What is a speci ? [ Formation assignment ]
Question 167-1 : A special aerodrome weather report issued when a significant change of the weather conditions have been observed a routine aerodrome weather report issued every 3 hours a warning of meteorological dangers at an aerodrome issued only when required an aerodrome forecast issued every 9 hours
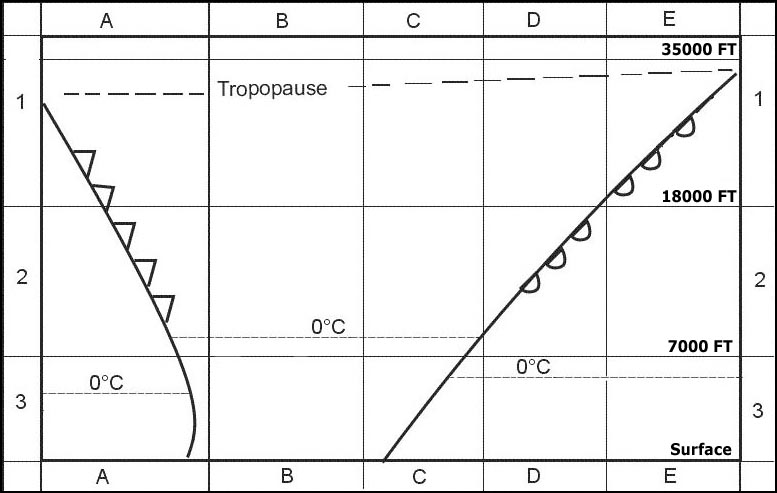
 A special aerodrome weather report, issued when a significant change of the weather conditions have been observed.
A special aerodrome weather report, issued when a significant change of the weather conditions have been observed. Refer to the following taf extract .becmg 1218/1221 2000 bkn004 becmg 1221/1224 ?
Question 167-2 : The new conditions are achieved between 1800 and 2100 utc a quick change to new conditions between 1800 and 1900 utc many short term changes in the original weather many long term changes in the original weather
 The new conditions are achieved between 1800 and 2100 utc
The new conditions are achieved between 1800 and 2100 utc Refer to the following taf extract .becmg 1218/1221 2000 br bkn004 becmg ?
Question 167-3 : 5 7 oktas ceiling 400 ft 1 4 oktas ceiling 400 ft 4 8 oktas ceiling 400 m 1 4 oktas ceiling 400 m
 5 - 7 oktas, ceiling 400 ft.
5 - 7 oktas, ceiling 400 ft. Refer to the following taf extract .becmg 1218/1221 2000 br bkn004 becmg ?
Question 167-4 : Probability of 30% conditions will last for at least 30 minutes the cloud ceiling should lift to 3000 ft change expected in less than 30 minutes
 Probability of 30%.
Probability of 30%. Select the true statement concerning isobars and wind flow patterns around high ?
Question 167-5 : When the isobars are close together the pressure gradient force is greater and wind velocities are stronger surface winds flow perpendicular to the isobars isobars connect contour lines of equal temperature when the isobars are far apart crest of standing waves may be marked by stationary lenticular clouds
 When the isobars are close together, the pressure gradient force is greater and wind velocities are stronger.
When the isobars are close together, the pressure gradient force is greater and wind velocities are stronger. What is the wind speed given in a metar report based on ?
Question 167-6 : The average speed of the previous 10 minutes the average speed of the previous 30 minutes the strongest gust in the previous hour the actual speed at the time of recording
 The average speed of the previous 10 minutes
The average speed of the previous 10 minutes What are the images of satellites provided daily by the weather service used for ?
Question 167-7 : To locate fronts in areas with few observation stations to measure wind currents on the ground to help provide 14 day forecasts to locate precipitation zones
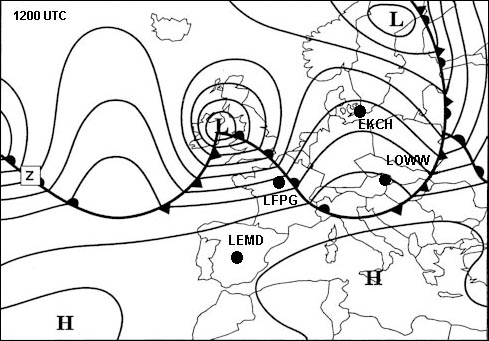 To locate fronts in areas with few observation stations
To locate fronts in areas with few observation stations Which constant pressure altitude chart is standard for fl 100 ?
