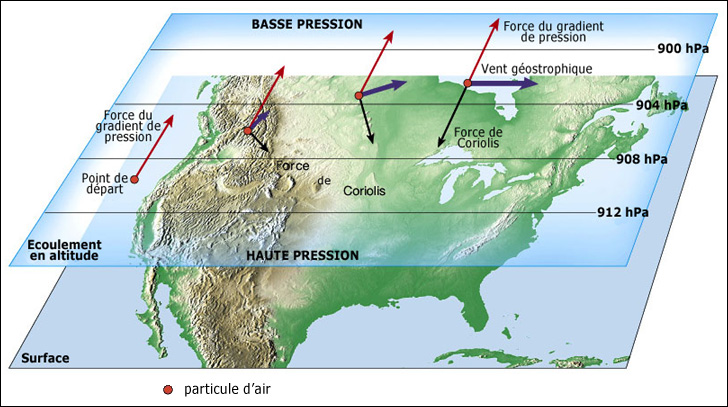
Which of these statements about the strength of wing tip vortices are correct ? [ Certification weather ]
Question 223-1 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Which of these statements about the effect of wing sweep on centre of pressure ?
Question 223-2 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Considering subsonic incompressible airflow through a venturi which statement ?
Question 223-3 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which statement about an aeroplane leaving ground effect at constant angle of ?
Question 223-4 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which statement about an aeroplane entering ground effect is correct .i the ?
Question 223-5 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which of these statements about induced drag are correct or incorrect .i ?
Question 223-6 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. The parameters that can be read from the aeroplane parabolic polar curve are the ?
Question 223-7 : Minimum glide angle and the parasite drag coefficient minimum rate of descent and the induced drag induced drag and the parasite drag aspect ratio of the wing and the induced drag coefficient
 Minimum glide angle and the parasite drag coefficient.
Minimum glide angle and the parasite drag coefficient. For most jet transport aeroplanes slat extension has ?
Question 223-8 : A greater effect on stall speed than flap extension the same significant effect on stall speed as flap extension a minor effect on stall speed whereas flap extension has a significant effect the same minor effect on stall speed as flap extension
 A greater effect on stall speed than flap extension.
A greater effect on stall speed than flap extension. One advantage of mounting the horizontal tailplane on top of the vertical fin is ?
Question 223-9 : To improve the aerodynamic efficiency of the vertical fin to decrease the susceptibility to deep stall that it does not require a de icing system to decrease fuel consumption by creating a tail heavy situation
 To improve the aerodynamic efficiency of the vertical fin.
To improve the aerodynamic efficiency of the vertical fin. Which drag components make up parasite drag .1 pressure drag.2 friction ?
Question 223-10 : 1 2 4 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 1 3 4
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. The transition point is where the boundary layer changes from ?
Question 223-11 : Laminar into turbulent turbulent into laminar attached flow into separated flow separated flow into attached flow
 Laminar into turbulent.
Laminar into turbulent. As angle of attack is increased on a conventional low speed aerofoil at low ?
Question 223-12 : Upper surface near the trailing edge upper surface near the leading edge lower surface near the trailing edge lower surface near the leading edge
 Upper surface near the trailing edge.
Upper surface near the trailing edge. Assuming no flow separation when speed is decreased in straight and level ?
Question 223-13 : 1 moves forward and 2 remains constant 1 moves forward and 2 decreases 1 moves aft and 2 remains constant 1 moves aft and 2 increases
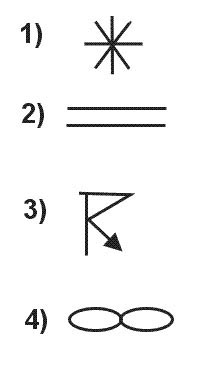 1 moves forward and 2 remains constant.
1 moves forward and 2 remains constant. Given the following characteristic points on a jet engine aeroplane's polar ?
