Airborne weather radar has been primarily developed to detect ? [ Answer reports ]
Question 192-1 : The kinds of precipitation which are usually accompanied by turbulence areas of severe clear air turbulence all kinds of frozen precipitation such as hail snow and graupel areas of wind sheer and severe aircraft icing
 The kinds of precipitation which are usually accompanied by turbulence.
The kinds of precipitation which are usually accompanied by turbulence. When an operator increases the range on a radar display in general ?
Question 192-2 : The prf becomes lower and the pulse length larger both the prf and the pulse length increase the prf becomes higher and the pulse length smaller both the prf and the pulse length decrease
 The prf becomes lower and the pulse length larger.
The prf becomes lower and the pulse length larger. The heaviest turbulence is likely to be encountered ?
Question 192-3 : Where the area of heaviest precipitation is closest to the edge of the thunderstorm cell in the area of heaviest precipitation about halfway between two thunderstorm cells in the very core of a thunderstorm cell
 Where the area of heaviest precipitation is closest to the edge of the thunderstorm cell.
Where the area of heaviest precipitation is closest to the edge of the thunderstorm cell. When using airborne weather radar in the mapping mode in polar areas one runs ?
Question 192-4 : Of mistaking the edge of coastal ice off shore for the real coastline of getting a distorted picture because of ice reflection of aurora borealis polar light causing false returns of underestimating distances because the cold seawater is causing super refraction
 Of mistaking the edge of coastal ice off shore for the real coastline.
Of mistaking the edge of coastal ice off shore for the real coastline. The three main components of vor airborne equipment are ?
Question 192-5 : Receiver antenna display receiver phase comparator range gate demodulator antenna cdu display pulse generator phase comparator
 Receiver, antenna, display.
Receiver, antenna, display. The pictures at reference are showing an aircraft's position with respect to ?
Question 192-6 : Increase the range setting of his radar switch over from normal to wx mode initiate a steep climb select the cosecant square beam for better alley detection
 Increase the range setting of his radar.
Increase the range setting of his radar. The 'gain' control knob of an awr airborne weather radar adjusts ?
Question 192-7 : The receiver sensitivity in order to achieve optimum target acquisition the brightness of the display the automatic gain control of the awr is activated the power level of the transmitted energy is made dependent on the selected range
 The receiver sensitivity in order to achieve optimum target acquisition.
The receiver sensitivity in order to achieve optimum target acquisition. Which statement is correct with respect to selections on the transponder ?
Question 192-8 : With alt selected a reply in the modes a c and s can be transmitted the correct icao 24 bits aircraft address code must be inserted on the control panel with on selected a reply in the modes a c and s can be transmitted with the selector knobs the four digits of the squawk can be selected using the decimal symbols 0 through 9
 With alt selected a reply in the modes a, c and s can be transmitted.
With alt selected a reply in the modes a, c and s can be transmitted. Echoes that do not change in distance from the antenna relative speed zero of a ?
Question 192-9 : The moving target indicator mti eliminates such echoes the radar is not able to display two echoes moving in the same direction the mti does not recognise this as a moving object due to the blind speed the frequency of the transmitted radar signals changes too much by the doppler effect
 The moving target indicator (mti) eliminates such echoes.
The moving target indicator (mti) eliminates such echoes. Mode s.the allocation of 24 bit aircraft addresses is described in the icao ?
Question 192-10 : Every aircraft will have been allocated with an icao aircraft address which is hard coded into the airframe military aircraft will have been allocated with an icao aircraft address which is hard coded into the transponder civil aircraft will have been allocated with an icao aircraft address which is hard coded into the airframe every aircraft will have been allocated with a nato aircraft address which is hard coded into the airframe
 Every aircraft will have been allocated with an icao aircraft address which is hard coded into the airframe.
Every aircraft will have been allocated with an icao aircraft address which is hard coded into the airframe. Mode s.how does a ground interrogation signal mode a and c is transmitted to a ?
Question 192-11 : In the form of pairs of interrogative pulses with an additional control pulse in the form of pairs of pulses by using the long p4 pulse in the form of a series of pulses and a special position identification spi pulse
 In the form of pairs of interrogative pulses with an additional control pulse.
In the form of pairs of interrogative pulses with an additional control pulse. The magnetic heading of an aircraft is 040° on the airborne weather radar ?
