An aeroplane whose maximum take off mass exceeds 5 700 kg or whose maximum ? [ Exam pilot ]
Question 206-1 : Crash axe or a crow bar in the flight crew compartment crash axe and a crow bar in the passenger compartment crash axe on the flight deck and a crow bar in the passenger compartment crow bar on the flight deck and a crash axe in the passenger compartment
 Crash axe or a crow-bar in the flight crew compartment.
Crash axe or a crow-bar in the flight crew compartment. Ops regulation.an aeroplane whose maximum approved passenger seating ?
Question 206-2 : 1 hand fire extinguisher conveniently located in the passenger compartment 2 hand fire extinguishers conveniently located in the passenger compartment 3 hand fire extinguishers conveniently located in the passenger compartment 4 hand fire extinguishers conveniently located in the passenger compartment
 1 hand fire-extinguisher conveniently located in the passenger compartment.
1 hand fire-extinguisher conveniently located in the passenger compartment. The operator shall ensure that ?
Question 206-3 : Special vfr flights are not commenced when visibility is less than 1 5 km for vfr flights conducted in class b airspace horizontal distance from clouds is at least 1000m for vfr flights conducted in class f airspace vertical distance from clouds is at least 250m for vfr flights conducted in class e airspace flight visibility at and above 3050m 10000ft is at least 5 km clear of cloud
 Special vfr flights are not commenced when visibility is less than 1.5 km.
Special vfr flights are not commenced when visibility is less than 1.5 km. If no meteorological information is available for the destination the operator ?
Question 206-4 : Select two destination alternates take extra fuel to fly two hours at holding speed take extra fuel to fly one hour at holding speed 1500 ft above the alternate aerodrome not take off until obtaining destination meteorological forecast
 Select two destination alternates.
Select two destination alternates. For two engined aeroplanes not approved for etops the take off alternate if ?
Question 206-5 : One hour flight time at one engine inoperative cruising speed two hours flight time at one engine inoperative cruising speed one hour flight time at cruising speed with all engines operating two hours flight time at cruising speed with all engines operating
 One hour flight time at one engine inoperative cruising speed.
One hour flight time at one engine inoperative cruising speed. Icao annex 6.for three and four engined aeroplanes the take off alternate if ?
Question 206-6 : 2 hours flight time at one engine inoperative cruising speed 2 hours flight time at cruising speed with all engines operating 1 hour flight time at one engine inoperative cruising speed 1 hour flight time at cruising speed with all engines operating
 2 hours flight time at one-engine-inoperative cruising speed.
2 hours flight time at one-engine-inoperative cruising speed. An operator must ensure that the mdh for a vor/dme approach is not lower than ?
Question 206-7 : 250 ft 200 ft 300 ft 350 ft
 250 ft.
250 ft. Ops regulation.in accordance with easa air ops a commander shall ensure that ?
Question 206-8 : Final reserve fuel remaining 15 minutes of remaining fuel fuel to hold 30 minutes at 1500 ft above the aedrodrome fuel to fly 20 minutes at best range speed
 Final reserve fuel remaining.
Final reserve fuel remaining. An operator must ensure that the lowest mdh for a ndb approach is ?
Question 206-9 : 350 ft 200 ft 250 ft 400 ft
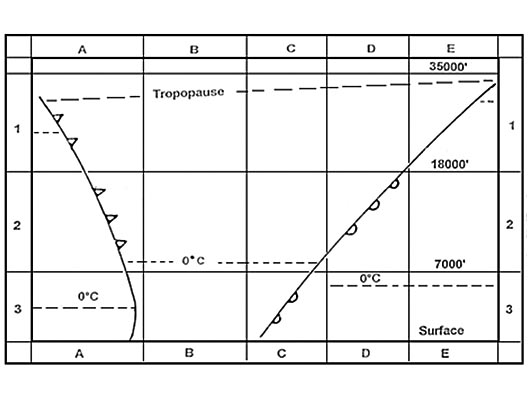 350 ft.
350 ft. For a pressurised aircraft the definition of supplemental oxygen is ?
Question 206-10 : Oxygen supplied to the aeroplane occupants in the case of cabin pressurisation failure oxygen supplied to a passenger who needs oxygen for physiological reasons oxygen used for protection against smoke and carbon dioxide oxygen specifically carried for therapeutic purposes
 Oxygen supplied to the aeroplane occupants in the case of cabin pressurisation failure.
