What are the potential dangers of operating an airborne weather radar awr on ? [ Answer reports ]
Question 194-1 : Harm human beings disturb radio communications with atc disturb nearby airport navigation systems cause misalignment of the aircraft’s air data and inertial reference system adirs
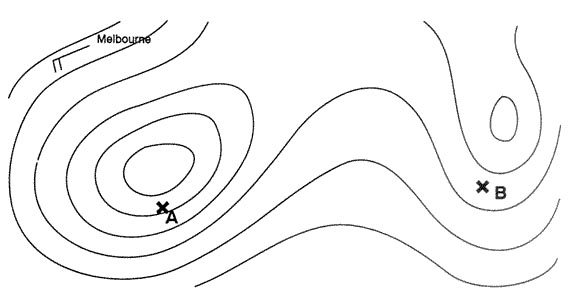 Harm human beings.
Harm human beings. What is an advantage of an ssr with a ‘selective addressing mode’ over ?
Question 194-2 : It allows for unambiguous aircraft identification it is independent from airborne and space based systems its range is unrelated to its transmitting power in case of a transponder malfunction the ssr can be used as a primary radar
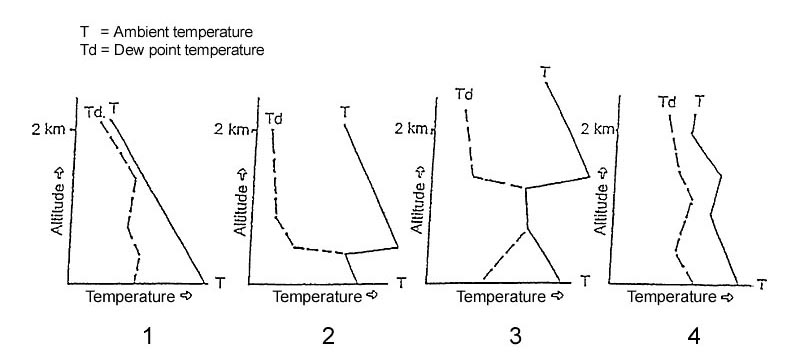 It allows for unambiguous aircraft identification.
It allows for unambiguous aircraft identification. When using awr in the climb what should be done ?
Question 194-3 : Tilt down tilt right tilt up tilt left
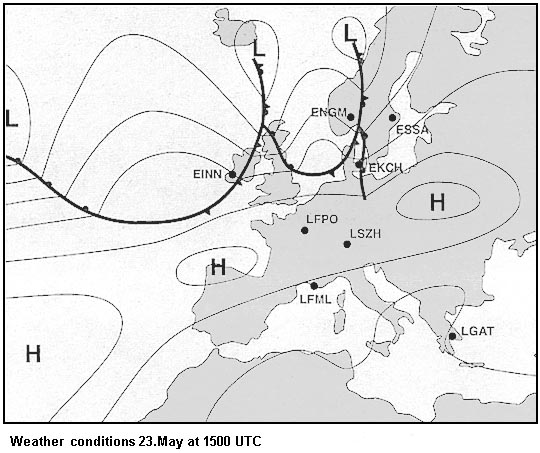 Tilt down
Tilt down What is the difference between a/c all call and a/c/s all call ?
Question 194-4 : Duration of p4 pulse duration p2 pulse presence of p4 pulse amplitude of p4 pulse
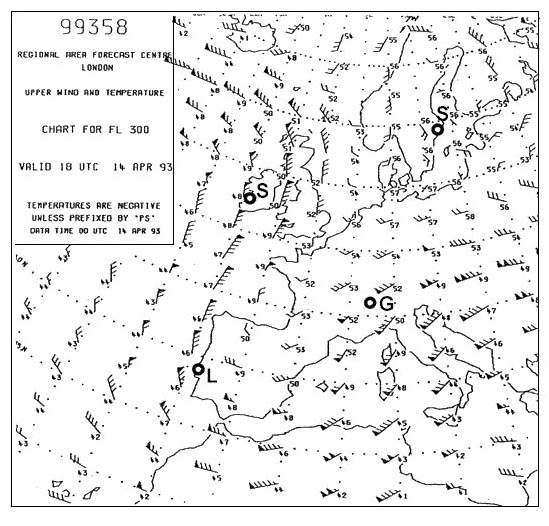 Duration of p4 pulse.
Duration of p4 pulse. Which statement is correct regarding the airborne weather radar and it autotilt ?
