An aircraft tracks radial 200° inbound to a vor station with a magnetic ? [ Multiple protocol ]
Question 171-1 : 320°/50 kt 310°/60 kt 300°/50 kt 330°/50 kt
 320°/50 kt.
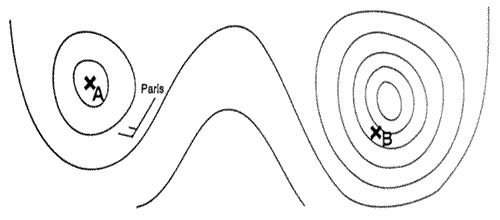
320°/50 kt. The fix of the aircraft position is determined by radials from three vor ?
Question 171-2 : 1 4 2 3
 1
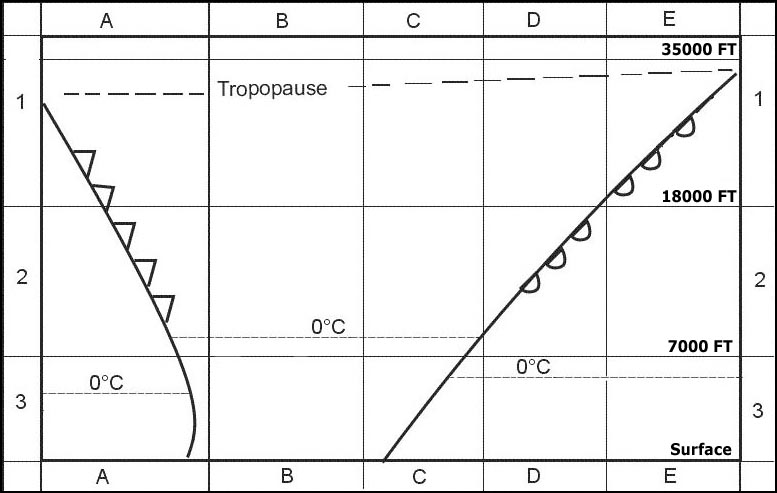
1 An aircraft flies at fl 250 with an oat of 45°c the qnh given by a ?
Question 171-3 : 4 200 ft 4 600 ft 3 500 ft 3 000 ft
 4 200 ft.
4 200 ft. Given .an aircraft is flying at fl100 oat = isa 15°c .the qnh given by a ?
Question 171-4 : 9900 ft 9400 ft 10600 ft 11200 ft
 9900 ft.
9900 ft. The accuracy of the manually calculated dead reckoning position of an aircraft ?
Question 171-5 : The accuracy of the forecasted wind the accuracy of the actual wind the accuracy of the adjustment of the position lines for the motion of the aircraft between the last fix and the dr position the accuracy of the adjustment of the position lines for the motion of the aircraft between the last and the new dr position
 The accuracy of the forecasted wind.
The accuracy of the forecasted wind. The accuracy of the manually calculated dead reckoning position of an aircraft ?
Question 171-6 : The flight time since the last position update the accuracy of the actual wind the accuracy of the adjustment of the position lines for the motion of the aircraft between the last fix and the dr position the accuracy of the adjustment of the position lines for the motion of the aircraft between the last and the new dr position
 The flight time since the last position update.
The flight time since the last position update. What may cause a difference between a dead rekoning position and a fix ?
Question 171-7 : The difference between the actual wind and the forecasted wind the difference between no wind and the actual wind the difference between no wind and the forecasted wind the difference between the magnetic and the true wind direction
 The difference between the actual wind and the forecasted wind.
The difference between the actual wind and the forecasted wind. Cas is 320 kt.flight level 330.oat isa +15°c.tas is approximately . ?
Question 171-8 : 530 kt 560 kt 265 kt 340 kt
 530 kt.
530 kt. Given .mach numer 0 8.flight level 330.oat isa +15°c .tas is approximately . ?
Question 171-9 : 480 kt 420 kt 450 kt 265 kt
 480 kt.
480 kt. The main purpose of dr dead reckoning is ?