Oxygen supplied to the aeroplane occupants in the case of cabin pressurisation failure. The commander of a turbojet engine aeroplane should have a final reserve fuel ?
Question 206-11 : 30 minutes of flight at holding speed at 1500 ft above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions 45 minutes of flight at holding speed at 1500 ft above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions 30 minutes of flight at cruising speed at fl140 45 minutes of flight at cruising speed at fl140
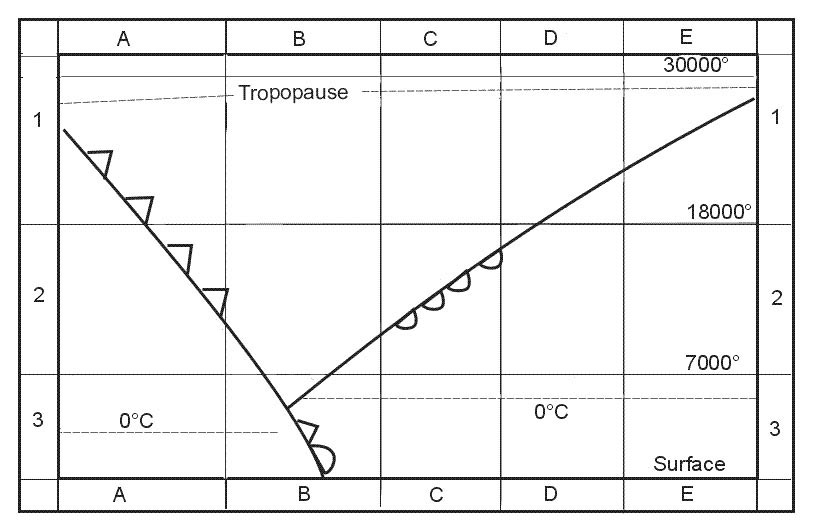 30 minutes of flight at holding speed at 1500 ft above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions.
30 minutes of flight at holding speed at 1500 ft above aerodrome elevation in standard conditions. Due to a cabin pressurisation defect the maximum differential pressure is ?
Question 206-12 : 24500 ft 22500 ft 27000 ft 29000 ft
 24500 ft.
24500 ft. Due to a cabin pressurisation defect the maximum differential pressure is ?
Question 206-13 : 15100 ft 14000 ft 12000 ft 5000 ft
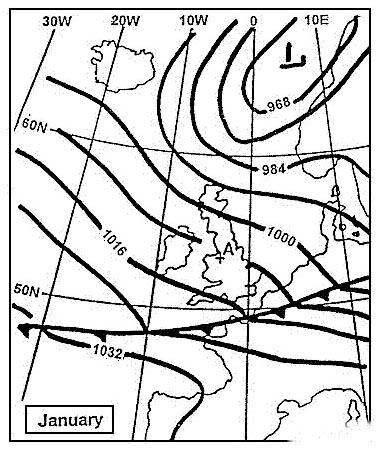 15100 ft.
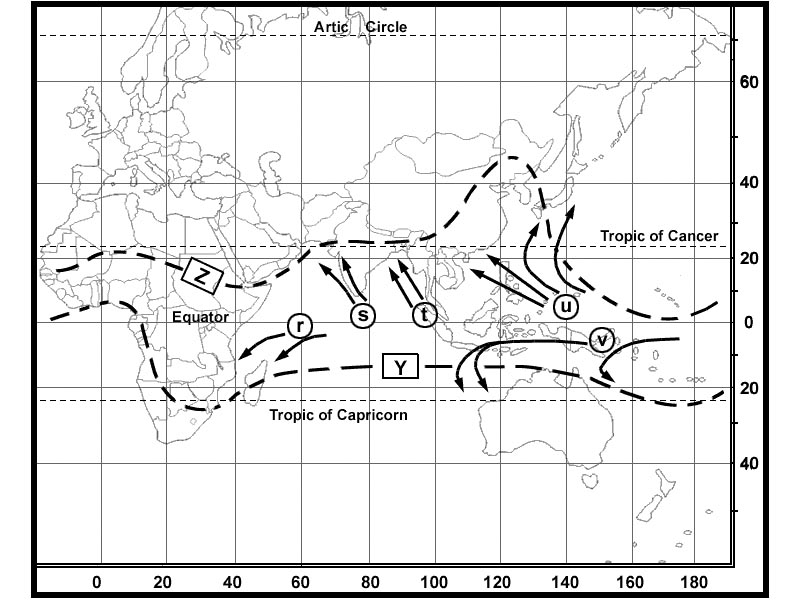
15100 ft. Long range flights and etops.on the diagram where .tn = true north.mn = ?
