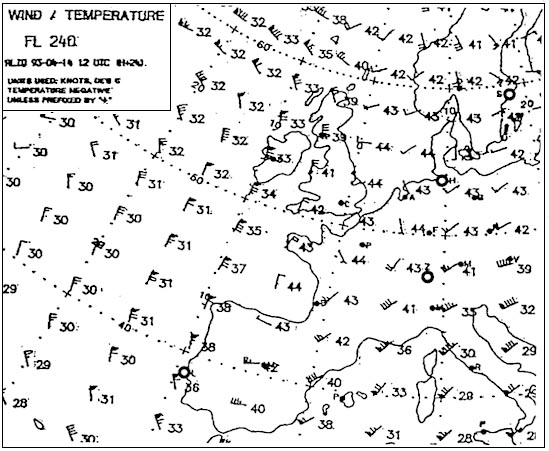
Given distance 'a' to 'b' is 90 nm fix obtained 60 nm along and 4 nm to the ? [ Multiple protocol ]
Question 173-1 : 12° left 16° left 4° left 8° left
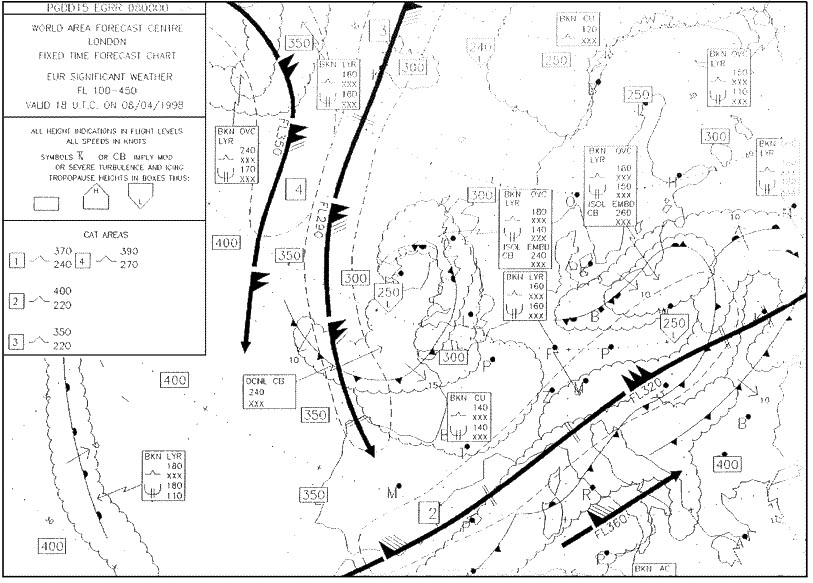 12° left.
12° left. Complete line 1 of the 'flight navigation log'.positions 'a' to 'b' what is the ?
Question 173-2 : Hdg 268° eta 1114 utc hdg 282° eta 1128 utc hdg 282° eta 1114 utc hdg 268° eta 1128 utc
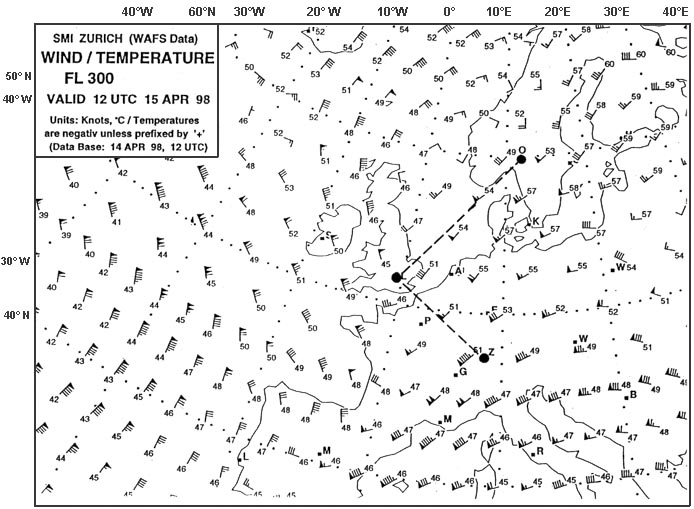 Hdg 268° - eta 1114 utc.
Hdg 268° - eta 1114 utc. Complete line 2 of the 'flight navigation log' positions 'c' to 'd' what is the ?