Question 171-10 : To obtain with reasonable accuracy the aircraft's position between fixes or in the absence of fixes to monitor an inertial navigation system to obtain without reasonable accuracy the aircraft's position between fixes to improve gps accuracy
 To obtain with reasonable accuracy, the aircraft's position between fixes or in the absence of fixes.
To obtain with reasonable accuracy, the aircraft's position between fixes or in the absence of fixes. An aircraft is flying at fl390 at a speed of mach 0 821 .oat isa 4°c.the ?
Question 171-11 : 467 kt 439 kt 459 kt 433 kt
 467 kt.
467 kt. An aircraft descends from fl240 to fl80 for the final approach .track = ?
Question 171-12 : 276 kt 288 kt 268 kt 282 kt
 276 kt.
276 kt. An aircraft is flying at fl 350 with cas = 300 kt .oat = isa + 4°c .the ?
Question 171-13 : 509 kt 540 kt 535 kt 479 kt
 509 kt.
509 kt. Given .track = 355°.tas = 190 kt.wind 270°/25 kt.after 30 minutes of flying ?
Question 171-14 : 254°/34 kt 251°/21 kt 246°/21 kt 248°/21 kt
 254°/34 kt.
254°/34 kt. Given .fl 400.oat = 65°c.ias = 260 kt.instrument and position error to be ?
Question 171-15 : 479 kt 470 kt 512 kt 533 kt
 479 kt.
479 kt. Given .tas = 210 kt.cas = 190 kt.pressure altitude = 9000 ft.calculate mach ?
Question 171-16 : 0 34 0 54 0 62 0 44
 0.34.
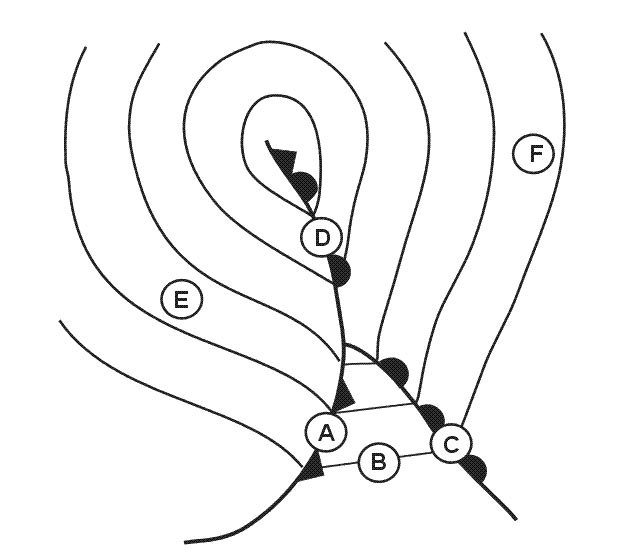
0.34. A dr position is to be found ?
Question 171-17 : On the desired track closeness to the destination perpendicular to the desired track at a distance not less than 50 km perpendicular to the desired track at a distance not less than 100 km
 On the desired track.