Question 206-14 : 3 4 1 2
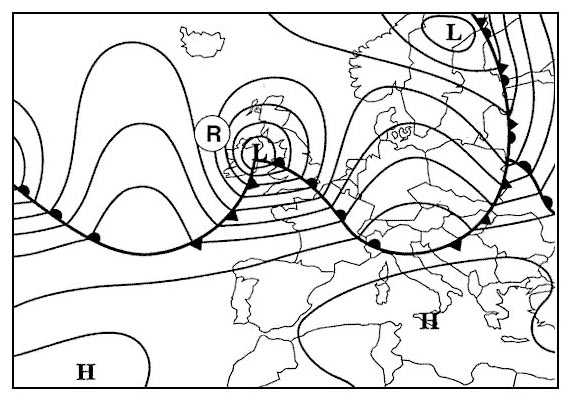 3
3 Long range flights and etops.at reference the inertial navigation system ins ?
Question 206-15 : 2 3 4 1
 2
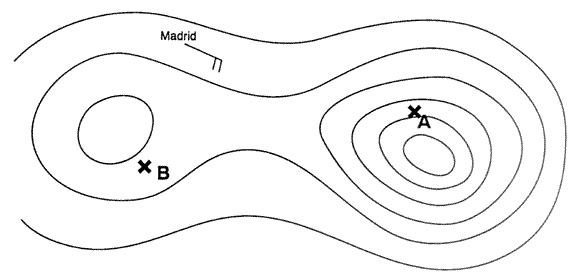
2 Long range flights and etops.a pilot is using a polar stereographic chart whose ?
Question 206-16 : 5° +5° 15° +15°
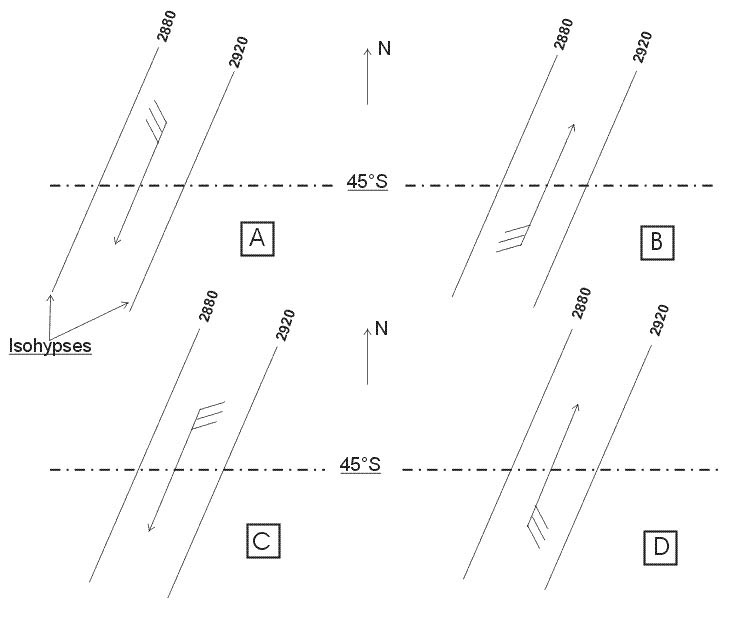 -5°.
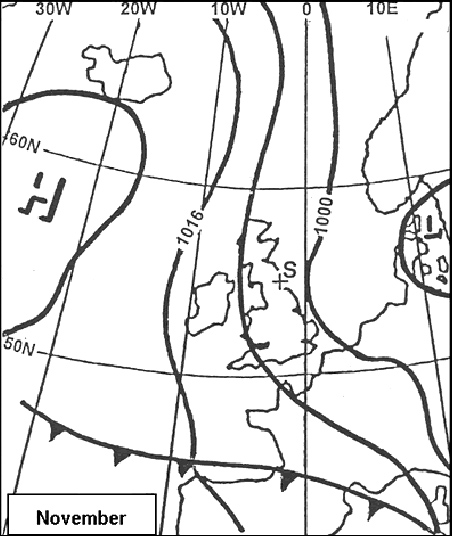
-5°. Long range flights and etops.an aircraft flying at flight level 370 fl 370 in ?
