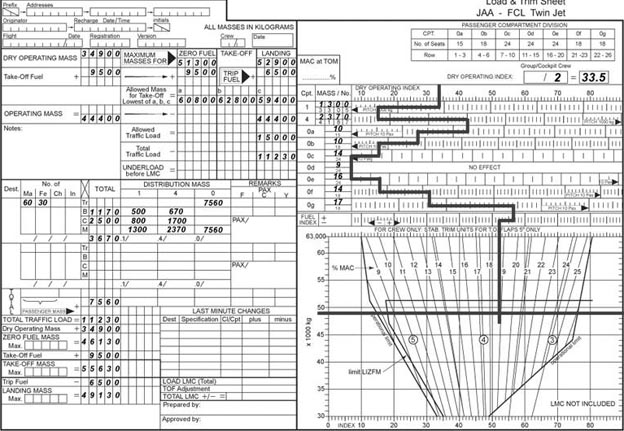
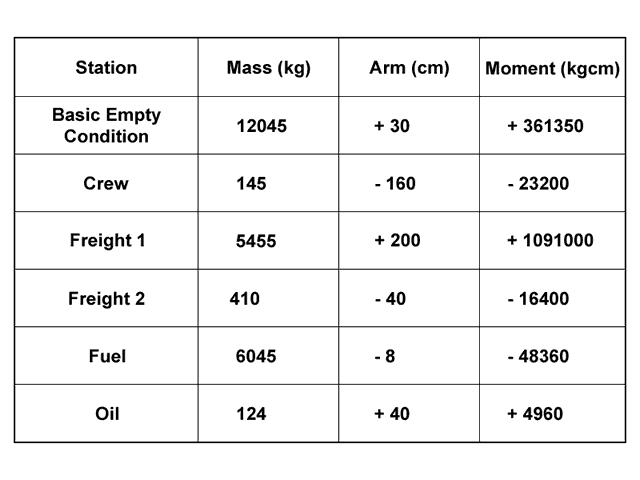
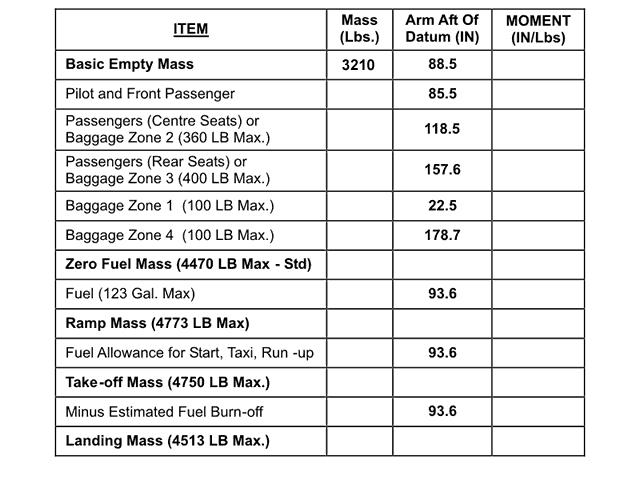
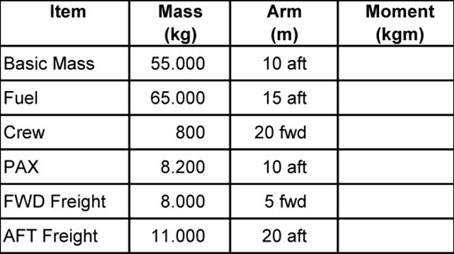
Which of the following statements is correct concerning the flight crew ? [ Validation Marking ]
Question 17-1 : This door shall be capable of being locked this door must be made of a fire proof material this door shall be marked as an emergency access and be kept clear of obstructions at all times this door must resist to small arms fire and grenade shrapnel for at least 5 minutes
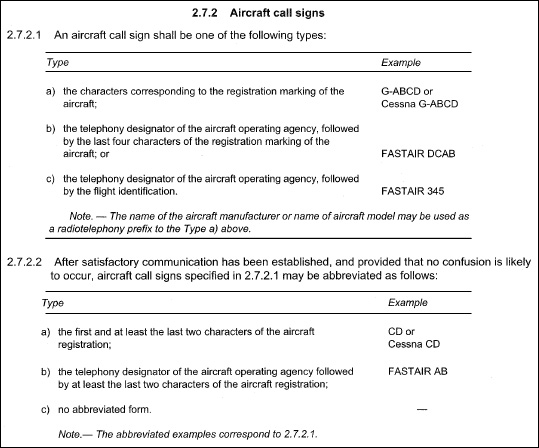
In all aeroplanes which are equipped with a flight crew compartment door this ?
