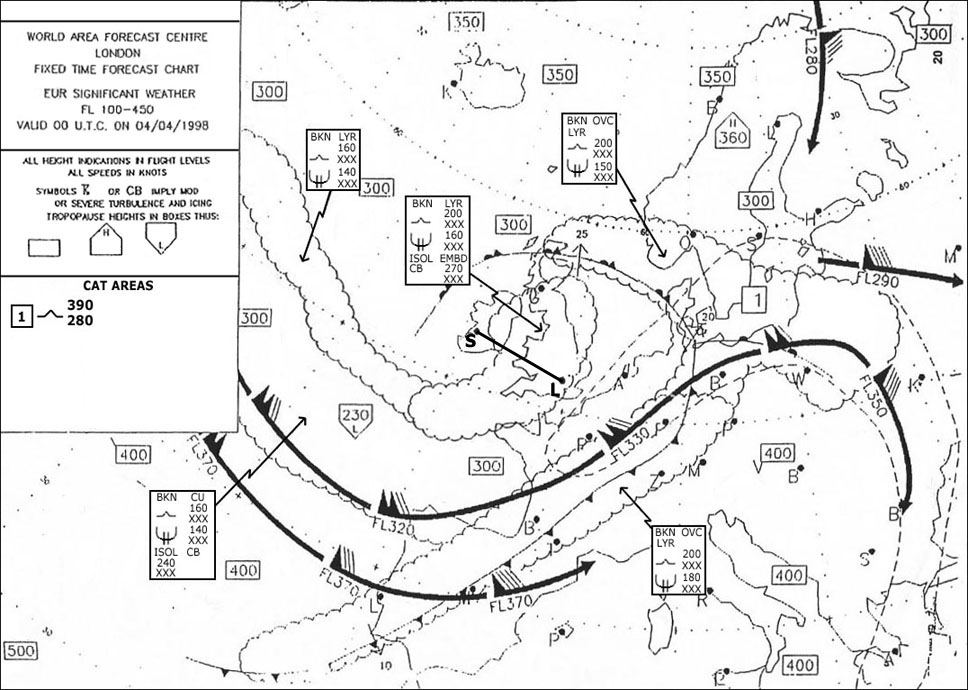
Tvor is a ? [ Question security ]
Question 186-1 : Vor with a limited range used in the terminal area low power dvor in the frequency range 112 mhz – 118 mhz test vor transmitting such a signal that the reference and variable signal are always in phase high power vor in the frequency range 108 mhz – 112 mhz
 Vor with a limited range used in the terminal area.
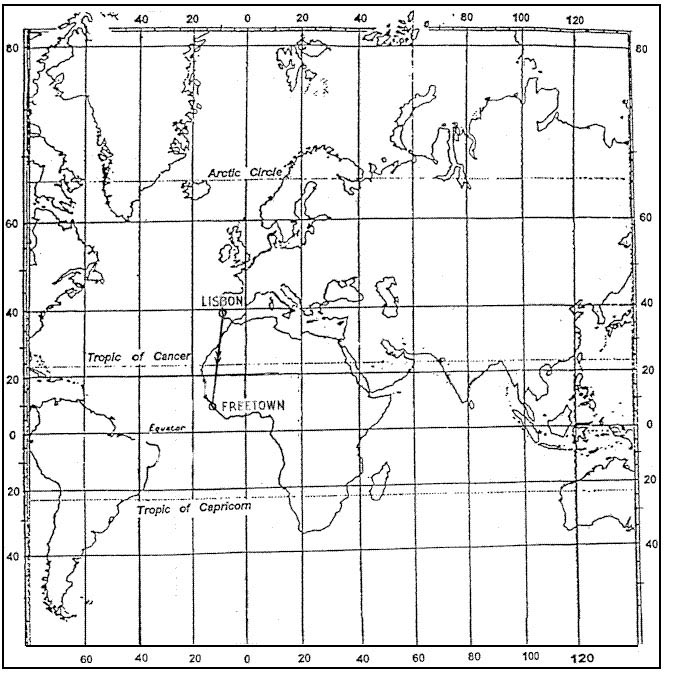
Vor with a limited range used in the terminal area. On an rmi the front end of a vor pointer indicates the ?
