An aircraft is approved for rnp apch will this mean that it is automatically ? [ Exam pilot ]
Question 202-1 : No because the aircraft may not meet all requirements for rnp 2 approval because rnp 2 is less stringent so it is automatically included under any stricter approvals no because an aircraft can either be approved for rnp 2 or rnp apch but it can never be approved for both because the navigation databases are the same for all rnp flights
 No, because the aircraft may not meet all requirements for rnp 2 approval.
No, because the aircraft may not meet all requirements for rnp 2 approval. Regarding the pbn specification rnp ar apch what requires specific authorisation ?
Question 202-2 : The published instrument approach performing an approach without onboard performance monitoring and alerting any arrival route directly to the initial approach fix a continuous descent final approach to the final approach fix
 The published instrument approach.
The published instrument approach. An aircraft plans to fly an rnp apch to lnav/vnav minima based on barometric ?
Question 202-3 : Final approach segment all stages of the flight for terrain clearance initial and final approach segments initial and intermediate approach segments
 Final approach segment.
Final approach segment. A flight crew is in the cruise preparing to fly an rnp apch which of the ?
Question 202-4 : 1 and 3 1 and 4 2 and 3 2 and 4
 1 and 3
1 and 3 During flight a pilot is alerted that the aircraft's anp is greater than the ?
Question 202-5 : 1 is not 2 true 1 is not 2 desired 1 is 2 desired 1 is 2 true
 (1) is not; (2) true
(1) is not; (2) true A student pilot wants to practise an rnp apch to lpv minima in the planning ?
Question 202-6 : Describe the final approach path both laterally and vertically select a minimum descent altitude depending on the outside air temperature feed the gnss receiver with the differential corrections for the area programme the arrival route through waypoints and path terminators
 Describe the final approach path, both laterally and vertically.
Describe the final approach path, both laterally and vertically. Your aircraft is approved for rnp apch lnav therefore it will automatically ?
Question 202-7 : No as the aircraft may fail to meet all the functional requirements for rnp2 a separate approval for rnp 2 is necessary an approval for rnp with strict accuracy requirements covers either rnp specifications with lower accuracy requirements on condition that the pilot holds a valid instrument rating including privilege to fly pbn operations because an operational approval is not required for either of the operations
 No, as the aircraft may fail to meet all the functional requirements for rnp2. a separate approval for rnp 2 is necessary.
No, as the aircraft may fail to meet all the functional requirements for rnp2. a separate approval for rnp 2 is necessary. For pbn operations what is true regarding fly by turns and fly over turns ?
Question 202-8 : The fly by turn can be used in rnp flight tracks but fly over turns are excluded fly by waypoints are used when the aircraft must first fly over the waypoint before starting a turn fly by and fly over waypoints are compatible with both rnav and rnp flight tracks pilots can change a route database waypoint type from a fly by to a fly over
 The fly-by turn can be used in rnp flight tracks but fly-over turns are excluded.
The fly-by turn can be used in rnp flight tracks but fly-over turns are excluded. Your aircraft is approved to conduct rnp app can you fly rnp 2 ?
Question 202-9 : No because your aircraft may not have the requeriments for rnp 2 because the most restricted procedure contains the least requirements because the requirements for all rnp operations are the same because your aircraft is approved for a more restricted procedure
 No, because your aircraft may not have the requeriments for rnp 2.
No, because your aircraft may not have the requeriments for rnp 2. What pbn will be used for north atlantic high level operations nat hla ?
Question 202-10 : Rnav10/rnp 10 rnp4 only rnp4 rnp1 only rnav 2 rnav 1 only rnav 1 only
 Rnav10/rnp 10, rnp4 only.
Rnav10/rnp 10, rnp4 only. An aircraft not equipped with temperature compensating system is executing an ?
Question 202-11 : Incorrect altimeter setting leading to the aircraft being lower than indicated the pilots miscalculated the rate of descent and selected an inappropriate vertical speed the temperature at the aerodrome is above the limiting temperature the vertical path in the fms was incorrectly coded as it is not shown to the pilots
 Incorrect altimeter setting leading to the aircraft being lower than indicated.
Incorrect altimeter setting leading to the aircraft being lower than indicated. According to icao doc 9613 rnav 5 is a navigation specification that only ?
Question 202-12 : En route continental navigation and arrival outside 30 nm and above msa arrivals approaches and departures en route continental navigation as well as arrival and departure routes arrivals and departures
 En-route continental navigation and arrival outside 30 nm and above msa.
En-route continental navigation and arrival outside 30 nm and above msa. What is the correct technique to choose a route for rnav sid/star ?