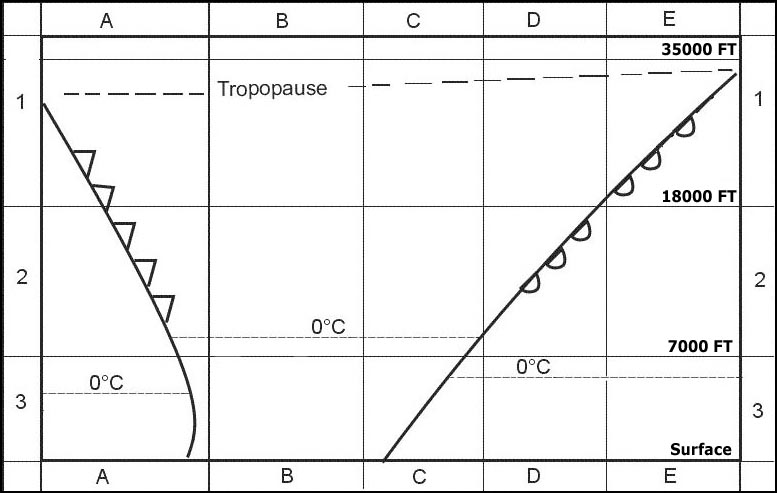
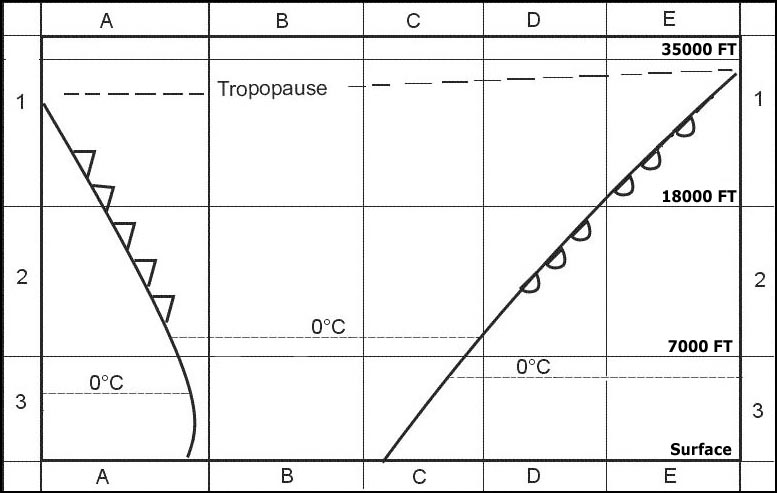
On the desired track. Which of the factors named hereafter should be considered by the pilot when ?
Question 171-18 : 1 3 4 1 2 3 2 3 4
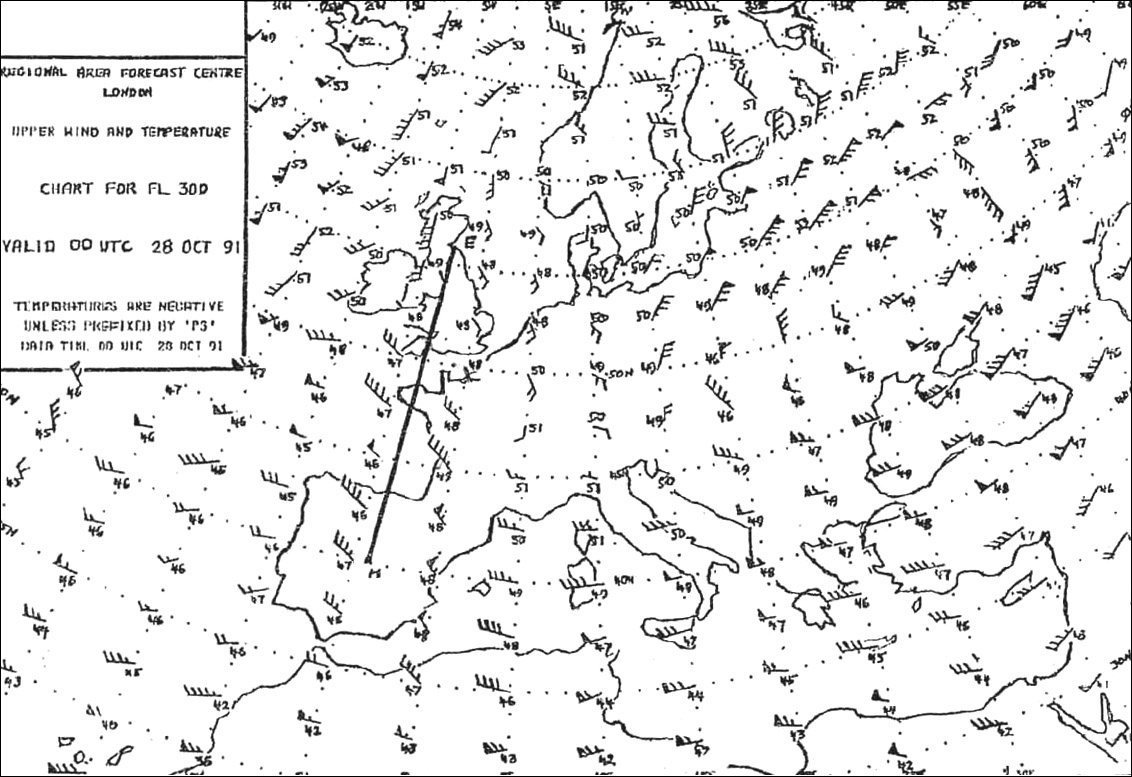 1, 3, 4.