Question 167-8 : 700 hpa 850 hpa 500 hpa 300 hpa
 700 hpa.
700 hpa. Which constant pressure altitude chart is standard for fl 180 ?
Question 167-9 : 500 hpa 300 hpa 200 hpa 700 hpa
 500 hpa.
500 hpa. Which constant pressure altitude chart is standard for fl 300 ?
Question 167-10 : 300 hpa 200 hpa 700 hpa 500 hpa
 300 hpa.
300 hpa. Which constant pressure altitude chart is standard for fl 390 ?
Question 167-11 : 200 hpa 500 hpa 700 hpa 300 hpa
 200 hpa.
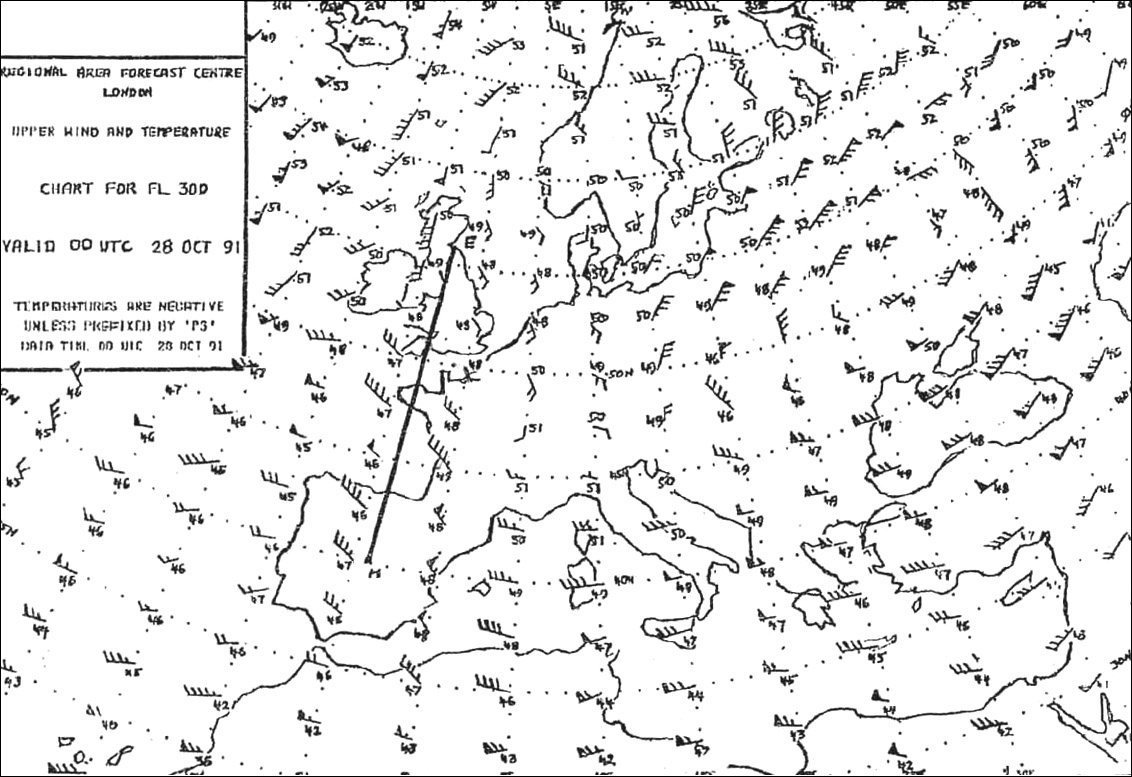
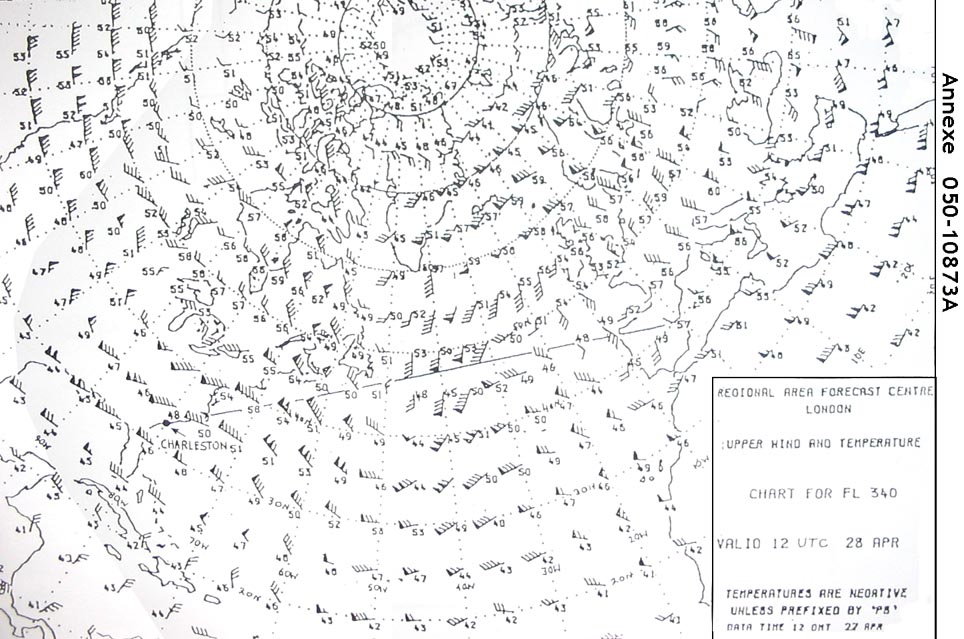
200 hpa. If you are planning a flight at fl 170 which of these upper wind and ?
Question 167-12 : 500 hpa 300 hpa 850 hpa 700 hpa
 500 hpa.
500 hpa. If you are planning a flight at fl 290 which of these upper wind and ?
Question 167-13 : 300 hpa 500 hpa 700 hpa 850 hpa
 300 hpa.
300 hpa. When planning a flight at fl 60 which upper wind and temperature chart would be ?
Question 167-14 : 850 hpa 700 hpa 500 hpa 300 hpa
 850 hpa.
850 hpa. When planning a flight at fl 110 which upper wind and temperature chart would ?
Question 167-15 : 700 hpa 850 hpa 300 hpa 500 hpa
 700 hpa.
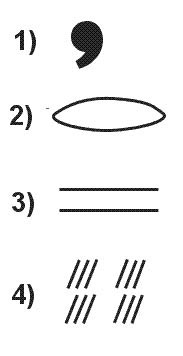
700 hpa. According to icao which symbol indicates severe icing . 300 ?
Question 167-16 : 1 2 3 4
 1.
1. According to icao which symbol indicates a tropical revolving storm . 301 ?
Question 167-17 : Symbol c symbol a symbol d symbol b
 Symbol c)
Symbol c) According to icao which symbol indicates widespread haze . 301 ?
Question 167-18 : Symbol b symbol c symbol a symbol d
 Symbol b)
Symbol b) According to icao which symbol indicates a severe line squall . 301 ?
Question 167-19 : Symbol a symbol c symbol d symbol b
 Symbol a)
Symbol a) What does the term sigmet signify ?
Question 167-20 : A sigmet is a warning of dangerous meteorological conditions a sigmet is a flight forecast issued by the meteorological station several times daily a sigmet is a brief landing forecast added to the actual weather report a sigmet is an actual weather report at an aerodrome and is generally issued at half ho y intervals
 A sigmet is a warning of dangerous meteorological conditions.
A sigmet is a warning of dangerous meteorological conditions. What does the term trend signify ?
Question 167-21 : It is a landing forecast added to the actual weather report it is the actual weather report at an aerodrome and is generally issued at half ho y intervals it is a warning of dangerous meteorological conditions it is a flight forecast issued by the meteorological station several times daily
 It is a landing forecast added to the actual weather report.