Question 192-12 : 49°25'n 007°30'w 48°50'n 006°22'w 49°35'n 007°36'w 49°45'n 007°42'w
 (49°25'n , 007°30'w)
(49°25'n , 007°30'w) The airborne weather radar ?
Question 192-13 : May receive no reflections from a thunderstorm in an area behind a heavy rain shower has a second transmitter working on a lower frequency in order to penetrate rain shower has the possibility to detect clear air turbulence deviates downward whatever the attitude of the aircraft is
 May receive no reflections from a thunderstorm in an area behind a heavy rain shower.
May receive no reflections from a thunderstorm in an area behind a heavy rain shower. The spacing between the two pulses transmitted by an ssr interrogator determines ?
Question 192-14 : What mode is used the identification of the ssr what service may be provided by the ssr the atc code to be set in the aircraft
 What mode is used.
What mode is used. When the atc transponder 'ident' button is pressed by the pilot ?
Question 192-15 : The airplane's symbol on the controller's display will flash or 'fill in' the airplane's identification will be sent to all ssrs within range mode a will automatically be selected the controller will be urged to identify the airplane
 The airplane's symbol on the controller's display will flash or 'fill in'.
The airplane's symbol on the controller's display will flash or 'fill in'. On a typical computer generated ssr display the following data on a particular ?
Question 192-16 : Squawk code flight level ground speed airplane callsign squawk code flight level true heading airplane callsign squawk code magnetic heading ground speed airplane callsign destination flight level ground speed airplane callsign
 Squawk code, flight level, ground speed, airplane callsign.
Squawk code, flight level, ground speed, airplane callsign. In the ssr response the operation of the transponder 'ident' button ?
Question 192-17 : Sends a special pulse after the normal response pulse train transmits the aeroplanes registration or flight number as a data coded sequence sends a special pulse in the x position on the pulse train sends a special pulse before the normal response pulse train
 Sends a special pulse after the normal response pulse train.
Sends a special pulse after the normal response pulse train. Which one of the following switch positions should be used when selecting a ?
Question 192-18 : Stby standby off normal ident identification
 Stby (standby).
Stby (standby). In the ssr terminology 'de fruiting' means ?
Question 192-19 : The removal from the display of random responses removing all different colors from the display making it a mono color display displaying only airplanes with a selected destination displaying only airplanes changing their altitude
 The removal from the display of random responses.
The removal from the display of random responses. The selection of code 2000 on an aircraft ssr transponder indicates ?
Question 192-20 : Entry into airspace from an area where ssr operation has not been required an emergency unlawful interference with the planned operation of the flight transponder malfunction
 Entry into airspace from an area where ssr operation has not been required.
Entry into airspace from an area where ssr operation has not been required. With ssr interrogation and response signals ?
Question 192-21 : Are standard frequencies separated by 60 mhz are separated by 63 mhz must be set by the pilot but are always 60 mhz apart are at variable frequencies set by the controller but are always 63 mhz apart
 Are standard frequencies separated by 60 mhz.
Are standard frequencies separated by 60 mhz. Using ssr the normal transmission from the atc transponder in the aircraft ?
Question 192-22 : The two pulses received plus an additional number of pulses between them the two pulses received plus the aircraft identification the aircraft identification plus pulses giving the altitude pulses giving the altitude plus any ident pulse
 The two pulses received plus an additional number of pulses between them.
The two pulses received plus an additional number of pulses between them. With regard to ssr ?
Question 192-23 : The interrogator is on the ground and transponder is in the aircraft the interrogator is on the ground and transponder is on the ground the interrogator is on the aircraft and transponder is in the aircraft the interrogator is on the aircraft and transponder is on the ground
 The interrogator is on the ground and transponder is in the aircraft.
The interrogator is on the ground and transponder is in the aircraft. When a mode c check is carried out and assuming the equipment is working ?
Question 192-24 : Fl351 fl350 3506 35064
 Fl351.
Fl351. In ssr the interrogations use different modes if altitude reporting is required ?
Question 192-25 : Mode c and a interrogations mode a interrogations only mode c interrogations only mode c and ident interrogations
 Mode c and a interrogations.
Mode c and a interrogations. The atc transponder system excluding mode s contains ?
Question 192-26 : Two modes each 4096 of codes four modes each of 1024 codes four modes each of 4096 codes two modes each of 1024 codes
 Two modes, each 4096 of codes.
Two modes, each 4096 of codes. A mode s transponder ?
