pressure higher than ambient pressure.
Has the capability to maintain a cabin pressure higher than ambient pressure. In a turbo compressor air conditioning system bootstrap system the supply of ?
Question 23-4 : Compressed passed through a heat exchanger and then across an expansion turbine passed across an expansion turbine compressed and then passed through a heat exchanger passed across an expansion turbine then directly to the heat exchanger compressed then passed across an expansion turbine and finally across a heat exchanger
 Compressed, passed through a heat exchanger, and then across an expansion turbine.
Compressed, passed through a heat exchanger, and then across an expansion turbine. The purpose of cabin air flow control valves in a pressurization system is to ?
Question 23-5 : Maintain a constant and sufficient mass air flow to ventilate the cabin and minimise cabin pressure surges regulate cabin pressure to the selected altitude discharge cabin air to atmosphere if cabin pressure rises above the selected altitude regulate cabin pressure at the maximum cabin pressure differential
 Maintain a constant and sufficient mass air flow to ventilate the cabin and minimise cabin pressure surges.
Maintain a constant and sufficient mass air flow to ventilate the cabin and minimise cabin pressure surges. If the pressure in the cabin tends to become lower than the outside ambient air ?
Question 23-6 : Negative pressure relief valve will open negative pressure relief valve will close air cycle machine will stop outflow valve open completely
 Negative pressure relief valve will open.
Negative pressure relief valve will open. Cabin air for cs 25 aeroplanes is usually taken from ?
Question 23-7 : The high pressure compressor and from the low pressure compressor if necessary the low pressure compressor the second fan stage the high pressure compressor
 The high pressure compressor and from the low pressure compressor if necessary.
The high pressure compressor and from the low pressure compressor if necessary. Under normal flight conditions cabin pressure is controlled by ?
Question 23-8 : Regulating the discharge of air through the outflow valve s pressurisation duct relief valve s engine rpm inward relief valve s
 Regulating the discharge of air through the outflow valve(s).
Regulating the discharge of air through the outflow valve(s). Pneumatic mechanical ice protection systems are mainly used for ?
Question 23-9 : Wings pitot tubes propellers windscreens
 Wings.
Wings. With regard to pneumatic mechanical devices that afford ice protection the only ?
Question 23-10 : They can only be used as de icing devices they can only be used as anti icing devices they are used extensively on modern aircraft as they are inexpensive and easy to maintain they can be used as both de icing and anti icing devices
 They can only be used as de-icing devices.
They can only be used as de-icing devices. Concerning electrically powered ice protection devices the only true statement ?
Question 23-11 : On modern aircraft electrically powered thermal devices are used to prevent icing on small surfaces pitot static windshield on modern aircraft electrically powered thermal devices are used as de icing devices for pitot tubes static ports and windshield on modern aircraft electrically powered thermal devices are very efficient therefore they only need little energy on modern aircraft electrical power supply being available in excess this system is very often used for large surfaces de icing
 On modern aircraft, electrically powered thermal devices are used to prevent icing on small surfaces (pitot-static, windshield...).
On modern aircraft, electrically powered thermal devices are used to prevent icing on small surfaces (pitot-static, windshield...). The elements specifically protected against icing on transport aircraft are .1 ?
Question 23-12 : 1 2 4 and 5 1 4 5 and 7 1 2 5 and 6 1 2 3 and 8
 1, 2, 4 and 5.
1, 2, 4 and 5. The wing anti ice system has to protect ?
Question 23-13 : The leading edge or the slats either partially or completely the whole upper wing surface and the flaps the whole leading edge except the slats because they cannot be de iced when extended the whole leading edge and the whole under wing surface
 The leading edge or the slats, either partially or completely.
The leading edge or the slats, either partially or completely. In jet aeroplanes the 'thermal anti ice system' is primarily supplied by ?
Question 23-14 : Bleed air from the engines turbo compressors ram air heated via a heat exchanger the apu
 Bleed air from the engines.
Bleed air from the engines. The de icing system which is mostly used for the wings of modern turboprop ?
Question 23-15 : Pneumatic boots fluid de icing thermal anti icing electrical heating
 Pneumatic boots.
Pneumatic boots. Concerning the sequential pneumatic impulses used in certain leading edge de ?
Question 23-16 : 2 and 3 1 and 3 1 and 4 2 and 4
 2 and 3
2 and 3 Generally for large aeroplanes electrical heating for ice protection is used on ?
Question 23-17 : Pitot tubes elevator leading edges slat leading edges fin leading edges
 Pitot tubes.
Pitot tubes. The wing ice protection system currently used for most large jet transport ?
Question 23-18 : Hot air system electrical de icing system pneumatic system with inflatable boots liquid de icing system
 Hot air system.
Hot air system. Pneumatic mechanical devices that provide ice protection ?
Question 23-19 : Are usually used as de icing devices require large quantities of bleed air can only be used as anti icing devices are usually used on aeroplanes equipped with turbo fan engines
 Are usually used as de-icing devices.
Are usually used as de-icing devices. The anti icing method for the wings of large jet transport aeroplanes most ?
Question 23-20 : Thermal use of hot air chemical glycol based liquid electrical electrical resistance mechanical pneumatic boots
 Thermal (use of hot air).
Thermal (use of hot air). Windshield heating of a transport aeroplane is ?
Question 23-21 : Essential to improve the strength of the cockpit windows not affecting the strength of a cockpit windows only used when hot air demisting is insufficient used only at low altitudes where there is a risk of ice formation
 Essential to improve the strength of the cockpit windows.
Essential to improve the strength of the cockpit windows. The heat for the anti icing system of a turbofan engine intake is provided by ?
Question 23-22 : Bleed air from the hp compressor bleed air from the lp compressor the electrical system of the aircraft a dedicated generator on the gearbox of that engine
 Bleed air from the hp compressor.
