A water fire extinguisher can be used without restriction for .1 a paper fire.2 ? [ Preparation civilian ]
Question 211-1 : 1 3 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 2 4 5
 1, 3, 5.
1, 3, 5. The protection time of an anti icing fluid depends on .1 the type and intensity ?
Question 211-2 : 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 4 6 2 3 4 5 1 3 5 6
 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. The anti icing fluid protecting film can wear off and reduce the holdover time ?
Question 211-3 : During strong winds or as a result of other aircraft engines jet blast when the outside temperature is close to 0°c when the temperature of the aircraft skin is close to 0°c when the aircraft is parked facing into wind
 During strong winds or as a result of other aircraft engines jet blast.
During strong winds or as a result of other aircraft engines jet blast. Windshear may be described as a change in wind direction and/or speed in space ?
Question 211-4 : Substantial small medium null
 Substantial.
Substantial. Wind shear and microburst.in the 'worst case' scenario of recovery from the ?
Question 211-5 : Increase the pitch angle until the stick shaker is felt and hold at slightly below this angle climb away at vat + 20 kt reduce speed to v2 and hold slowly increase speed whilst maintaining a positive rate of climb
 Increase the pitch angle until the stick shaker is felt and hold at slightly below this angle
Increase the pitch angle until the stick shaker is felt and hold at slightly below this angle For the purpose of wake turbulence separation what is the icao minimum radar ?
Question 211-6 : 7 4 km 4 nm 9 3 km 5 nm 11 1 km 6 nm 3 7 km 2 nm
 7.4 km (4 nm).
7.4 km (4 nm). For purpose of wake turbulence separation what is the icao minimum separation ?
Question 211-7 : 3 minutes 5 minutes 2 minutes 4 minutes
 3 minutes.
3 minutes. What is the transponder code to be used by the commander of an aircraft that is ?
Question 211-8 : 7500 7600 7700 7800
 7500
7500 Information concerning emergency evacuation procedures shall be found in the ?
Question 211-9 : Operations manual flight manual journey logbook operational flight plan
 Operations manual.
Operations manual. A list of dangerous goods which may not be transported by air can be found in ?
Question 211-10 : The technical instructions for the safe transport of dangerous goods by air annex 18 to the chicago convention annex 6 to the chicago convention the shipper's declaration for dangerous goods
 The technical instructions for the safe transport of dangerous goods by air.
The technical instructions for the safe transport of dangerous goods by air. The minimum equipment list mel defines the equipment which can be inoperative ?
Question 211-11 : The operator and may be more restrictive than the master minimum equipment list mmel the manufacturer and may be less restrictive than the master minimum equipment list mmel the operator and may be less restrictive than the master minimum equipment list mmel the manufacturer and may be more restrictive than the master minimum equipment list mmel
 The operator and may be more restrictive than the master minimum equipment list (mmel)
The operator and may be more restrictive than the master minimum equipment list (mmel) The correct statement about extinguishing agents on board aeroplanes is ?
Question 211-12 : Halotron is an effective extinguishing agent for use in aeroplanes water may only be used for minor fires a powder extinguisher is suitable for extinguishing a cockpit fire burning cargo in a cargo aeroplane is usually extinguished by using carbon dioxide
 Halotron is an effective extinguishing agent for use in aeroplanes.
Halotron is an effective extinguishing agent for use in aeroplanes. When an aircraft flies into a horizontal tail wind gust the aircraft tends ?
Question 211-13 : To descend to climb not to change its trajectory to climb or descend depending on the gust strength
 To descend.
To descend. Tip vortices which are responsible for wake turbulence appear as soon as the ?
Question 211-14 : Lift drag full flaps extension lift destruction
 Lift.
Lift. One of the main characteristics of windshear is that it ?
Question 211-15 : Can occur at any altitude in both the vertical and horizontal planes occurs only at a low altitude 2000 ft and never in the vertical plane occurs only at a low altitude 2000 ft and never in the horizontal plane can occur at any altitude and only in the horizontal plane
 Can occur at any altitude in both the vertical and horizontal planes.
Can occur at any altitude in both the vertical and horizontal planes. Wake turbulence risk is highest ?
Question 211-16 : When a heavy aircraft has just performed a take off at a closely situated parallel runway with a light crosswind if just before landing a much lighter aircraft has landed at the same runway with heavy crosswind following a preceding aircraft at high speed when a preceding aircraft has briefly applied take off thrust just prior to take off
 When a heavy aircraft has just performed a take-off at a closely situated parallel runway with a light crosswind.
When a heavy aircraft has just performed a take-off at a closely situated parallel runway with a light crosswind. The accumulation of frost snow or ice on an aeroplane in flight induces amongst ?
Question 211-17 : Stalling speed value of the stall angle of attack tuck under roll rate
 Stalling speed.
Stalling speed. Icao annex 18 is a document dealing with ?
Question 211-18 : The safety of the air transport of dangerous goods the air transport of live animals the noise pollution of aircraft the technical operational use of aircraft
 The safety of the air transport of dangerous goods
The safety of the air transport of dangerous goods In final approach you encounter a strong rear wind gust or strong down wind ?
Question 211-19 : 1 3 2 4 1 4 2 3
 1, 3.
1, 3. Which of the following requirements should be met when planning a flight with ?
Question 211-20 : The aircraft shall be equipped with approved ice protection systems the flight should be planned so that a change of cruising level can be initiated rapidly the aircraft shall before flight be sprayed with anti icing fluid a meteorologist shall decide whether the flight may be performed without ice protection systems
 The aircraft shall be equipped with approved ice-protection systems.
