What is the wavelength of an ndb transmitting on 375 khz ? [ Multiple protocol ]
Question 175-1 : 800 m 8000 m 8 m 80 m
 800 m.
800 m. Phase modulation is ?
Question 175-2 : A modulation form used in gps where the phase of the carrier wave is reversed a modulation form used in ils where the navigation phase signal changed from 90° or 150° the cause of an amplitude change of the carrier the cause of polarisation of the modulated signal
 A modulation form used in gps where the phase of the carrier wave is reversed.
A modulation form used in gps where the phase of the carrier wave is reversed. Factors liable to affect most ndb/adf system performance and reliability include ?
Question 175-3 : Static interference night effect absence of failure warning system static interference station interference latitude error height error station interference mountain effect coastal refraction lane slip mountain effect
 Static interference - night effect - absence of failure warning system.
Static interference - night effect - absence of failure warning system. Due to 'doppler' effect an apparent decrease in the transmitted frequency which ?
Question 175-4 : The transmitter moves away from the receiver the transmitter and receiver move towards each other the transmitter moves toward the receiver there is no relative movement between the transmitter and the receiver
 The transmitter moves away from the receiver.
The transmitter moves away from the receiver. Which one of the following disturbances is most likely to cause the greatest ?
Question 175-5 : Local thunderstorm activity coastal effect quadrantal error precipitation interference
 Local thunderstorm activity.
Local thunderstorm activity. The advantage of the use of slotted antennas in modern radar technology is to ?
Question 175-6 : Virtually eliminate lateral lobes and as a consequence concentrate more energy in the main beam simultaneously transmit weather and mapping beams have a wide beam and as a consequence better target detection eliminate the need for azimuth slaving
 Virtually eliminate lateral lobes and as a consequence concentrate more energy in the main beam.
Virtually eliminate lateral lobes and as a consequence concentrate more energy in the main beam. The frequency which corresponds to a wavelength of 12 cm is ?
Question 175-7 : 2500 mhz 2500 khz 360 mhz 3600 mhz
 2500 mhz.
2500 mhz. A cumulonimbus cloud in the vicinity of an aeroplane can cause certain ?
Question 175-8 : Adf vor weather radar dme
 Adf.
Adf. A radio altimeter employing a continuous wave signal would have ?
Question 175-9 : A directional aerial for transmission and another one for reception an omni directional aerial for transmission and directional aerial for reception a directional aerial for transmission and an omni directional aerial for reception a directional aerial for both transmission and reception
 A directional aerial for transmission and another one for reception.
A directional aerial for transmission and another one for reception. Which statement relating to the stabilization of airborne weather radar ?
Question 175-10 : They are stabilized with respect to the pitch and rollaxis but not with respect to the yaw axis they are stabilized with respect to the pitch roll and yaw axis they are stabilized with respect to the yaw axis but not with respect to the pitch and roll axis the pilot can choose the axes of stabilization with the system's stabilization selector switch
 They are stabilized with respect to the pitch and rollaxis but not with respect to the yaw-axis.
They are stabilized with respect to the pitch and rollaxis but not with respect to the yaw-axis. The antennae of modern airborne weather radars are stabilized by means of ?
Question 175-11 : Inputs from the aircraft's attitude system artificial gravity switches mercury switches feedback from the antenna accelerometers
 Inputs from the aircraft's attitude system.
Inputs from the aircraft's attitude system. The type of modulation used for the ils frequency carrier is ?
Question 175-12 : Amplitude modulation frequency modulation phase modulation dual modulation
 Amplitude modulation.
Amplitude modulation. The quadrantal error of an adf ?
Question 175-13 : Is caused by the refraction from the aircraft's fuselage and is compensated for is caused by aircraft magnetism and varies with the deviation as shown on the deviation table is caused by interference from the sky wave may be caused by the interference of vor's within range of the adf receiver and cannot be compensated for
 Is caused by the refraction from the aircraft's fuselage and is compensated for.