Bleed air from the hp compressor. The use of a hot air wing anti icing system ?
Question 23-23 : Does not affect aerodynamic performance of the wing and causes a reduction in maximum thrust does not affect aerodynamic performance of the wing and causes no reduction in maximum thrust reduces aerodynamic performance of the wing and causes no reduction in maximum thrust reduces aerodynamic performance of the wing and causes a reduction in maximum thrust
 Does not affect aerodynamic performance of the wing and causes a reduction in maximum thrust.
Does not affect aerodynamic performance of the wing and causes a reduction in maximum thrust. Ice formation on turbofan engine intakes is usually ?
Question 23-24 : Prevented by using compressor bleed air removed by using pneumatic boots prevented by using turbine bleed air removed by using electrical heating
 Prevented by using compressor bleed air.
Prevented by using compressor bleed air. The ice protection for propellers of modern turboprop aeroplanes works ?
Question 23-25 : Electrically pneumatically with hot air with anti icing fluid
 Electrically.
Electrically. The heating facility for the windshield of an aircraft is ?
Question 23-26 : Used on a continual basis as it reduces the thermal gradients which adversely affect the useful life of the components harmful to the integrity of the windows in the event of a bird strike only used when hot air demisting is insufficient used only at low altitudes where there is a risk of ice formation
 Used on a continual basis as it reduces the thermal gradients which adversely affect the useful life of the components.
Used on a continual basis as it reduces the thermal gradients which adversely affect the useful life of the components. The wing ice protection system currently used for most large turboprop ?
Question 23-27 : A pneumatic system with inflatable boots an electrical de icing system a hot air system a liquid de icing system
 A pneumatic system with inflatable boots.
A pneumatic system with inflatable boots. Electrically powered ice protection devices on aircraft are ?
Question 23-28 : Used as anti icing devices for pitot tubes static ports and windshield used for large surfaces only used primarily because they are very efficient used as de icing devices for pitot tubes static ports and windshield
 Used as anti-icing devices for pitot-tubes, static ports and windshield.
Used as anti-icing devices for pitot-tubes, static ports and windshield. On most transport aircraft the low pressure pumps of the fuel system are ?
Question 23-29 : Centrifugal pumps driven by an electric motor removable only after the associated tank has been emptied mechanically driven by the engine's accessory gearbox electro mechanical wobble pumps with self regulated pressure
 Centrifugal pumps, driven by an electric motor.
Centrifugal pumps, driven by an electric motor. The fuel supply system on a jet engine includes a fuel heating device upstream ?
Question 23-30 : Prevent at low fuel temperature the risk of ice formation from water contained in the fuel maintain and improve fuel heating power ease low pressure pumps work by increasing fuel fluidity prevent fuel from freezing in fuel pipes due to low temperatures at high altitude
 Prevent, at low fuel temperature, the risk of ice formation from water contained in the fuel.
Prevent, at low fuel temperature, the risk of ice formation from water contained in the fuel. On most transport jet aircraft the low pressure pumps of the fuel system are ?
Question 23-31 : 115 v ac 28 v ac 28 v dc 115 v dc
The pressure usually produced by the booster pumps of the fuel supply system of ?
Question 23-32 : 20 to 50 psi 5 to 10 psi 3000 to 5000 psi 300 to 500 psi
 20 to 50 psi.
20 to 50 psi. In a gas turbine engine lubrication system the oil to fuel heat exchanger ?
Question 23-33 : Oil cooling through thermal exchange with the fuel fuel cooling to prevent vapour locking interrupting the fuel supply to the nozzles automatic controlled fuel heating by engine oil to prevent icing in the fuel filter fuel heating as required whenever fuel filter clogging is detected
 Oil cooling through thermal exchange with the fuel.
Oil cooling through thermal exchange with the fuel. The fuel cross feed system ?
Question 23-34 : Allows feeding of any engine from any fuel tank is only used to feed an engine from the tank of the opposite wing is only used on the ground for fuel transfer from one tank to another is only used in flight for fuel transfer from one tank to another
 Allows feeding of any engine from any fuel tank.
Allows feeding of any engine from any fuel tank. The purpose of baffles in an aeroplane's integral fuel tank is to ?
Question 23-35 : Restrict the fuel movements in the tank prevent overpressure in the tank prevent the fuel from flowing in the vent lines prevent mixture of the fuel and hydraulic fluid
 Restrict the fuel movements in the tank.
Restrict the fuel movements in the tank. On a transport type aircraft the fuel tank system is vented through ?
Question 23-36 : Ram air scoops on the underside of the wing a pressure regulator in the wing tip bleed air from the engines the return lines of the fuel pumps
 Ram air scoops on the underside of the wing.
Ram air scoops on the underside of the wing. The types of fuel tanks used on most modern transport aircraft are ?
Question 23-37 : Integral tanks cell tanks combined fuel tanks fixed built in tanks
 Integral tanks.
Integral tanks. The pressurization of fuel tanks is maintained by ?
Question 23-38 : The fuel vent system the fuel tank drains the fuel top off unit the fuel dump system
 The fuel vent system.
The fuel vent system. On a jet aircraft fuel heaters are ?
Question 23-39 : Located on the engines installed in each tank installed only in the centre tank not necessary at all
 Located on the engines.
Located on the engines. The automatic fuelling shut off valve ?
Question 23-40 : Stops fuelling as soon as a certain fuel level is reached inside the tank cuts off the fuel in case of engine fire stops fuelling as soon as the fuel spills into the vent line stops fuelling as soon as a certain pressure is reached
 Stops fuelling as soon as a certain fuel level is reached inside the tank.
Stops fuelling as soon as a certain fuel level is reached inside the tank. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
879 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 23
