The main advantage of ssr over a primary radar is ? [ Answer reports ]
Question 193-1 : Air traffic control ssr systems can interrogate the transponder of an aircraft and obtain answers air traffic control ssr systems continually interrogating the aircraft in range the follow up is uninterrupted air traffic control ssr systems can respond to an aircraft interrogation and provide the required information ssr has the ability to discriminate mobile targets moving target indicators mti which eliminates returns and permits to track more aircraft
 Air traffic control ssr systems can interrogate the transponder of an aircraft and obtain answers.
Air traffic control ssr systems can interrogate the transponder of an aircraft and obtain answers. What is the accuracy of mode s altitude reporting ?
Question 193-2 : 25 feet 200 feet 100 feet 50 feet
 25 feet.
25 feet. To increase the maximum range of a radar it is necessary to ?
Question 193-3 : Decrease the recurrence frequency and to increase the wavelength decreases the recurrence frequency and the wavelength increase the recurrence frequency and the wavelength increase the recurrence frequency and to decrease the wavelength
 Decrease the recurrence frequency and to increase the wavelength.
Decrease the recurrence frequency and to increase the wavelength. Ssr transponder .with the 'enhanced' mode s additional aircraft parameters can ?
Question 193-4 : Ias vertical rate roll angle angle of attack pitch angle ground speed fuel remaining oat cross track error usable fuel pitch angle
 Ias, vertical rate, roll angle.
Ias, vertical rate, roll angle. An antenna is defined as a ?
Question 193-5 : Wave type transducer for the process of converting a line ac into a free electromagnetic wave transformer for the process of converting ac into a radio wave device used for the purpose of receiving a free electromagnetic radio wave and converting it into an audible frequency wave type transducer for the process of converting a dc into a free electromagnetic wave
 Wave-type transducer for the process of converting a line ac into a free electromagnetic wave.
Wave-type transducer for the process of converting a line ac into a free electromagnetic wave. Ssr transponder .what is involved in enhanced downlink . tas. ground speed. ?
Question 193-6 : Tas ground speed magnetic heading tas eas flight level ground speed magnetic heading course eas course flight level
 Tas, ground speed, magnetic heading.
Tas, ground speed, magnetic heading. Ssr transponder .a mode s surveillance protocols implicitly use the principle ?
Question 193-7 : It permits unambiguous aircraft identification the range does not depend on transmitter power there is no interaction with the air or space segment in the event of an ssr failure it can act as a primary radar
 It permits unambiguous aircraft identification.
It permits unambiguous aircraft identification. A vertical aerial antenna needs the receiver to be oriented in the plane to ?
Question 193-8 : Vertical vertical horizontal vertical horizontal horizontal vertical horizontal
 Vertical, vertical.
Vertical, vertical. Which of the following statements about a primary radar are correct .1 target ?
Question 193-9 : 1 2 3 1 3 2 3 1 2
 1, 2, 3.
1, 2, 3. Ssr transponder mode s enhanced surveillance .the controller's information ?
Question 193-10 : Magnetic heading indicated airspeed vertical rate and selected altitude landing mass aircraft turbulence category computed approach speed magnetic heading altitude and identification pressure altitude flight level flight number or aircraft registration ground speed
 Magnetic heading, indicated airspeed, vertical rate and selected altitude.
Magnetic heading, indicated airspeed, vertical rate and selected altitude. Ssr transponder mode s enhanced surveillance .automatic extraction of an ?
Question 193-11 : Radio telephony workload and will free them to concentrate on ensuring the safe and efficient passage of air traffic attention and may lead to routine errors awareness of the situation and may lead to interpretation errors workload but will increase radio telephony exchanges
 Radio-telephony workload and will free them to concentrate on ensuring the safe and efficient passage of air traffic.
Radio-telephony workload and will free them to concentrate on ensuring the safe and efficient passage of air traffic. Ssr transponder mode s enhanced surveillance .the reduction in radio ?
Question 193-12 : Reduce pilot workload and remove a potential source of error reduce pilot awareness of the situation and may lead to interpretation errors increase attention but may lead to routine errors reduce the static interferences experienced by gps receivers
 Reduce pilot workload and remove a potential source of error.