1, 3, 4. Given .fl 300.oat = 45°c.ias = 260 kt.instrument and position error to be ?
Question 171-19 : 408 kt 400 kt 435 kt 424 kt
 408 kt.
408 kt. On a mercator chart one minute on n55° parallel is 3 1 mm .the map scale at ?
Question 171-20 : 1 457 650 1 779 880 1 447 320 1 797 890
 1 : 457 650
1 : 457 650 The nominal scale of a north stereopolar map is ?
Question 171-21 : At the north pole at the south pole at the equator the 45°north parallel
 At the north pole.
At the north pole. Given .tas = 140 kt true hdg = 302° w/v = 045° t /45kt .calculate the drift ?
Question 171-22 : 16°l 156 kt 9°r 143 kt 9°l 146 kt 18°r 146 kt
 16°l - 156 kt.
16°l - 156 kt. Given .tas = 290 kt.true hdg = 171°.w/v = 310° t /30kt .calculate the drift ?
Question 171-23 : 4°l 314 kt 4°r 310 kt 4°r 314 kt 4°l 310 kt
 4°l - 314 kt
4°l - 314 kt Given .tas = 485 kt .true heading = 226° .true wind = 110°/95kt .calculate ?
Question 171-24 : 9°r 533 kt 7°r 531 kt 9°r 433 kt 8°l 435 kt
 9°r - 533 kt.
9°r - 533 kt. Given .tas = 472 kt .true heading = 005° .true wind = 110°/50kt .calculate ?
Question 171-25 : 6°l/490 kt 7°r/491 kt 7°l/487 kt 7°r/491 kt
 6°l/490 kt.
6°l/490 kt. Given .tas = 375 kt true heading = 124° wind = 130°/55 kt .calculate the true ?
Question 171-26 : 123° 320 kt 125° 322 kt 126° 320 kt 125° 318 kt
 123° - 320 kt.
123° - 320 kt. Given .tas = 198 kt.hdg °t = 180.w/v = 359/25 .calculate the track °t and gs ?
Question 171-27 : 180° 223 kt 179° 220 kt 181° 180 kt 180° 183 kt
 180° - 223 kt
180° - 223 kt Given .tas = 135 kt true heading = 278° true wind = 140°/20 kt .calculate the ?
Question 171-28 : 283° 150 kt 279° 152 kt 272° 121 kt 275° 150 kt
 283° - 150 kt.
283° - 150 kt. Given .tas = 155 kt.true heading = 216°.wind = 090°/60 kt.calculate the true ?
Question 171-29 : 231° 196 kt 224° 175 kt 222° 181 kt 226° 186 kt
 231° - 196 kt.
231° - 196 kt. Given .tas = 465 kt true heading = 124° wind = 170°/80 kt .calculate drift ?
Question 171-30 : 8l 415 kt 3l 415 kt 4l 400 kt 6l 400 kt
 8l - 415 kt
8l - 415 kt Given tas = 140 kt hdg t = 005° w/v = 265/25kt calculate the drift and gs ?
Question 171-31 : 10r 146 kt 9r 140 kt 11r 142 kt 11r 140 kt
 10r - 146 kt
10r - 146 kt Given .tas = 190 kt hdg t = 355° w/v = 165/25kt .calculate the drift and gs ?
