An aircraft is following a defined rnp 2 route and approaching a waypoint where ? [ Exam pilot ]
Question 201-1 : Fixed radius transition frt fly over waypoint radius to fix rf path terminator fly by waypoint
 Fixed radius transition (frt)
Fixed radius transition (frt) The pbn concept specifies that aircraft rnav and rnp system performance ?
Question 201-2 : Accuracy integrity and continuity the navigation equipment integrity and functionality the procedures accuracy and integrity the procedures accuracy and redundancy
 Accuracy, integrity and continuity.
Accuracy, integrity and continuity. When flying an rf leg without autopilot the flight director must be used for ?
Question 201-3 : The rf leg is based on fixed radius turn with guidance calculated by the aircraft’s rnav system the flight director will give a visual and audible alert if the actual navigation performance exceeds the rnp during the rf leg the rnp system uploads the rf procedure to the fac which then provides guidance via the flight director the flight director displays guidance based on the information received from ground based transmitters
 The rf leg is based on fixed radius turn with guidance calculated by the aircraft’s rnav system.
The rf leg is based on fixed radius turn with guidance calculated by the aircraft’s rnav system. Why is it necessary for both pilots and air traffic controllers to be aware of ?
Question 201-4 : To be confident that the aircraft is capable of navigating with the appropriate accuracy to ensure adherence to procedures and separation it ensures that both pilots and air traffic controllers are confident that the aircraft will follow published tracks also in the event of systems downgrade to be confident that all aircraft follow the same path and follow the same turn radius giving the same predictable track keeping performance it ensures that all aircraft entering are capable of following the procedures and therefore reduces workload by eliminating the need for monitoring
 To be confident that the aircraft is capable of navigating with the appropriate accuracy to ensure adherence to procedures and separation.
To be confident that the aircraft is capable of navigating with the appropriate accuracy to ensure adherence to procedures and separation. Icao doc 9613 defines the concept of pbn and its components these components ?
Question 201-5 : Navigation specifications navigation applications navaid applications navaid infrastructures
 Navigation specifications.
Navigation specifications. Consider rnav and rnp system functions an offset flight path’’ is ?
Question 201-6 : A lateral offset from a defined route which is specified in increments of 1 nm up to 20 nm a variable lateral offset from a defined route that can be applied for the entire length of the route including the approach procedure a lateral offset from a defined route and the offset must be intercepted at an angle of 45 degrees or more a parallel path that is offset only to the left of the original active route
 A lateral offset from a defined route, which is specified in increments of 1 nm up to 20 nm.
A lateral offset from a defined route, which is specified in increments of 1 nm up to 20 nm. Icao doc 9613 defines a set of navigation specifications for different airspace ?
Question 201-7 : The en route phase of flight in oceanic/remote and continental areas arrival approach except for the final approach and departure phases of flight en route arrival and departure phases of flight arrival approach and departure phases of flight
 The en-route phase of flight in oceanic/remote and continental areas.
The en-route phase of flight in oceanic/remote and continental areas. In the context of pbn operations what is navigation system error nse ?
Question 201-8 : It refers to the difference between the aircraft’s estimated position and its actual position nse occurs when the path defined in the rnav system does not correspond to the desired path that is the path expected to be flown over the ground nse is part of the total system error which relates to the air crew or autopilot’s ability to follow the defined path or track including any display error it is a system error that relates specifically to longitudinal accuracy
 It refers to the difference between the aircraft’s estimated position and its actual position.
It refers to the difference between the aircraft’s estimated position and its actual position. The performance based navigation pbn concept expresses performance requirements ?
Question 201-9 : Integrity availability accuracy continuity
 Integrity.
Integrity. Consider pbn operations what is one advantage of navigating using computed data ?
Question 201-10 : Check the validity and in some cases consistency of sensor data before use provide 3d navigation for the whole route give a more accurate position regardless of the sensor data that is being used only use data from one sensor for navigation
 Check the validity and in some cases consistency of sensor data before use.
Check the validity and in some cases consistency of sensor data before use. 3d approach operations are very common nowadays which of the following options ?
Question 201-11 : 1 2 3 5 and 6 2 3 4 5 and 6 only 1 5 and 6 1 3 4 and 6
 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6
1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 Why is strict adherence to flight director guidance important when manually ?
Question 201-12 : Is required to provide the necessary level of guidance and precision during the turn must be used in place of the autopilot as it provides more precise guidance provides guidance based on a fixed radius calculated with current tas and bank angle allows the pilot to cross check the dme arc guidance along the rf procedure
 Is required to provide the necessary level of guidance and precision during the turn.
