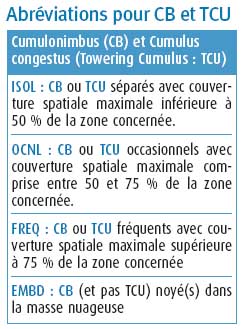
What is the primary use of the radar fitted onboard a modern civilian transport ? [ Answer reports ]
Question 195-1 : Detecting areas of wet convective weather transmitting data to atc for surveillance purposes detecting other aircraft providing the main input to an anti collision system
 Detecting areas of wet, convective weather.
Detecting areas of wet, convective weather. Radar has many uses in civil aviation for which tasks are both primary and ?
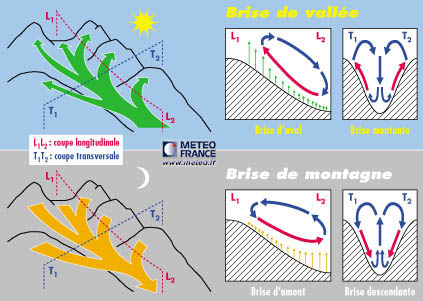
Question 195-2 : For atc to provide tracking of aircraft and manage traffic within a given airspace for the pilot to navigate and avoid areas of significant weather for atc to reduce the workload of the pilot by taking over the task of navigating for the pilot to detect other aircraft and reduce the risk of collision
 For atc to provide tracking of aircraft and manage traffic within a given airspace.
For atc to provide tracking of aircraft and manage traffic within a given airspace. A mode s transponder knows that it is receiving interrogations from a mode s ?
Question 195-3 : Extra pulses are transmitted directly following the mode a and mode c pulses the ground interrogator will transmit extra pulses once it has had the initial reply from the airborne transponder the ground interrogator transmits the same pulses for all modes but for mode s the pulses are stronger only pulses specific to mode s are transmitted by the ground interrogator
 Extra pulses are transmitted directly following the mode a and mode c pulses.
Extra pulses are transmitted directly following the mode a and mode c pulses. The pilot is given a 25 ft altitude increment which ssr mode does this apply to ?
Question 195-4 : Mode s mode a mode c mode a and c
 Mode s
Mode s A primary surveillance radar psr is capable of calculating a ?
Question 195-5 : Two dimensional position by measuring the bearing and travel time of the interrogation signal one dimensional position by measuring the bearing of the interrogation signal four dimensional position by measuring the bearing travel time height and time of the interrogation signal three dimensional position by measuring the bearing travel time and height of the interrogation signal
 Two-dimensional position by measuring the bearing and travel time of the interrogation signal.
Two-dimensional position by measuring the bearing and travel time of the interrogation signal. A primary route surveillance radar provides ?
Question 195-6 : Direction by measuring antenna azimuth range by signal travel during time no altitude 4 digit squawk code no direction no range no altitude altitude by angle elevation direction by antenna's angle of azimuth no range range by interrogating dme transponder altitude by interrogating mode c transponder no direction
 Direction by measuring antenna azimuth, range by signal travel during time, no altitude.
Direction by measuring antenna azimuth, range by signal travel during time, no altitude. A functional mode s transponder interrogated in mode a what is provided to the ?
Question 195-7 : Transponder code only transponder code and pressure altitude transponder code pressure altitude and aircraft address transponder code pressure altitude aircraft address and other flight data
 Transponder code only.
Transponder code only. In a satellite assisted navigation system gnss/gps a fix is obtained by ?
Question 195-8 : Measuring the time taken for a minimum number of satellites' transmissions in known positions to reach the aircraft's receiver the aircraft's receiver measuring the phase angle of signals received from a number of satellites in known positions measuring the time taken for an aircraft's transmissions to travel to a number of satellites in known positions and return to the aircraft's receiver measuring the pulse lengths of signals received from a minimum number of satellites received in a specific sequential order
 Measuring the time taken for a minimum number of satellites' transmissions, in known positions, to reach the aircraft's receiver.
Measuring the time taken for a minimum number of satellites' transmissions, in known positions, to reach the aircraft's receiver. What is the minimum number of satellites required by a gps in order to obtain a ?
Question 195-9 : 4 24 3 5
 4.
4. Gps satellites transmit on two l band frequencies with different types of ?
Question 195-10 : L1 coarse acquisition c/a with selected availability s/a l2 coarse acquisition c/a l1 precise p l2 for communications purpose
 L1-coarse acquisition (c/a) with selected availability (s/a).
L1-coarse acquisition (c/a) with selected availability (s/a). Which of the following coordinate systems is used by the navstar/gps receiver ?
Question 195-11 : Wgs 84 ed 87 ed 50 pz 90
 Wgs 84.
Wgs 84. Which of the following lists all the parameters that can be determined by a gps ?
Question 195-12 : Latitude longitude altitude and time latitude and longitude latitude longitude and time latitude longitude and altitude
 Latitude, longitude, altitude and time.