Reduce pilot workload and remove a potential source of error. Airborne weather radar awr should be used with extreme caution when on the ?
Question 193-13 : It can hurt the ground staff it may interfere with the alignment of the inertial reference system it can disrupt communication with the tower it can disrupt the airport's radio navigation systems
 It can hurt the ground staff.
It can hurt the ground staff. The main disadvantage of using an airborne weather radar awr on the ground is ?
Question 193-14 : Shf waves it emits can damage tissues of the people on whom it radiates reflections on ground and buildings can overheat the radar and switch it off momentarily reflections on ground and buildings are very strong and prevent to see potentially dangerous phenomena when align for take off its antenna can be damaged while taxiing especially on rough runway and taxiway
 Shf waves it emits can damage tissues of the people on whom it radiates.
Shf waves it emits can damage tissues of the people on whom it radiates. Which of the following is a complete list of airborne weather radar antenna ?
Question 193-15 : Roll and pitch pitch and yaw roll and yaw roll pitch and yaw
 Roll and pitch
Roll and pitch In an airborne weather radar that has a colour cathode display increasing ?
Question 193-16 : Green to yellow red magenta yellow to orange red green to red black yellow to amber blue
 Green to yellow, red, magenta.
Green to yellow, red, magenta. Considering a primary radar system what kind of aerials are used ?
Question 193-17 : One directional antenna both for transmitting and for receiving an omnidirectional antenna for transmitting and a directional antenna for receiving a directional antenna for transmitting and an omnidirectional antenna for receiving one directional antenna for transmitting and one for receiving
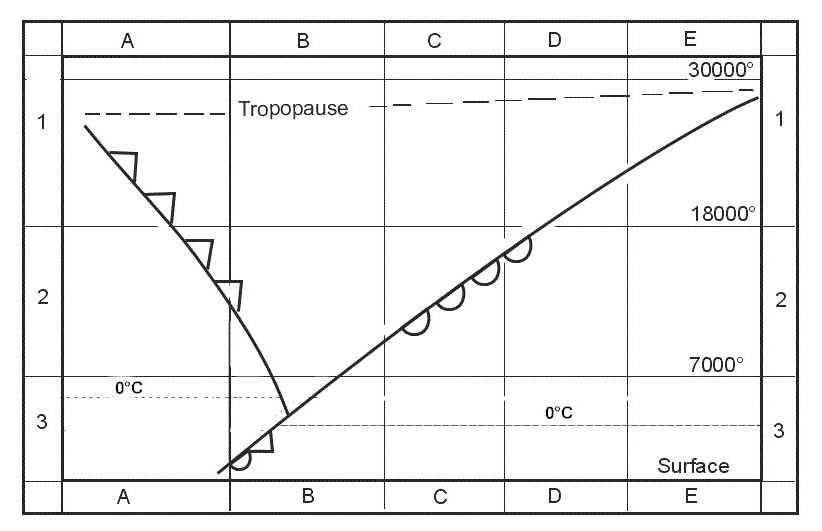 One directional antenna both for transmitting and for receiving.
One directional antenna both for transmitting and for receiving. What information may be displayed on an atc radar screen connected only to a ?
Question 193-18 : Aircraft position only aircraft altitude aircraft position and ssr code aircraft position ssr code and altitude
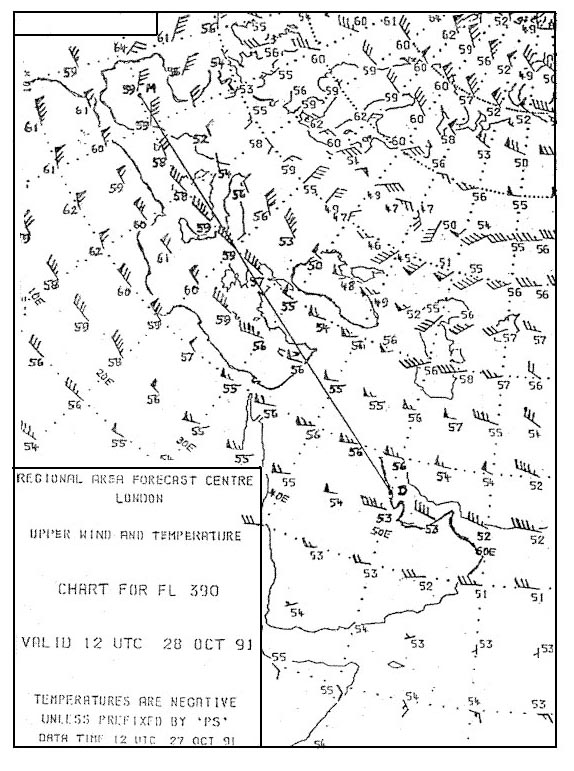 Aircraft position only.
