Amongst others sbas allows for the implementation of ? [ Answer reports ]
Question 199-1 : Three dimensional type a and type b approaches two dimensional precision and non precision approaches one dimensional baro vnav approaches four dimensional fms approaches
 Three dimensional type-a and type-b approaches.
Three dimensional type-a and type-b approaches. An aircraft flying out of sight of land using gnss and abas without sbas ?
Question 199-2 : Reducing abas to raim and barometric altitude only loss of raim leaving only barometric altitude for abas loss of all integrity monitoring of the gnss reduced accuracy of the gnss position
 Reducing abas to raim and barometric altitude only.
Reducing abas to raim and barometric altitude only. The accuracy of the navstar gps position depends on the geometry of the ?
Question 199-3 : If the satellites as viewed by the gps receiver are close together there will be a poor angle of intersection resulting in a loss of accuracy there will be a good angle of intersection if the satellites as viewed by the gps receiver are close together resulting in an increase in accuracy the position accuracy will increase if the satellites as viewed by the gps receiver are paced 60° apart and close to the horizon the worst configuration to give an accurate fix would be three satellites spaced 120°apart and a fourth satellite overhead
 If the satellites, as viewed by the gps receiver, are close together, there will be a poor angle of intersection, resulting in a loss of accuracy.
If the satellites, as viewed by the gps receiver, are close together, there will be a poor angle of intersection, resulting in a loss of accuracy. If a gps malfunction occurs egnos provides an alert time within ?
Question 199-4 : 6 seconds 3 hours 3 seconds 6 minutes
 6 seconds.
6 seconds. A navstar gps satellite broadcasts on two frequencies what is broadcast on both ?
Question 199-5 : Ranging signals sbas signals raim code c/a code
 Ranging signals
Ranging signals User equivalent range error uere or user range accuracy ura is a signal in ?
Question 199-6 : Lonospheric propagation delay ipd dilution of precision dop satellite clock errors dilution of position
 Lonospheric propagation delay (ipd)
Lonospheric propagation delay (ipd) What is correct concerning the l1 and l2 navstar gps transmission frequencies ?
Question 199-7 : The c/a code is the only code available for civilian use it is transmitted only on l1 the c/a code is for authorised military use only it is transmitted on both l1 and l2 the p code is the only code available for civilian use it is transmitted only on l1 the p code is for authorised military use only it is transmitted only on l2
 The c/a code is the only code available for civilian use. it is transmitted only on l1.
The c/a code is the only code available for civilian use. it is transmitted only on l1. Assume that one of the satellites used by a gps receiver is faulty and that the ?
Question 199-8 : Able to detect that one of the satellites is faulty and is able to identify and isolate the faulty one able to detect that one of the satellites is faulty but is unable to identify the faulty one not active as the software needs at least eight satellites to function correctly unable to detect and identify the faulty satellite
 Able to detect that one of the satellites is faulty and is able to identify and isolate the faulty one.
Able to detect that one of the satellites is faulty and is able to identify and isolate the faulty one. How does the gbas system provide improved position accuracy to an aircraft by ?
Question 199-9 : Vhf data broadcast uhf data broadcast uhf reference signal vhf reference signal
 Vhf data broadcast.
Vhf data broadcast. The satellite navigation system navstar gps uses two navigation frequencies l1 ?
Question 199-10 : Both l1 and l2 frequencies are used for pps the l1 frequency is used for pps and the l2 frequency is used for sps only the l2 frequency is used for pps only the l1 frequency is used for pps
 Both l1 and l2 frequencies are used for pps.
Both l1 and l2 frequencies are used for pps. What does raim determine ?
Question 199-11 : Integrity of the gnss navigation signals using only gps signals or gps signals augmented with altitude predicted positions of gnss satellites to ensure that the required geometric dilution of precision gdop will be available at all times aircraft's position in three dimensions from at least 4 available satellites and one on board inertial system accuracy of the computed aircraft position based on input from at least one ground based radio transmitter
 Integrity of the gnss navigation signals using only gps signals or gps signals augmented with altitude.