Is required to provide the necessary level of guidance and precision during the turn. In pbn operations rnav 2 can be used for which of these phases of flight ?
Question 201-13 : En route continental arrival and departure en route oceanic en route continental and approach arrival departure and approach en route remote intermediate approach and final approach
 En-route continental, arrival, and departure.
En-route continental, arrival, and departure. A pilot is planning to conduct a flight under the specifications of pbn an rnp ?
Question 201-14 : Certified for the purpose from a barometric altimeter from a radio altimeter from an ils or mls glide slope
 Certified for the purpose.
Certified for the purpose. In order to navigate an aircraft under the specifications of pbn the pilot must ?
Question 201-15 : Is valid for the current airac cycle is updated by notams via acars contains an up to date wgs 84 model contains the latest gps navigation message
 Is valid for the current airac cycle.
Is valid for the current airac cycle. The icao pbn manual doc 9613 defines a set of navigation specifications for ?
Question 201-16 : Approaches that require a specific authorisation to fly en route and approach segments requiring augmented navigation capability en route segments requiring augmented navigation capability a route or part of a route that is airway regulated
 Approaches that require a specific authorisation to fly.
Approaches that require a specific authorisation to fly. Which of the following navigation aspects are related to the rnp specification ?
Question 201-17 : Lateral navigation lateral and vertical navigation vertical navigation full 3d navigation
 Lateral navigation
Lateral navigation You are flying in imc at night above the 73°north latitude because of the high ?
Question 201-18 : The temperature has fallen below 8°c invalidating the indicated altitudes of the current barometric vnav setup atc has detected interference from the glide slope signals of the parallel runway the gbas signal has been lost loss of the gnss signal because of the low satellite elevations above the horizon
 The temperature has fallen below -8°c, invalidating the indicated altitudes of the current barometric vnav setup.
The temperature has fallen below -8°c, invalidating the indicated altitudes of the current barometric vnav setup. An aircraft is being flown under the specifications of rnp using a suitable ?
Question 201-19 : Rnp 1 to rnp apch rnav 10 to rnp 1 rnp ar to rnp apch rnav 5 to rnav 1
 Rnp 1 to rnp apch.
Rnp 1 to rnp apch. You are established on a 10 nm parallel track to your airway what will happen ?
Question 201-20 : The rnav system will discontinue the offset the aircraft will return to the defined route lnav will disengage and control wheel steering mode will engage the rnav system will command a holding
 The rnav system will discontinue the offset.
The rnav system will discontinue the offset. A flight management system fms can provide an estimated position error epe that ?
Question 201-21 : A measure of the reasonableness and accuracy of the given flight management position by applying a specific set of rules to the available navigation inputs a sum of all the navigational errors accumulated over time that may be used as a measure of the performance of the navigation system after a flight an average of the navigation errors computed by two or more fmss when compared against each other and subsequently applied as a correction to improve position accuracy a measure of the accuracy of the flight management system for navigation and is demonstrated during initial certification of the aircraft
 A measure of the reasonableness and accuracy of the given flight management position by applying a specific set of rules to the available navigation inputs.
A measure of the reasonableness and accuracy of the given flight management position by applying a specific set of rules to the available navigation inputs. During the final approach segment of an rnp apch using sbas augmentation the ?
Question 201-22 : An alert within six seconds a warning within ten seconds guidance to the missed approach a reversion to a conventional approach
 An alert within six seconds.
An alert within six seconds. An operator operates multiple of the same type of aircraft however some of the ?
Question 201-23 : Fms requires an additional final approach segment fas data block function to fly lpv minima fms requires a localiser and glideslope input from the ils receiver in order to achieve ils performance ils receiver does not include the enhanced localiser and glideslope function for cat iii operations ils sbas and/or gbas signals are not integrated to achieve a similar performance standard
 Fms requires an additional final approach segment (fas) data block function to fly lpv minima.
Fms requires an additional final approach segment (fas) data block function to fly lpv minima. When conducting an rnp apch to lnav/vnav minima an aircraft's lateral guidance ?
Question 201-24 : Sbas or baro vnav gbas or sbas rad alt or baro vnav gbas or rad alt
 Sbas or baro-vnav.
Sbas or baro-vnav. In the pbn concept which of the following factors are used to define aircraft ?
Question 201-25 : 1 3 and 5 2 3 and 5 2 3 and 4 1 2 and 3
 1, 3, and 5.
1, 3, and 5. Which term refers to the difference between the aircraft's estimated position ?