Latitude, longitude, altitude and time. In a satellite assisted navigation system gnss/gps a position line is obtained ?
Question 195-13 : Timing the period that is taken for a satellite's transmission to reach the aircraft's receiver the aircraft's receiver measuring the phase angle of the signal received from a satellite in a known position timing the period that is taken for a transmission from the aircraft's transmitter/receiver to reach and return from a satellite in a known position the aircraft's receiver measuring the time difference between signals received from a minimum number of satellites
 Timing the period that is taken for a satellite's transmission to reach the aircraft's receiver.
Timing the period that is taken for a satellite's transmission to reach the aircraft's receiver. In which frequency band do satellite assisted navigation systems gnss/gps ?
Question 195-14 : Uhf shf ehf vhf
 Uhf.
Uhf. What is the minimum number of satellites required for the navstar/gps to carry ?
Question 195-15 : 3 24 5 2
 3.
3. Ignoring pulse length the maximum pulse repetition frequency prf that can be ?
Question 195-16 : 405 pps 782 pps 308 pps 810 pps
 405 pps.
405 pps. Which of the following lists are all errors that affect the accuracy and ?
Question 195-17 : Satellite clock satellite ephemeris atmospheric propagation satellite mutual interference satellite ephemeris atmospheric propagation satellite to ground time lag atmospheric propagation satellite clock satellite mutual interference frequency drift satellite to ground time lag
 Satellite clock; satellite ephemeris; atmospheric propagation.
Satellite clock; satellite ephemeris; atmospheric propagation. In order to carry out an independent three dimensional fix receiver autonomous ?
Question 195-18 : 6 7 5 4
 6.
6. Signal reception is required from a minimum number of satellites that have ?
Question 195-19 : 4 6 5 3
 4.
4. The distance between a navstar/gps satellite and receiver is ?
Question 195-20 : Determined by the time taken for the signal to arrive from the satellite multiplied by the speed of light calculated from the doppler shift of the known frequencies calculated using the wgs 84 reference system from the known positions of the satellite and the receiver determined by the phase shift of the pseudo random noise code multiplied by the speed of light
 Determined by the time taken for the signal to arrive from the satellite multiplied by the speed of light.
Determined by the time taken for the signal to arrive from the satellite multiplied by the speed of light. The reason why the measured distance between a navstar/gps satellite navigation ?
Question 195-21 : Calculated range includes receiver clock error measured distance is based on the pseudo random noise code movement of satellite and receiver during the distance calculation is not taken into account calculated range is based on an idealised keplerian orbit
 Calculated range includes receiver clock error.
Calculated range includes receiver clock error. What type of satellite navigation system navstar/gps receiver is most suitable ?
Question 195-22 : Multichannel sequential multiplex any hand held type
 Multichannel.
Multichannel. The receiver aerial for a navstar/gps system should be mounted ?
Question 195-23 : On the upper side of the fuselage in the vicinity of the centre of gravity inside the tail fin to minimise the influence of reflections from the wing and fuselage in the vicinity of the receiver to avoid long transmission lines under the fuselage in order to receive correction data transmitted by d gps stations
 On the upper side of the fuselage in the vicinity of the centre of gravity.
On the upper side of the fuselage in the vicinity of the centre of gravity. In the navstar/gps satellite navigation system re use of selective availability ?
Question 195-24 : Dithering the satellite clock shutting off selected satellites using a less accurate atomic clock in a satellite for signal processing offsetting satellite atomic clocks by a predetermined constant amount
 Dithering the satellite clock.
Dithering the satellite clock. In the event of the re use of selective availability how does this affect if at ?
Question 195-25 : It degrades position accuracy by manipulating satellite signals it increases because only signals from satellites in the most suitable geometric constellation are selected by the receiver it has no influence because by selecting of the most suitable signals the computing process in the receiver is quicker it degrades accuracy by reducing the number of available satellites
 It degrades position accuracy by manipulating satellite signals.
It degrades position accuracy by manipulating satellite signals. In the navstar/gps satellite navigation system receiver clock error ?
Question 195-26 : Is corrected by using signals from four satellites is the biggest part of the total error it cannot be corrected can be minimised by synchronisation of the receiver clock with the satellite clocks is negligible small because of the great accuracy the atomic clocks installed in the satellites
 Is corrected by using signals from four satellites.
Is corrected by using signals from four satellites. The influence of the ionosphere on the accuracy of the satellite navigation ?
Question 195-27 : Minimised by the receiver using a model of the atmosphere and comparing signals transmitted by the satellites minimised by computing the average of all signals only significant if the satellites are located at a small elevation angle above the horizon negligible
 Minimised by the receiver using a model of the atmosphere and comparing signals transmitted by the satellites.
Minimised by the receiver using a model of the atmosphere and comparing signals transmitted by the satellites. What are the effects if any of shadowing by parts of the aircraft e g wing on ?
