During approach the following data are obtained .dme 12 0 nm altitude 3000 ? [ Multiple protocol ]
Question 174-1 : 570 ft/min 600 ft/min 730 ft/min 700 ft/min
 570 ft/min.
570 ft/min. The distance between a and b is 90 nm at a distance of 75 nm from a the ?
Question 174-2 : 3°r 6°r 19°r 22°r
 3°r.
3°r. The true course according to the flight log is 270° the forecast wind is 045° ?
Question 174-3 : 5°l 6°r 2°l 3°r
 5°l.
5°l. An aircraft flies from waypoint 7 63°00'n 073°00'w to waypoint 8 62°00'n ?
Question 174-4 : 4 7 nm right 8 8 nm right 8 8 nm left 4 7 nm left
 4,7 nm right.
4,7 nm right. An aircraft is departing from an airport which has an elevation of 2000 ft and ?
Question 174-5 : 7 2 nm 8 8 nm 10 8 nm 6 6 nm
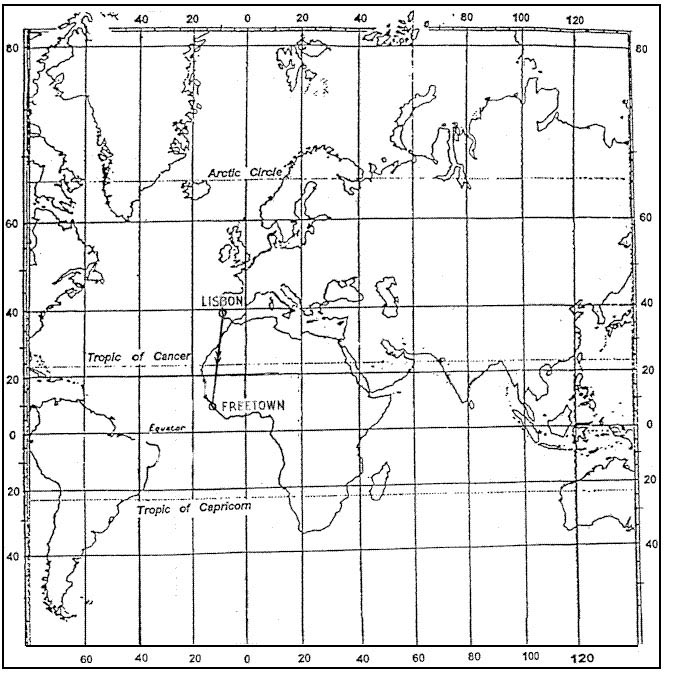 7.2 nm.
7.2 nm. You are departing from an airport which has an elevation of 1500 ft the qnh is ?
Question 174-6 : 800 ft/min 870 ft/min 730 ft/min 530 ft/min
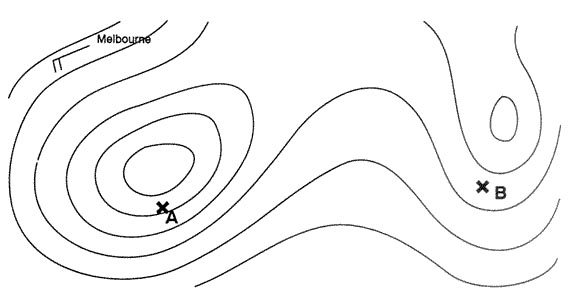 800 ft/min.
800 ft/min. An aircraft is flying at fl200 .the qnh given by a meteorological station at an ?
Question 174-7 : 10 500 ft 9 200 ft 11 800 ft 20 200 ft
 10 500 ft.
10 500 ft. The qnh given by a station at 2500 ft is 980hpa .the elevation of the highest ?
Question 174-8 : 10 400 ft 10 000 ft 11 200 ft 9 700 ft
 10 400 ft.
10 400 ft. An aircraft is departing from an airport which has an elevation of 2000 ft ?