Question 194-5 : It adjusts its tilt according to the altitude it adjusts its tilt according to the bank angle it adjusts its tilt on the ground to avoid harming ground personnel it adjusts its tilt according to the attitude
 It adjusts its tilt according to the altitude.
It adjusts its tilt according to the altitude. Which of the following statements is correct about the 'gain' knob of an awr ?
Question 194-6 : It adjusts the receiver sensitivity in order to achieve optimum target acquisition it adjusts the brightness of the display it can be used to activate the automatic gain control of the awr it is used to adjust antenna tilt
 It adjusts the receiver sensitivity in order to achieve optimum target acquisition.
It adjusts the receiver sensitivity in order to achieve optimum target acquisition. One of the advantages of the secondary surveillance radar ssr systems over the ?
Question 194-7 : Atc ssr systems can interrogate aircraft transponders and elicit replies atc ssr systems have moving target indicator capability which eliminates clutter so more aircraft can be tracked atc ssr systems permanently interrogate aircraft within range so the tracking is not interrupted atc ssr systems can reply to an aircraft interrogation and provide requested information
 Atc ssr systems can interrogate aircraft transponders and elicit replies.
Atc ssr systems can interrogate aircraft transponders and elicit replies. Complete the following statement . on a multicolor awr magenta indicates a ?
Question 194-8 : Rainfall intensity lightning intensity turbulence intensity rainfall gradient
 Rainfall intensity.
Rainfall intensity. During the flight you observe that what you saw as one return on your awr ?
Question 194-9 : This is normal since with decreasing range the beam width azimuth will also decrease the awr is malfunctioning and the information cannot be trusted this is due to unwanted returns from contamination on the radome this is a function that shows areas of cat
 This is normal since with decreasing range the beam width azimuth will also decrease.
This is normal since with decreasing range the beam width azimuth will also decrease. Regarding the awr what is the shadowing effect ?
Question 194-10 : A cloud behind another cloud which cannot be detected the aircraft’s parts hiding the awr antenna vor signal not received due to man built infrastructures i e buildings reduction of signal strength during transmission
 A cloud behind another cloud which cannot be detected.
A cloud behind another cloud which cannot be detected. How should one avoid a thunderstorm ?
Question 194-11 : Fly on the upwind side of the storm avoiding red and magenta coloured areas on the screen fly 5 nm to the side of the thunderstorm fly through avoiding magenta on your awr fly through turning on the anti icing equipment available
 Fly on the upwind side of the storm, avoiding red and magenta coloured areas on the screen.
Fly on the upwind side of the storm, avoiding red and magenta coloured areas on the screen. Mode s transponders receive interrogations from ?
Question 194-12 : Ssr ground station and tcas ssr ground station and awr ground station mode c transponders and ground stations only
 Ssr ground station and tcas.
Ssr ground station and tcas. State which information can be presented on the atc display system .1 pressure ?
Question 194-13 : 1 2 3 and 4 1 3 and 4 2 4 and 5 1 2 3 and 5
 1, 2, 3, and 4.
1, 2, 3, and 4. No radar returns are received from an area which is located behind an area ?
Question 194-14 : The weather conditions are unknown the area is clear from precipitation there is less intense precipitation the precipitation is more intense
 The weather conditions are unknown.
The weather conditions are unknown. Complete the following sentence . the secondary surveillance radar ssr mode s ?
Question 194-15 : 1 ssr modes a and c 2 automatic dependent surveillance broadcast ads b 1 airborne weather radar awr 2 the traffic alert and collision avoidance system tcas 1 distance measuring equipment dme 2 enhanced vertical tracking 1 the radio altimeter 2 ssr mode c
 (1) ssr modes a and c; (2) automatic dependent surveillance - broadcast (ads-b).
(1) ssr modes a and c; (2) automatic dependent surveillance - broadcast (ads-b). What does the mode s provide information to ?
Question 194-16 : Ssr and tcas dme and radio altimeter awr and tcas ssr and ads b
 Ssr and tcas.
Ssr and tcas. You are flying in an area with several ts you are flying at fl330 what is the ?
Question 194-17 : Tilt down as ice crystals at this level are not reflective tilt up to see how high the cloud tops are in order to fly over it with a suitable margin tilt up in order to see the holes to fly through in between thunderstorms tilt down to account for the curvature of the earth
 Tilt down as ice crystals at this level are not reflective.
Tilt down as ice crystals at this level are not reflective. Mode s transponders can provide vertical tracking by using a altitude ?
Question 194-18 : 25 ft 35 ft 50 ft 100 ft
 25 ft
25 ft Which of the following statements in reference to the display of aircraft on a ?