Question 206-17 : Climb or descend 500 ft climb or descent 1000 ft climb or descent 1000 ft or descend 500 ft climb 500 ft or descend 1000 ft
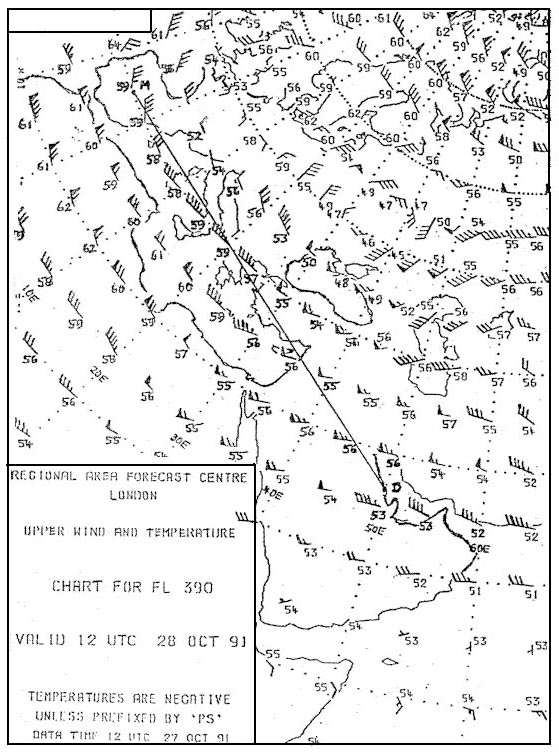 Climb or descend 500 ft.
Climb or descend 500 ft. With the exception of amphibians and seaplanes the carriage of a life jacket ?
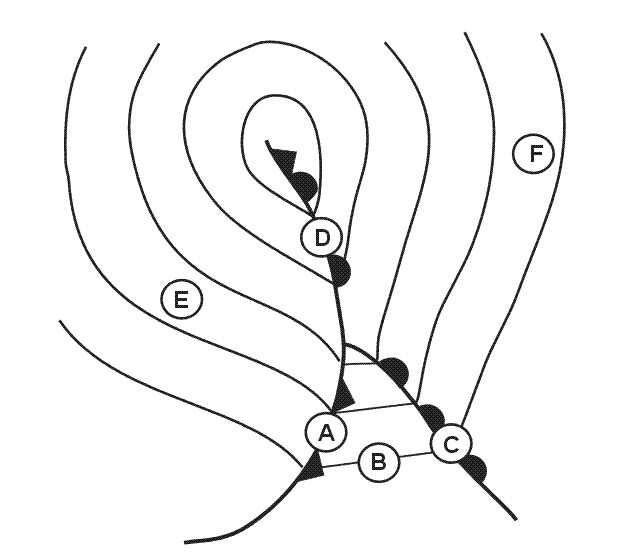
Question 206-18 : 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
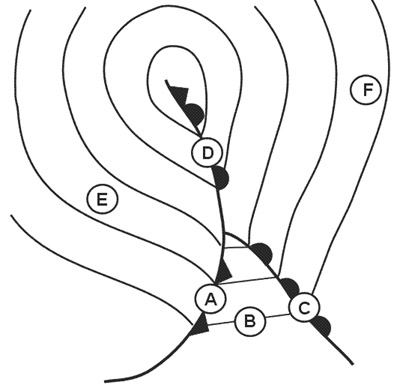 2, 3.
2, 3. In the event of a contingency which required an en route diversion to an ?