Question 174-9 : 276 kt 289 kt 244 kt 331 kt
 276 kt.
276 kt. During visual navigation in freezing conditions after heavy snowfall which of ?
Question 174-10 : A large river a country road a railway an electrical line
 A large river.
A large river. During a climb at a constant cas below the tropopause in standard conditions ?
Question 174-11 : Both tas and mach number will increase tas will decrease but mach number will increase both tas and mach number will decrease tas will increase and mach number will decrease
 Both tas and mach number will increase.
Both tas and mach number will increase. An aircraft is descending down a 12% slope whilst maintaining a gs of 540 kt ?
Question 174-12 : 6500 ft/min 650 ft/min 4500 ft/min 3900 ft/min
 6500 ft/min.
6500 ft/min. The departure airfield is at 2000 ft elevation temperature at the field is ?
Question 174-13 : Fl 200 with temperature 20°c fl 290 with temperature 40°c fl 100 with temperature 10°c fl 150 with temperature 0°c
 Fl 200 with temperature -20°c.
Fl 200 with temperature -20°c. The departure is from an airfield at 2000 ft elevation temperature at the field ?
Question 174-14 : 249 kt 230 kt 221 kt 180 kt
 249 kt.
249 kt. Given .w/v at arrival aerodrome at 1000 ft amsl is 230°/15kt w/v at tod at fl ?
Question 174-15 : 163 kt 155 kt 180 kt 174 kt
 163 kt.
163 kt. Given .w/v at arrival aerodrome at msl is 200°/20kt w/v at tod at fl 100 is ?
Question 174-16 : 135 kt 145 kt 120 kt 150 kt
 135 kt.
135 kt. An aircraft is cruising in fl180 and thereafter descends to ground level the ?
Question 174-17 : 270°/40 kt 270°/20 kt 270°/35 kt 280°/50 kt
 270°/40 kt.
270°/40 kt. The distance between two waypoints is 150 nm to calculate compass heading the ?
Question 174-18 : 10 nm 15 nm 7 nm 20 nm
 10 nm.
10 nm. True track 085°.groundspeed 180 kt.wind 290°/30kt.variation 4°e .the ?
Question 174-19 : 2 5° l 2 5° r 1° l 1° r
 2.5° l.
2.5° l. With only a visual straight line as visual cue a canal for example this line ?
Question 174-20 : More or less perpendicular to our track more or less parallel to our track curved across our track oblique to our track
 More or less perpendicular to our track.
More or less perpendicular to our track. Given .a descending aircraft flies in a straight line to a dme .dme 55 nm ?
Question 174-21 : 3 70% 4 10% 3 50% 3 90%
 3.70%.
3.70%. The descent gradient of an aircraft with the following data is . 60 nm norths ?
Question 174-22 : 5 4% 6 4% 7 6% 4 5%
 5.4%
5.4% The average tas climbing from 1500 ft to fl180 with a given temperature of isa ?
Question 174-23 : 283 kt 309 kt 261 kt 274 kt
 283 kt.
283 kt. An aircraft is turning on a final approach to intercept a 3° glide slope which ?
Question 174-24 : 1916 ft 700 ft 1220 ft 1290 ft
 1916 ft.
1916 ft. Given .tas 220 kt.cruising level fl180.track during climb 080°.wind at msl ?