Question 194-19 : Both the range and bearing to the aircraft can be estimated simultaneously both the range and bearing to the aircraft can be estimated but not simultaneously only the bearing to the aircraft can be estimated only the range to the aircraft can be estimated
 Both the range and bearing to the aircraft can be estimated simultaneously.
Both the range and bearing to the aircraft can be estimated simultaneously. What aircraft system will reply to ssr interrogations ?
Question 194-20 : Mode s transponder automatic dependant surveillance broadcast ads b air data computer adc flight management computer fmc
 Mode s transponder
Mode s transponder When in the wx+t mode what is the airborne weather radar able to detect ?
Question 194-21 : Turbulence by looking for a frequency shift in combination with pulse flattening clear air turbulence at cruising altitude by using doppler techniques with an increased prf pulse repetition frequency thunderstorms with strong updraft and downdraft by measuring static emitted from lightning turbulent clouds by looking for ice crystals in the upper part of a thunderstorm at a reduced wavelength
 Turbulence by looking for a frequency shift in combination with pulse flattening.
Turbulence by looking for a frequency shift in combination with pulse flattening. The following system s can report an aircraft’s altitude to a precision of 25 ?
Question 194-22 : A mode s transponder mode a and mode s transponders a mode c transponder and primary radar mode c and mode s transponders
 A mode s transponder.
A mode s transponder. The airborne weather radar awr is displayed on a coloured screen showing the ?
Question 194-23 : Fly on the upwind side of the thunderstorm and avoid red or magenta coloured areas the areas that have the worst precipitation are coloured yellow and they should be avoided at all times fly towards the area where the contours are the steepest and avoid any areas that are yellow aim to avoid the thunderstorm by at least 5nm so as to avoid any turbulence
 Fly on the upwind side of the thunderstorm and avoid red or magenta coloured areas.
Fly on the upwind side of the thunderstorm and avoid red or magenta coloured areas. How will an ssr interrogation be directed toward a specific aircraft ?
Question 194-24 : With a unique 24 bit address in the interrogation controller pilot data link communications cpdlc will reply with a unique aircraft identifier by limiting the beam width of the ssr transmission the ssr interrogation is directed to the aircraft’s position
 With a unique 24-bit address in the interrogation.
With a unique 24-bit address in the interrogation. How is the special position identification spi pulse transmitted ?
Question 194-25 : By the transponder as a result of the pilot pushing the ident button by the ssr interrogator if it is suspected that responses are received from aircraft that are located in the direction of the side lobes of the interrogator antenna by the ssr interrogator in order to request the identification of an aircraft automatically when the transponder responds to a mode a interrogation
 By the transponder as a result of the pilot pushing the ident button.
By the transponder as a result of the pilot pushing the ident button. The information available on an air traffic controller's screen about an ?
Question 194-26 : 1 ground speed 2 ssr 1 heading 2 primary radar 1 flight level 2 primary radar 1 pitch angle 2 ssr
 (1) ground speed; (2) ssr
(1) ground speed; (2) ssr The crew of a large jet aircraft want to use their airborne weather radar to ?
Question 194-27 : Becomes clear in the area of the storm shows green or yellow in the area of the storm shows magenta in the area of the storm shows hooks and scalloping in the area of the storm
 Becomes clear in the area of the storm.
Becomes clear in the area of the storm. Which of these is one of the main functions of the tilt control on an airborne ?
Question 194-28 : To search for areas of intense precipitation at different levels from the aircraft to keep the transmitter level during the aircraft’s pitch changes to allow the identification of clear air above a developing thunderstorm to allow the pilots to prevent ground personnel being exposed to radiation
 To search for areas of intense precipitation at different levels from the aircraft.
To search for areas of intense precipitation at different levels from the aircraft. Which of the following describes a correct tilt setting for an airborne weather ?
Question 194-29 : During a climb the tilt needs to be decreased to scan for hazardous clouds a high tilt setting is helpful to detect a thunderstorm during a climb during any phase of flight the tilt of the weather radar will always be adjusted to the optimum tilt a low tilt setting should be used during descent if thunderstorms are expected
 During a climb, the tilt needs to be decreased to scan for hazardous clouds.
During a climb, the tilt needs to be decreased to scan for hazardous clouds. Flying at fl330 ahead of you there are thunderstorms above which is the proper ?