Integrity of the gnss navigation signals using only gps signals or gps signals augmented with altitude. A gbas system communicates with an aircraft using gps to provide aircraft with ?
Question 199-12 : 1 and 3 1 and 4 2 and 3 2 and 4
 1 and 3
1 and 3 Complete the following sentence .receiver autonomous integrity monitoring raim ?
Question 199-13 : 1 five 2 six 1 six 2 seven 1 three 2 four 1 four 2 five
 (1) five; (2) six
(1) five; (2) six You are approaching an airport in sweden at 73ºn due to this high latitude the ?
Question 199-14 : Aaim with baro barometric altimeter and clock only on board clock to aid time reference and sbas ins and clock
 Aaim with baro.
Aaim with baro. Gps uses two frequencies l1 and l2 choose the correct statement from these ?
Question 199-15 : L1 is required for the standard positioning and timing service sps l1 and l2 are both required for the standard positioning service sps l2 is required for civilian users in order to achieve basic accuracy the l2c part of l2 is required to achieve the required accuracy
 L1 is required for the standard positioning and timing service, sps.
L1 is required for the standard positioning and timing service, sps. One of the more significant errors that reduces the accuracy of the gnss signal ?
Question 199-16 : Dilution of precision caused by the relative positions of the navigation satellites interference from other space vehicles operating in the same frequency band tropospheric propagation delay caused by pollution in lower atmospheric layers receiver clock error caused by variations in the satellites' orbits
 Dilution of precision caused by the relative positions of the navigation satellites.
Dilution of precision caused by the relative positions of the navigation satellites. A gnss approach may achieve lower minima by using correction signals from a ?
Question 199-17 : Gls approach gbas landing system to cat i ii or iii standard ils approach instrument landing system to cat i ii or iii standard apv approach procedure with vertical guidance to cati ii or iii standard lnav/vnav approach procedure to cat i ii or iii standard
 Gls approach (gbas landing system) to cat i, ii or iii standard.
Gls approach (gbas landing system) to cat i, ii or iii standard. What does a satellite based augmentation system sbas use to improve integrity ?
Question 199-18 : Up to 4 geostationary satellites are used to improve accuracy to within 1 m to 2 m horizontally and to advise of any gnss malfunction at least 1 geostationary satellite is required to relay integrity and safety messages to the user error signals are sent to the gnss satellite to correct any position error 2 geostationary satellites are used to broadcast gnss malfunctions using the l2 frequency which includes an additional ranging signal to augment the signals from the gps satellites
 Up to 4 geostationary satellites are used to improve accuracy to within 1 m to 2 m horizontally and to advise of any gnss malfunction.
Up to 4 geostationary satellites are used to improve accuracy to within 1 m to 2 m horizontally and to advise of any gnss malfunction. A flight is planned to longyear airport in svalbard lat 78°15'n due to the ?
Question 199-19 : Aaim aircraft autonomous integrity monitoring using the irs and barometric altimeter aaim aircraft autonomous integrity monitoring using the vor and dme gbas using the dme only gbas using the ins and barometric altimeter
 Aaim (aircraft autonomous integrity monitoring) using the irs and barometric altimeter.
Aaim (aircraft autonomous integrity monitoring) using the irs and barometric altimeter. What is one of the primary tasks of the space segment of navstar/gps ?
Question 199-20 : Transmitting signals which can be used by suitable receivers to determine time position and velocity transmitting signals to suitable receivers and monitoring the orbital planes autonomously monitoring the satellites' orbits and status computing the user position from the receiver user messages and transmitting the computed position back to the user segment
 Transmitting signals which can be used, by suitable receivers, to determine time, position and velocity.
Transmitting signals which can be used, by suitable receivers, to determine time, position and velocity. What is the meaning of the term receiver autonomous integrity monitoring raim ?
Question 199-21 : It is a technique by which a receiver checks the reliability of the signals it is receiving and can detect if one of the signals is incorrect it is a method whereby a receiver ensures the integrity of the pseudo random noise prn code transmitted by the satellites it is a technique whereby the receivers of the world wide distributed monitor stations ground segment automatically determine the integrity of the navigation message it is the ability of the gps satellites to check the integrity of the data transmitted by the monitoring stations of the ground segment
 It is a technique by which a receiver checks the reliability of the signals it is receiving and can detect if one of the signals is incorrect.