Question 192-27 : Responds normally to mode a or c interrogations will not respond to mode a interrogations responds to mode a interrogations but not to mode c interrogations will not respond to mode a or c interrogations as it operates on a different frequency
 Responds normally to mode a or c interrogations.
Responds normally to mode a or c interrogations. 'fruiting' is caused by ?
Question 192-28 : Aeroplane at range responding to interrogations from another atc radar station aeroplane in close proximity responding to the same interrogation an aeroplane's transponder responding to side lobes or reflections of the interrogation signal doppler effect on targets moving radially towards or away from the atc radar station
 Aeroplane at range responding to interrogations from another atc radar station.
Aeroplane at range responding to interrogations from another atc radar station. The carrier frequency of the ssr atc reply transmission air to ground is ?
Question 192-29 : 1090 mhz + or 3 mhz 1030 mhz + or 2 mhz 1020 mhz + or 4 mhz 1050 mhz + ou 2 mhz
 1090 mhz + or - 3 mhz.
1090 mhz + or - 3 mhz. A mode s transponder receives among other pulses a long p4 pulse from an ?
Question 192-30 : The interrogator transmits a mode a/c/s all call the interrogator transmits a mode a/c only all call the interrogator transmits a mode s only all call the interrogator transmits a mode a only all call
 The interrogator transmits a mode a/c/s all call.
The interrogator transmits a mode a/c/s all call. A mode a/c transponder receives a p2 pulse from which the amplitude is smaller ?
Question 192-31 : The transponder is located in the direction of the main lobe of the interrogator antenna the transponder is beyond the usable range of the ssr ground station the interrogation is only meant for mode s transponders the transponder is located in the direction of one of the side lobes of the interrogator antenna
 The transponder is located in the direction of the main lobe of the interrogator antenna.
The transponder is located in the direction of the main lobe of the interrogator antenna. A mode a/c transponder receives a p2 pulse from which the amplitude is larger ?
Question 192-32 : The transponder is located in the direction of one of the side lobes of the interrogator antenna the transponder is located in the direction of the main lobe of the interrogator antenna the transponder is beyond the usable range of the ssr ground station the interrogation is only meant for mode s transponders
 The transponder is located in the direction of one of the side lobes of the interrogator antenna.
The transponder is located in the direction of one of the side lobes of the interrogator antenna. What determines the operating mode a or c of the ssr transponder ?
Question 192-33 : The time interval between the pulses p1 and p3 the travel time of the pulses transmitted by the interrogator the position of the spi pulse the difference in amplitude of the pulses p1/p3 and p2
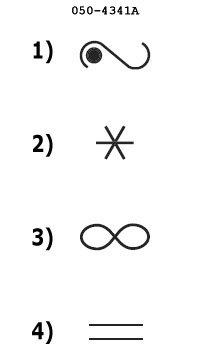 The time interval between the pulses p1 and p3.
The time interval between the pulses p1 and p3. What is one of the differences between a mode a/c/s all call and a mode a/c ?
Question 192-34 : The length of the pulse p4 the presence of mode a/c addresses the time interval between the pulses p1 and p3 the presence of mode s addresses
 The length of the pulse p4.
The length of the pulse p4. The time interval between the interrogating pulses p1 and p3 in mode c is ?
Question 192-35 : 21 us 8 us 1 6 us 0 8 us
 21 us.
21 us. The time interval between the interrogating pulses p1 and p3 in mode a is ?
Question 192-36 : 8 us 21 us 1 6 us 0 8 us
 8 us.
8 us. Ssr transponder .mode s provides ?
Question 192-37 : 25 possible reply forms 50 possible reply forms 100 possible reply forms 3 possible reply forms
 25 possible reply forms.
25 possible reply forms. The equipment that uses the pulse modulation technique is the ?
Question 192-38 : Radar vor localizer vhf radio
 Radar.
Radar. Ssr transponder .in intermode a 'short' p4 pulse makes it possible to perform a ?
Question 192-39 : A/c a/c/s mode s only c
 A/c.
A/c. Ssr transponder .a mode a/c transponder ?
Question 192-40 : Responds to mode s interrogations but can not send data responds to mode s interrogations with limited data does not respond to mode s because frequency is different does not respond to mode s interrogations
 Responds to mode s interrogations but can not send data.
Responds to mode s interrogations but can not send data. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7639 Free Training Exam