Question 174-25 : 262 kt 259 kt 254 kt 273 kt
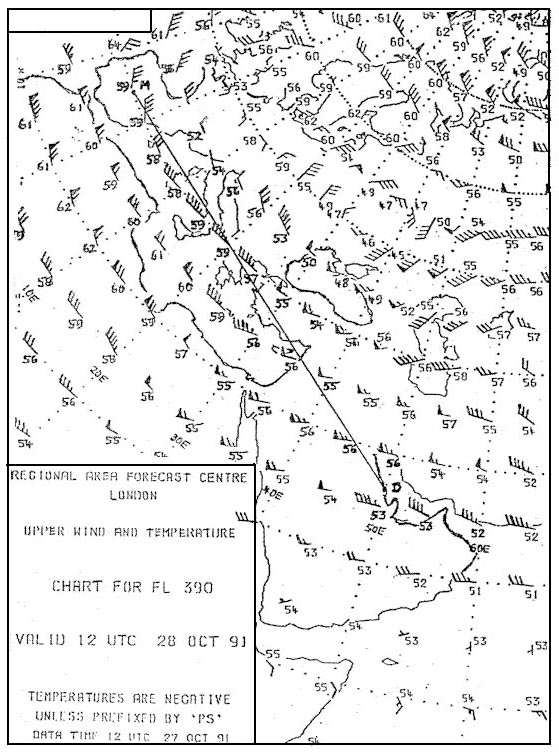 262 kt.
262 kt. An aircraft climbs from ground level to fl180 the following wind information is ?
Question 174-26 : 280°/50 kt 285°/55 kt 290°/55 kt 270°/30 kt
 280°/50 kt.
280°/50 kt. An aircraft descends from fl240 to fl040 for the final approach .cas = 220 ?
Question 174-27 : 273 kt 244 kt 254 kt 259 kt
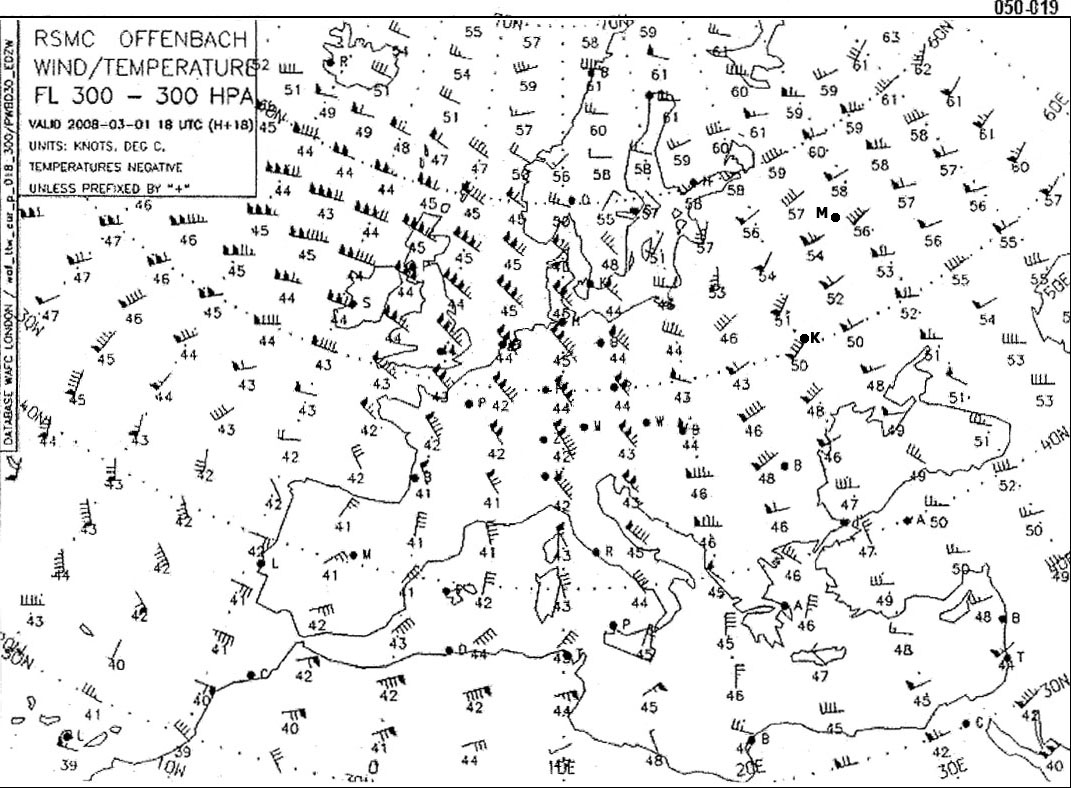 273 kt.