Question 186-2 : Radial plus 180° magnetic bearing from the station radial relative bearing
 Radial plus 180°.
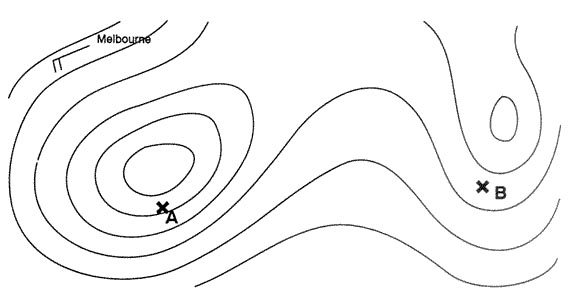
Radial plus 180°. Which statement about the interrogation by the dme interrogator is correct ?
Question 186-3 : The interrogation does not start before pulse pairs of the tuned dme station are received the interrogation starts directly after the correct dme frequency has been selected on the frequency selecting panel by the pilot the interrogation starts when the interrogator has been warmed up sufficiently whether pulse pairs are received or not the interrogation can only take place if the echo protection circuit has been locked
 The interrogation does not start before pulse-pairs of the tuned dme-station are received.
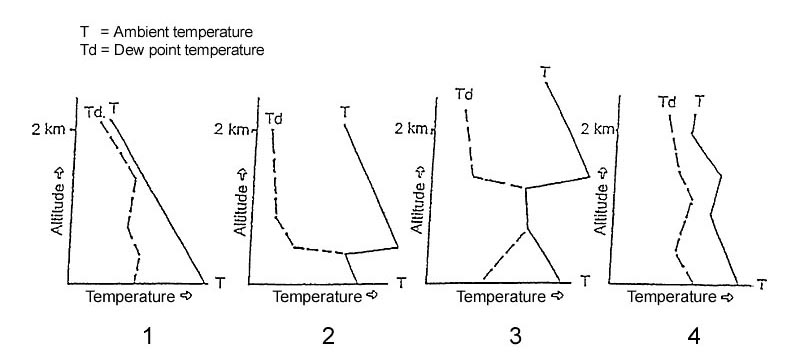
The interrogation does not start before pulse-pairs of the tuned dme-station are received. An aeroplane is on approach with nav 1 tuned to the ils frequency and nav 2 ?
Question 186-4 : Quarter scale deflection half scale deflection full scale deflection no deflection
 Quarter scale deflection.
Quarter scale deflection. Mls is primarily being installed at airports where ?
Question 186-5 : Ils encounters difficulties because of surrounding buildings and/or the terrain or interference from local music stations meteorological conditions are likely to cause ils ducting by super refraction the main approach paths lead over water topographical conditions preclude the installation of ils marker beacons
 Ils encounters difficulties because of surrounding buildings and/or the terrain or interference from local music stations.
Ils encounters difficulties because of surrounding buildings and/or the terrain or interference from local music stations. Concerning adf and ndb ?
Question 186-6 : Ndb is a ground equipment and adf is an airborne equipment adf is a civilian equipment whereas ndb is a military equipment used by civilians too adf is an ground equipment and ndb can be a ground equipment or an airborne equipment ndb is a locator and adf is an en route nav aid
 Ndb is a ground equipment, and adf is an airborne equipment.
Ndb is a ground equipment, and adf is an airborne equipment. The adf indication in the cockpit is a ?
Question 186-7 : Relative bearing on a fixed card indicator magnetic bearing on a fixed card indicator relative bearing on an rmi true bearing on an rmi
 Relative bearing on a fixed card indicator
Relative bearing on a fixed card indicator Night effect in an adf may cause ?
Question 186-8 : Fluctuating indications of the needle on the rmi noise in the received em wave which hardly will be noticed by the pilot looking at the rmi no bearing error because of the built in compensator unit a constant error in the indicated bearing
 Fluctuating indications of the needle on the rmi.
Fluctuating indications of the needle on the rmi. Which statement is correct with respect to the different types of vor ?
Question 186-9 : A tvor has a limited range a dvor is less accurate than a cvor a cvor is primarily used for instrument approaches a vot is located along an airway with the purpose to provide an in flight check of the airborne equipment
 A tvor has a limited range.