Aircraft position only. Airborne weather radar has been primarily developed to detect ?
Question 193-19 : The kinds of intense precipitation which are usually accompanied by turbulence all kinds of frozen precipitation such as hail snow and graupel areas of wind shear and severe aircraft icing areas of severe clear air turbulence
 The kinds of intense precipitation which are usually accompanied by turbulence.
The kinds of intense precipitation which are usually accompanied by turbulence. An airborne transponder can provide coded reply signals in response to ?
Question 193-20 : Ground secondary surveillance radar and from aircraft equipped with tcas primary ground radar and from aircraft equipped with a transponder ground secondary surveillance radar and from aircraft equipped with a mode a and c transponder ground secondary surveillance radar and from primary ground radar
 Ground secondary surveillance radar and from aircraft equipped with tcas.
Ground secondary surveillance radar and from aircraft equipped with tcas. A mode c transponder is able to report the pressure altitude in ?
Question 193-21 : 100 ft increments 100 m increments 50 m increments 25 ft increments
 100 ft increments.
100 ft increments. Why should airborne weather radar awr systems be used with extreme caution when ?
Question 193-22 : People could be exposed to super high frequency shf radiation which if absorbed in large enough amounts can lead to tissue damage the radar system may overheat and shut down due to the intensity of the returns from the ground buildings and surrounding terrain the radar antenna can be easily damaged during ground taxi manoeuvres especially on uneven taxiways the intense returns from the ground and surrounding terrain will not allow accurate identification of potentially hazardous weather when lined up for departure
 People could be exposed to super high frequency (shf) radiation which, if absorbed in large enough amounts, can lead to tissue damage.
People could be exposed to super high frequency (shf) radiation which, if absorbed in large enough amounts, can lead to tissue damage. Which data can be determined and displayed by atc secondary surveillance radar ?
Question 193-23 : Psr target range and bearing ssr target range and bearing aircraft identification codes aircraft altitude selective addressing and full two way data link psr target range bearing and aircraft altitude ssr target range and bearing aircraft identification codes aircraft height selective addressing and full two way data link psr target range ssr target range and bearing aircraft altitude and height selective addressing and full two way data link psr target range bearing and aircraft identification ssr aircraft identification codes aircraft altitude selective addressing and full two way data link
 Psr: target range and bearing. ssr: target range and bearing, aircraft identification codes, aircraft altitude, selective addressing, and full two-way data link.
Psr: target range and bearing. ssr: target range and bearing, aircraft identification codes, aircraft altitude, selective addressing, and full two-way data link. The main factor which determines the minimum range that can be measured by a ?
Question 193-24 : Pulse length pulse amplitude pulse frequency pulse repetition rate
 Pulse length.
Pulse length. The airborne weather radar ?
Question 193-25 : May receive no reflections from a thunderstorm in an area behind a heavy rain shower uses circular polarisation in order to reduce echoes of heavy showers has a second transmitter working on a lower frequency in order to penetrate rain showers has the possibility to detect clear air turbulence behind a thunder storm by measuring phase differences caused by the doppler effect
 May receive no reflections from a thunderstorm in an area behind a heavy rain shower.
May receive no reflections from a thunderstorm in an area behind a heavy rain shower. What determines the operating mode a or c of the ssr transponder ?
Question 193-26 : The time interval between the pulses p1 and p3 the position of the spi pulse the difference in amplitude of the pulses p1/p3 and p2 the travel time of the pulses transmitted by the interrogator
 The time interval between the pulses p1 and p3.