273 kt. When flying a visual navigation exercise in controlled airspace it is confirmed ?
Question 174-28 : 034° 038° 030° 042°
 034°.
034°. An aircraft in cruise at fl120 is cleared to descend to 3000 ft .the distance ?
Question 174-29 : 6% 6 3% 4 7% 5%
 6%.
6%. Given .descent from 15000 ft to 3000 ft msl.glide path angle during descent ?
Question 174-30 : It decreases from 900 ft/min to 750 ft/min 900 ft/min during the whole descent 825 ft/min during the whole descent 750 ft/min during the whole descent
 It decreases from 900 ft/min to 750 ft/min.
It decreases from 900 ft/min to 750 ft/min. Which formula can be used to calculate the rate of climb/descent .rate of ?
Question 174-31 : Groundspeed kt x gradient ft/nm / 60 altitude difference ft x 100 / ground difference ft climb/descent angle ° x 100 / 60 arctg altitude difference ft / ground distance covered ft
 Groundspeed (kt) x gradient (ft/nm) / 60
Groundspeed (kt) x gradient (ft/nm) / 60 The correct formula for climb/descent gradient in % is .gradient in % = ?
Question 174-32 : Vertical distance x 100 / ground distance height difference / altitude difference x 100 rate of climb or descent x ground speed arctg altitude difference / ground distance
 (vertical distance x 100) / ground distance.
(vertical distance x 100) / ground distance. The correct formula for climb/descent gradient in ° is .gradient in ° = ?
Question 174-33 : Vertical distance ft / 100 / ground distance nm vertical distance ft x 60 / ground distance nm rate of climb or descent x ground speed height difference / altitude difference x 100
 (vertical distance (ft) / 100) / ground distance (nm)).
(vertical distance (ft) / 100) / ground distance (nm)). An aircraft climbs from ground level to fl180 the following wind information is ?
Question 174-34 : The wind at fl120 the wind at fl190 the average wind speed from ground to fl180 the average wind speed from ground to fl120
 The wind at fl120.
The wind at fl120. An aircraft is flying according the flight log at the annex after 15 minutes of ?
Question 174-35 : 078° 115 ° 107° 090°
 078°.
078°. The 'night effect' which causes loss of signal and fading resulting in bearing ?
Question 174-36 : Skywave distortion of the null position and is maximum at dawn and dusk interference from other transmissions and is maximum at dusk when east of the ndb static activity increasing at night particularly in the lower frequency band the effect of the aurora borealis
 Skywave distortion of the null position and is maximum at dawn and dusk.
Skywave distortion of the null position and is maximum at dawn and dusk. Quadrantal errors associated with aircraft automatic direction finding adf ?
Question 174-37 : Signal bending by the aircraft metallic surfaces signal bending caused by electrical interference from aircraft wiring misalignment of the loop aerial skywave/groundwave contamination
 Signal bending by the aircraft metallic surfaces.
Signal bending by the aircraft metallic surfaces. Errors caused by the effect of coastal refraction on bearings at lower ?
Question 174-38 : Inland and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle near the coast and the bearing crosses the coast at right angles inland and the bearing crosses the coast at right angles near the coast and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle
 Inland and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle.
Inland and the bearing crosses the coast at an acute angle. Transmissions from vor facilities may be adversely affected by ?
Question 174-39 : Uneven propagation over irregular ground surfaces static interference night effect quadrantal error
 Uneven propagation over irregular ground surfaces.
Uneven propagation over irregular ground surfaces. If vor bearing information is used beyond the published protection range errors ?
Question 174-40 : Interference from other transmitters noise from precipitation static exceeding the signal strength of the transmitter sky wave interference from the same transmitter sky wave interference from distant transmitters on the same frequency
 Interference from other transmitters.
Interference from other transmitters. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6919 Free Training Exam