Question 171-32 : 1l 215 kt 1l 225 kt 1r 175 kt 1r 165 kt
 1l - 215 kt
1l - 215 kt Given .tas = 250 kt.hdg t = 029°.w/v = 035/45kt.calculate the drift and gs ?
Question 171-33 : 1l 205 kt 1r 205 kt 1l 265 kt 1r 295 kt
 1l - 205 kt
1l - 205 kt Given .tas = 485 kt true heading = 168° wind = 130/75 kt .calculate true track ?
Question 171-34 : 174° 428 kt 173° 424 kt 175° 420 kt 175° 432 kt
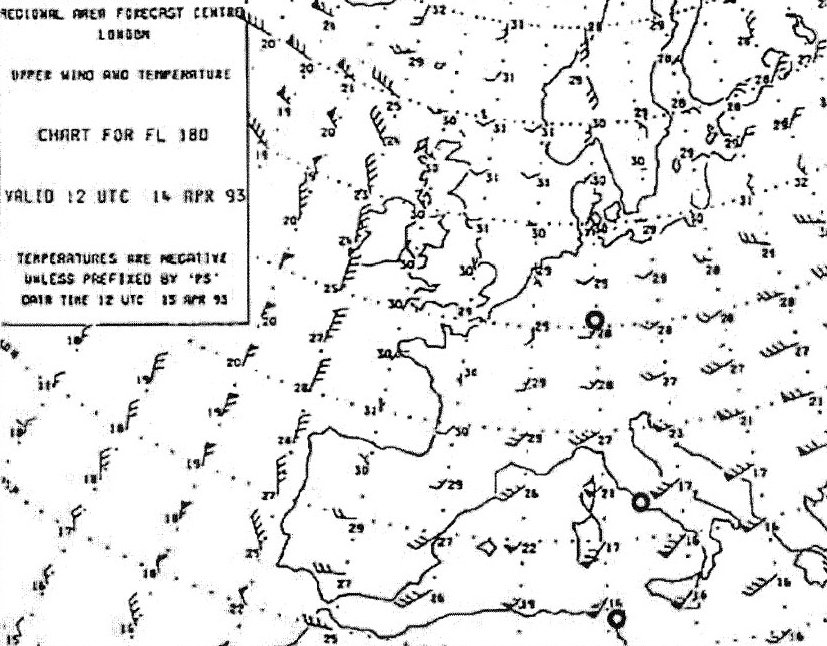 174° - 428 kt.
174° - 428 kt. Given .tas = 130 kt.track t = 003°.w/v = 190/40 kt.calculate the hdg °t and gs ?
Question 171-35 : 001° 170 kt 002° 173 kt 359° 166 kt 357° 168 kt
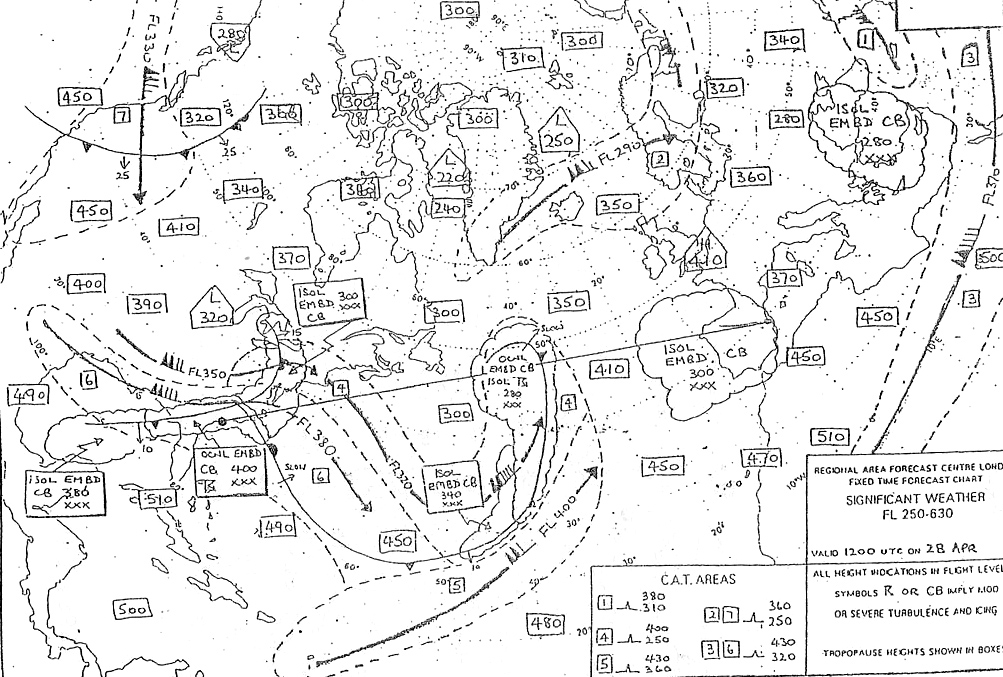 001° - 170 kt.
