Ehf extremely high frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ? [ Multiple protocol ]
Question 176-1 : 30 ghz 300 ghz 30 mhz 300 mhz 3 mhz 30 mhz 3 ghz 30 ghz
 30 ghz - 300 ghz
30 ghz - 300 ghz Frequency is defined as the ?
Question 176-2 : Number of cycles occurring in one second in a radio wave expressed in hertz hz maximum deflection in a radio wave expressed in hertz hz minimum number of cycles occurring in one minute in a radio wave expressed in hertz hz length of a radio wave expressed as an angle
 Number of cycles occurring in one second in a radio wave expressed in hertz (hz).
Number of cycles occurring in one second in a radio wave expressed in hertz (hz). Which statement about vhf/uhf frequencies is correct ?
Question 176-3 : For both vhf/uhf propagation the space wave is the only propagation path of practical use there is no sky wave under normal conditions vhf has under normal conditions a sky wave wherease uhf has not for both vhf/uhf propagation the space wave is the main propagation path vhf frequencies below 120 mhz may be subjected to sporadic e reflection and then have a sky wave for both vhf/uhf the surface wave is the main propagation path of practical use neither vhf/uhf has a sky wave under any conditions for vhf the surface wave is the main propagation path and for the uhf the space wave
 For both vhf/uhf propagation, the space wave is the only propagation path of practical use. there is no sky wave under normal conditions.
For both vhf/uhf propagation, the space wave is the only propagation path of practical use. there is no sky wave under normal conditions. Diffraction is the process by which ?
Question 176-4 : Radio wave travel over and around obstacles a space wave penetrates the ionosphere a ground wave is attenuated over rough ground a direct wave is bent around the form of the earth
 Radio wave travel over and around obstacles.
Radio wave travel over and around obstacles. Antennas .an ac will be induced ?
Question 176-5 : In a wire parallel to a wire fed with an ac but remote from it in a wire perpendicular to the wire fed with an ac but remote from it in a wire parallel to the wire fed with a dc but remote from it in a wire connected in series to a wire fed with a dc
 In a wire, parallel to a wire fed with an ac, but remote from it.
In a wire, parallel to a wire fed with an ac, but remote from it. In aviation the reflection on ionosphere layers phenomenon is used in the ?
Question 176-6 : Hf uhf vlf vhf
 Hf.
Hf. The wavelength of a radio signal transmitted at the frequency 118 7 mhz is ?
Question 176-7 : 2 53 m 25 3 m 2 53 cm 25 3 cm
 2.53 m.
2.53 m. In the propagation of mf waves the phenomenon of fading is particularly found ?
Question 176-8 : At night due to the combination of the sky and ground waves by day due to the combination of sky and ground waves at night and when raining by day and when raining
 At night, due to the combination of the sky and ground waves.
At night, due to the combination of the sky and ground waves. A radio signal looses strength as range from the transmitter increases this is ?
Question 176-9 : Attenuation refraction propagation ducting
 Attenuation.
Attenuation. Skip distance is the ?
Question 176-10 : Range from the transmitter to the first sky wave highest critical frequency distance wavelength distance of a certain frequency thickness of the ionosphere
 Range from the transmitter to the first sky wave.
Range from the transmitter to the first sky wave. The wavelength of a radio transmitted on frequency 121 95 mhz is ?
Question 176-11 : 2 46 m 24 60 cm 2 46 cm 24 60 m
 2.46 m.
2.46 m. What describes polarization ?
Question 176-12 : Orientation of the plane of oscillation of the electrical component of the electromagnetic wave orientation of the antenna to the north pole orientation of the plane of oscillation of the magnetic component of the electromagnetic wave rotation of the antenna around a fixed axis
 Orientation of the plane of oscillation of the electrical component of the electromagnetic wave.
Orientation of the plane of oscillation of the electrical component of the electromagnetic wave. On which bearings errors caused by the shoreline/coastal effect reach their ?
Question 176-13 : Bearings 000° 030° degrees to the coastline bearings 030° 060° degrees to the coastline bearings perpendicular to the coastline any bearings in hf band
 Bearings 000°-030° degrees to the coastline.
Bearings 000°-030° degrees to the coastline. The doppler effect onto the radio signals is ?
Question 176-14 : The shift of frequency of the wave due to the relative movement between the transmitter and the receiver increasing or decreasing of the emitting aircraft ground speed the interference between the direct wave and that reflected by the ground the fluctuation of their propagation velocity
 The shift of frequency of the wave due to the relative movement between the transmitter and the receiver.