Question 17-2 : The time all external doors are closed following embarkation until any such door is opened for disembarkation at engines start up until shut down after the flight at line up for take off until the beginning of taxiing on the taxiway after landing commencement of pushback
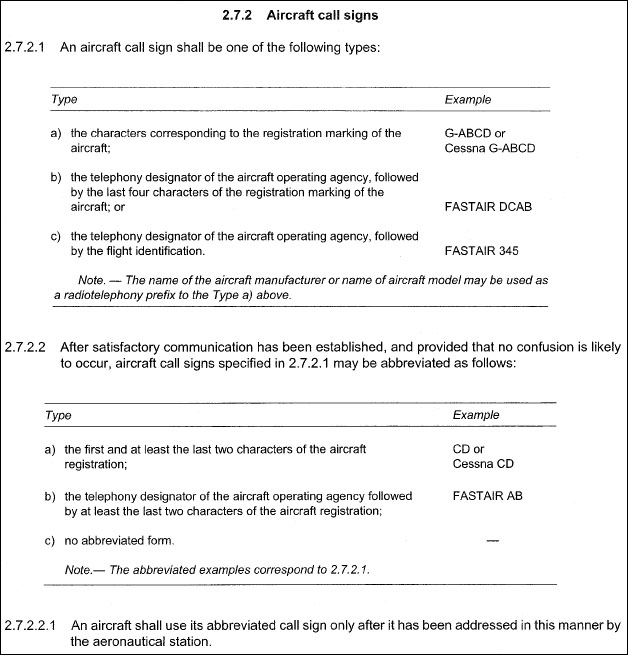 The time all external doors are closed following embarkation until any such door is opened for disembarkation.
The time all external doors are closed following embarkation until any such door is opened for disembarkation. Accident investigation objective .the sole objective of the investigation of an ?
Question 17-3 : Prevention of future accidents or incidents prevention of accidents or incidents and to establish liability prevention of accidents or incidents and to provide legal evidence for subsequent court cases prevention of accidents or incidents and to provide the manufacturer with investigation data for the improvement of the design
 Prevention of future accidents or incidents.
Prevention of future accidents or incidents. Accident investigation .who is responsible for the initiation of an accident ?
Question 17-4 : The state of occurrence the state of registration the state of design the aircraft manufacturer
 The state of occurrence.
The state of occurrence. Accident incident notification and reporting .after landing while taxiing ?
Question 17-5 : This is an accident and the crew must follow the procedure relevant to this case this is an incident and the pilot in command must report it to the airport authority within the next 48 hours since there is no person injured and the flight is terminated a damage report has to be made out with the services of the aerodrome in charge of the runway and taxiways for the insurance company this is an irregularity in the operation the crew must inform the operator of the aerodrome and establish a report
 This is an accident and the crew must follow the procedure relevant to this case.
This is an accident and the crew must follow the procedure relevant to this case. The icao document that primarily deals with accident investigation is ?
Question 17-6 : Annex 13 annex 20 annex 15 annex 17
 Annex 13.
Annex 13. Icao annex 13 accident/incident notification and reporting .the aircraft has ?
Question 17-7 : This is an accident the crew must follow the procedure relevant for this case this is a matter of passenger insurance as the flight is terminated and the aeroplane doors are open the airport operator or the company in charge of the handling shall establish a report for the insurance company this is an irregularity in the handling the handling agent must inform his insurance company this is an incident the pilot in command must report it to the airport authority within the next 48 hours
 This is an accident. the crew must follow the procedure relevant for this case.
This is an accident. the crew must follow the procedure relevant for this case. Icao annex 13 notification and reporting.during the climb out phase of a ?
Question 17-8 : This is a serious incident the crew must follow the procedure relevant to an incident this is an accident the crew must follow the procedure relevant to an accident this is an irregularity in the operation the operator must inform the authority by writing an irregularity report this is an irregularity the pilot in command or the operator must deposit a report on behalf of the involved airport authority within the following 48 hours
 This is a serious incident. the crew must follow the procedure relevant to an incident.
This is a serious incident. the crew must follow the procedure relevant to an incident. The report on the inquiry requires by icao under an accident or an incident ?
Question 17-9 : Has for sole objective the prevention of future accidents it is not the purpose of this activity to apportion blame or liability has for objective the prevention of accidents or similar incidents and to apportion blame and liability has for sole objective to apportion blame and liability to improve air and navigation safety level is to apportion blame and liability
 Has for sole objective the prevention of future accidents. it is not the purpose of this activity to apportion blame or liability.
Has for sole objective the prevention of future accidents. it is not the purpose of this activity to apportion blame or liability. In the case of serious incidents .the report on the inquiry requires by icao ?
Question 17-10 : Institute by the state of occurrence this state may consider delegating the whole or any part of the conducting of such investigation to another state or a regional accident and incident investigation organization raio under the responsibility of the state of the operator the states of registry operator design or construction may be requested for the purposes of the investigation institute by the state of the operator to conduct any necessary investigation of the accident or serious incident under the responsibility of the state of registry the state of occurrence is responsible for the opening of the investigation and its conduct until the arrival of the investigators designated by the state of registry
 Institute by the state of occurrence. this state may consider delegating the whole or any part of the conducting of such investigation to another state or a regional accident and incident investigation organization (raio).