Question 202-13 : Enter the name of the route use of electronic flight bag upload it from the efb select a route from the company database
 Enter the name of the route.
Enter the name of the route. According to icao doc 9613 a specific form of fixed radius path frp is designed ?
Question 202-14 : Fix radius transition frt fly by fb turn radius to fix rf leg radius leg rl
 Fix-radius transition (frt).
Fix-radius transition (frt). For terminal & en route phases of flight pbn is limited to ?
Question 202-15 : Lateral navigation vertical navigation lateral & vertical navigation full 3d navigation
 Lateral navigation.
Lateral navigation. What is the correct statement regarding baro vnav ?
Question 202-16 : Cold temperature reduces the effective glide path angle hot temperature reduces the effective glide path angle hot temperature makes the aircraft lower than indicated cold temperature makes the aircraft higher than indicated
 Cold temperature reduces the effective glide path angle.
Cold temperature reduces the effective glide path angle. Which of the following requires fas data block ?
Question 202-17 : A rnp approach an ils approach an mls approach a radar approach
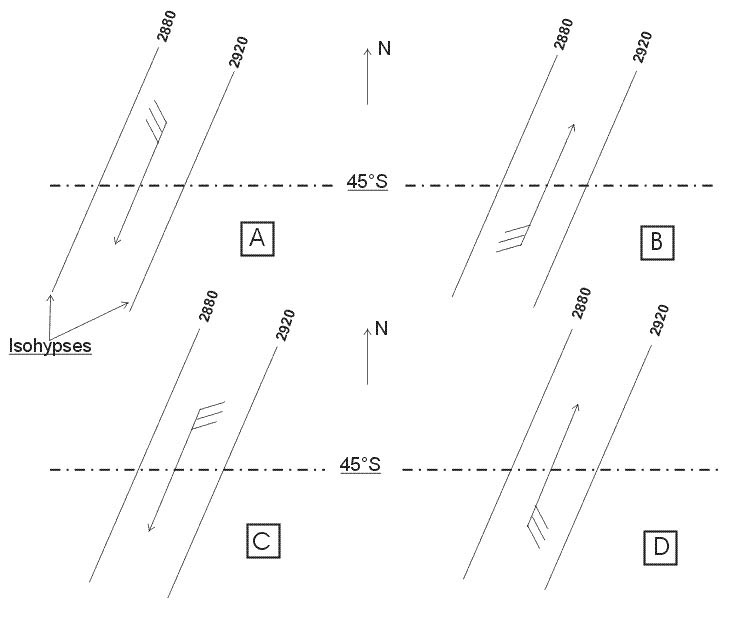 A rnp approach
A rnp approach An aircraft equipped with rnav 1 navigation specifications is cleared by the ?
Question 202-18 : Advise atc that he/she is unable to comply and should request a different sid he/she shall accept the sid since the requirement for lateral accuracy is assured he/she shall accept the sid and monitor system performance during departure he/she should first check the integrity of the system and then advise atc accordingly
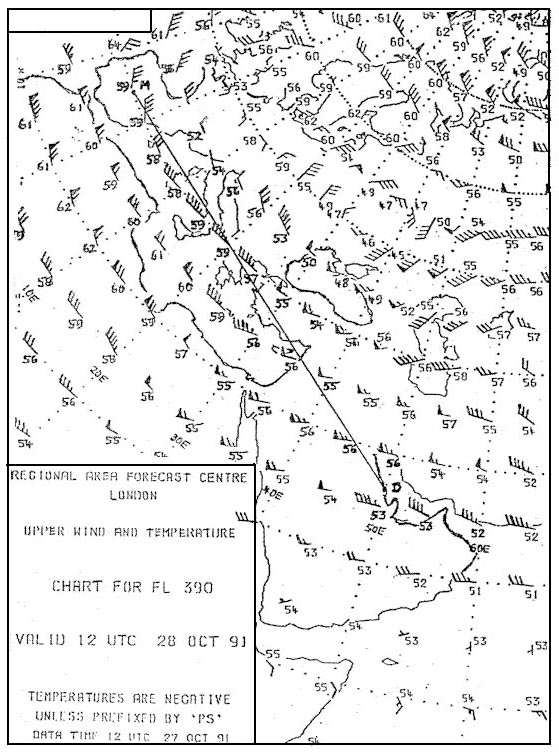 Advise atc, that he/she is unable to comply and should request a different sid.
Advise atc, that he/she is unable to comply and should request a different sid. With a rnp aircraft automatically meets the requirements for ?