001° - 170 kt. Given .tas = 227 kt track t = 316° w/v = 205/15kt .calculate the hdg °t and gs ?
Question 171-36 : 312° 232 kt 311° 230 kt 313° 235 kt 310° 233 kt
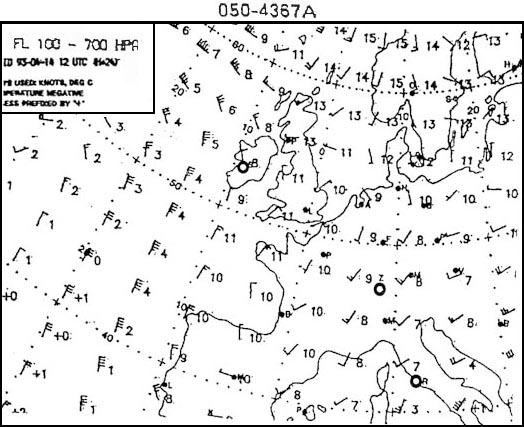 312° - 232 kt.
312° - 232 kt. Given tas = 200 kt track t = 073° w/v = 210/20kt calculate the hdg °t and gs ?
Question 171-37 : 077 214 kt 079 211 kt 075 213 kt 077 210 kt
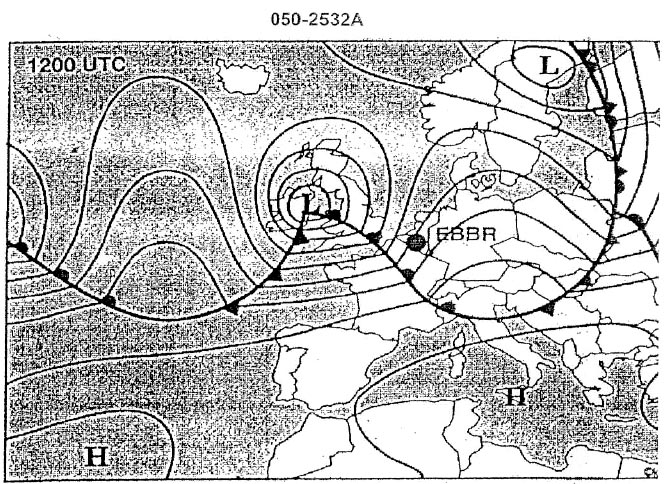 077 - 214 kt
077 - 214 kt Given .tas = 270 kt track t = 260° wind = 275°/30kt .calculate the hdg °t ?
Question 171-38 : 262° 241 kt 262° 237 kt 264° 241 kt 264° 237 kt
 262° - 241 kt.
262° - 241 kt. Given .true hdg = 233° tas = 480 kt track t = 240° gs = 523 kt .calculate the ?
Question 171-39 : 110/75kt 115/70kt 110/80kt 105/75kt
 110/75kt.
110/75kt. Given .true heading = 074° tas = 230 kt true track = 066° ground speed = 242 ?
Question 171-40 : 180/35 kt 180/30 kt 185/35 kt 180/40 kt
 180/35 kt
180/35 kt ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6799 Free Training Exam