It is a technique by which a receiver checks the reliability of the signals it is receiving and can detect if one of the signals is incorrect. User equivalent range error uere or user range error ure is a signal in space ?
Question 199-22 : Solar winds and gravitational forces of the sun and the moon high solar activity causing variations to the depth of the ionosphere stronger than forecast ionospheric winds and electromagnetic forces jet streams and areas of significant weather along the orbit
 Solar winds and gravitational forces of the sun and the moon.
Solar winds and gravitational forces of the sun and the moon. Some of the inherent errors in navstar/gps signals can be corrected by using a ?
Question 199-23 : Is located in an accurately surveyed position and analyses the received signals to provide an error correction checks the position calculated by the received signals against its own position then sends error signals back to the satellites which correct the errors transmits error information to each satellite where there is a conflict as regards position will only calculate errors in the signals that are being viewed by the users receiver
 Is located in an accurately surveyed position and analyses the received signals to provide an error correction.
Is located in an accurately surveyed position and analyses the received signals to provide an error correction. How many satellites are required for gbas to function correctly ?
Question 199-24 : 4 satellites are required for gbas operations gbas uses the signals from at least 3 geostationary satellites gbas requires at least 5 satellites to detect and exclude the possible faulty satellite gbas uses the exact same satellites as the receiver in the aircraft
 4 satellites are required for gbas operations.
4 satellites are required for gbas operations. What is receiver autonomous integrity monitoring raim ?
Question 199-25 : An aircraft based augmentation system a ground based augmentation system a space based augmentation system an atc based augmentation system
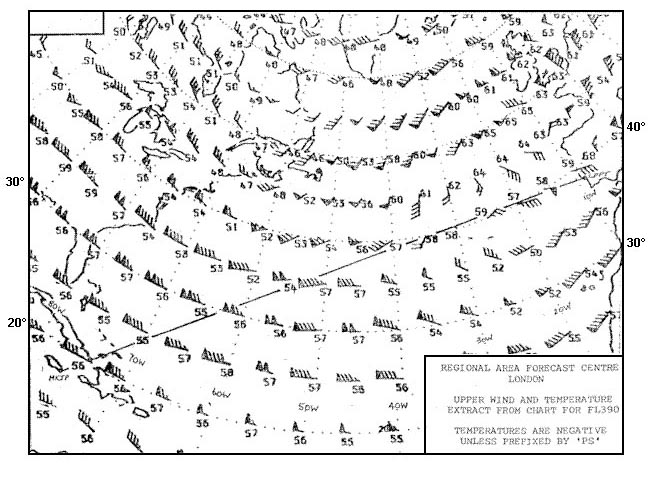 An aircraft-based augmentation system.
An aircraft-based augmentation system. How is gbas information sent from the ground station to the aircraft ?
Question 199-26 : Vhf datalink vhf voice transmission uhf datalink uhf voice transmission
 Vhf datalink.
Vhf datalink. Select the correct statement about the european satellite based augmentation ?
Question 199-27 : Egnos uses up to 4 geostationary satellites to transmit integrity data and ranging signals to aircraft egnos uses at least 1 geostationary satellite to transmit integrity and safety related messages to aircraft egnos uses at least 3 geostationary satellites to transmit receiver clock error and integrity data egnos uses up to 2 geostationary satellites to transmit ranging signals in the l2 frequency
 Egnos uses up to 4 geostationary satellites to transmit integrity data and ranging signals to aircraft.
Egnos uses up to 4 geostationary satellites to transmit integrity data and ranging signals to aircraft. What is true about the visibility of navstar gps satellites ?
Question 199-28 : Visibility varies depending on time and position of the observer visibility is greatest at the poles visibility is greatest at the equator visibility is the same across the entire globe
 Visibility varies depending on time and position of the observer.
Visibility varies depending on time and position of the observer. With regards to icao annex 10 volume 1 gps and glonass ?