Question 201-26 : Navigation system error nse estimated position error epe path definition error pde flight technical error fte
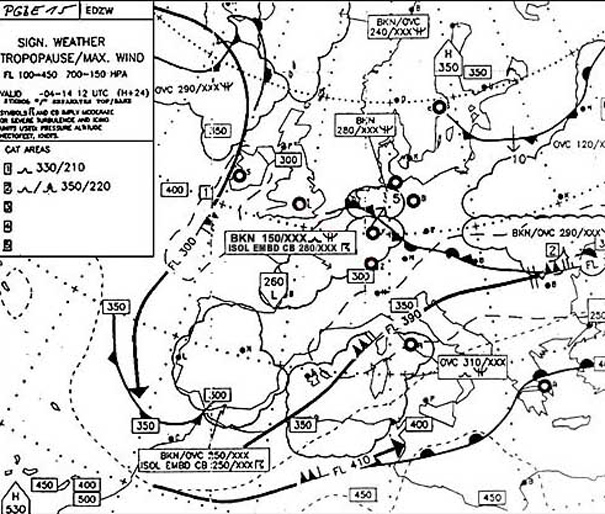 Navigation system error (nse)
Navigation system error (nse) Which of the following statements is correct with regards to the scope of the ?
Question 201-27 : In the approach phases of flight pbn accommodates both linear and angular laterally guided operations for oceanic/remote en route and terminal phases of flight pbn accommodates both linear and angular laterally guided operations for oceanic/remote en route and terminal phases of flight pbn is limited to operations with angular laterally guided operations in the approach phases of flight pbn is limited to operations with guidance to fly the ils procedure
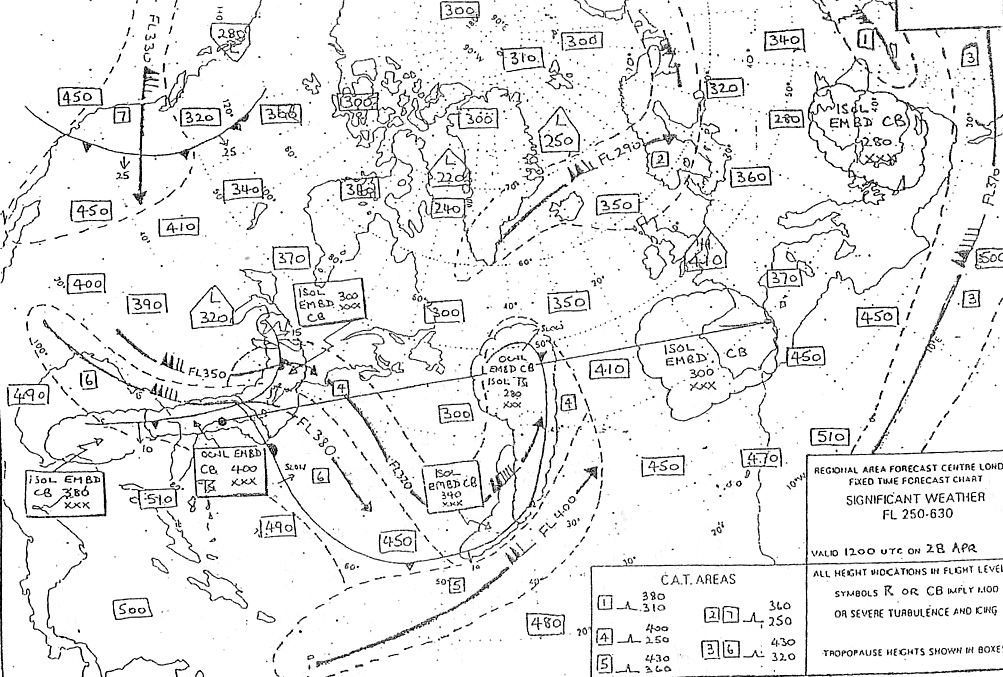 In the approach phases of flight, pbn accommodates both linear and angular laterally guided operations.
In the approach phases of flight, pbn accommodates both linear and angular laterally guided operations. An aeroplane is following a terminal procedure requiring the use of rnp 1 the ?
Question 201-28 : The navigation accuracy is less than required accuracy of +/ 1 nm some gnss signals have been lost and raim is no longer available the aeroplane is outside the coverage of navigation aids the fms position is now based on the irs position alone epe may be less than 1 nm
 The navigation accuracy is less than required accuracy of +/- 1 nm.
The navigation accuracy is less than required accuracy of +/- 1 nm. Within the pbn concept how can 'accuracy' be defined ?