Question 223-14 : 2 5 3 4 1 1 2 4 3 5 3 2 5 1 4 4 5 2 3 1
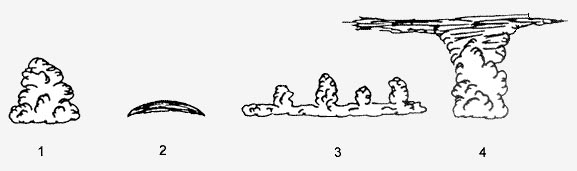 2, 5, 3, 4, 1.
2, 5, 3, 4, 1. Assuming standard atmospheric conditions in order to generate the same amount ?
Question 223-15 : A higher tas for any given angle of attack a lower tas and a lower angle of attack a lower tas for any given angle of attack the same tas regardless of angle of attack
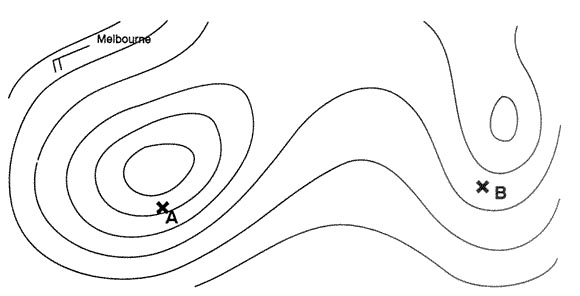 A higher tas for any given angle of attack.
A higher tas for any given angle of attack. In comparison to a conventional aerofoil section typical shape characteristics ?
Question 223-16 : A larger nose radius flatter upper surface and negative as well as positive camber a sharper pointed nose negative camber and a flatter upper surface a larger nose radius flatter lower surface and negative as well as positive camber a sharper pointed nose flatter lower surface and positive camber at the rear of the aerofoil section
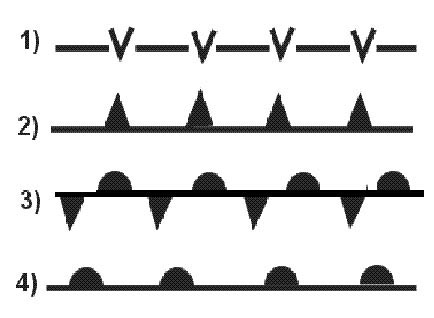 A larger nose radius, flatter upper surface and negative as well as positive camber.
A larger nose radius, flatter upper surface and negative as well as positive camber. Induced drag is the result of ?
Question 223-17 : Downwash generated by tip vortices aerodynamic interaction between aeroplane parts boundary layer separation on the aft portion of the wing propeller slipstream over the wing
 Downwash generated by tip vortices.
Downwash generated by tip vortices. Given an aeroplane in steady straight and level flight at low speed and ?
Question 223-18 : Forward cg and idle thrust forward cg and take off thrust aft cg and take off thrust aft cg and idle thrust
 Forward cg and idle thrust.
Forward cg and idle thrust. The main function of a trailing edge flap is to ?
Question 223-19 : Increase the maximum lift coefficient of the wing alter the position of the centre of gravity trim the aeroplane longitudinally increase the angle of attack at which a wing will stall
 Increase the maximum lift coefficient of the wing.
Increase the maximum lift coefficient of the wing. Stall speed ias varies with ?
Question 223-20 : Weight altitude below approximately 10000 ft temperature density
 Weight.
Weight. What will happen if a large transport aeroplane slowly decelerates in level ?
Question 223-21 : Stick shaker activation or low speed buffeting an accelerated stall clmax will increase due to shock stall high speed buffet
 Stick shaker activation or low speed buffeting.
Stick shaker activation or low speed buffeting. Which of the following increases the maximum duration of a glide ?
Question 223-22 : A decrease in mass an increase in mass a headwind a tailwind
 A decrease in mass.
A decrease in mass. Wing spoilers are deflected symmetrically in flight in order to ?