Question 173-3 : Hdg 193° eta 1239 utc hdg 188° eta 1229 utc hdg 193° eta 1249 utc hdg 183° eta 1159 utc
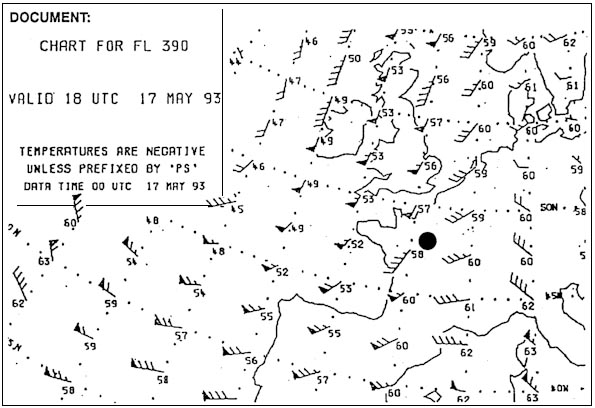 Hdg 193° - eta 1239 utc.
Hdg 193° - eta 1239 utc. Complete line 3 of the 'flight navigation log' positions 'e' to 'f' what is the ?
Question 173-4 : Hdg 105° eta 1205 utc hdg 095° eta 1155 utc hdg 106° eta 1215 utc hdg 115° eta 1145 utc
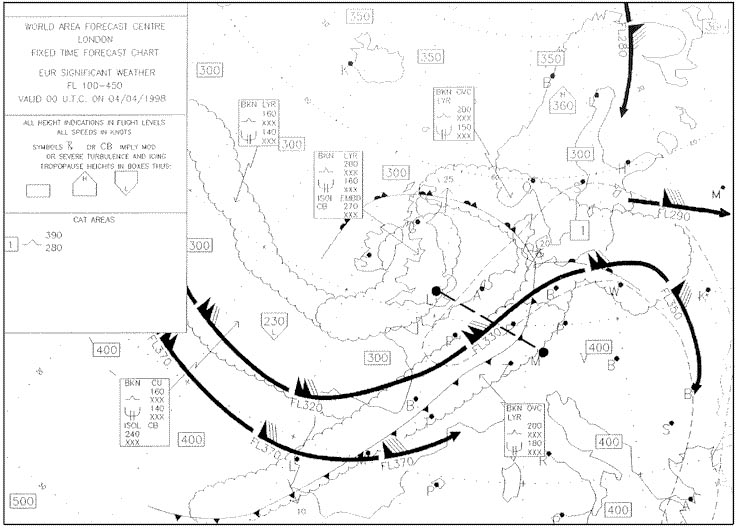 Hdg 105° - eta 1205 utc.
Hdg 105° - eta 1205 utc. Complete line 4 of the 'flight navigation log' positions 'g' to 'h' what is the ?
Question 173-5 : Hdg 344° eta 1336 utc hdg 354° eta 1326 utc hdg 334° eta 1336 utc hdg 344° eta 1303 utc
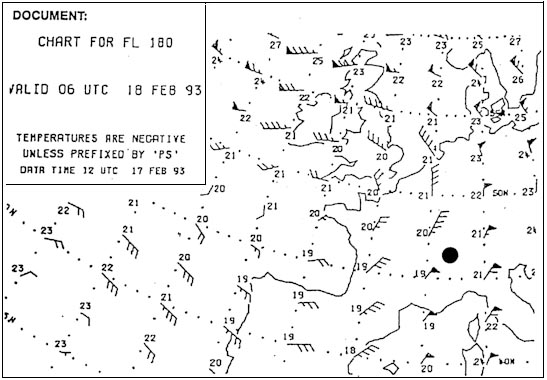 Hdg 344° - eta 1336 utc.
Hdg 344° - eta 1336 utc. Complete line 5 of the 'flight navigation log' positions 'j' to 'k' what is the ?
Question 173-6 : Hdg 337° eta 1422 utc hdg 320° eta 1412 utc hdg 337° eta 1322 utc hdg 320° eta 1432 utc
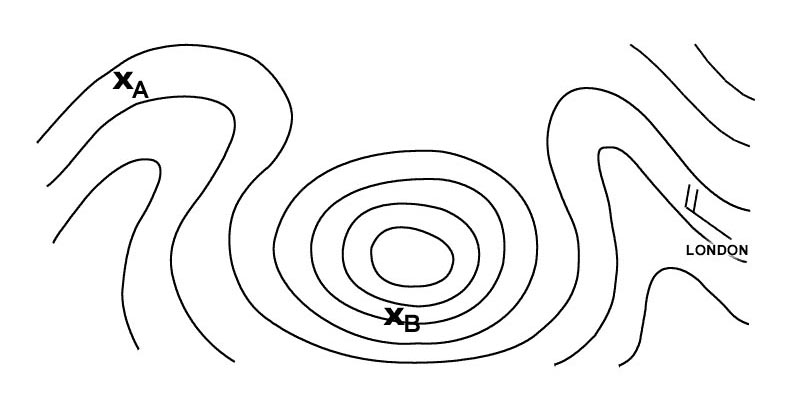 Hdg 337° - eta 1422 utc.