The aircraft shall be equipped with approved ice-protection systems. During an explosive decompression at flight level 370 fl 370 your first action ?
Question 211-21 : To put on the oxygen mask to set the transponder to 7700 to warn the atc to inform cabin crew
 To put on the oxygen mask.
To put on the oxygen mask. When taking off after a widebody aircraft which has just landed you should take ?
Question 211-22 : Beyond the point where the aircraft's wheels have touched down in front of the point where the aircraft's wheels have touched down at the point where the aircraft's wheels have touched down and on the wind side of the runway at the point where the aircraft's wheels have touched the ground and on the underwind side of the runway
 Beyond the point where the aircraft's wheels have touched down.
Beyond the point where the aircraft's wheels have touched down. An aircraft which experiences a headwind of 40 kt while making its way towards ?
Question 211-23 : 80 kt 40 kt 60 kt 20 kt
 80 kt.
80 kt. In addition to informing each state whose citizens are known to be on board an ?
Question 211-24 : State of registry of the aircraft the state of the operator and icao state of the operator the easa and icao state of registry of the aircraft and the easa state of registry of the aircraft and the state of the operator only
 State of registry of the aircraft, the state of the operator and icao.
State of registry of the aircraft, the state of the operator and icao. The holdover time of an anti icing procedure for a given ambient temperature ?
Question 211-25 : Frost freezing fog rain on a cold soaked wing steady snow
 Frost.
Frost. At any ambient temperature up to +30° c and with a relative humidity as low as ?
Question 211-26 : Can occur but only at a low power setting cannot occur can occur but only at full power or cruise settings can occur at any setting
 Can occur, but only at a low power setting.
Can occur, but only at a low power setting. As regards the detection of bird strike hazard the pilot's means of information ?
Question 211-27 : 1 2 3 5 2 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 3 4
 1, 2, 3, 5.
1, 2, 3, 5. Emergency and precautionary landings.following an emergency landing which will ?
Question 211-28 : 1 4 2 4 2 3 1 3
 1, 4.
1, 4. While approaching a mountainous airfield the captain of a transport aircraft ?
Question 211-29 : Maintain the aircraft on the glide path accept a positive speed deviation monitor the speed evolution reduce rapidly the selected thrust in order to reach 1 2 vs and try a precision landing take a level flight attitude to reduce speed then come back to glide path from above reduce rapidly the selected thrust maintain on the glide path
 Maintain the aircraft on the glide path, accept a positive speed deviation, monitor the speed evolution.
Maintain the aircraft on the glide path, accept a positive speed deviation, monitor the speed evolution. Wind shear and microburst.while approaching the outer marker the tower informs ?
Question 211-30 : Windshears vertical and horizontal wake turbulence supercooled water convection motion of air mass
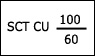 Windshears (vertical and horizontal).
Windshears (vertical and horizontal). Fuel jettisoning.if obliged to jettison part of the fuel in flight it would be ?
Question 211-31 : In a straight line and at a relatively high flight level in a holding stack after control clearance under flight level 50 fl50 during final phase of approach
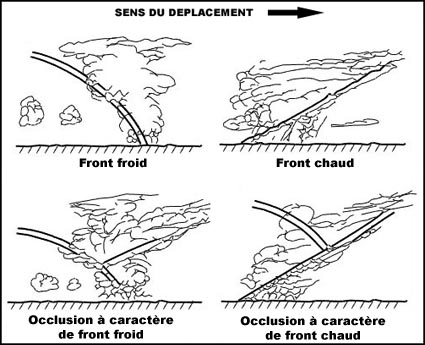 In a straight line and at a relatively high flight level.
In a straight line and at a relatively high flight level. Wind shear and microburst.just after take off an aircraft encounters a ?
Question 211-32 : 1 3 1 4 4 5 2 4
 1, 3.
1, 3. When taking off in winter conditions the wing contamination by ice or frost ?
Question 211-33 : 1 3 5 2 4 5 1 2 3 2 3 5
 1, 3, 5.
1, 3, 5. The application of a type ii anti icing fluid on an aircraft on the ground will ?
Question 211-34 : Limited holdover time protection time up to 24 hours limited time of protection independent of the outside temperature protection against icing for the duration of the flight
 Limited holdover time.
Limited holdover time. You will use a water fire extinguisher straight jet on a fire of . 1 solids ?
Question 211-35 : 1 3 3 and 4 2
 1.
1. Fire and smoke.you will use a halon extinguisher for a fire of .1 solids ?
Question 211-36 : 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 1 2 4
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. A runway covered with 4 mm thick water is said to be ?
Question 211-37 : Contaminated wet flooded damp
 Contaminated.
Contaminated. Icing conditions.an aircraft having undergone an anti icing procedure must be ?
Question 211-38 : It is rotating before taking off releasing the brakes in order to take off it is implementing its own anti icing devices leaving the icing zone
 It is rotating (before taking-off).
It is rotating (before taking-off). An aircraft having undergone an anti icing procedure and having exceeded the ?
Question 211-39 : Must undergo a de icing procedure before a new application of anti icing fluid for take off must only undergo a new anti icing procedure for take off need not undergo a new anti icing procedure for take off must only undergo a de icing procedure for take off
 Must undergo a de-icing procedure before a new application of anti-icing fluid for take-off.
Must undergo a de-icing procedure before a new application of anti-icing fluid for take-off. The time of useful consciousness in case of an explosive decompression at an ?
Question 211-40 : 12 seconds 30 seconds 1 minute 5 minutes
 12 seconds.
12 seconds. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
8399 Free Training Exam