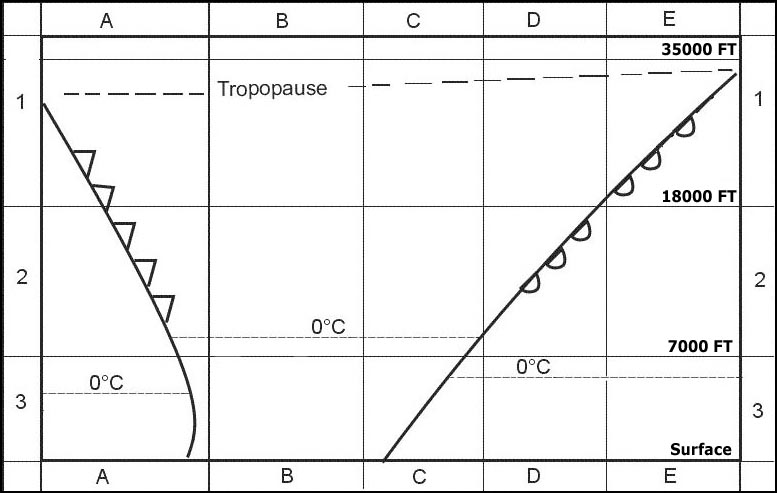
It is a landing forecast added to the actual weather report. Which of these statements best describes the weather most likely to be ?
Question 167-22 : Visibility 10 kilometres or more main cloudbase 3000 feet wind 250° temperature 18°c visibility 10 kilometres or more main cloudbase 1200 feet gusts up to 45 knots severe rainshowers meteorological visibility 4000 metres temperature 15°c gusts up to 35 knots visibility 4000 metres gusts up to 25 knots temperature 18°c
 Visibility 10 kilometres or more, main cloudbase 3000 feet, wind 250°, temperature 18°c.
Visibility 10 kilometres or more, main cloudbase 3000 feet, wind 250°, temperature 18°c. Which of the following weather reports could be in accordance with the ?
Question 167-23 : 15003kt 9999 bkn100 17/11 q1024 nosig = 24009kt 6000 ra sct010 ovc030 12/11 q1007 tempo 4000 = 29010kt 9999 sct045tcu 16/12 q1015 reshra nosig = 04012g26kt 9999 bkn030 11/07 q1024 nosig =
 15003kt 9999 bkn100 17/11 q1024 nosig =
15003kt 9999 bkn100 17/11 q1024 nosig = Which of the following statements is an interpretation of the metar .25020g38kt ?
Question 167-24 : Gusts of 38 knots thunderstorm with heavy hail dew point 18°c mean wind speed 20 38 knots visibility 1200 metres temperature 23°c broken cloud base 600 feet and 1500 feet temperature 18°c wind 250° thunderstorm with moderate hail qnh 1016 hpa
 Gusts of 38 knots, thunderstorm with heavy hail, dew point 18°c.
Gusts of 38 knots, thunderstorm with heavy hail, dew point 18°c. Which of the following statements is an interpretation of the sigmet .lsas ?
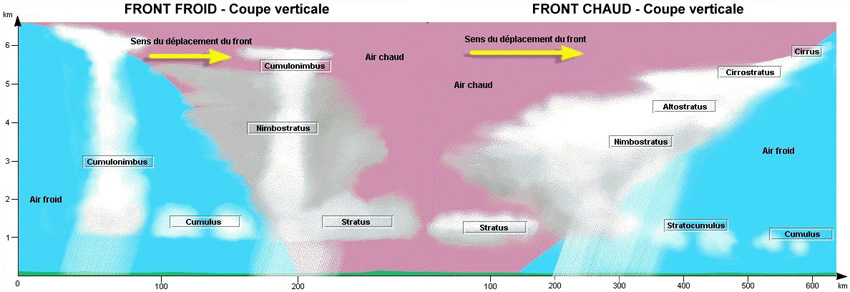
Question 167-25 : Moderate to severe clear air turbulence to be expected north of the alps intensity increasing danger zone between fl 260 and fl 380 zone of moderate to severe turbulence moving towards the area north of the alps intensity increasing pilots advised to cross this area above fl 260 severe turbulence observed below fl 260 north of the alps pilots advised to cross this area above fl 380 moderate to severe clear air turbulence of constant intensity to be expected north of the alps
 Moderate to severe clear air turbulence to be expected north of the alps. intensity increasing. danger zone between fl 260 and fl 380.
Moderate to severe clear air turbulence to be expected north of the alps. intensity increasing. danger zone between fl 260 and fl 380. Which of the following statements is an interpretation of the sigmet .lggg ?
