Assuming an accumulator is pre charged with air to 1000 psi and the hydraulic ? [ Admission airport ]
Question 20-1 : 1500 psi 2500 psi 1000 psi 500 psi
 1500 psi.
1500 psi. Internal leakage in a hydraulic system will cause ?
Question 20-2 : An increased fluid temperature a decreased fluid temperature an increased fluid pressure fluid loss
 An increased fluid temperature.
An increased fluid temperature. On large aeroplanes equipped with power brakes the main source of power is ?
Question 20-3 : The aeroplane's hydraulic system the master cylinders the brake actuators pressure to the rudder pedals
 The aeroplane's hydraulic system.
The aeroplane's hydraulic system. When powering up a hydraulic system the level in the reservoir will ?
Question 20-4 : Decrease slightly always remain the same initially increase with system pressurisation increase as ambient temperature decreases
 Decrease slightly.
Decrease slightly. An accumulator in a hydraulic system will ?
Question 20-5 : Store fluid under pressure increase pressure surges within the system reduce fluid temperature and pressure reduce fluid temperature only
 Store fluid under pressure.
Store fluid under pressure. In the typical hydraulic system represented in the graphic assuming hydraulic ?
Question 20-6 : A condition of hydraulic lock exists and no movement of the piston will take place the piston is free to move in response to external forces since pressures are equal the piston moves to the left due to pressure acting on differential areas the piston moves to the right due to equal pressure acting on differential areas
 A condition of hydraulic lock exists and no movement of the piston will take place.
A condition of hydraulic lock exists and no movement of the piston will take place. A hydraulic shuttle valve ?
Question 20-7 : Enables an alternate supply to operate an actuator is a non return valve allows two units to be operated by one pressure source regulates pump delivery pressure
 Enables an alternate supply to operate an actuator.
Enables an alternate supply to operate an actuator. To protect against excessive system pressure a hydraulic system usually ?
Question 20-8 : A high pressure relief valve a standby hydraulic pump an accumulator auxiliary hydraulic motors
 A high pressure relief valve.
A high pressure relief valve. The ram air turbine rat provides emergency hydraulic power for ?
Question 20-9 : Flight controls in the event of loss of engine driven hydraulic power nose wheel steering after the aeroplane has landed undercarriage selection and automatic brake system flap extension only
 Flight controls in the event of loss of engine driven hydraulic power.
Flight controls in the event of loss of engine driven hydraulic power. A hydraulic low pressure alert is the first indication of ?
Question 20-10 : The pump output pressure being insufficient the reservoir level being at a minimum acceptable level a leak in the reservoir return line the hydraulic system accumulator becoming deflated
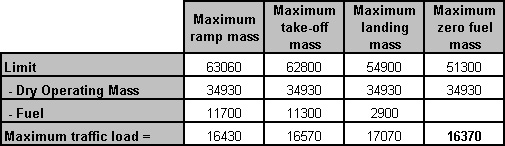 The pump output pressure being insufficient.
The pump output pressure being insufficient. For an aeroplane hydraulic supply circuit the correct statement is ?
Question 20-11 : The accumulators constitute a reserve of hydraulic fluid maintained under pressure by a pneumatic back pressure air or nitrogen the pumps are always electric due to the high pressures which they must deliver 140 to 210 kg/cm² the regulation system deals only with emergency operation and is not applied to all hydraulic services but only those considered as essential the security components comprise the filters the pressure relief valves the by passes and the fire shut off valve
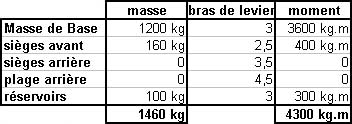 The accumulators constitute a reserve of hydraulic fluid maintained under pressure by a pneumatic back pressure (air or nitrogen).
The accumulators constitute a reserve of hydraulic fluid maintained under pressure by a pneumatic back pressure (air or nitrogen). The reservoirs of a hydraulic system can be pressurized ?
