An aircraft departs from position a 04°10' s 178°22'w and flies northward ? [ Formation assignment ]
Question 168-1 : 45°00'n 172°38'e 53°20'n 169°22w 45°00'n 169°22w 53°20'n 172°38'e
 45°00'n 172°38'e.
45°00'n 172°38'e. What is the time required to travel along the parallel of latitude 60°n ?
Question 168-2 : 2 h 30 1 h 15 1 h 45 5 h 00
 2 h 30.
2 h 30. Given the following .magnetic heading 060° magnetic variation 8°w drift angle ?
Question 168-3 : 056° 064° 048° 072°
 056°.
056°. An aircraft is following a true track of 048° at a constant tas of 210 kt .the ?
Question 168-4 : 192 kt 7° right 200 kt 3 5° right 192 kt 7° left 225 kt 7° left
 192 kt, 7° right.
192 kt, 7° right. Given .fl 350 mach 0 80 oat 55°c .calculate the values for tas and local speed ?
Question 168-5 : 461 kt lss 576 kt 237 kt lss 296 kt 490 kt lss 461 kt 461 kt lss 296 kt
 461 kt, lss 576 kt.
461 kt, lss 576 kt. Given .true heading = 180°.tas = 500 kt.w/v 225° / 100 kt.calculate the gs ?
Question 168-6 : 435 kt 600 kt 535 kt 450 kt
 435 kt.
435 kt. Given .true heading = 310° tas = 200 kt gs = 176 kt drift angle 7° right ?
Question 168-7 : 270° / 33 kt 360° / 33 kt 090° / 33 kt 180° / 33 kt
 270° / 33 kt.
270° / 33 kt. Given .true heading = 090° tas = 200 kt wind = 220°/30 kt .calculate the ?
Question 168-8 : 220 kt 230 kt 180 kt 200 kt
 220 kt.
220 kt. The reported surface wind from the control tower is 240°/35 kt runway 30 300° ?
Question 168-9 : 30 kt 24 kt 27 kt 21 kt
 30 kt.
30 kt. Given magnetic heading 311° drift angle 10° left relative bearing of ndb ?
Question 168-10 : 221° 208° 211° 180°
 221°.
221°. Given the following .true track 192° magnetic variation 7°e drift angle 5° ?
Question 168-11 : 190° 194° 204° 180°
 190°.
190°. The angle between the plane of the ecliptic and the plane of equator is ?
Question 168-12 : 23 5° 25 3° 27 5° 66 5°
 23.5°.
23.5°. Given .tas = 485 kt.oat = isa +10°c .fl 410 .calculate the mach number ?
Question 168-13 : 0 825 0 9 0 85 0 87
 0.825
0.825 At 1215 utc lajes vortac 38°46'n 027°05'w rmi reads 178° range 135 nm ?
Question 168-14 : 40°55'n 027°55'w 40°50'n 027°30'w 41°00'n 028°10'w 41°05'n 027°50'w
 40°55'n 027°55'w.
40°55'n 027°55'w. At reference .1300 utc dr position 37°30'n 021°30'w alter heading port santo ?
Question 168-15 : 1348 1344 1341 1354
 1348
1348 For a distance of 1860 nm between q and r a ground speed 'out' of 385 kt a ?
Question 168-16 : 1685 nm 1532 nm 930 nm 1865 nm
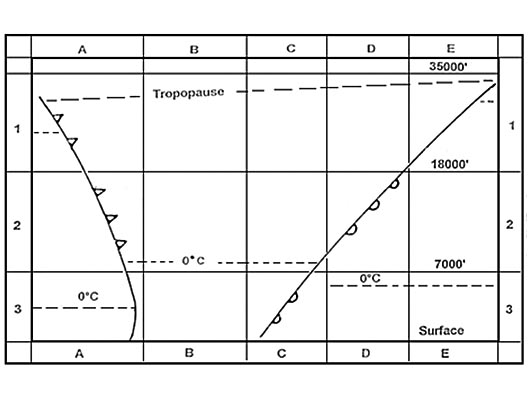 1685 nm.
1685 nm. Two points a and b are 1000 nm apart tas = 490 kt .on the flight between a and ?
Question 168-17 : 530 nm 455 nm 500 nm 470 nm
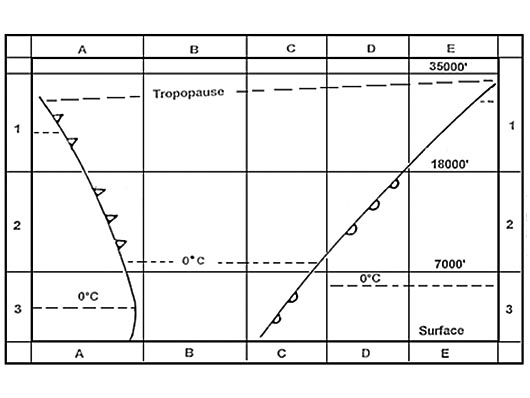 530 nm.
530 nm. Given ad = air distance gd = ground distance tas = true airspeed gs = ?
Question 168-18 : Gd = ad x gs /tas gd = ad tas /tas gd = ad x gs tas /gs gd = tas/ gs x ad
 Gd = (ad x gs)/tas
Gd = (ad x gs)/tas What is the isa temperature value at fl 330 ?