Institute by the state of occurrence. this state may consider delegating the whole or any part of the conducting of such investigation to another state or a regional accident and incident investigation organization (raio). Annex 13 definitions .a recorder installed in the aircraft for the purpose of ?
Question 17-11 : A flight recorder a black box a snitch a routeur
 A flight recorder.
A flight recorder. In accordance to regulation eu 996/2010 is considered as serious incident ?
Question 17-12 : A near collision requiring an avoidance manoeuvre a belly landing abnormal engine vibrations wake turbulence encounters
 A near collision requiring an avoidance manoeuvre.
A near collision requiring an avoidance manoeuvre. The accident investigation preliminary report shall be submitted to appropriate ?
Question 17-13 : One of the working languages of icao the language of the investigating state english any of the world's major languages
 One of the working languages of icao.
One of the working languages of icao. Upon receipt of the notification and a request by the state of occurrence for ?
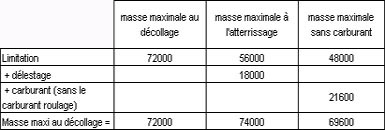
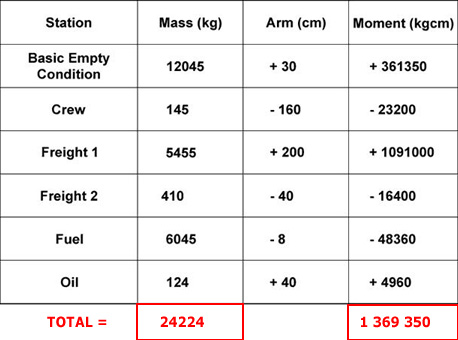
Question 17-14 : 2250 kg 27000 kg 5700 kg 80000 kg
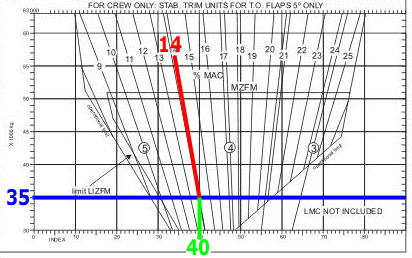 2250 kg.
2250 kg. Which of the following according to icao annex 13 shall be entitled to appoint ?
Question 17-15 : Any state which on request provides information facilities or experts to the state conducting the investigation all icao members states state conducting the investigation and state of design state conducting the investigation and the state of aircraft registry
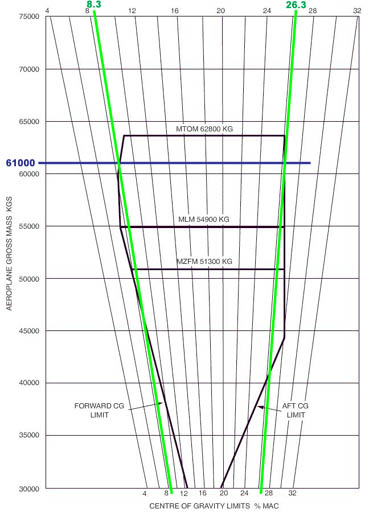 Any state which, on request, provides information, facilities or experts to the state conducting the investigation.
Any state which, on request, provides information, facilities or experts to the state conducting the investigation. Icao annex 13 definitions.an accident is an occurrence associated with the ?
Question 17-16 : The aircraft sustains damage or structural failure which adversely affects the structural strength and would require major repair the circumstances indicate the need for a major repair or replacement of an affected component during which a person suffers injuries due to natural causes it could affect the safety of operation
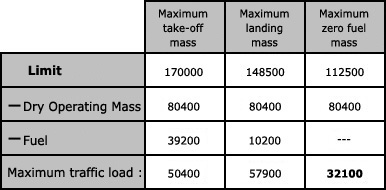 The aircraft sustains damage or structural failure which adversely affects the structural strength and would require major repair.
The aircraft sustains damage or structural failure which adversely affects the structural strength and would require major repair. Annex 13 .the geographical limits if any within which the specifications given ?
Question 17-17 : Wherever they occurred only over the high seas in all geographical areas except over the high seas in the territories of contracting states
Annex 13 .when the location of an accident or a serious incident cannot ?
Question 17-18 : The state of registry the state of manufacture the state of design the state of the operator
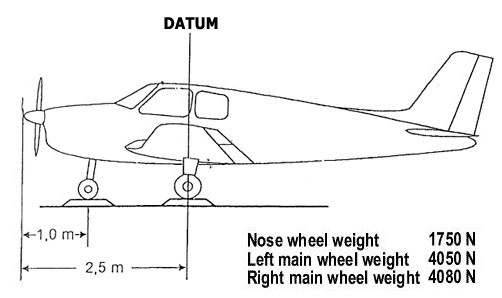 The state of registry.