Hdg 337° - eta 1422 utc. Complete line 6 of the 'flight navigation log' positions 'l' to 'm' what is the ?
Question 173-7 : Hdg 075° eta 1502 utc hdg 064° eta 1449 utc hdg 075° eta 1452 utc hdg 070° eta 1459 utc
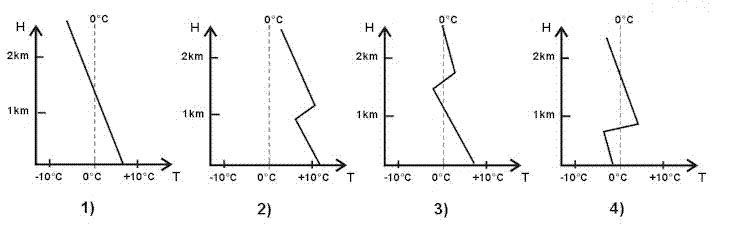 Hdg 075° - eta 1502 utc.
Hdg 075° - eta 1502 utc. Given .tas = 197 kt true course = 240° w/v = 180/30kt .descent is initiated at ?
Question 173-8 : 1400 ft/min 800 ft/min 950 ft/min 1500 ft/min
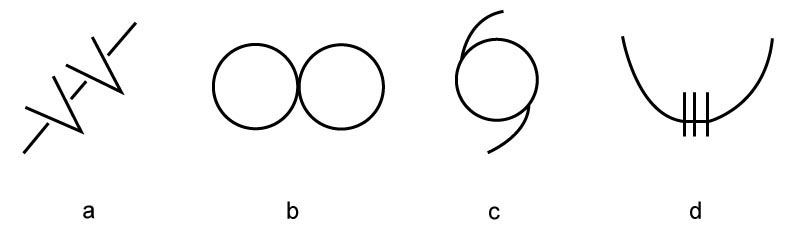 1400 ft/min.
1400 ft/min. Given .ils glide path angle = 3 5° ground speed = 150 kt .what is the ?
Question 173-9 : 900 ft/min 350 ft/min 700 ft/min 300 ft/min
 900 ft/min.
900 ft/min. Given aircraft height 2500 ft ils gp angle 3° at what approximate distance ?
Question 173-10 : 8 3 nm 7 0 nm 13 1 nm 14 5 nm
 8.3 nm.
8.3 nm. An island appears 60° to the left of the centre line on an airborne weather ?
Question 173-11 : 046° 086° 226° 026°
 046°.
046°. An island appears 45° to the right of the centre line on an airborne weather ?
Question 173-12 : 059° 101° 239° 329°
 059°.
059°. An island appears 30° to the right of the centre line on an airborne weather ?
Question 173-13 : 220° 160° 130° 190°
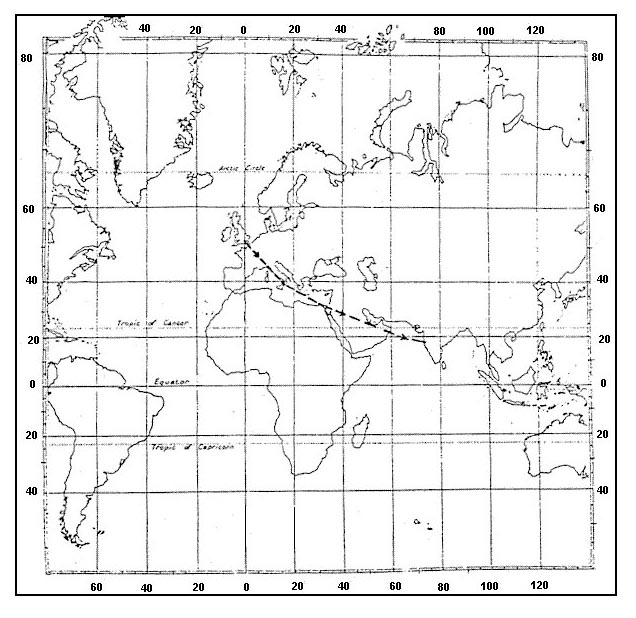 220°.
220°. An island appears 30° to the left of the centre line on an airborne weather ?