Question 168-19 : 51°c 56°c 66°c 81°c
 -51°c
-51°c Given .tas 487kt fl 330 temperature isa + 15 .calculate the mach number ?
Question 168-20 : 0 81 0 76 0 78 0 84
 0.81
0.81 How many nm would an aircraft travel in 1 minute 45 secondes if gs is 135 kt ?
Question 168-21 : 3 94 nm 2 36 nm 39 nm 3 25 nm
 3.94 nm.
3.94 nm. An aircraft travels 100 statute miles in 20 min how long does it take to travel ?
Question 168-22 : 50 min 100 min 90 min 80 min
 50 min.
50 min. Given .tas = 220 kt.magnetic course = 212°.wind = 160 ° m / 50 kt.calculate ?
Question 168-23 : 186 kt 290 kt 246 kt 250 kt
 186 kt.
186 kt. Given .fl250.oat 15 °c.tas 250 kt.calculate the mach number ?
Question 168-24 : 0 40 0 42 0 44 0 39
 0.40
0.40 During a low level flight 2 parallel roads that are crossed at right angles by ?
Question 168-25 : Groundspeed drift position track
 Groundspeed.
Groundspeed. Given .magnetic track = 315° magnetic heading = 301° variation = 5°w tas = ?
Question 168-26 : 190°/63 kt 355°/15 kt 195°/61 kt 195°/63 kt
 190°/63 kt.
190°/63 kt. Given .tas = 270 kt true hdg = 270° actual wind 205° t /30kt .calculate the ?
Question 168-27 : 6r 259kt 6l 256kt 6r 251kt 8r 259kt
 6r - 259kt
6r - 259kt Given .tas = 270 kt true hdg = 145° actual true wind = 205°/30kt .calculate ?
Question 168-28 : 6°l 256 kt 6°r 251 kt 8°r 261 kt 6°r 259 kt
 6°l - 256 kt
6°l - 256 kt Given .tas = 470 kt true heading = 317° wind = 045° t /45 kt .calculate the ?
Question 168-29 : 5°l 470 kt 3°r 470 kt 5°l 475 kt 5°r 475 kt
 5°l - 470 kt
5°l - 470 kt Given .tas = 190 kt .true heading = 085° .true wind = 110°/50kt .calculate ?
Question 168-30 : 8°l 146 kt 7°l 156 kt 4°l 168 kt 4°l 145 kt
 8°l - 146 kt.
8°l - 146 kt. Given .tas = 132 kt true hdg = 257° true wind = 095°/35 kt .calculate the ?
Question 168-31 : 4°r 165 kt 2°r 166 kt 4°l 167 kt 3°l 166 kt
 4°r - 165 kt.
4°r - 165 kt. Given .tas = 370 kt true heading = 181° wind = 095°/35 kt.calculate true ?
Question 168-32 : 186° 370 kt 176° 370 kt 192° 370 kt 189° 370 kt
 186° - 370 kt.
186° - 370 kt. Given .tas = 125 kt true heading = 355° true wind = 320°/30 kt .calculate the ?
Question 168-33 : 005° 102 kt 345° 100 kt 348° 102 kt 002° 98 kt
 005° - 102 kt.
005° - 102 kt. Given .tas = 225 kt .hdg °t = 123° .w/v = 090/60kt .calculate the track °t ?
Question 168-34 : 134° 178 kt 134° 188 kt 120° 190 kt 128° 180 kt
 134° - 178 kt.
134° - 178 kt. Given .tas = 480 kt true heading = 040° wind = 090°/60 kt .calculate true ?
Question 168-35 : 034° 445 kt 028° 415 kt 032° 425 kt 036° 435 kt
 034° - 445 kt.
034° - 445 kt. Given .tas = 170 kt.true heading = 100°.wind = 350/30kt .calculate the true ?
Question 168-36 : 109° 182 kt 091° 183 kt 103° 178 kt 098° 178 kt
 109° - 182 kt.
109° - 182 kt. Given . tas = 235 kt hdg t = 076° w/v = 040/40kt .calculate the drift angle ?
Question 168-37 : 7r 204 kt 7l 269 kt 5l 255 kt 5r 207 kt
 7r - 204 kt.
7r - 204 kt. Given .tas = 440 kt true heading = 349° wind = 040/40kt .calculate drift and ?
Question 168-38 : 4l 415 kt 2l 420 kt 6l 395 kt 5l 385 kt
 4l - 415 kt
4l - 415 kt Given tas = 95 kt hdg t = 075° w/v = 310/20kt calculate the drift and gs ?
Question 168-39 : 9r 108 kt 10l 104 kt 9l 105 kt 8r 104 kt
 9r - 108 kt
9r - 108 kt Given .tas = 230 kt hdg t = 250° wind = 205/10kt .calculate the drift and gs ?
Question 168-40 : 2r 223 kt 2l 224 kt 1l 225 kt 1r 221 kt
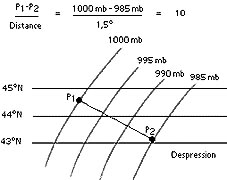 2r - 223 kt.
2r - 223 kt. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6679 Free Training Exam