A tvor has a limited range. On an ils approach when flying overhead the middle marker the colour of the ?
Question 186-10 : Amber blue green white
 Amber.
Amber. On an ils approach when flying overhead the inner marker if available the ?
Question 186-11 : White blue green amber
 White.
White. On final on an ils approach you are flying overhead the outer marker you can ?
Question 186-12 : 4 nm from the threshold 10 nm from the threshold 1 nm from the threshold 25 nm from the threshold
 4 nm from the threshold.
4 nm from the threshold. The uhf band is the assigned frequency band of the ?
Question 186-13 : Ils glide path transmitter all the 3 ils marker beacons outer marker beacon ils localiser transmitter
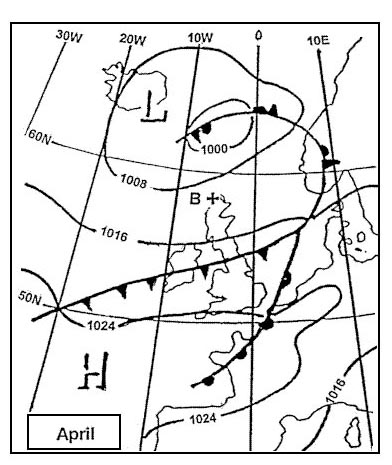 Ils glide path transmitter.
Ils glide path transmitter. Ils transmitters use the ?
Question 186-14 : Uhf and vhf bands vhf uhf and hf bands vhf band only uhf band only
 Uhf and vhf bands.
Uhf and vhf bands. The localiser transmitters operate in a frequency band between ?
Question 186-15 : 108 mhz and 111 975 mhz 108 mhz and 117 975 mhz 111 975 mhz and 117 975 mhz 329 15 mhz and 335 mhz
 108 mhz and 111.975 mhz.
108 mhz and 111.975 mhz. 108 35 mhz can only be ?
Question 186-16 : An ils frequency a ndb frequency a vor frequency an atc frequency
 An ils frequency.
An ils frequency. Which statement about adfs is correct ?
Question 186-17 : Adfs can receive and take bearings on any broadcasting station transmitting within the frequency band 190 – 1750 khz adfs cannot receive broadcasting stations transmitting within the frequency band 190 – 1750 khz because ndbs are amplitude modulated and not frequency modulated like broadcasting stations adfs can receive any broadcasting station transmitting within the frequency band 190 – 1750 khz but cannot take bearings on them adfs cannot receive broadcasting stations transmitting within the frequency band 190 – 1750 khz because ndbs are either n0n/a1a or a2a modulated and not a3e modulated like broadcasting stations
 Adfs can receive and take bearings on any broadcasting station transmitting within the frequency band 190 – 1750 khz.
Adfs can receive and take bearings on any broadcasting station transmitting within the frequency band 190 – 1750 khz. What is the reason that a dme station can generally respond to a maximum of 100 ?
Question 186-18 : The number of reply pulse pairs per second that a dme transponder can transmit is limited to a certain maximum value the minimum allowable accuracy of the range measurement cannot be guaranteed when more than about 100 aircraft are using the same dme station the automatic ground monitoring station of each dme station has a limited capacity the memory of the dme transponder is limited
 The number of reply pulse pairs per second that a dme-transponder can transmit is limited to a certain maximum value.
The number of reply pulse pairs per second that a dme-transponder can transmit is limited to a certain maximum value. If the number of pulse pairs received by the dme transponder exceeds the ?
Question 186-19 : The aircraft from which the weakest pulse pairs are received the aircraft at the largest distance from the dme station the aircraft at the lowest altitude the smallest aircraft which is using the dme station for range measurement
 The aircraft from which the weakest pulse pairs are received.
The aircraft from which the weakest pulse pairs are received. If during an ils approach after having been established the pilot deviates by ?
Question 186-20 : An immediate missed approach should be executed because obstacle clearance may no longer be guaranteed the approach may be completed as long as the associated locator gives the information that the aircraft is on the centre line the approach may be continued but a warning for excessive beam bends should be generated the approach may be continued as long as the gp needle has less than a half scale deflection
 An immediate missed approach should be executed because obstacle clearance may no longer be guaranteed.