Question 202-19 : Rnp 2 and rnp 1 rnp apch and rnp ar apch rnav 5 and rnp 4 rnp ar apch and rnp 1
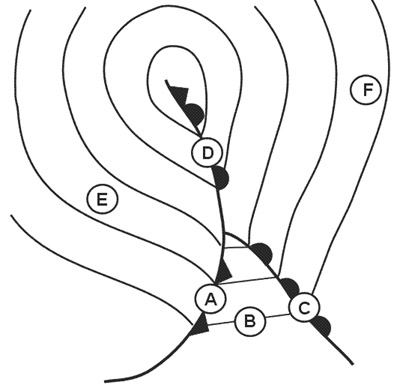 Rnp 2 and rnp 1.
Rnp 2 and rnp 1. When leaving the mnps oceanic control area for a domestic controlled area the ?
Question 202-20 : Maintain the mach number previously assigned up to the last position shown in the oceanic clearance take the mach number specified in this initial flight plan take any mach number take the mach number provided for this type of flight by his airline
 Maintain the mach number previously assigned up to the last position shown in the oceanic clearance.
Maintain the mach number previously assigned up to the last position shown in the oceanic clearance. Long range flights and etops.a polar stereographic chart has a grid printed ?
Question 202-21 : 136° 164° 316° 276°
 136°.
136°. Long range flights and etops.on a polar stereographic chart whose grid is ?
Question 202-22 : 295° 298° 301° 292°
 295°.
295°. Long range flights and etops.the chart is a south polar stereographic ?
Question 202-23 : 360° 260° 080° 100°
 360°.
360°. Long range flights and etops.in mnps airspace the speed reference for turbo jet ?
Question 202-24 : Mach number ground speed true airspeed indicated airspeed
 Mach number.
Mach number. Ops regulation.according to ops the minimum number of crash axes or crowbars on ?
Question 202-25 : 1 2 3 4
 1.
1. Amc3 spa lvo 100 ecqb2022 v4 .a category i precision approach cat i has ?
Question 202-26 : A decision height equal to at least 200 ft a decision height equal to at least 100 ft a decision height equal to at least 50 ft no decision height
 A decision height equal to at least 200 ft.
A decision height equal to at least 200 ft. Long range flights and etops.aircraft may operate in mnps airspace along a ?
Question 202-27 : One long range navigation system lrns three inertial navigation system ins two inertial navigation systems ins two independent long range navigation systems lrns
 One long range navigation system (lrns).
One long range navigation system (lrns). North atlantic high level airspace nat hla .a check on the operation of the ?
Question 202-28 : At or prior entering the oceanic airspace on atc request only as soon as possible after entering the nat region within 15 minutes after crossing the oceanic airspace boundary
 At or prior entering the oceanic airspace.
At or prior entering the oceanic airspace. North atlantic high level airspace nat hla .if a flight is planned to operate ?
Question 202-29 : The abbreviation 'nat' followed by the code letter assigned to the track inserting coordinates as detailed in the nat track message using the abbreviation 'ots' followed by the code letter assigned to the track inserting coordinates defining significant points with intervals of 10° of longitude
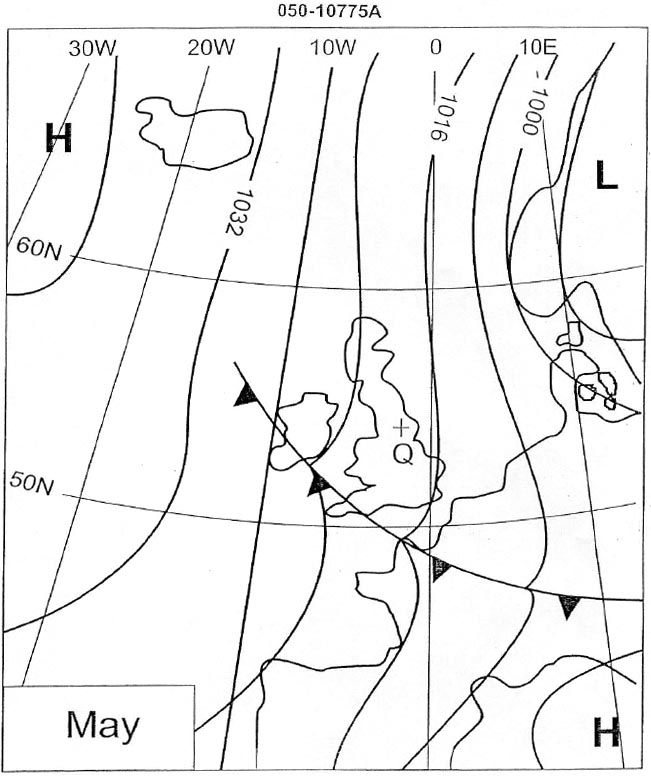 The abbreviation 'nat' followed by the code letter assigned to the track.