Question 20-12 : By bleed air from the engine in flight only by the air conditioning system by an auxiliary system
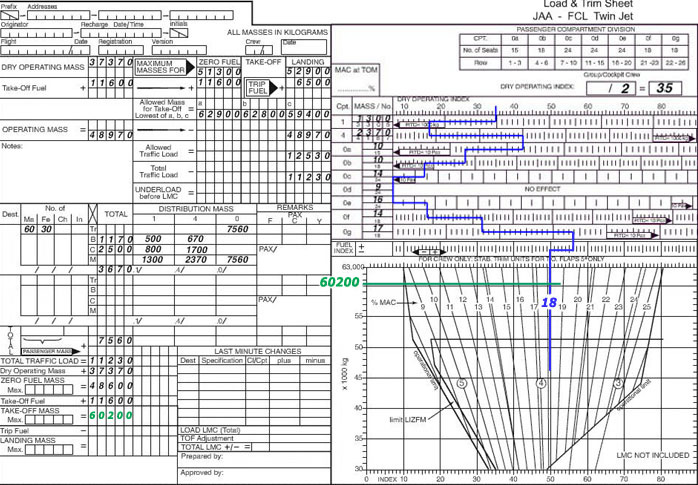 By bleed air from the engine.
By bleed air from the engine. A pressure regulator is used in a hydraulic system ?
Question 20-13 : In conjunction with a constant delivery type pump in conjunction with a variable delivery type pump to ensure that an equal pressure flow is delivered to critical components such as servo actuators as an interface between the system and the cockpit indicators
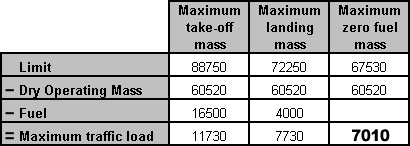 In conjunction with a constant delivery type pump.
In conjunction with a constant delivery type pump. Filters in hydraulic systems often incorporate pop out indicators to ?
Question 20-14 : Warn of an impending by pass situation indicate that the filter is clogged and unfiltered oil is passing around the system warn of a hydraulic system overheat indicate that the filter is due maintenance
 Warn of an impending by-pass situation.
Warn of an impending by-pass situation. Maximum power output and low mass of aeroplane hydraulic systems can be ?
Question 20-15 : High system pressure and low volume flow medium system pressure and low volume flow medium system pressure and high volume flow low system pressure and high volume flow
 High system pressure and low volume flow.
High system pressure and low volume flow. Parameters to monitor a hydraulic system in the cockpit can be ?
Question 20-16 : Pressure fluid temperature and quantity pressure and hydraulic pump output pressure and fluid viscosity pressure and rpm of the hydraulic pump
The purpose of an accumulator in a hydraulic system is ?
Question 20-17 : To damp the fluid pressure variations to eliminate the fluid flow variations to bypass the pumps in the hydraulic system to enable the starting of some devices
 To damp the fluid pressure variations.