An immediate missed approach should be executed because obstacle clearance may no longer be guaranteed. Fm broadcast stations transmitting just below 108 mhz are ?
Question 186-21 : Likely to cause interference to ils receivers not equipped with an immunity filter causing interference only in extreme cases affecting exclusively the glide path unlikely to cause any interference to ils receivers likely to cause interference to all ils receivers
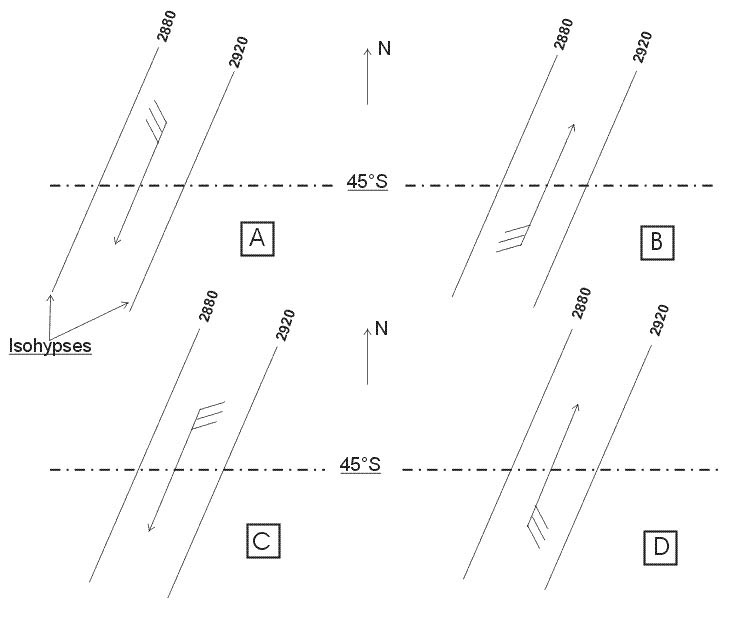 Likely to cause interference to ils receivers not equipped with an immunity filter.
Likely to cause interference to ils receivers not equipped with an immunity filter. The definition of the term qdr is… ?
Question 186-22 : The magnetic bearing from the station the magnetic bearing to the station the true bearing to the station the true bearing from the station
 The magnetic bearing from the station
The magnetic bearing from the station Reflections from large objects within the ils coverage area may cause ?
Question 186-23 : Multi path interference doppler errors single path interference static noise
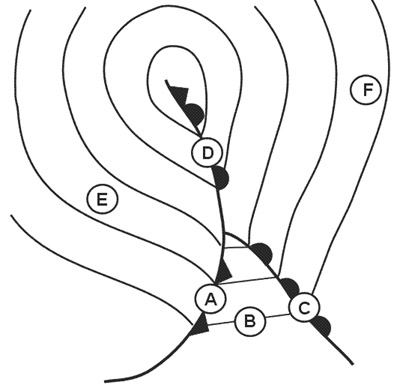 Multi-path interference.
Multi-path interference. The accuracy the pilot has to fly the required bearing in order to be ?
Question 186-24 : 5° 2 5° 2° 7 5°
 5°
5° With respect to the monitoring system of a vor which statement is correct ?
Question 186-25 : Failure of the vor station to stay within the required limits can cause the removal of identification and navigation components from the carrier or radiation to cease failure of the vor station to stay within the required limits will trigger a vor caution annunciator in the cockpit the system monitors directly the phase of the reference signal and the phase of the variable signal if the monitoring system detects a change in the measured radial the transmission power will be reduced and consequently only aircraft in the terminal area can use the vor
 Failure of the vor station to stay within the required limits can cause the removal of identification and navigation components from the carrier or radiation to cease.
Failure of the vor station to stay within the required limits can cause the removal of identification and navigation components from the carrier or radiation to cease. Which frequency can be used by a terminal vor ?
Question 186-26 : 108 20 mhz 111 975 mhz 118 15 mhz 108 10 mhz
 108.20 mhz.
108.20 mhz. A pilot is tracking inbound to a vor on a designated radial using the hsi the ?
Question 186-27 : Scalloping night effect quadrantal error coastal refraction
 Scalloping
Scalloping The magnetic variation to convert the rmi bearings of ndbs and vors to true ?