The abbreviation 'nat' followed by the code letter assigned to the track. North atlantic high level airspace nat hla .in the event of a contingency which ?
Question 202-30 : If above fl410 climb or descend 1000 ft while turning towards the alternate aerodrome if below fl410 climb or descend 1000 ft while turning towards the alternate aerodrome if below fl410 climb 500 ft or descend 1000 ft while turning towards the alternate aerodrome if above fl410 climb 1000 ft or descend 500 ft while turning towards the alternate aerodrome
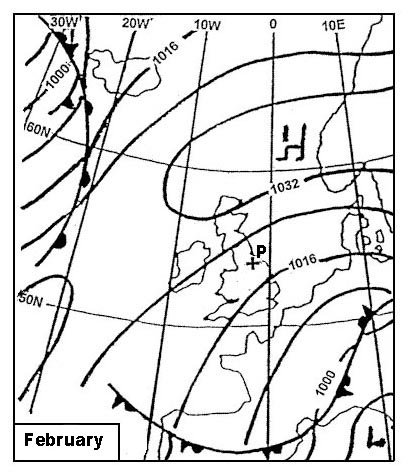 If above fl410, climb or descend 1000 ft, while turning towards the alternate aerodrome.
If above fl410, climb or descend 1000 ft, while turning towards the alternate aerodrome. Extended range operations with two engined aeroplanes etops .an aircraft leaves ?
Question 202-31 : 328° 003° 334° 345°
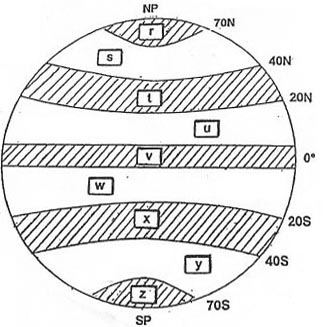 328°.
328°. Extended range operations with two engined aeroplanes etops .you plan to fly ?
Question 202-32 : 076° 066° 085° 080°
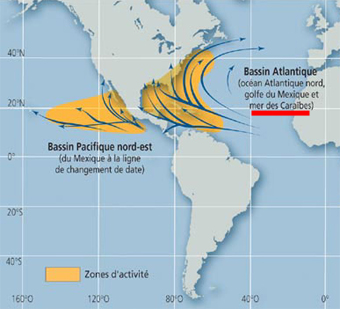 076°.
076°. Extended range operations with two engined aeroplanes etops .the chart type is ?
Question 202-33 : 32 5° +13° +73 5° +32 5°
 -32.5°.
-32.5°. Extended range operations with two engined aeroplanes etops .the pilot uses a ?
Question 202-34 : 240° 340° 060° 110°
 240°.
240°. Extended range operations with two engined aeroplanes etops .the mnps airspace ?
Question 202-35 : 27° north to 90° north 30° north to 90° north 27° north to 70° north 30° north to 70° north
 27° north to 90° north.
27° north to 90° north. Extended range operations with two engined aeroplanes etops .the mnps airspace ?
Question 202-36 : 285 and 420 280 and 400 280 and 390 275 and 400
 285 and 420.
285 and 420. When refuelling is being performed while passengers are boarding or ?
Question 202-37 : The ground area beneath the exits intended for emergency evacuation and slide deployment areas must be kept clear the aircraft's stairs be completely extended refuelling is prohibited while passengers are boarding and/or disembarking all flight crew shall remain at their station
 The ground area beneath the exits intended for emergency evacuation and slide deployment areas must be kept clear.
The ground area beneath the exits intended for emergency evacuation and slide deployment areas must be kept clear. The regulatory green navigation light is located on the starboard side with a ?
Question 202-38 : 110° 70° 140° 220°
 110°.
110°. North atlantic high level airspace nat hla .the validity period of a night time ?
Question 202-39 : 01h00 utc to 08h00 utc 10h30 utc to 19h00 utc 11h30 utc to 18h00 utc 00h00 utc to 08h00 utc
 01h00 utc to 08h00 utc
01h00 utc to 08h00 utc North atlantic high level airspace nat hla .the validity period of a day time ?
Question 202-40 : 11h30 utc to 19h00 utc 10h30 utc to 19h00 utc 01h00 utc to 08h00 utc 00h00 utc to 08h00 utc
 11h30 utc to 19h00 utc.
11h30 utc to 19h00 utc. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
8039 Free Training Exam