The time interval between the pulses p1 and p3. Airborne weather radar systems use a wavelength of approximately 3 cm in order ?
Question 193-27 : Detect larger water droplets obtain optimum use of the cosecant squared beam transmit at a higher pulse repetition frequency for extended range detect small as well as large cloud formations
 Detect larger water droplets.
Detect larger water droplets. What beam is used in the mapping mode of an airborne weather radar that can ?
Question 193-28 : A cosecant squared beam effective up to a maximum of 50 nm to 60 nm a cosecant squared beam effective up to a range of 150 nm a pencil beam effective up to a maximum range of 60 nm a pencil beam effective up to a range of 150 nm
 A cosecant squared beam effective up to a maximum of 50 nm to 60 nm.
A cosecant squared beam effective up to a maximum of 50 nm to 60 nm. Ground secondary surveillance radar ssr equipment incorporates a transmitter ?
Question 193-29 : Transmits on 1030 mhz and receives on 1090 mhz transmits on 1090 mhz and receives on 1030 mhz transmits and receives on 1030 mhz transmits and receives on 1090 mhz
 Transmits on 1030 mhz and receives on 1090 mhz.
Transmits on 1030 mhz and receives on 1090 mhz. Ignoring pulse length the maximum pulse repetition frequency prf that can be ?
Question 193-30 : 405 pps 810 pps 782 pps 308 pps
 405 pps.
405 pps. To double the effective range of a primary radar the power output must be ?
Question 193-31 : 16 8 2 4
 16.
16. The prime factor in determining the maximum unambiguous range of a primary ?
Question 193-32 : Pulse repetition frequency size of the parabolic receiver aerial power output height of the transmitter above the ground
 Pulse repetition frequency.
Pulse repetition frequency. Airborne weather radars are generally based on the use of ?
Question 193-33 : Primary radar in the shf band secondary radar in the vhf band secondary radar in the shf band primary radar in the uhf band
 Primary radar in the shf band.
Primary radar in the shf band. Which of the following types of radar equipment operate by means of the pulse ?
Question 193-34 : 1 2 3 and 4 1 2 and 4 only 2 3 and 4 only 2 and 4 only
 1, 2, 3 and 4
1, 2, 3 and 4 Which of the following phenomena is least likely to be detected by radar ?
Question 193-35 : Clear air turbulence wet snow and turbulence in cloud that has precipitation turbulence in cloud that has precipitation precipitation
What equipment works on the interrogator/transponder principle ?
Question 193-36 : Secondary surveillance radar ssr airborne weather radar awr aerodrome surface movement radar global positioning system gps
 Secondary surveillance radar (ssr)
Secondary surveillance radar (ssr) If the airborne weather radar system is fitted with an auto tilt function what ?
Question 193-37 : Based on the altitude of the aircraft to tilt fully down when taxiing to reduce the possibility of injury to ground personnel to track the areas with the greatest intensity of precipitation based on the attitude of the aircraft
 Based on the altitude of the aircraft.
Based on the altitude of the aircraft. To improve the detection of precipitation area s in e g thunderstorms in which ?
Question 193-38 : Lower when the aircraft climbs to a higher altitude higher when the aircraft climbs to a higher altitude lower when the selected range increases higher when the selected range decreases
When using airborne weather radar in the mapping mode in polar areas one runs ?
Question 193-39 : Mistaking the edge of coastal ice off shore for the real coastline aurora borealis polar light causing false returns getting a distorted picture because of ice reflection underestimating distances because the cold seawater is causing super refraction
In order to provide an air traffic services ats surveillance service what ?
Question 193-40 : Any map information needed to provide the surveillance service and when available the aircraft identification and level any map information needed to provide the surveillance service aircraft speed and when available the aircraft identification and level level speed vertical speed an overlay of the terrain and when available the aircraft identification and destination an overlay of the terrain and the aircraft identification speed vertical speed and level
 Any map information needed to provide the surveillance service, and (when available) the aircraft identification and level.
Any map information needed to provide the surveillance service, and (when available) the aircraft identification and level. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7679 Free Training Exam