Question 186-28 : Aircraft position for ndbs and at the beacon position for vors aircraft position for ndbs and at the aircraft position for vors beacon position for ndbs and at the beacon position vors beacon position for nds and at the aircraft position for vors
 Aircraft position for ndbs and at the beacon position for vors.
Aircraft position for ndbs and at the beacon position for vors. The frequency range of a vor receiver is ?
Question 186-29 : 108 to 117 95 mhz 118 to 135 95 mhz 108 to 135 95 mhz 108 to 111 95 mhz
 108 to 117.95 mhz
108 to 117.95 mhz Which of the following is the icao allocated frequency band for aeronautical ?
Question 186-30 : 190 khz to 1750 khz 300 khz to 3000 khz 200 khz to 2000 khz 255 khz to 455 khz
 190 khz to 1750 khz
190 khz to 1750 khz Errors caused by the effect of coastal refraction on bearings at lower ?
Question 186-31 : Inland and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle near the coast and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle near the coast and the bearing crosses the coast at right angles inland and the bearing crosses the coast at right angles
 Inland and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle.
Inland and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle. The dme distance measuring equipment operates in which frequency range ?
Question 186-32 : 960 to 1215 mhz 329 to 335 mhz 108 to 118 mhz 960 to 1215 khz
 960 to 1215 mhz
960 to 1215 mhz The frequency of the amplitude modulation and the colour of an ils outer marker ?
Question 186-33 : 400 hz and blue 400 hz and amber 3000 hz and blue 1300 hz and blue
 400 hz and blue.
400 hz and blue. A dvor is less sensitive to site errors than a cvor because ?
Question 186-34 : The variable phase is frequency modulated rather than amplitude modulated of the presence of a monitoring system of the smaller vor antenna of the use of vertical polarised waves instead of horizontal polarised waves
 The variable phase is frequency modulated rather than amplitude modulated.
The variable phase is frequency modulated rather than amplitude modulated. The ils receiver of an aircraft on approach and flying to the right of the ?