Question 201-29 : A comparison between the required position and the true position being in compliance with the reference ellipsoid wgs 95 having total system error that is expected to be achieved at least 50% of the time being within 1 nm laterally and within 200 ft vertically of the required position
 A comparison between the required position and the true position.
A comparison between the required position and the true position. Within pbn operations what is the make up of the 'total system error' tse .pde ?
Question 201-30 : Pde + fte + nse pde + fte / nse pde x fte x nse pde + fte nse
 Pde + fte + nse
Pde + fte + nse Within the performance based navigation concept rnp requires on board ?
Question 201-31 : The fms will use several sources of navigation information and depending on their expected accuracy create a comparison between these position data and the fms position the inertial reference system irs provides the ultimate reference for the aircraft's position the position determined by radio navigation will be a measure of the error of the fms position this process requires at least two independent fmss in order for them to compare each other’s position thereby calculating a correction to be applied to the fms positions aircraft with a single fms will compare the fm position with the irs position and will use the difference if any to calculate a bias that is applied to the fms position to improve its accuracy
 The fms will use several sources of navigation information and, depending on their expected accuracy, create a comparison between these position data and the fms position.
The fms will use several sources of navigation information and, depending on their expected accuracy, create a comparison between these position data and the fms position. Icao doc 9613 pbn manual defines a set of navigation specifications applicable ?
Question 201-32 : Rnav 10 / rnp 10 and rnp 4 only rnp 4 and rnp 1 only rnav 10 / rnp 10 only rnp 1 only
 Rnav 10 / rnp 10 and rnp 4 only
Rnav 10 / rnp 10 and rnp 4 only Within the pbn concept what is the flight technical error ?
Question 201-33 : It is part of the total system error which relates to the air crew or autopilot's ability to follow the defined path or track including any display error fte is the difference between the aircraft's estimated position and its actual position it is a system error that relates to longitudinal accuracy fte occurs when the path defined in the rnav system does not correspond to the desired path that is the path expected to be flown over the ground
A pilot is planning to fly an rnp 1 star standard terminal arrival but notices ?
Question 201-34 : Not fly the planned procedure and must request an alternative star create a waypoint based on the known latitude and longitude of the missing waypoint create a waypoint based on a radial and distance from a nearby vor dme station fly the star provided there are no gaps in the coding of the arrival
 Not fly the planned procedure and must request an alternative star.
Not fly the planned procedure and must request an alternative star. Within the pbn concept 'availability' is a measure of the ability of the system ?
Question 201-35 : The percentage of time during which the system is to be used for navigation during which reliable navigation information is presented the ability of a system to provide timely warnings to users when the system should not be used for navigation the capability of the total system comprising all elements necessary to maintain aircraft position within the defined airspace to perform its function without non scheduled interruptions during the intended operation a method of navigation that permits aircraft operation on any desired flight path
 The percentage of time during which the system is to be used for navigation during which reliable navigation information is presented.
The percentage of time during which the system is to be used for navigation during which reliable navigation information is presented. You are flying in imc at night above the 73°north latitude because of the high ?
Question 201-36 : The wrong vnav barometric data for the given conditions is being used the wrong qnh was given leading to reduced terrain separation due to indicated altitude being higher than true altitude the temperature has increased above the limiting value incorrect fms setup
Why is temperature correction important on the approach ?
Question 201-37 : Cold temperatures cause a decrease in the effective glide path angle hot temperatures cause a decrease in the glide path angle cold temperatures cause a higher elevation hot temperatures cause a lower elevation
A helicopter crew are to fly in rnp 2 airspace what must they be aware of to ?
Question 201-38 : The helicopter and the crew must be approved to fly in rnp 2 airspace the pilot must confirm that they are able to maintain the required lateral accuracy along the route the pilot and aircraft must be certified for rnp 2 rnp 1 or rnp 0 3 the equipment must comply to rnav2/rnp2 specifications
 The helicopter and the crew must be approved to fly in rnp 2 airspace.
The helicopter and the crew must be approved to fly in rnp 2 airspace. Aircraft 1 is flying using a pbn navigation specification aircraft 2 is flying ?
Question 201-39 : Is using computed data instead of raw data is using raw data instead of computed data is always using gps is reliant on the presence of vors and ndbs
 Is using computed data instead of raw data.
Is using computed data instead of raw data. You are approaching an aerodrome on an rnp apch to lnav/vnav minima using baro ?
Question 201-40 : You made a mistake inputting barometric data raim error gbas signal has been lost loss of the gnss signal because of the low satellite elevations above the horizon
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7999 Free Training Exam