Question 195-28 : It may prevent the reception of signals it causes multipath propagation the signals will be distorted however the error can be corrected for using an algorithm and information from unaffected signals it has no influence because high frequency signals are unaffected
 It may prevent the reception of signals.
It may prevent the reception of signals. Which of the following geometric satellite constellations provides the most ?
Question 195-29 : 3 satellites with a low elevation above the horizon and an azimuth of 120° from each other together with a fourth directly overhead 3 satellites with an azimuth of 120° from each other and an elevation of 45° above the horizon 4 satellites with an azimuth of 90° from each other and a low elevation above the horizon 4 satellites with an azimuth of 90° from each other and an elevation of 45° above the horizon
 3 satellites with a low elevation above the horizon and an azimuth of 120° from each other together with a fourth directly overhead.
3 satellites with a low elevation above the horizon and an azimuth of 120° from each other together with a fourth directly overhead. In relation to the navstar/gps satellite navigation system what is involved in ?
Question 195-30 : Fixed ground stations compute position errors and transmit correction data to a suitable receiver on the aircraft the difference between signals transmitted on the l1 and l2 frequencies are processed by the receiver to determine an error correction receivers from various manufacturers are operated in parallel to reduce the characteristic receiver noise error signals from satellites are received by 2 different antennas which are located a fixed distance apart this enables a suitable receiver on the aircraft to recognise and correct for multipath errors
 Fixed ground stations compute position errors and transmit correction data to a suitable receiver on the aircraft.
Fixed ground stations compute position errors and transmit correction data to a suitable receiver on the aircraft. Which of the following statements about the accuracy that can be obtained with ?
Question 195-31 : The nearer a receiver is situated to a d gps ground station the more accurate the position fix only d gps allows position fixes accurate enough for 'non precision approaches' the increase in accuracy of position fixes is independent of the receiver position in relation to a d gps ground station a d gps receiver can detect and correct for sa providing a more accurate position fix
 The nearer a receiver is situated to a d-gps ground station, the more accurate the position fix.
The nearer a receiver is situated to a d-gps ground station, the more accurate the position fix. How does a receiver of the navstar/gps satellite navigation system determine ?
Question 195-32 : It calculates it by using almanac data transmitted by the satellites the data is stored in the receiver together with the pseudo random noise prn code the data is based on the direction to the satellite determined at the location of the antenna the data is determined by the satellite and transmitted together with the navigation message
 It calculates it by using almanac data transmitted by the satellites.
It calculates it by using almanac data transmitted by the satellites. In relation to the navstar/gps satellite navigation system 'search the sky' is a ?
Question 195-33 : Procedure that starts after switching on a receiver if there is no stored satellite data available continuous process by the ground segment to monitor the gps satellites procedure performed by the receiver to recognise new satellites becoming operational continuous procedure performed by the receiver that searches the sky for satellites rising above the horizon
 Procedure that starts after switching on a receiver if there is no stored satellite data available.
Procedure that starts after switching on a receiver if there is no stored satellite data available. Which of the following if any is a prerequisite if a receiver of a navstar/gps ?
Question 195-34 : The prescribed ifr equipment must be installed and operational the prescribed ifr equipment must be in working correctly and the navigation information continuously displayed the raim function of the gps receiver must be able to monitor all prescribed navigation systems multi sensor systems are not certificated for flights under ifr conditions
 The prescribed ifr-equipment must be installed and operational.
The prescribed ifr-equipment must be installed and operational. Which of the following is the datum for altitude information when conducting ?
Question 195-35 : Barometric altitude the average of gps altitude and barometric altitude gps altitude gps altitude if 4 or more satellites are received otherwise barometric altitude
 Barometric altitude.
Barometric altitude. Which of the following statements about the 'visibility' of navstar/gps ?
Question 195-36 : It varies depending on the time and observer's location it is the same throughout the globe it is greatest at the equator it is greatest at the poles
 It varies, depending on the time and observer's location.
It varies, depending on the time and observer's location. How many operational satellites are required for full operational capability ?
Question 195-37 : 24 18 12 30
 24.
24. Which of the following satellite navigation systems has full operational ?
Question 195-38 : Navstar/gps nnss transit cospas sarsat glonass
 Navstar/gps.
Navstar/gps. Gps system satellites transmit their signals on two carrier waves 1575 mhz and ?
Question 195-39 : Only the 1575 mhz carrier wave and one code only the 1575 mhz carrier wave and two codes only the 1227 mhz carrier wave and one code the two carrier waves and one public code
 Only the 1575 mhz carrier wave and one code.
Only the 1575 mhz carrier wave and one code. Which statement about dilution of precision dop is correct ?
Question 195-40 : The value of dop depends upon the geometry and number of satellites in view the value of dop depends upon the accuracy with which the range between satellite and receiver can be measured the value of dop depends upon the availability of abas the value of dop depends upon the availability of raim software in the gps receiver
 The value of dop depends upon the geometry and number of satellites in view.
The value of dop depends upon the geometry and number of satellites in view. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7759 Free Training Exam