The shift of frequency of the wave due to the relative movement between the transmitter and the receiver. The d layer and e layer of the atmosphere are part of the ?
Question 176-15 : Ionosphere troposphere tropopause stratosphere
 Ionosphere.
Ionosphere. When raising the frequency of an electromagnetic wave the ?
Question 176-16 : Wavelength decreases wavelength and amplitude increases wavelength remains the same wavelength increases
 Wavelength decreases.
Wavelength decreases. The phenomenon when a wave bends when it passes around an impenetrable obstacle ?
Question 176-17 : Diffraction attenuation refraction propagation
 Diffraction.
Diffraction. The phenomenon of a change in direction of an radio wave em wave occurring due ?
Question 176-18 : Refraction absorption diffraction attenuation
 Refraction.
Refraction. A reason that gps satellites use helical antennae is ?
Question 176-19 : That the signal has a circular polarization that the signal has a linear polarization the reduced size of the antennae the reduced weight of the antennae
 That the signal has a circular polarization.
That the signal has a circular polarization. The mix of an electromagnetic wave with another is called ?
Question 176-20 : Interference reflection diffraction refraction
 Interference.
Interference. Speed of a radio wave ?
Question 176-21 : 300 000 km/s 300 000 m/s 300 000 km/h 300 000 m/h
 300 000 km/s.
300 000 km/s. For long range ndb's the most common type is ?
Question 176-22 : Lf non a1a mf non a1a mf non a2a lf non a2a
 Lf, non a1a.
Lf, non a1a. Mountain effect occurring for instance with ndbs is caused by what physical ?
Question 176-23 : Reflection diffraction absorption refraction
 Reflection.
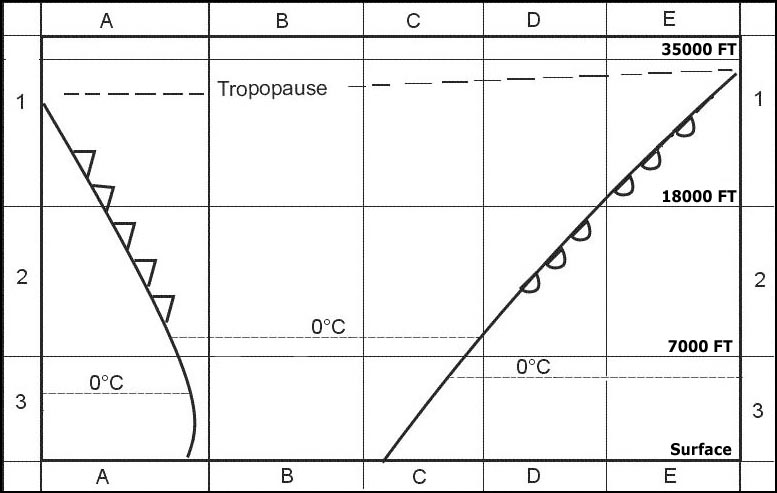
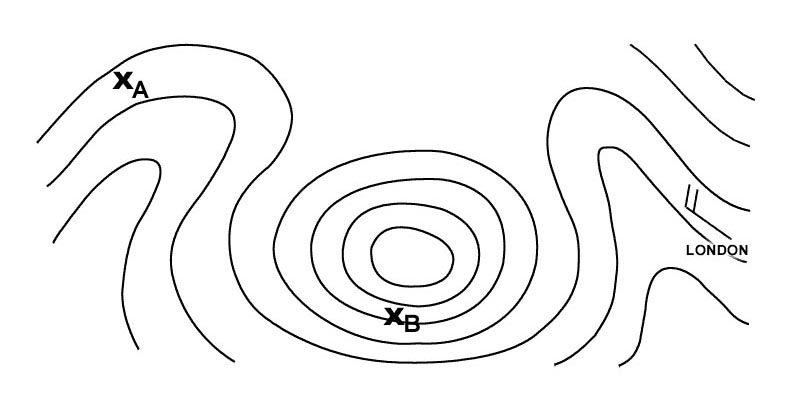
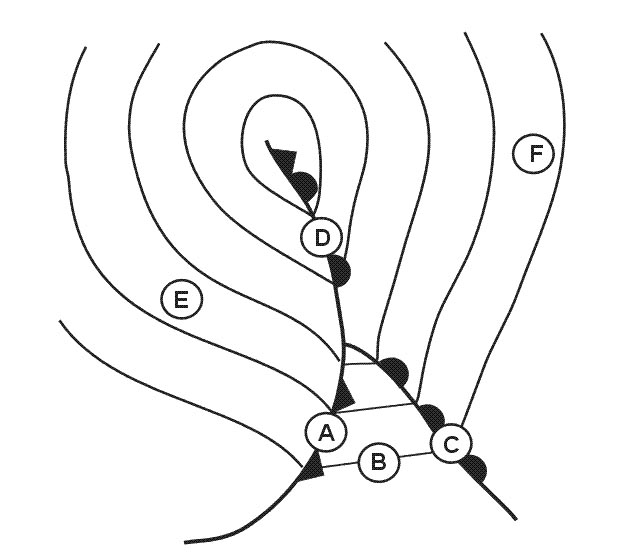
Reflection. Which physical effects affecting wave propagation as shown in the figure . 2556 ?