To damp the fluid pressure variations. The viscosity of a hydraulic fluid should be ?
Question 20-18 : The lowest to minimize power consumption and resistance to flow the lowest to provide excellent lubrication properties the highest to minimize power consumption and resistance to flow the highest to provide excellent lubrication properties
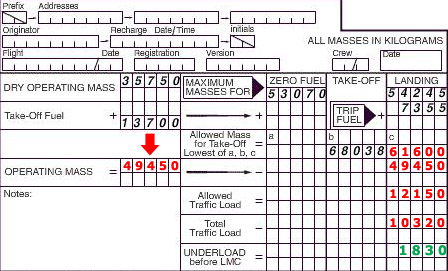
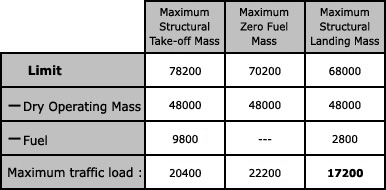
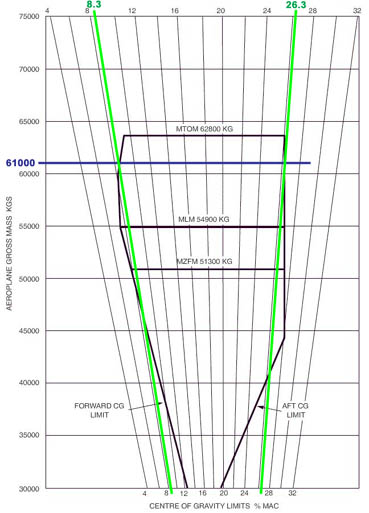
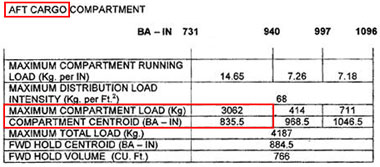
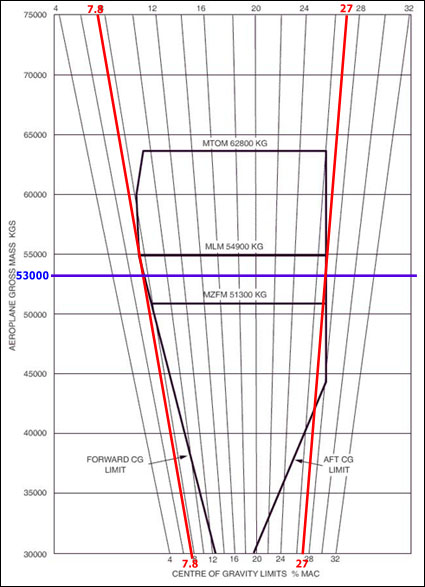
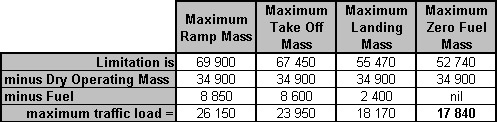
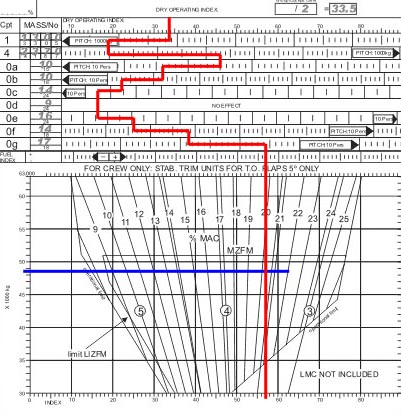
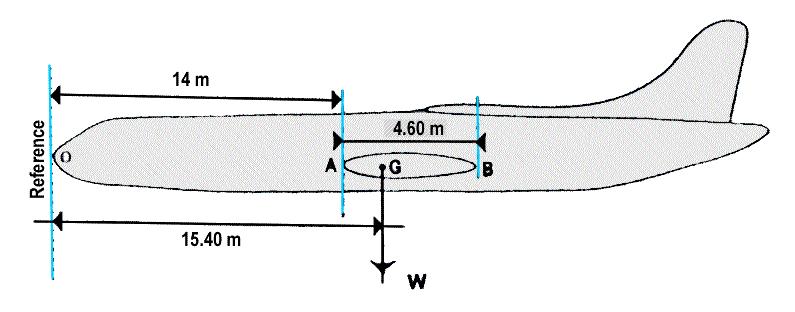
The hydraulic systems which works correctly is shown in the figure . 831 ?
Question 20-19 : N°2 n°4 n°3 n°1
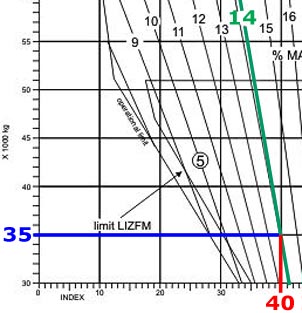 N°2.
N°2. One of the functions of an accumulator in a hydraulic system is ?
Question 20-20 : To damp pressure surges in the system to store fluid to increase the flow to act as a pressure relief valve
 To damp pressure surges in the system.
To damp pressure surges in the system. In a hydraulic system overheat detectors are mostly installed ?
Question 20-21 : At the pumps in the reservoirs at the actuators at the coolers
 At the pumps.
At the pumps. Which of these statements about an aeroplane's hydraulic system is correct ?
Question 20-22 : The filters the pressure relief valve s the by pass valve s and the fire shut off valve are safety features installed in the system the pumps are always electrically driven because they need to deliver a high pressure of 3000 psi a hydraulic leak in a return line does not affect the functioning of the hydraulic system the hydraulic reservoir contains a membrane and is pressurised by nitrogen on one side of this membrane
 The filters, the pressure relief valve(s), the by-pass valve(s), and the fire shut-off valve are safety features installed in the system.