Question 173-14 : 145° 325° 205° 195°
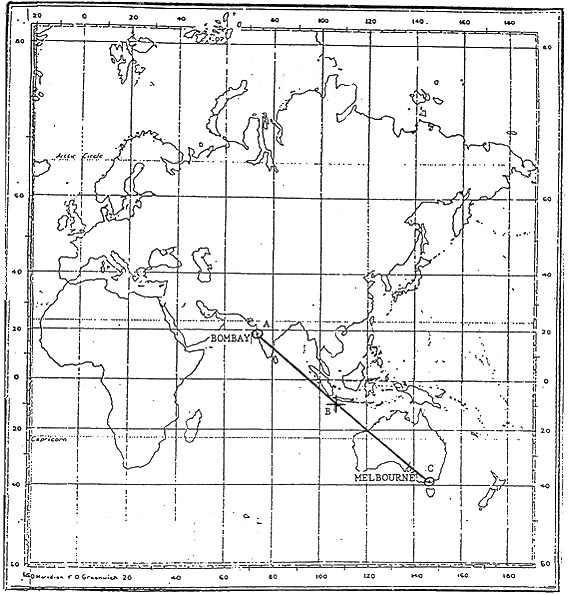 145°.
145°. Given an aircraft is flying a track of 255° m 2254 utc it crosses radial ?
Question 173-15 : The same as it was at 2254 utc greater than it was at 2254 utc randomly different than it was at 2254 utc less than it was at 2254 utc
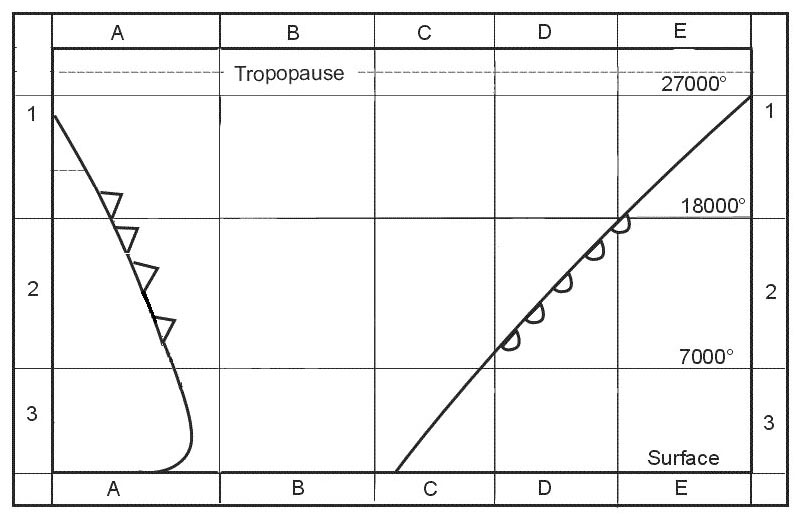 The same as it was at 2254 utc
The same as it was at 2254 utc The distance between two waypoints is 200 nm to calculate compass heading the ?
Question 173-16 : 14 nm 7 nm 0 nm 21 nm
 14 nm.
14 nm. Given .eta to cross a meridian is 2100 utc.gs is 441 kt.tas is 491 kt.at 2010 ?
Question 173-17 : 40 kt 90 kt 75 kt 60 kt
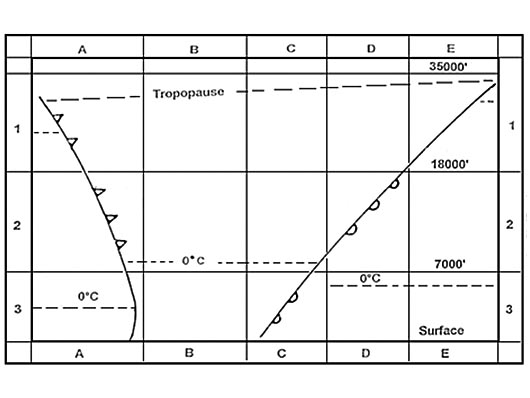 40 kt.
40 kt. The flight log gives the following data 'true track drift true heading magnetic ?
