When a dme is associated with an mls the delay is .1 50 microseconds for mode ? [ Question security ]
Question 185-1 : 1 and 3 1 and 4 2 and 3 3 and 4
 1 and 3.
1 and 3. In tracking mode the airborne dme interrogates with a recurrence frequency ?
Question 185-2 : Variable from 5 to 25 times per second fixed according to the distance between 5 and 25 times per second of 2700 times per second of 150 times per second
 Variable from 5 to 25 times per second.
Variable from 5 to 25 times per second. A vor station automatically stops transmitting if a variation in the ?
Question 185-3 : 1° 2° 1 5° 0 5°
 1°.
1°. Dvor is less sensitive to site errors than cvor because of the ?
Question 185-4 : Relatively large antenna of dvor compared to cvor relatively small antenna of dvor compared to cvor
 Relatively large antenna of dvor (compared to cvor).
Relatively large antenna of dvor (compared to cvor). The difference between a cvor and a dvor indicates that dvor is more accurate ?
Question 185-5 : It is less sensitive to errors generated by the environment buildings hills the reference signal is 50 hz instead of 30 hz one is modulated in frequency the other in phase it has a monitoring system
 It is less sensitive to errors generated by the environment (buildings, hills).
It is less sensitive to errors generated by the environment (buildings, hills). The pulse p2 of an interrogation in a/c mode has the function ?
Question 185-6 : Of avoiding responses of aircraft located in the direction of the side lobes of the antenna of the interrogator of avoiding garbling if two aircraft in the same direction from the interrogator and at a distance of less than 1 7 nm of determining the interrogation mode of avoiding 'fruiting' is an aircraft is interrogated by more than one secondary radar
 Of avoiding responses of aircraft located in the direction of the side lobes of the antenna of the interrogator.
Of avoiding responses of aircraft located in the direction of the side lobes of the antenna of the interrogator. A transponder receives a p2 pulse which is larger than that of the p1 and p3 ?
Question 185-7 : Transponder transmissions will be suppressed for a short time the transmitting station is out of order transponder transmission will be increased the pulses p1 and p3 will be strengthened to reach the same level
 Transponder transmissions will be suppressed for a short time.
Transponder transmissions will be suppressed for a short time. The integrity of a vor system is improved by ?
Question 185-8 : An automatic ground monitoring system test vor vot beacons on airports areas at least two independent airborne vor receivers one autonomous airborne monitoring receiver
 An automatic ground monitoring system.
An automatic ground monitoring system. The controller of a vdf ground station pass you the following message .'your ?
Question 185-9 : Qte accurate to a range within ± 2° qdr accurate to a range within ± 2° quj accurate to a range within ± 3° qte accurate to a range within ± 5°
 Qte accurate to a range within ± 2°.
Qte accurate to a range within ± 2°. Which of the following is the correct class and accuracy for a vdf direction ?
Question 185-10 : Class a ± 2° class a ± 10° class c ± 2° class d ± 5°
 Class a ± 2°.
Class a ± 2°. An aircraft is inbound to vor x on the 073° radial and experiences a drift of ?
Question 185-11 : Heading 265° x pointer 253° y pointer 313° heading 085° x pointer 073° y pointer 133° heading 265° x pointer 073° y pointer 313° heading 085° x pointer 253° y pointer 133°
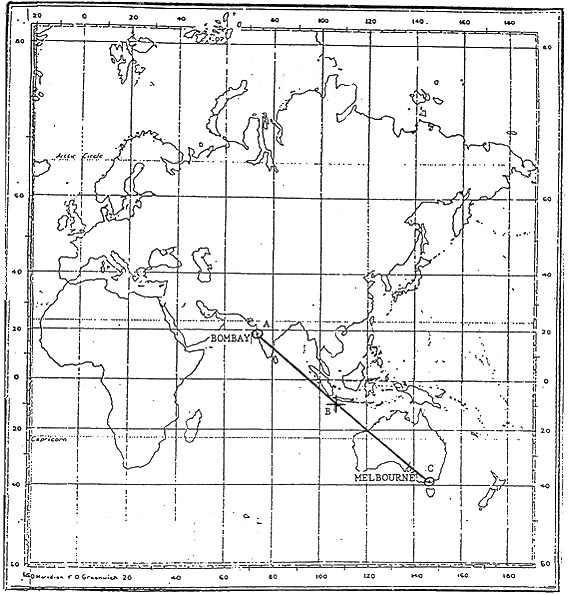 Heading 265°, x pointer 253°, y pointer 313°.