The state of registry. A french registered aircraft piloted by a dutchman citizen with a german fcl ?
Question 17-19 : Spain germany france netherlands
The wing of an aircraft in flight powered by engines located under the wing is ?
Question 17-20 : Compression and then tension tension and then compression tension compression
 Compression, and then tension.
Compression, and then tension. Among the different types of aircraft structures the shell structures ?
Question 17-21 : 1 2 and 3 1 2 and 4 1 3 and 4 2 3 and 4
 1, 2 and 3.
1, 2 and 3. On a non stressed skin type wing the wing structure elements which take up the ?
Question 17-22 : The spars the ribs the skin the webs
 The spars.
The spars. With regard to an aircraft structure 'fail safe' is one ?
Question 17-23 : In which the load is carried by other components if a part of the structure fails that is easily manufactured used for small aircraft only that is only used for a limited time
 In which the load is carried by other components if a part of the structure fails.
In which the load is carried by other components if a part of the structure fails. For fail safe designed structural components .1 there is more than one load ?
Question 17-24 : 1 4 2 3 1 3 2 4
 1, 4.
1, 4. Loads on the cylindrical part of the fuselage during pressurisation are carried ?
Question 17-25 : Skin spars stringers ribs
 Skin.
Skin. The bending loads on a cantilever wing due to lift are carried by the .1 upper ?
Question 17-26 : 1 2 4 2 3 1 3 4 3 4
 1, 2, 4.
1, 2, 4. Which of these statements about structural design principles are correct or ?
Question 17-27 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which of these statements about sandwich structural parts are correct or ?
Question 17-28 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which of these statements concerning a sandwich structural part are correct or ?
Question 17-29 : I is correct ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. According jar/cs 25 the worst effect of a hazardous failure on the occupants of ?
Question 17-30 : Serious or fatal injury to a small number of passengers or cabin crew multiple fatalities physical distress possibly including injuries physical discomfort
 Serious or fatal injury to a small number of passengers or cabin crew.
Serious or fatal injury to a small number of passengers or cabin crew. For safe life designed structural components .1 there is more than one load ?
Question 17-31 : 2 3 1 4 2 4 1 3
 2, 3.
2, 3. According jar/cs 25 the allowable average failure probability per flight hour ?
Question 17-32 : Between 10^ 5 and 10^ 7 remote between 10^ 3 and 10^ 5 probable less than 10^ 9 extremely improbable between 10^ 7 and 10^ 9 extremely remote
According jar/cs 25 the allowable average failure probability per flight hour ?
Question 17-33 : Between 10^ 3 and 10^ 5 probable between 10^ 5 and 10^ 7 remote between 10^ 7 and 10^ 9 extremely remote less than 10^ 9 extremely improbable
 Between 10^ -3 and 10^ -5. (probable)
Between 10^ -3 and 10^ -5. (probable) According jar/cs 25 the allowable quantitative average failure probability per ?
Question 17-34 : Less than 10^ 9 extremely improbable between 10^ 7 and 10^ 9 extremely remote between 10^ 5 and 10^ 7 remote between 10^ 3 and 10^ 5 probable
According jar/cs 25 the worst effect of a hazardous failure on the flight crew ?
Question 17-35 : Physical distress or excessive workload impairs ability to perform tasks fatalities or incapacitation physical discomfort or a significant increase in workload a slight increase in workload
 Physical distress or excessive workload, impairs ability to perform tasks.
Physical distress or excessive workload, impairs ability to perform tasks. According jar/cs 25 the worst effect of a hazardous failure on the aeroplane ?
Question 17-36 : Large reduction in functional capabilities or safety margins hull loss significant reduction in functional capabilities or safety margins slight reduction in functional capabilities or safety margins
 Large reduction in functional capabilities or safety margins.
Large reduction in functional capabilities or safety margins. Which of these statements about structural design principles are correct or ?
Question 17-37 : I is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is incorrect.
I is incorrect, ii is incorrect. Which of these statements about structural design principles are correct or ?
Question 17-38 : I is correct ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is correct
 I is correct, ii is correct.
I is correct, ii is correct. Which of these statements about structural design principles are correct or ?
Question 17-39 : I is incorrect ii is correct i is correct ii is incorrect i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is correct.
I is incorrect, ii is correct. Which of these statements about structural design principles are correct or ?
Question 17-40 : I is incorrect ii is correct i is incorrect ii is incorrect i is correct ii is incorrect i is correct ii is correct
 I is incorrect, ii is correct.
I is incorrect, ii is correct. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
639 Free Training Exam Other source study: Ppl exam examen 17