Question 186-35 : More of the 150 hz localiser signal than the 90 hz localiser signal the left lobe modulation only a modulated signal that will move the localiser needle to the right according to the magnitude of the difference between the two amplitudes the modulation from both lobes at equal amplitude
 More of the 150 hz localiser signal than the 90 hz localiser signal.
More of the 150 hz localiser signal than the 90 hz localiser signal. Regarding ils operations which of the following circumstances will trigger ?
Question 186-36 : 2 and 4 3 and 4 1 and 3 1 and 2
 2 and 4
2 and 4 An aircraft tracking to intercept the instrument landing system ils localiser ?
Question 186-37 : May receive false course indications can expect signals to give correct indications only glide path information is available will receive signals without identification coding
 May receive false course indications.
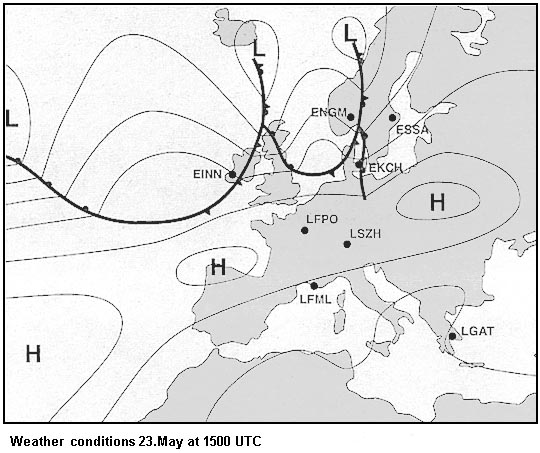
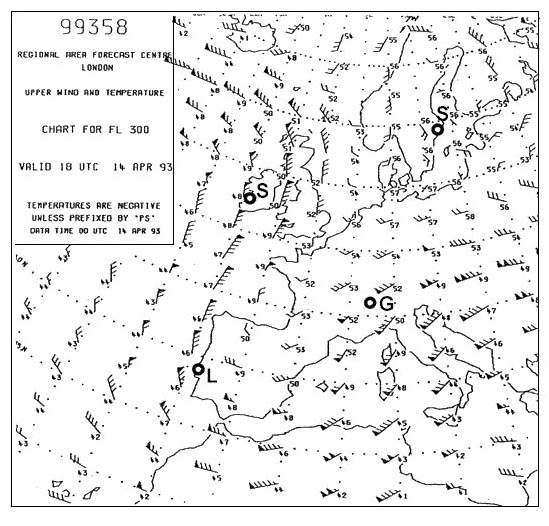
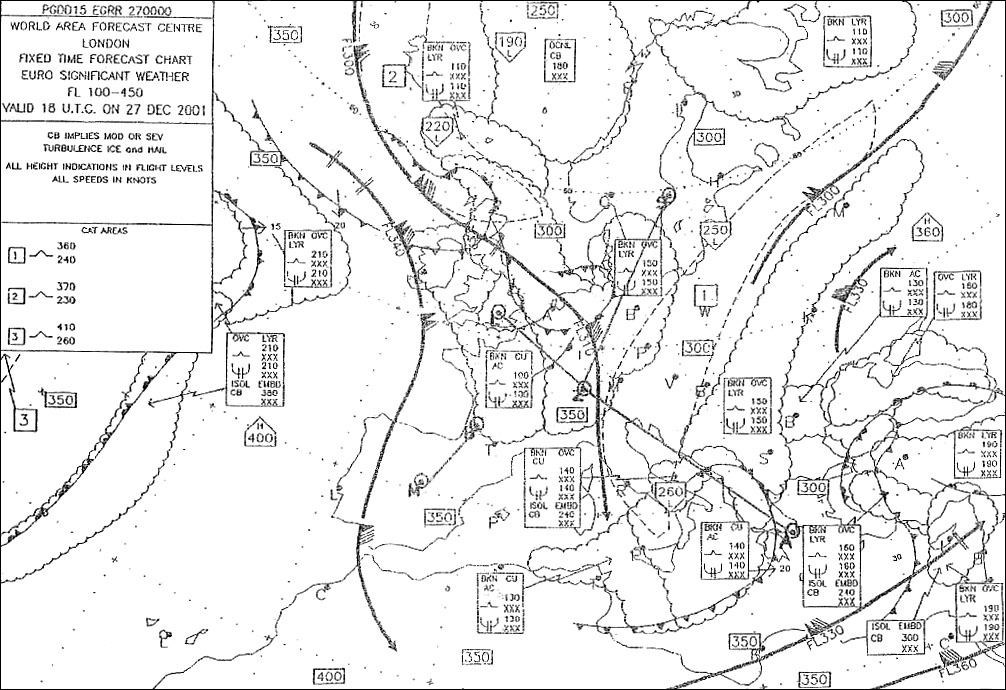
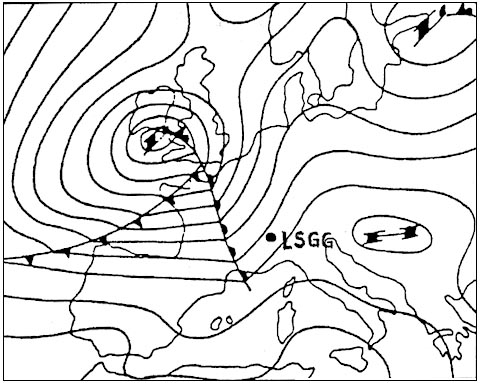
May receive false course indications. An aircraft at fl300 in isa conditions and with a ground speed of 300 kt is ?
Question 186-38 : Less than 300 kt and 7 nm less than 300 kt and 5 nm 300 kt and 5 nm 300 kt and 7 nm
 Less than 300 kt and 7 nm.
Less than 300 kt and 7 nm. An ils glide path provides azimuth coverage i each side of the localiser ?
Question 186-39 : I 8° ii 10 i 25° ii 17 i 35° ii 25 i 5° ii 8
 (i) 8° (ii) 10
(i) 8° (ii) 10 The vor radial an aircraft is on depends upon ?
Question 186-40 : The phase difference between the reference and variable phases the difference between the selected radial and the radial the aircraft is on the difference between the selected course and the radial the aircraft is on the time difference between the reference and variable phases
 The phase difference between the reference and variable phases.
The phase difference between the reference and variable phases. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7399 Free Training Exam