Question 173-18 : 119° 3°l 122° 2°e 120° +4° 116° 115° 5°r 120° 3°w 123° +2° 121° 117° 4°l 121° 1°e 122° 3° 119° 125° 2°r 123° 2°w 121° 4° 117°
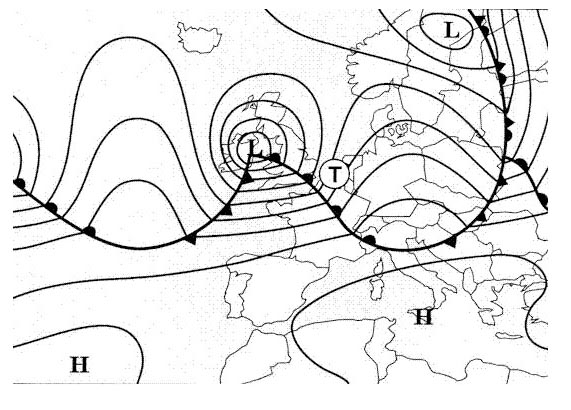 119°, 3°l, 122°, 2°e, 120°, +4°, 116°
119°, 3°l, 122°, 2°e, 120°, +4°, 116° At 0020 utc an aircraft is crossing the 310° radial at 40 nm of a vor/dme ?
Question 173-19 : 085° 226 kt 090° 232 kt 080° 226 kt 088° 232 kt
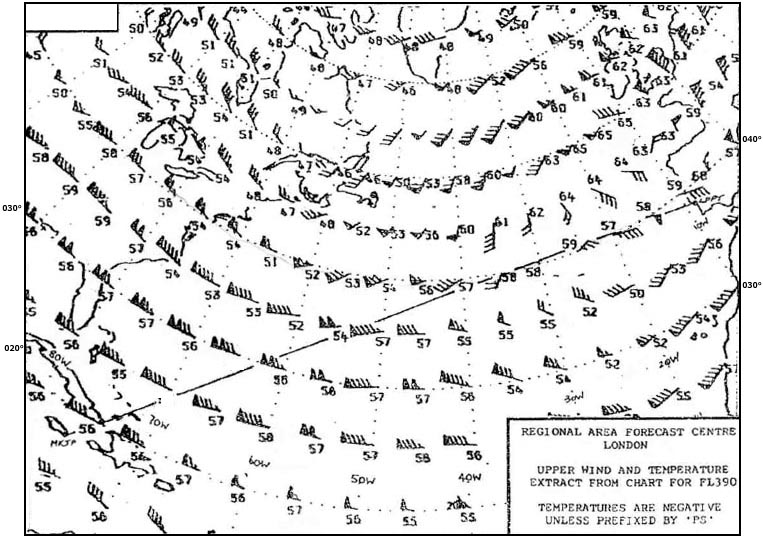 085° - 226 kt.
085° - 226 kt. Given .tas is 120 kt.ata 'x' 1232 utc.eta 'y' 1247 utc.ata 'y' is 1250 utc.what ?
Question 173-20 : 1302 utc 1257 utc 1300 utc 1303 utc
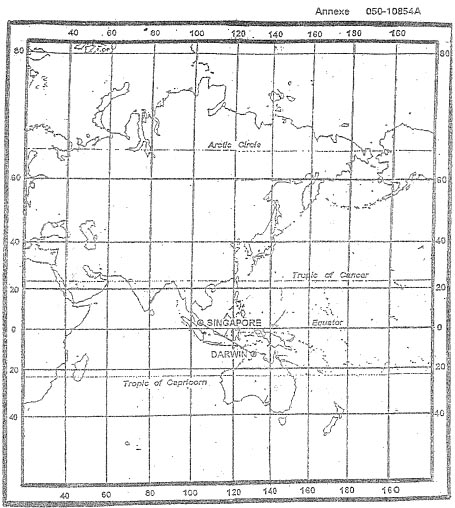 1302 utc.
1302 utc. Given .fl120 oat is isa standard cas is 200 kt track is 222° m heading is ?
Question 173-21 : 050° t / 70 kt 040° t / 105 kt 055° t / 105 kt 065° t / 70 kt
 050°(t) / 70 kt.
050°(t) / 70 kt. A useful method of a pilot resolving during a visual flight any uncertainty in ?
Question 173-22 : Set heading towards a line feature such as a coastline motorway river or railway fly the reverse of the heading being flown prior to becoming uncertain until a pinpoint is obtained fly expanding circles until a pinpoint is obtained fly reverse headings and associated timings until the point of departure is regained
 Set heading towards a line feature such as a coastline, motorway, river or railway
Set heading towards a line feature such as a coastline, motorway, river or railway An aircraft is descending down a 6% slope whilst maintaining a ground speed of ?
Question 173-23 : 1800 ft/min 10800 ft/min 3600 ft/min 900 ft/min
 1800 ft/min.
1800 ft/min. An aircraft is flying according the flight log at the annex .after 15 minutes ?
Question 173-24 : 258° 292° 270° 253°
 258°.