Question 176-24 : A = refraction b = absorption c = reflection a = diffraction b = reflection c = reflection a = absorption b = absorption c = diffraction a = refraction b = attenuation c = interference
 A = refraction b = absorption c = reflection
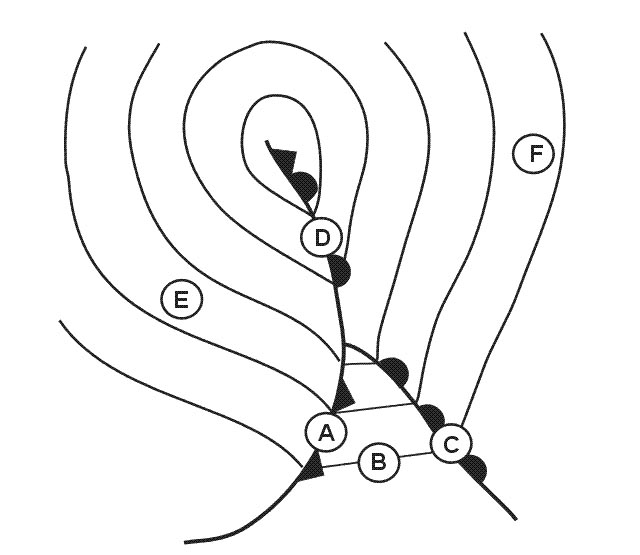
A = refraction b = absorption c = reflection Which letter in the figure below indicates the 'skip zone' . 2557 ?
Question 176-25 : C d a b
 C.
C. Which letter in the figure below indicates the 'skip distance' . 2557 ?
Question 176-26 : D c a b
 D.
D. You are flying over sea parallel to the coastline an ndb is situated 10 nm ?
Question 176-27 : Sectors a + b sectors a + d sectors c + d sectors b + d
 Sectors a + b
Sectors a + b You are flying parallel to the coastline an ndb is positioned about 10 nm ?
Question 176-28 : Area c + d deflection to the coastline area a + b deflection to the coastline area a + d deflection to the coastline area b + d deflection to the coastline
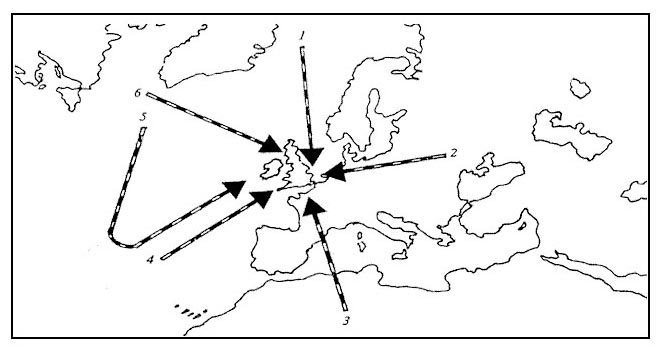 Area c + d, deflection to the coastline.
Area c + d, deflection to the coastline. The phenomenon of a change in direction of an em wave occurring at an interface ?