Question 167-26 : Thunderstorms must be expected in the western part of the athens fir the thunderstorm zone is moving east intensity is constant thunderstorms have formed in the eastern part of the athens fir and are slowly moving west athens airport is closed due to thunderstorms the thunderstorm zone should be east of athens by 1820 utc the thunderstorms in the athens fir are increasing in intensity but are stationary above the western part of the athens fir
 Thunderstorms must be expected in the western part of the athens fir. the thunderstorm zone is moving east. intensity is constant
Thunderstorms must be expected in the western part of the athens fir. the thunderstorm zone is moving east. intensity is constant Compare the following taf and volmet reports for nice .taf 240600z 240716 ?
Question 167-27 : That the weather at nice is clearly more volatile than the taf could have predicted earlier in the morning that the weather conditions at 0920 were actually predicted in the taf that the weather in nice after 0920 is also likely to be as predicted in the taf that the volmet speaker has got his locations mixed up because there is no way the latest volmet report could be so different from the taf
 That the weather at nice is clearly more volatile than the taf could have predicted earlier in the morning.
That the weather at nice is clearly more volatile than the taf could have predicted earlier in the morning. Runway visual range rvr is ?
Question 167-28 : Usually better than visibility reported when visibility is less than 2000 m reported in airmet and metar measured with ceilometers alongside the runway
 Usually better than visibility.
Usually better than visibility. What information is given on a significant weather chart ?
Question 167-29 : The significant weather forecast for the time given on the chart the significant weather that is observed at the time given on the chart the significant weather in a period 3 hours before and 3 hours after the time given on the chart the significant weather forecast for a period 6 hours after the time given on the chart
 The significant weather forecast for the time given on the chart
The significant weather forecast for the time given on the chart A pilot is warned of severe icing at certain flight levels by information ?
Question 167-30 : Swc and sigmet taf and metar metar and sigmet taf and sigmet
 Swc and sigmet.
Swc and sigmet. An isohypse of the 500 hpa pressure surface is labelled with the number 552 ?
Question 167-31 : Topography is 552 decameters above msl pressure is 552 hpa topography is 552 meters above msl pressure altimeter will overread by 552 ft
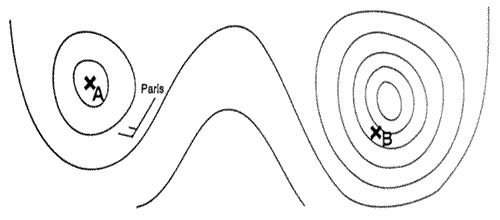 Topography is 552 decameters above msl.
Topography is 552 decameters above msl. The validity of a taf is ?
Question 167-32 : Stated in the taf 2 hours between 6 and 9 hours 9 hours from the time of issue
 Stated in the taf.
Stated in the taf. Atis information contains ?
Question 167-33 : Meteorological and operational information only meteorological information operational information and if necessary meteorological information only operational information
 Meteorological and operational information
Meteorological and operational information If cavok is reported then ?
Question 167-34 : No low drifting snow is present no clouds are present low level wind shear has not been reported any cb's have a base above 5000 ft
 No low drifting snow is present.
No low drifting snow is present. Runway visual range can be reported in ?
Question 167-35 : A metar a taf a sigmet both a taf and a metar
 A metar.
A metar. Sigmet information is issued as a warning for significant weather to ?
Question 167-36 : All aircraft light aircraft only vfr operations only heavy aircraft only
 All aircraft
All aircraft The wind direction in a metar is measured relative to ?
Question 167-37 : True north magnetic north grid north the 0 meridian
 True north.
True north. A speci is ?
Question 167-38 : An aviation special weather report an aviation routine weather report a warning for special weather phenomena a forecast for special weather phenomena
 An aviation special weather report
An aviation special weather report On the european continent metars of main airports are compiled and distributed ?
Question 167-39 : 0 5 hour 1 hour 2 hours 3 hours
 0.5 hour.
0.5 hour. The rvr as reported in a metar is always the ?
Question 167-40 : Value representative of the touchdown zone average value of the a b and c positions highest value of the a b and c positions lowest value of the a b and c positions
 Value representative of the touchdown zone.
Value representative of the touchdown zone. ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6639 Free Training Exam