The filters, the pressure relief valve(s), the by-pass valve(s), and the fire shut-off valve are safety features installed in the system. The level in a hydraulic reservoir will ?
Question 20-23 : Fluctuate with accumulator pressure always remain the same initially increase with system pressurisation increase as ambient temperature decreases
 Fluctuate with accumulator pressure.
Fluctuate with accumulator pressure. Purposes of an accumulator in an hydraulic system are .1 to damp pressure ?
Question 20-24 : 1 3 2 4 1 4 2 3
 1, 3.
1, 3. The purpose of an accumulator in an hydraulic system is to ?
Question 20-25 : Store energy store fluid cool the fluid store pressure
 Store energy.
Store energy. The type of hydraulic fluid which has the greatest resistance to cavitation is ?
Question 20-26 : Synthetic fluid mineral oil based fluid vegetable oil based fluid caster oil water and glycol based fluid
 Synthetic fluid.
Synthetic fluid. Filtration in a hydraulic system is usually ensured by ?
Question 20-27 : Filters in both the pressure and return lines a filter in the pressure line only a filter on the return line only the use of sealed containers only during replenishment
 Filters in both the pressure and return lines.
Filters in both the pressure and return lines. The relationship between pressure force and area is ?
Question 20-28 : Force = pressure x area pressure = force x area pressure = area x distance force = volume / area
 Force = pressure x area
Force = pressure x area In a commercial transport aeroplane the landing gear normal operating system is ?
Question 20-29 : Hydraulically driven electrically driven mechanically driven pneumatically driven
 Hydraulically driven.
Hydraulically driven. Generally on modern jet transport aircraft how can the landing gear be extended ?
Question 20-30 : Mechanically electrically by hydraulic accumulators pneumatically
 Mechanically.
Mechanically. The type of brake unit found on most transport aeroplanes is a ?
Question 20-31 : Multiple disk brake belt brake drum type brake single disk brake
 Multiple disk brake.
Multiple disk brake. The reason for fitting thermal plugs to aeroplane wheels is that they ?
Question 20-32 : Release air from the tyre in the event of overheating prevent the brakes from overheating prevent heat transfer from the brake disks to the tyres release air from the tyre in the event of overpressure
 Release air from the tyre in the event of overheating.
Release air from the tyre in the event of overheating. Thermal plugs are installed in ?
Question 20-33 : Wheel rims cargo compartments fire warning systems cabin windows
 Wheel rims.
Wheel rims. In a hydraulic braking system an accumulator is pre charged to 1200 psi if an ?
Question 20-34 : 3000 psi 4200 psi 1800 psi 1200 psi
 3000 psi.
3000 psi. The modern anti skid processes are based on the use of a computer whose input ?
Question 20-35 : 1 2 and 4 1 and 3 1 2 3 4 and 5 2 and 4
 1, 2 and 4.
1, 2 and 4. When a landing gear wheel is hydroplaning its friction factor is around ?
Question 20-36 : 0 0 1 0 5 1
 0.
0. From the following fuselage profile sort them from the worst to the best one ?
Question 20-37 : 1 3 4 2 2 1 3 4 3 4 1 2 3 1 2 4
 1, 3, 4, 2.
1, 3, 4, 2. The illumination of the green landing gear light indicates that the landing ?
Question 20-38 : Locked down locked down and its door is locked in the required position not in the required position
 Locked-down.
Locked-down. The damping element in a landing gear shock absorber used on large aircrafts is ?
Question 20-39 : Oil and viscous liquid nitrogen oxygen springs
 Oil and viscous liquid.
Oil and viscous liquid. 'nose wheel shimmy' may be described as ?
Question 20-40 : A possibly damaging vibration of the nose wheel when moving on the ground aircraft vibration caused by the nose wheel upon extension of the gear the oscillatory movement of the nose wheel when extended prior to landing the amount of free movement of the nose wheel before steering takes effect
 A possibly damaging vibration of the nose wheel when moving on the ground.
A possibly damaging vibration of the nose wheel when moving on the ground. Organize.
This page gathers the questions that you have marked as requiring additional review by clicking on the Review button under the questions of your choice. You can also add a personal annotation to each question to better organize your revisions. This tool helps you better target the concepts to be deepened and to progress effectively.
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
759 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 20