258°. An island is observed to be 30° to the right of the nose of the aircraft the ?
Question 173-25 : 330° 270° 250° 310°
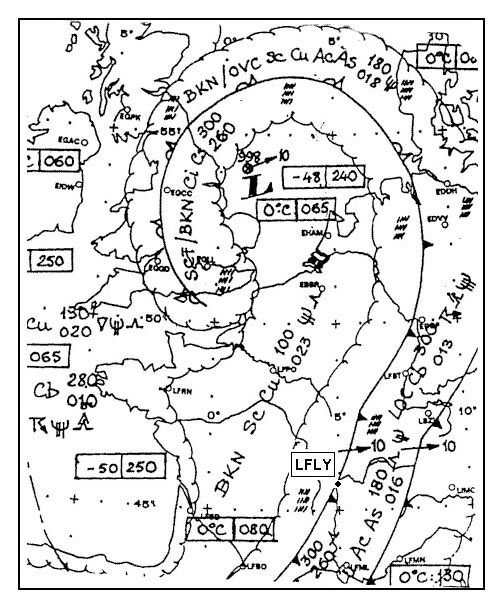 330°.
330°. An aircraft follows a radial to a vor/dme station at 10 00 the dme reads 120 nm ?
Question 173-26 : 10 24 10 27 10 18 10 21
 10:24.
10:24. You are departing from an airport which has an elevation of 2000 ft .the qnh is ?
Question 173-27 : 920 ft/min 1080 ft/min 590 ft/min 750 ft/min
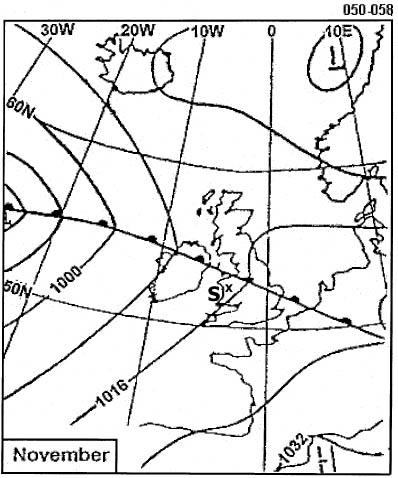 920 ft/min.
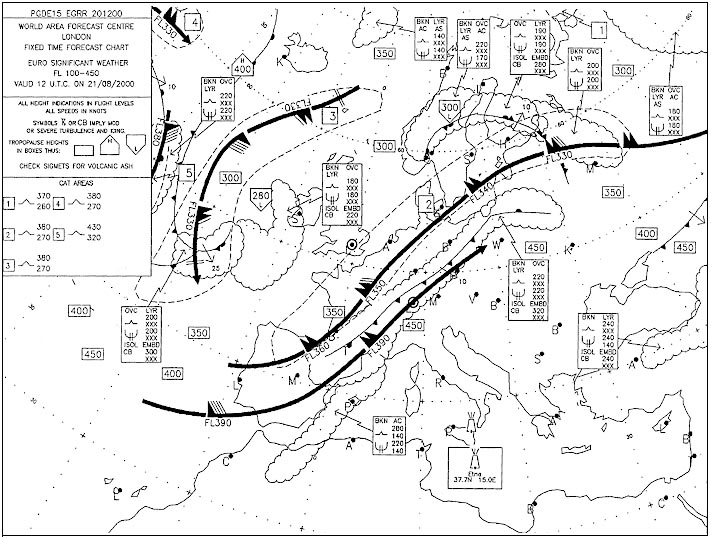
920 ft/min. At reference or see europe low altitude enroute chart e lo 1a.an aircraft is ?
Question 173-28 : 280 kt 385 kt 485 kt 180 kt
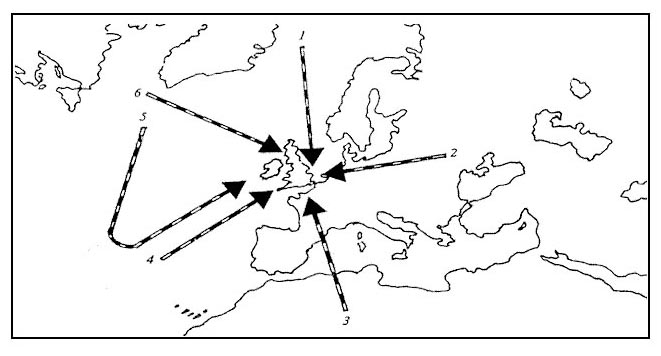 280 kt.
280 kt. The distance between point of departure and destination is 340 nm and wind ?