Question 206-19 : Minimise its rate of descent while acquiring a 15 nm offset track minimise its rate of descent while acquiring a 60 nm offset track immediatelly descend below fl280 and then acquire a 15 nm offset track immediatelly descend below fl280 and then acquire a 60 nm offset track
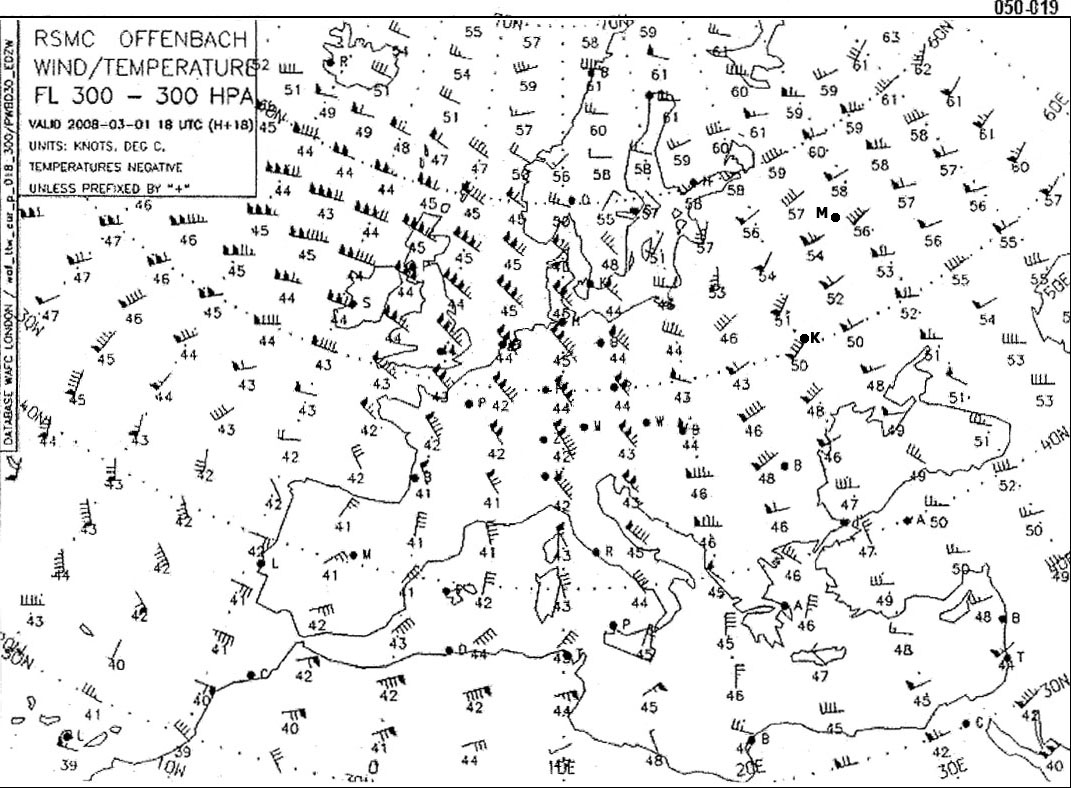 Minimise its rate of descent while acquiring a 15 nm offset track.
Minimise its rate of descent while acquiring a 15 nm offset track. The minimum requirements for supplemental oxygen to be supplied in pressurised ?
Question 206-20 : 13000 ft 14000 ft 15000 ft 25000 ft
 13000 ft.
13000 ft. When establishing an instrument approach procedure five aeroplane categories ?
Question 206-21 : 1 3 1 45 1 5 1 15
 1.3
1.3 At least one of the following hand fire extinguishers must be conveniently ?
Question 206-22 : A hafex fire extinguisher or equivalent a powder fire extinguisher a water fire extinguisher a foam fire extinguisher
 A hafex fire-extinguisher or equivalent.
A hafex fire-extinguisher or equivalent. A crew member is allowed to carry safety matches .1 on himself.2 in his hand ?
Question 206-23 : 1 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 4 2 3
 1, 4.
1, 4. According to air ops and assuming the following circumstances for a category a ?
Question 206-24 : 150 m 200 m 300 m 250 m
 150 m.
150 m. The number of spare fuses available for use in flight must be ?
Question 206-25 : 10% of the number of fuses of each rating or at least 3 for each rating 5% of the number of fuses of each rating or at least 3 for each rating 20% of the number of fuses of each rating or at least 2 for each rating at least 2 for each rating
 10% of the number of fuses of each rating or at least 3 for each rating.
10% of the number of fuses of each rating or at least 3 for each rating. During an ils procedure if the information transmitted by the appropriate ?
Question 206-26 : The outer marker om the faf the middle marker the start final descent point glide slope intersection
 The outer marker (om).
The outer marker (om). The number of crash axes or crowbars on board an aeroplane whose maximum ?
Question 206-27 : 2 1 3 4
 2.