Is caused by the refraction from the aircraft's fuselage and is compensated for. The skip distance of hf transmission will increase with ?
Question 175-14 : Higher frequency and higher position of the reflecting ionospheric layer lower frequency and higher position of the reflecting ionospheric layer higher frequency and lower position of the reflecting ionospheric layer lower frequency and lower position of the reflecting ionospheric layer
 Higher frequency and higher position of the reflecting ionospheric layer.
Higher frequency and higher position of the reflecting ionospheric layer. Which statement about the errors and effects on ndb radio signals is correct ?
Question 175-15 : The mountain effect is caused by reflections onto steep slopes of mountainous terrain which may cause big errors in the bearing night effect is a result of interference of the surface wave and the space wave causing a reduction in range lightning during atmospheric disturbances may cause a reduction of the signal strength that may result in only slight bearing errors shore line effects may cause a huge bearing error due to reflection of the radio signal onto steep coasts
 The mountain effect is caused by reflections onto steep slopes of mountainous terrain which may cause big errors in the bearing.
The mountain effect is caused by reflections onto steep slopes of mountainous terrain which may cause big errors in the bearing. What causes the so called night effect ?
Question 175-16 : A change in the direction of the plane of polarisation due to reflection in the ionosphere the difference in velocity of the em waves over land and over sea at night the absence of the surface wave at distances larger than the skip distance interference between the ground and the space wave
 A change in the direction of the plane of polarisation due to reflection in the ionosphere.
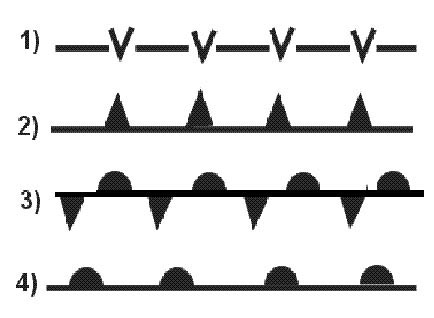
A change in the direction of the plane of polarisation due to reflection in the ionosphere. An amplitude modulation is shown in the figure . 2069 ?
Question 175-17 : A b c d
 A.
A. In his basic type a dipole antenna adapted for a frequency of 110 mhz will have ?
Question 175-18 : 136 cm 273 cm 91 cm 205 cm
 136 cm.
136 cm. How is the unit 'hertz' hz defined ?
Question 175-19 : The number of electromagnetic oscillations per second duration of an oscillation the distance covered by a radio wave in one second the number of electromagnetic oscillations per minute
 The number of electromagnetic oscillations per second.
The number of electromagnetic oscillations per second. An ndb transmits on 427 khz the corresponding wavelength is ?
Question 175-20 : 702 5 m 702 5 cm 7025 cm 70 25 cm
 702,5 m.
702,5 m. An electromagnetic wave consists of an oscillating electric field e and an ?
Question 175-21 : The speed of light the speed of sound for field e and the speed of light for field h the speed of light for field e and the speed of sound for field h the speed of sound
 The speed of light.
The speed of light. The electromagnetic waves refracted from the e and f layers of the ionosphere ?
Question 175-22 : Sky waves ground waves refracted waves space waves
 Sky waves.
Sky waves. The simplest type of antenna construction is a ?
Question 175-23 : Dipole antenna which is a wire of length equal to one half of the wavelength parabolic antenna used in weather radars slotted antenna used in modern weather radars loop antenna used in old adf receivers
 Dipole antenna which is a wire of length equal to one half of the wavelength.
Dipole antenna which is a wire of length equal to one half of the wavelength. An electromagnetic wave consists of an oscillating electric field e and an ?
Question 175-24 : The e and h fields are perpendicular to each other a dipole antenna can only transmit field h the h field is parallel to the wire and field e is perpendicular to the wire when ac current pass through the antenna fields e and h are parallel
 The (e) and (h) fields are perpendicular to each other.