Question 173-29 : 1h and 49 min 1h and 30 min 1h and 37 min 1h and 21 min
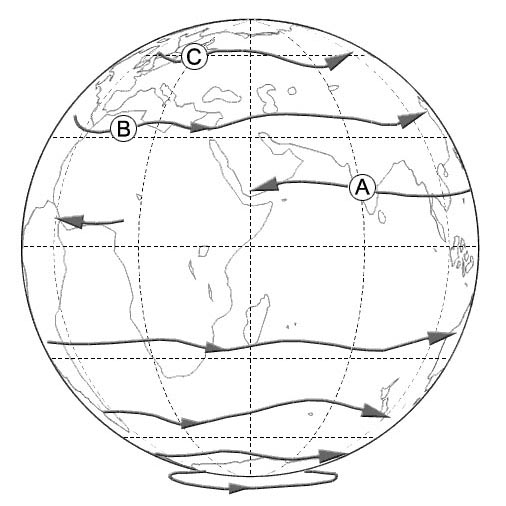 1h and 49 min.
1h and 49 min. You are tracking the 200° radial inbound to a vor and your true heading is ?
Question 173-30 : 310°/65 320°/55 330°/50 300°/50
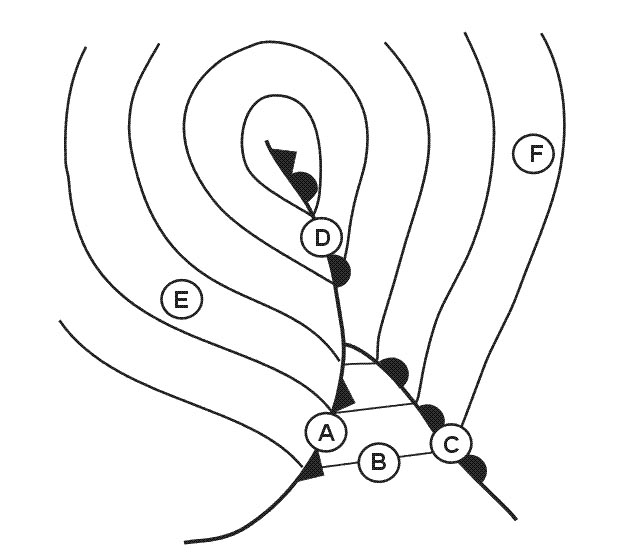 310°/65.
310°/65. An aircraft is flying according the flight log at the annex after 15 minutes of ?
Question 173-31 : 112° 080° 090° 107°
 112°.
112°. An aircraft is departing from an airport which has an elevation of 2000 ft and ?
Question 173-32 : 11 1 nm 10 3 nm 13 3 nm 16 6 nm
 11.1 nm.
11.1 nm. At 10 15 the reading from a vor/dme station is 211°/ 90nm at 10 20 the reading ?
Question 173-33 : 110°/70kt 100°/60kt 120°/50kt 110°/40kt
 110°/70kt.
110°/70kt. An aircraft is departing from an airport which has an elevation of 2000 ft and ?
Question 173-34 : 10 3 nm 11 1 nm 13 3 nm 15 4 nm
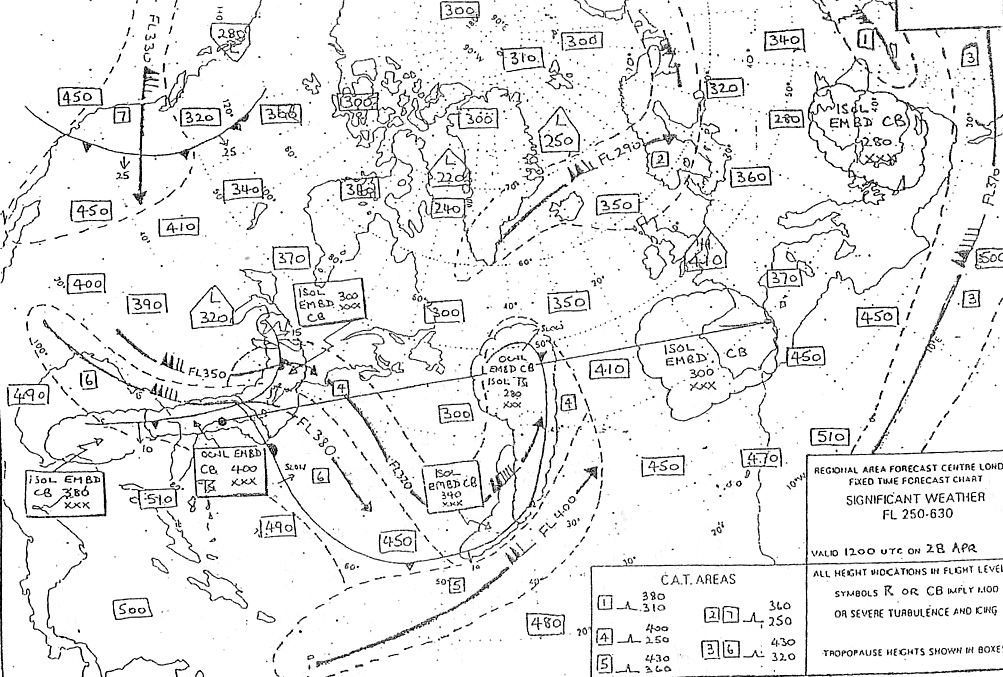 10.3 nm.