2. Ops regulation.an operator shall not operate an aeroplane unless it is equipped ?
Question 206-28 : Prior to the aeroplane moving under its own power until the termination of the flight when the aeroplane is no longer capable of moving under its own power when the parking brake is released until the termination of flight when the parking brake is set when full thrust is applied until the termination of the flight when the aeroplane is no longer capable of moving under its own power prior to the aeroplane moving under its own power until the termination of flight when the parking brake is set
 Prior to the aeroplane moving under its own power until the termination of the flight when the aeroplane is no longer capable of moving under its own power.
Prior to the aeroplane moving under its own power until the termination of the flight when the aeroplane is no longer capable of moving under its own power. Long range flights and etops.if a pilot has connected the automatic pilot to ?
Question 206-29 : Great circle rhumb line curve of some type or other spherical flight segment
 Great circle.
Great circle. An aeroplane with 8 passengers on board is operated at fl 270 the supply of ?
Question 206-30 : 1 passenger for the remainder of the flight after cabin depressurisation when the cabin altitude exceeds 8000 ft no first aid required 1 passenger for the remainder of the flight after cabin depressurisation when the cabin altitude exceeds 14000 ft 2 passengers for the remainder of the flight after cabin depressurisation when the cabin altitude exceeds 10000 ft
 1 passenger for the remainder of the flight after cabin depressurisation when the cabin altitude exceeds 8000 ft.
1 passenger for the remainder of the flight after cabin depressurisation when the cabin altitude exceeds 8000 ft. The route of a twin engine aircraft non etops with a maximum certificated take ?
Question 206-31 : 60 minutes at the cruise speed one engine inoperative 30 minutes at the cruise speed one engine inoperative 90 minutes at the cruise speed one engine inoperative 120 minutes at the cruise speed one engine inoperative
 60 minutes at the cruise speed, one engine inoperative.
60 minutes at the cruise speed, one engine inoperative. An ifr flight with no alternate aerodrome can be undertaken only if the minimum ?
Question 206-32 : 1 hour before to at least 1 hour after the expected time of arrival 2 hours before to at least 2 hours after the expected time of arrival 3 hours before to at least 1 hour after the expected time of arrival 3 hours before to at least 3 hours after the expected time of arrival
 1 hour before to at least 1 hour after the expected time of arrival.
1 hour before to at least 1 hour after the expected time of arrival. You intend to operate a public transport aeroplane land aeroplane with 60 ?
Question 206-33 : 60 66 0 none if equipped with life rafts
 60.
60. An operator shall ensure that each cabin crew member is at least ?
Question 206-34 : 18 years of age 21 years of age 17 years of age 20 years of age
 18 years of age.
18 years of age. Which of the following is the correct definition of 'wet lease' ?
Question 206-35 : The aircraft is operated under the aoc of the lessor the aircraft is operated under the aoc of the lessee the aircraft is operated overseas the aircraft is leased from a non easa operator
 The aircraft is operated under the aoc of the lessor.
The aircraft is operated under the aoc of the lessor. For a flight from paris to washington with.etops authorisation 105 minutes at ?
Question 206-36 : Track c track a track d track b
 Track c.
Track c. An operator must select a take off alternate ?
Question 206-37 : If it would not be possible to return to the aerodrome of departure for meteorological or performance reasons when conducting a flight over water of more than 2 hours or 400 nm whichever is the lesser when the flight duration exceeds 6 hours for an ifr flight with a single engine aeroplane
 If it would not be possible to return to the aerodrome of departure for meteorological or performance reasons.
If it would not be possible to return to the aerodrome of departure for meteorological or performance reasons. Ops regulation.under what circumstances may an operator introduce alternative ?
Question 206-38 : When needed and when an equivalent safety case has first been approved by the authority and supported by easa member authorities when needed and when an equivalent safety case has been established no prior approval is needed from the authority when needed to expedite maintenance procedures never
 When needed and when an equivalent safety case has first been approved by the authority and supported by easa member authorities.
When needed and when an equivalent safety case has first been approved by the authority and supported by easa member authorities. The minimum number of hand fire extinguishers to be located in the passenger ?
Question 206-39 : 2 1 3 0
 2.
2. According to annex 6 'rnp type' is defined as a containment value expressed as ?
Question 206-40 : I nautical miles ii 95% i nautical miles ii 90% i kilometers ii 95% i kilometers ii 90%
 (i) nautical miles (ii) 95%
(i) nautical miles (ii) 95% ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
8199 Free Training Exam