Question 199-29 : Can both be used in a suitably equipped aircraft as the systems are compatible and their functions are interoperable are two completely separate systems but only gps is capable of providing approved position data can both be used but because their information is not compatible an aircraft cannot use both systems are two separate systems and only gps is covered by eu regulations so only that service can be used by european operators
 Can both be used in a suitably equipped aircraft as the systems are compatible and their functions are interoperable.
Can both be used in a suitably equipped aircraft as the systems are compatible and their functions are interoperable. Which of the following is an aircraft based augmentation system ?
Question 199-30 : Raim gbas sbas waas
 Raim
Raim How many satellites are required for signal reception to perform an independent ?
Question 199-31 : Six four five three
 Six
Six Which pair of factors when brought together can establish the estimate of the ?
Question 199-32 : The user equivalent range error uere and the geometric dilution of precision gdop the time dilution of precision tdop and the geometric dilution of precision gdop the horizontal dilution of precision hdop and vertical dilution of precision vdop the user equivalent range error uere and position dilution of precision pdop
 The user equivalent range error (uere) and the geometric dilution of precision (gdop).
The user equivalent range error (uere) and the geometric dilution of precision (gdop). Egnos european geostationary navigation overlay system informs the users of any ?
Question 199-33 : Data is broadcast from geostationary satellites alerts are sent to all the satellites in view and then re transmitted to the user differential corrections and integrity messages are broadcast every 3 hours the data are broadcast from all satellites with navigation packages
 Data is broadcast from geostationary satellites.
Data is broadcast from geostationary satellites. Gps employs two frequencies l1 and l2 to offer standard positioning service sps ?
Question 199-34 : Sps using only the c/a code while pps requires the p code which is transmitted on both l1 and l2 pps using only the c/a code while sps requires both the c/a code and the p code transmitted on l1 and l2 pps using both the c/a code and the p code while sps requires the c/a code transmitted on l2 sps using the p code while pps requires both the c/a code and the p code transmitted on l1 and l2
 Sps using only the c/a code, while pps requires the p code, which is transmitted on both l1 and l2.
Sps using only the c/a code, while pps requires the p code, which is transmitted on both l1 and l2. An aircraft is executing the gls rwy 19r approach that is a gnss 1 approach ?
Question 199-35 : 1 precision 2 ground 1 non precision 2 ground 1 precision 2 satellite 1 non precision 2 satellite
 (1) precision; (2) ground
(1) precision; (2) ground What factors contribute to the formation of user equivalent range error uere ?
Question 199-36 : Combination of various errors including selective availability sa ephemeris error ee satellite clock error and atmospheric delays position dilution of precision pdop and ephemeris error ee satellite clock error and tropospheric delay geometric dilution of precision gdop and ionospheric delay
 Combination of various errors including selective availability (sa), ephemeris error (ee), satellite clock error, and atmospheric delays.
Combination of various errors including selective availability (sa), ephemeris error (ee), satellite clock error, and atmospheric delays. Required navigation performance rnp is a concept that applies to navigation ?
Question 199-37 : Within an airspace within an airspace and with a specific time interval only in an airspace using satellite navigation systems within rnav tracks only
 Within an airspace.
Within an airspace. According to annex 6 rnp type is defined as a containment value expressed as a ?
Question 199-38 : I nautical miles ii 95% i nautical miles ii 90% i kilometers ii 95% i kilometers ii 90%
 (i) nautical miles (ii) 95%
(i) nautical miles (ii) 95% According to annex 6 what is the definition of required navigation performance ?
Question 199-39 : A statement of the navigation performance necessary for operation within a defined airspace a statement of the navigation performance required during a pilot skill test a statement of the navigation performance necessary during flight tests for a new aircraft type a statement of the navigation performance required when installing a new navigation aid on the ground
 A statement of the navigation performance necessary for operation within a defined airspace.
A statement of the navigation performance necessary for operation within a defined airspace. Which of the following statements best describes pbn performance based ?
Question 199-40 : Is not sensor specific is similar to conventional navigation requiring ground based infrastructure requires the development of sensor specific routes and procedures is based on sensor specific navigation specifications
 Is not sensor-specific.
Is not sensor-specific. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7919 Free Training Exam