Question 223-23 : Decelerate the aeroplane and/or increase its rate of descent assist the ailerons in obtaining a higher roll rate prevent aeroplane yaw improve glide performance increase lift /drag ratio
 Decelerate the aeroplane and/or increase its rate of descent.
Decelerate the aeroplane and/or increase its rate of descent. A positively cambered aerofoil will generate zero lift ?
Question 223-24 : At a negative angle of attack at a positive angle of attack at zero angle of attack it can never generate zero lift
 At a negative angle of attack.
At a negative angle of attack. The lift coefficient cl versus angle of attack curve of a negatively cambered ?
Question 223-25 : To the right of the origin at the origin to the left of the origin nowhere
 To the right of the origin.
To the right of the origin. Regarding the lift formula if density doubles lift will ?
Question 223-26 : Also double be 4 times greater halve remain the same
 Also double.
Also double. Assuming all bodies have the same cross sectional area and are in motion which ?
Question 223-27 : Body b body a body c body d
 Body b.
Body b. When a wing spoiler is extended at constant angle of attack ?
Question 223-28 : Drag increases but lift decreases both drag and lift increase drag increases but lift remains constant both drag and lift decrease
 Drag increases but lift decreases.
Drag increases but lift decreases. The point where the single resultant aerodynamic force acts on an aerofoil is ?
Question 223-29 : Centre of pressure centre of gravity neutral point aerodynamic centre
 Centre of pressure.
Centre of pressure. Wing loading is the ratio between ?
Question 223-30 : Aeroplane weight and wing area chord and aeroplane weight aeroplane weight and lift coefficient aeroplane weight and wing span
 Aeroplane weight and wing area.
Aeroplane weight and wing area. Increasing the aspect ratio of a wing ?
Question 223-31 : Decreases induced drag decreases gust load increases stall speed increases induced drag
 Decreases induced drag.
Decreases induced drag. What may happen if the 'ultimate load factor' is exceeded ?
Question 223-32 : Structural failure elastic or temporary deformation only no structural failure only plastic or permanent deformation flutter
 Structural failure.
Structural failure. The increase in stall speed ias with increasing altitude is due to ?
Question 223-33 : Compressibility effects exceedance of mcrit an increase in tas the larger angle of attack necessary in lower density air to obtain the same lift as at sea level
 Compressibility effects.
Compressibility effects. An large jet transport aeroplane has the following four flap positions up take ?
Question 223-34 : Slats from retracted to extended flaps from approach to landing flaps from up to take off flaps from take off to approach
 Slats from retracted to extended.
Slats from retracted to extended. In a straight steady climb the thrust must be ?
Question 223-35 : Greater than the drag because it must also balance a component of weight greater than drag because more lift has to be produced lower than the drag because it is assisted by a component of weight equal to the drag
 Greater than the drag because it must also balance a component of weight.
Greater than the drag because it must also balance a component of weight. Regarding a positively cambered aerofoil section which statement is correct .i ?
Question 223-36 : I is correct and ii is correct i is correct and ii is incorrect i is incorrect and ii is correct i is incorrect and ii is incorrect
 I is correct and ii is correct.
I is correct and ii is correct. Regarding a symmetric aerofoil section which statement is correct .i the angle ?
Question 223-37 : I is correct and ii is correct i is correct and ii is incorrect i is incorrect and ii is incorrect i is incorrect and ii is correct
 I is correct and ii is correct.
I is correct and ii is correct. Regarding a symmetric aerofoil section which statement is correct .i the angle ?
Question 223-38 : I is incorrect and ii is incorrect i is correct and ii is incorrect i is incorrect and ii is correct i is correct and ii is correct
 I is incorrect and ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect and ii is incorrect. Which of these statements about wing sweepback are correct or incorrect .i ?
Question 223-39 : I is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect
Considering subsonic incompressible airflow through a venturi which statement ?
Question 223-40 : I is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
8879 Free Training Exam