Question 194-30 : During a climb the tilt needs to be decreased to scan for hazardous clouds during any phase of flight the tilt of the weather radar will always be adjusted to the optimum tilt a low tilt setting should be used during descent if thunderstorms are expected a high tilt setting is helpful to detect a thunderstorm during a climb
 During a climb, the tilt needs to be decreased to scan for hazardous clouds.
During a climb, the tilt needs to be decreased to scan for hazardous clouds. The control panel of an airborne weather radar awr has a knob for adjusting the ?
Question 194-31 : To adjust the sensitivity of the radar receiver to widen the beam width of the radar signal to adjust the brightness on the display to increase the range on the display
 To adjust the sensitivity of the radar receiver.
To adjust the sensitivity of the radar receiver. On the control panel for an airborne weather radar there is a setting called ?
Question 194-32 : To change the shape and orientation of the transmission beam down toward the ground to assist navigation during the missed approach procedure to display the weather returns as an overlay on a map on the navigation display to display a modified route based on detected areas of intense precipitation
 To change the shape and orientation of the transmission beam down toward the ground.
To change the shape and orientation of the transmission beam down toward the ground. Which of the following types of interrogations will a mode s transponder reply ?
Question 194-33 : Ssr and tcas interrogations ssr and ads b interrogations ssr and primary radar interrogations tcas and ads b interrogations
 Ssr and tcas interrogations.
Ssr and tcas interrogations. In what ways can information from a typical airborne weather radar from a ?
Question 194-34 : Paths through areas of weather may be determined to ensure the safety and comfort of the flight all areas of turbulence may be identified to ensure the safety and comfort of the persons on board it is the prime source for navigating through mountainous areas due to its ability to detect terrain it detects ground features to enable navigation referenced to the ground when flying above clouds
 Paths through areas of weather may be determined to ensure the safety and comfort of the flight.
Paths through areas of weather may be determined to ensure the safety and comfort of the flight. The secondary surveillance radar ssr system used by aircraft transponders is ?
Question 194-35 : 1 interrogations 2 replies 1 transmission of pulse pairs 2 coded pulses 1 interrogations 2 pulse pairs 1 replies 2 interrogations
 (1) interrogations; (2) replies
(1) interrogations; (2) replies In general the operation of an aircraft's airborne weather radar awr whilst on ?
Question 194-36 : Only permitted whilst following certain precautions to safeguard health of ground personnel and to protect equipment totally prohibited unrestrictedly permitted in aerodrome maintenance areas permitted anywhere
 Only permitted whilst following certain precautions, to safeguard health of ground personnel and to protect equipment.
Only permitted whilst following certain precautions, to safeguard health of ground personnel and to protect equipment. A young adult interested in becoming a pilot is invited into the cockpit they ?
Question 194-37 : Detecting significant weather and ground mapping detecting thunderstorms and turbulence ground mapping and controlling the gain of the beam detecting turbulence and functioning in wx+t mode
 Detecting significant weather and ground mapping.
Detecting significant weather and ground mapping. Some of the advantages of secondary surveillance radar ssr in comparison to ?
Question 194-38 : 1 collects more data 2 of the active participation of the aircraft's transponder 1 enables the controller to have a more organised display 2 it uses longer interrogation pulses 1 provides coded replies 2 of its naturally higher transmission power 1 uses smaller aerials 2 it operates at higher frequencies
 (1) collects more data; (2) of the active participation of the aircraft's transponder
(1) collects more data; (2) of the active participation of the aircraft's transponder The tilt of an airborne weather radar is lowered whilst searching for ?
Question 194-39 : The greatest reflectivity occurs from wet hail and rain these elements usually exist in the lower levels of a thunderstorm the greatest reflectivity occurs from dry hail and snow these elements exist mainly in the lower levels of a thunderstorm ground clutter is more evident and therefore less likely to be confused with thunderstorm activity ground clutter enhances the display by automatically turning up the gain and increasing the likelihood of detecting thunderstorm activity
 The greatest reflectivity occurs from wet hail and rain, these elements usually exist in the lower levels of a thunderstorm.
The greatest reflectivity occurs from wet hail and rain, these elements usually exist in the lower levels of a thunderstorm. What is shown on the atc radar screen when the pilot pushes the special ?
Question 194-40 : A flashing indication of the aircraft which is 'squawking ident' a flashing indication of all the aircraft which are not 'squawking ident' the removal of that aircraft from the radar display a flashing indication of all the aircraft on the radar display
 A flashing indication of the aircraft which is 'squawking ident'.
A flashing indication of the aircraft which is 'squawking ident'. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7719 Free Training Exam