10.3 nm. Two consecutive waypoints of a flight plan are stornoway vordme n58°12 4' ?
Question 173-35 : 11 36 11 34 11 38 11 33
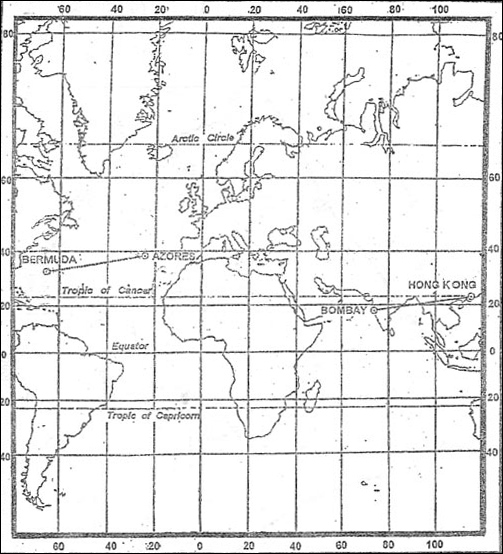 11:36
11:36 An aircraft at fl360 is required to descent to fl120 .the aircraft should reach ?
Question 173-36 : 124 nm 88 nm 236 nm 166 nm
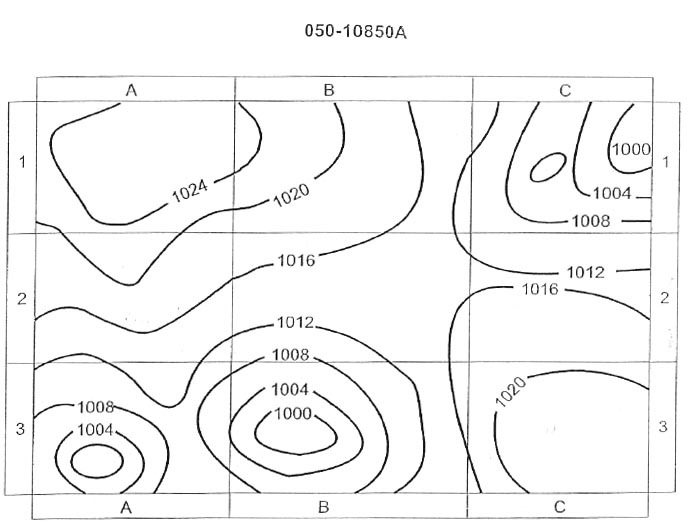 124 nm.
124 nm. The distance between a and b is 90 nm at a distance of 15 nm from a the ?
Question 173-37 : 19° 16° 3° 21°
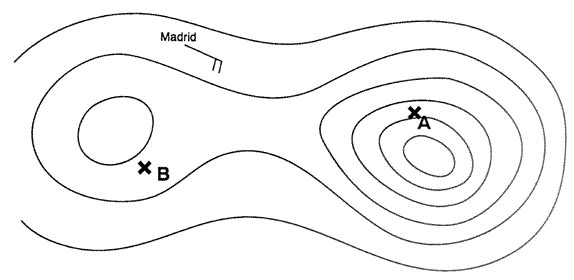 19°.
19°. After 15 minutes of flying with the planned tas and true heading the aircraft ?
Question 173-38 : 292° 258° 287° 280°
 292°.
292°. An aircraft is flying from salco to berry head on magnetic track 007° tas 445 ?
Question 173-39 : 272° t 268° t 277° t 275° t
 272° (t).
272° (t). An aircraft is departing from an airport which has an elevation of 2000 ft and ?
Question 173-40 : 3 6 nm 4 4 nm 4 0 nm 5 4 nm
~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6879 Free Training Exam