The (e) and (h) fields are perpendicular to each other. The frequency which corresponds to a wavelength of 8 25 m is ?
Question 175-25 : 36 36 mhz 3636 mhz 363 6 mhz 3 63 mhz
 36.36 mhz
36.36 mhz The frequency which corresponds to a wavelength of 3 km is ?
Question 175-26 : 100 khz 10 khz 1000 khz 1 mhz
 100 khz.
100 khz. Wavelength of frequency 117 95 mhz is ?
Question 175-27 : 2 5 m 25 m 250 m 254 m
 2.5 m.
2.5 m. Concerning the wave propagation in the ionosphere we denote three layers those ?
Question 175-28 : D e and f layers and their depth varies with time d e and f layers and their depth does not vary with time a b and c layers and their depth varies with time a c and e layers with equal depth
 D, e and f layers and their depth varies with time.
D, e and f layers and their depth varies with time. Radio waves travel at ?
Question 175-29 : The speed of light the speed of sound a speed depending on the type of the electromagnetic waves a speed just below the speed of sound
 The speed of light.
The speed of light. In accordance with the itu international telecommunication union a radio signal ?
Question 175-30 : Nature of information to be transmitted type of modulation of the main carrier nature of signal s modulating the main carrier type of modulation of the secondary carrier
 Nature of information to be transmitted.
Nature of information to be transmitted. In accordance with the itu international telecommunication union a radio signal ?
Question 175-31 : Nature of signal s modulating the main carrier type of information to be transmitted type of modulation of the secondary carrier type of modulation of the main carrier
 Nature of signal(s) modulating the main carrier.
Nature of signal(s) modulating the main carrier. In accordance with the itu international telecommunication union a radio signal ?
Question 175-32 : Type of modulation of the main carrier nature of signal s modulating the main carrier type of information to be transmitted type of modulation of the secondary carrier
 Type of modulation of the main carrier.
Type of modulation of the main carrier. Vhf very high frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ?
Question 175-33 : 30 mhz 300 mhz 3 mhz 30 mhz 300 mhz 3000 mhz 3 ghz 30 ghz
 30 mhz - 300 mhz
30 mhz - 300 mhz With regard to radio waves propagation a cycle is defined as ?
Question 175-34 : A complete series of values of a periodical process a number of oscillation per second the lenght of the pulse the distance covered by a radio wave in one second
 A complete series of values of a periodical process.
A complete series of values of a periodical process. Vlf very low frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ?
Question 175-35 : 3 khz 30 khz 30 mhz 300 mhz 300 mhz 3000 mhz 3 ghz 30 ghz
 3 khz - 30 khz
3 khz - 30 khz Lf low frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ?
Question 175-36 : 30 khz 300 khz 30 hz 300 hz 300 mhz 3000 mhz 3 mhz 30 mhz
 30 khz - 300 khz
30 khz - 300 khz Mf medium frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ?
Question 175-37 : 300 khz 3000 khz 30 mhz 300 mhz 3 mhz 30 mhz 30 ghz 300 ghz
 300 khz - 3000 khz
300 khz - 3000 khz Hf high frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ?
Question 175-38 : 3 mhz 30 mhz 30 mhz 300 mhz 300 mhz 3000 mhz 3 khz 30 khz
 3 mhz - 30 mhz
3 mhz - 30 mhz Uhf ultra high frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ?
Question 175-39 : 300 mhz 3000 mhz 30 mhz 300 mhz 3 mhz 30 mhz 3 ghz 30 ghz
 300 mhz - 3000 mhz
300 mhz - 3000 mhz Shf super high frequency waves appear in the frequency spectrum ?
Question 175-40 : 3 ghz 30 ghz 30 mhz 300 mhz 3 mhz 30 mhz 300 mhz 3000 mhz
 3 ghz - 30 ghz
3 ghz - 30 ghz ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6959 Free Training Exam