Heading 265°, x pointer 253°, y pointer 313°. In the case where a dme station is subjected to more than 100 interrogations ?
Question 185-12 : Those who have the lowest transmission the closest the most distant those over 200 nm
 Those who have the lowest transmission.
Those who have the lowest transmission. In the case where a dme station is subjected to more than 100 interrogations ?
Question 185-13 : Those who have the most powerful transmission the closest the most distant those over 200 nm
 Those who have the most powerful transmission.
Those who have the most powerful transmission. What is the reason that a dme station can generally respond to a maximum of 100 ?
Question 185-14 : The number of reply pulse pairs per second that a dme transponder can transmit is limited to a certain maximum value the minimum allowable accuracy of the range measurement can not be guaranteed when more than 100 aircraft use the same dme station the memory of the dme transponder which is limited in size the automatic tracking ground station of each dme station that has limited capacity
 The number of reply pulse pairs per second that a dme transponder can transmit is limited to a certain maximum value.
The number of reply pulse pairs per second that a dme transponder can transmit is limited to a certain maximum value. Which entrance sectors should you use to enter a dme arc holding pattern ?
Question 185-15 : Sector 1 or 3 sector 1 or 2 sector 1 2 or 3 sector 2 or 3
 Sector 1 or 3.
Sector 1 or 3. A direction finding station working alone should give the following as requested ?
Question 185-16 : Magnetic and true bearing to the station magnetic and true heading for the station true bearing to the station magnetic and true heading for the station true bearing to the station true heading for the station true bearing to the station
 Magnetic and true bearing to the station, magnetic and true heading for the station.
Magnetic and true bearing to the station, magnetic and true heading for the station. In vdf service the report 'qdr 235° class c' means ?
Question 185-17 : The magnetic bearing from the station to the aircraft is 235° ± 10° the magnetic bearing from the aircraft to the station is 235° ± 10° the true bearing from the aircraft to the station is 235 ± 10° the magnetic bearing from the station to the aircraft is 235 ± 15°
 The magnetic bearing from the station to the aircraft is 235° ± 10°.
The magnetic bearing from the station to the aircraft is 235° ± 10°. The sensitive area of an ils is the area vehicles or taxiing aircraft may not ?
Question 185-18 : Category ii/iii ils operations are in progress category i ils operations are in progress the ils is undergoing calibration ils operations are in progress
 Category ii/iii ils operations are in progress.
Category ii/iii ils operations are in progress. You are flying along an airway which is 10 nm wide 5 nm either side of the ?
Question 185-19 : 1 5 4 5 3 0 6 0
 1.5
1.5 If an aircraft flies along a vor radial it will follow a ?
Question 185-20 : Great circle track rhumb line track constant magnetic track line of constant bearing
 Great circle track
Great circle track Locators are .1 high powered ndbs used for en route and airways navigation . .2 ?
Question 185-21 : 2 and 4 1 and 4 2 and 3 1 and 3
 2 and 4.
2 and 4. An aircraft is flying at fl 240 the dme reading uncorrected for altitude is 8 ?
Question 185-22 : 7 0 nm 7 3 nm 7 5 nm 6 5 nm
 7.0 nm
7.0 nm What is the minimum level isa conditions that an aircraft at a range of 111 nm ?
Question 185-23 : Fl60 fl100 fl80 fl50
 Fl60
Fl60 To determine the vor radial the aircraft vor receiver… ?
Question 185-24 : Measures the phase difference between the reference phase and the variable phase signals uses pulse techniques measures the time difference between sending the interrogation signal and receiving the transponder signal measures the time difference between reception of the two signals transmitted by the ground installation
 Measures the phase difference between the reference phase and the variable phase signals.
Measures the phase difference between the reference phase and the variable phase signals. Which of the following correctly describes the instrument landing system ils ?
Question 185-25 : Two overlapping lobes on the same vhf carrier frequency two overlapping lobes on the same uhf carrier frequency two overlapping lobes on different radio carrier frequencies but with the same modulation a pencil beam comprising a series of smaller beams each carrying a different modulation
 Two overlapping lobes on the same vhf carrier frequency
Two overlapping lobes on the same vhf carrier frequency The middle marker of an instrument landing system ils facility is identified ?