Question 176-29 : Reflection diffraction absorption refraction
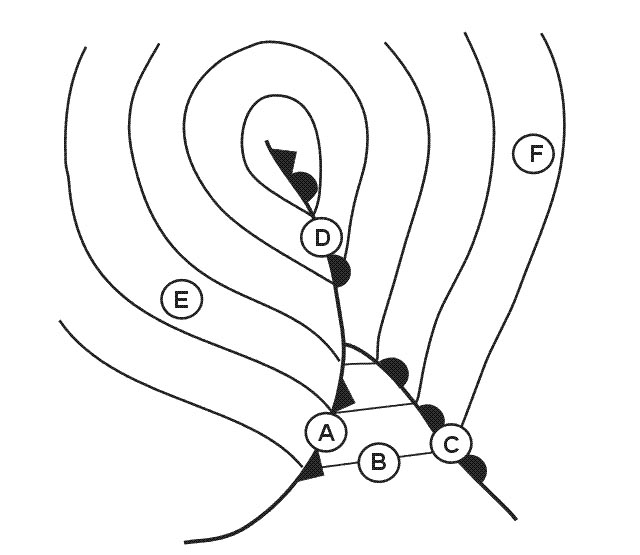 Reflection.
Reflection. What is required to enable an antenna to transmit an electromagnetic wave ?
Question 176-30 : The antenna has to be fed with an alternating current of high frequency the antenna mast must be normal to the ground the antenna has to be fed with a direct current of high frequency the antenna has to be fed with a direct current of low frequency
 The antenna has to be fed with an alternating current of high frequency.
The antenna has to be fed with an alternating current of high frequency. An electromagnetic wave has two types of energy field ?
Question 176-31 : An e electrical field and h magnetic field an h electrical field and an e magnetic field a z electrical field and an h magnetic field a z magnetic field and an e electrical field
 An e electrical field and h magnetic field.
An e electrical field and h magnetic field. In aviation electronic systems the so called doppler principle may be used in ?
Question 176-32 : Vor gps and mts and the turbulence mode of awr vor dme and ils vor mti and the mapping mode of awr vor dme and gps
 Vor, gps and mts and the turbulence mode of awr.
Vor, gps and mts and the turbulence mode of awr. The wavelength of a radio signal transmitted at the frequency of 3 ghz is ?
Question 176-33 : 10 cm 1 m 1 cm 100 cm
 10 cm.
10 cm. The phase angle of a wave is ?
Question 176-34 : The fraction of one wavelength expressed in degrees from 000° to 360° the position of a modulation on a wavelength expressed in degrees from 000° to 360° the angle of the modulation on a wavelength expressed in degrees from 000° to 360° the deflection on a wave expressed in degrees from 000° to 360°
 The fraction of one wavelength expressed in degrees from 000° to 360°.
The fraction of one wavelength expressed in degrees from 000° to 360°. Wavelength is defined as the ?
Question 176-35 : Physical distance travelled by a radio wave during one cycle of transmission maximum variation of an oscillation distance traveled by a radio wave in one second number of oscillations per second
 Physical distance travelled by a radio wave during one cycle of transmission.
Physical distance travelled by a radio wave during one cycle of transmission. Antenna .the ils glide path antenna must be located ?
Question 176-36 : At approximately 300 m after the threshold and approximately 120 m laterally from the runway centreline as close as possible from the runway threshold at 150 m after the threshold and about 300 m left from the runway centreline with the localizer antenna 300 m after the threshold in the axis
 At approximately 300 m after the threshold and approximately 120 m laterally from the runway centreline.
At approximately 300 m after the threshold and approximately 120 m laterally from the runway centreline. The maximum separation distance between a vor and a dme having the same ?
Question 176-37 : 2000 ft 600 m 600 ft 180 m 60 ft 18 m 200 ft 60 m
 2000 ft (600 m).
2000 ft (600 m). The ground wave surface wave propagates as follows ?
Question 176-38 : It travels along the earth' surface and follows the curvature of the earth it is reflected by the ionosphere towards the ground it travels under the ground it is transmitted to the surface of the earth and will be reflected
 It travels along the earth' surface and follows the curvature of the earth.
It travels along the earth' surface and follows the curvature of the earth. The sky wave propagates as follows ?
Question 176-39 : A wave transmitted into space will be reflected back to the earth's surface by the ionosphere it travels under the ground it travels along the earth's surface and follows the curvature of the earth a wave transmitted through the air directly from the transmitter to the receiver
 A wave transmitted into space will be reflected back to the earth's surface by the ionosphere.
A wave transmitted into space will be reflected back to the earth's surface by the ionosphere. An electromagnetic waves travelling through the air directly from the ?
Question 176-40 : Space wave sky wave ground wave air wave
 Space wave.
Space wave. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6999 Free Training Exam