Question 185-26 : Alternate dots and dashes and an amber light flashing dashes and an amber light flashing two dashes per second and a blue light flashing dots and a white light flashing
 Alternate dots and dashes and an amber light flashing
Alternate dots and dashes and an amber light flashing The mls frequencies and available channels are ?
Question 185-27 : In the shf band 300 khz frequency separation giving 200 available channels in the shf band for the mls elements and the vhf band for the dme 100 available channels in the range 5060 – 5090 mhz 200 khz separation giving 150 available channels in the vhf and uhf band 40 available channels
 In the shf band, 300 khz frequency separation giving 200 available channels.
In the shf band, 300 khz frequency separation giving 200 available channels. An aircraft is 'homing' to a radio beacon whilst maintaining a relative bearing ?
Question 185-28 : Right drift zero drift left drift a wind from the west
 Right drift
Right drift Which one of the following disturbances is most likely to cause the greatest ?
Question 185-29 : Local thunderstorm activity coastal effect precipitation interference quadrantal error
 Local thunderstorm activity
Local thunderstorm activity Of what use if any is a military tacan station to civil aviation ?
Question 185-30 : It can provide dme range it is of no use to civil aviation it can provide a dme distance and magnetic bearing it can provide a magnetic bearing
 It can provide dme range.
It can provide dme range. Which of the following is an ils localiser frequency ?
Question 185-31 : 109 15 mhz 112 10 mhz 110 20 mhz 108 25 mhz
 109.15 mhz
109.15 mhz An ndb transmits a signal pattern in the horizontal plane which is ?
Question 185-32 : Omnidirectional a cardioid balanced at 30 hz a beam rotating at 30 hz bi lobal circular
 Omnidirectional
Omnidirectional A vor and an ndb are located in the same position both the vor and the adf ?
Question 185-33 : The direction of the adf pointer will change the direction of the vor pointer will not change the direction of the vor pointer will change the direction of the adf pointer will not change neither the direction of the adf pointer nor the direction of the vor pointer will change both the direction of the adf pointer and the direction of the vor pointer will change
 The direction of the adf pointer will change, the direction of the vor pointer will not change.
The direction of the adf pointer will change, the direction of the vor pointer will not change. Which of the following is correct regarding false beams on a glide path ?
Question 185-34 : False beams will only be found above the correct glide path false beams will only be found below the correct glide path false beams will only be found more than 10 degrees to the left or to the right of the localiser centreline false beams are only present when flying a back beam ils approach
 False beams will only be found above the correct glide path.
False beams will only be found above the correct glide path. Which one of the following correctly lists the major ground based components of ?
Question 185-35 : Separate azimuth and elevation transmitters dme facility separate azimuth and elevation transmitters outer and middle marker beacons combined azimuth and elevation transmitter dme facility combined azimuth and elevation transmitter outer and inner marker beacons
 Separate azimuth and elevation transmitters, dme facility
Separate azimuth and elevation transmitters, dme facility One of uses of the vdf service is providing aircraft with ?
Question 185-36 : Homing ground speed altitude heading
 Homing.
Homing. To provide a pilot with the position of the aircraft in the absence of radar ?
Question 185-37 : Two vdfs at different locations able to take bearings simultaneously on the transmitted frequency three vdfs at different locations able to take simultaneous bearings on different frequencies one vdf able to take simultaneous bearings on different frequencies two co located vdfs able to take bearings simultaneously on the transmitted frequency
Allocated frequencies for ndb are ?
Question 185-38 : 190 khz to 1750 khz 1900 khz to 17500 khz 1 90 khz to 17 50 khz 19 hz to 17500 hz
 190 khz to 1750 khz.
190 khz to 1750 khz. Locators are ?
Question 185-39 : Lf/mf ndbs used as an aid for final approach beacons with a range of 10 to 250 nm low powered adfs used for airfield or runway approach high powered ndbs used for en route and airways navigation
 Lf/mf ndbs used as an aid for final approach.
Lf/mf ndbs used as an aid for final approach. According to icao annex 10 a locator has a range of ?
Question 185-40 : 10 to 25 nm 75 to 250 nm 7 5 to 15 nm 75 to 150 nm
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
7359 Free Training Exam
