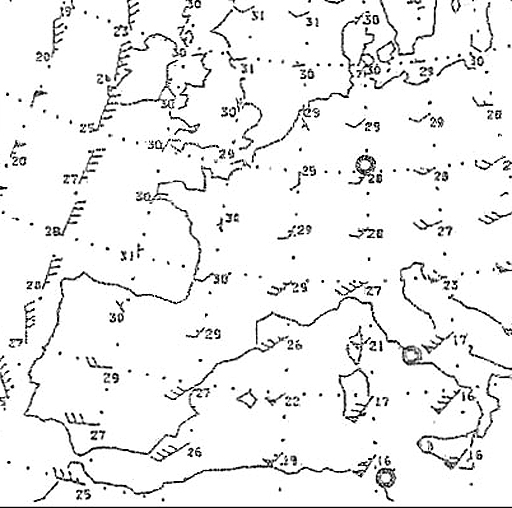
What is the average track °m and distance between wtd ndb n5211 3 w00705 0 and ? [ Formation assignment ]
Question 164-1 : 278° 90 nm 090° 91 nm 270° 89 nm 098° 90 nm
 278° - 90 nm.
278° - 90 nm. What is the average track °m and distance between crn ndb n5318 1 w00856 5 and ?
Question 164-2 : 142° 95 nm 315° 94 nm 135° 96 nm 322° 95 nm
 142° - 95 nm.
142° - 95 nm. What is the average track °m and distance between ker ndb n5210 9 w00931 5 and ?
Question 164-3 : 025° 70 nm 197° 71 nm 205° 71 nm 017° 70 nm
 025° - 70 nm.
025° - 70 nm. On a direct mercator chart at latitude 15°s a certain length represents a ?
Question 164-4 : 122 3 nm 177 7 nm 124 2 nm 118 2 nm
 122.3 nm.
122.3 nm. On a direct mercator chart at latitude 45°n a certain chart length along 45°n ?
Question 164-5 : 110 nm 73 5 nm 78 nm 45 nm
 110 nm.
110 nm. On a transverse mercator chart the scale is exactly correct along the ?
Question 164-6 : Meridians of tangency equator and parallel of origin meridian of tangency and the parallel of latitude perpendicular to it prime meridian and the equator
 Meridians of tangency.
Meridians of tangency. On a transverse mercator chart with the exception of the equator parallels of ?
Question 164-7 : Ellipses straight lines hyperbolic lines parabolas
 Ellipses.
Ellipses. An oblique mercator projection is used specifically to produce ?
Question 164-8 : Charts of the great circle route between two points radio navigational charts in equatorial regions topographical maps of large east/west extent plotting charts in equatorial regions
 Charts of the great circle route between two points.
Charts of the great circle route between two points. Transverse mercator projections are used for ?
Question 164-9 : Maps of large north/south extent maps of large east/west extent in equatorial areas radio navigation charts in equatorial areas plotting charts in equatorial areas
 Maps of large north/south extent
Maps of large north/south extent On a polar stereographic chart a straight line between a 75° 00'n 166° 00'e ?
Question 164-10 : 323° 329° 311° 305°
 323°.
323°. The scale on a lambert conformal conic chart ?
Question 164-11 : Is constant along a parallel of latitude is constant along a meridian of longitude is constant across the whole map varies slightly as a function of latitude and longitude
 Is constant along a parallel of latitude.
Is constant along a parallel of latitude. A direct mercator graticule is based on a projection that is ?
Question 164-12 : Cylindrical conical spherical concentric
 Cylindrical.
Cylindrical. On a chart the distance along a meridian between latitudes 45°n and 46°n is 6 ?
Question 164-13 : 1 1 850 000 1 1 000 000 1 18 500 000 1 185 000
 1: 1 850 000
1: 1 850 000 Given chart scale is 1 1 850 000 the chart distance between two points is 4 ?
Question 164-14 : 40 nm 74 nm 100 nm 4 nm
 40 nm.
40 nm. On a mercator chart at latitude 60°n the distance measured between w002° and ?
Question 164-15 : 1 2 780 000 1 278 000 1 5 560 000 1 556 000
 1: 2 780 000
1: 2 780 000 Assume a mercator chart the distance between positions a and b located on the ?
Question 164-16 : 60°n or s 30°n or s 0° 45°n or s
 60°n or s.
60°n or s. On a lambert chart standard parallels 37°n and 65°n with respect to the ?
Question 164-17 : Great circle and rhumb line are to the south great circle and rhumb line are to the north great circle is to the north the rhumb line is to the south rhumb line is to the north the great circle is to the south
 Great circle and rhumb line are to the south.
Great circle and rhumb line are to the south. A straight line on a chart 4 89 cm long represents 185 nm the scale of this ?
Question 164-18 : 1 7 000 000 1 3 500 000 1 6 000 000 1 5 000 000
 1: 7 000 000
1: 7 000 000 At latitude 60°n the scale of a mercator projection is 1 5 000 000 the length ?
Question 164-19 : 17 8 cm 16 2 cm 35 6 cm 19 2 cm
 17.8 cm.
17.8 cm. The two standard parallels of a conical lambert projection are at n10°40' and ?
Question 164-20 : 0 44 0 9 0 66 0 18
 0.44
0.44 On a direct mercator chart meridians are ?
Question 164-21 : Parallel equally spaced vertical straight lines inclined equally spaced straight lines that meet at the nearer pole parallel unequally spaced vertical straight lines inclined unequally spaced curved lines that meet at the nearer pole
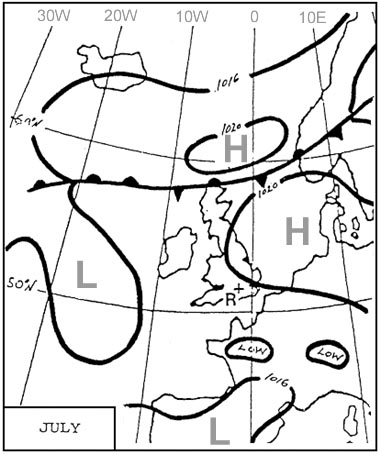 Parallel, equally spaced, vertical straight lines.
Parallel, equally spaced, vertical straight lines. On which of the following chart projections is it not possible to represent the ?
Question 164-22 : Direct mercator lambert's conformal transverse mercator polar stereographic
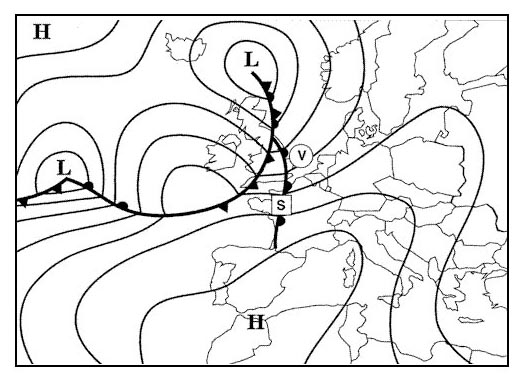 Direct mercator.
Direct mercator. Which one of the following concerning great circles on a direct mercator chart ?
Question 164-23 : With the exception of meridians and the equator they are curves concave to the equator they are all curves concave to the equator they approximate to straight lines between the standard parallels they are all curves convex to the equator
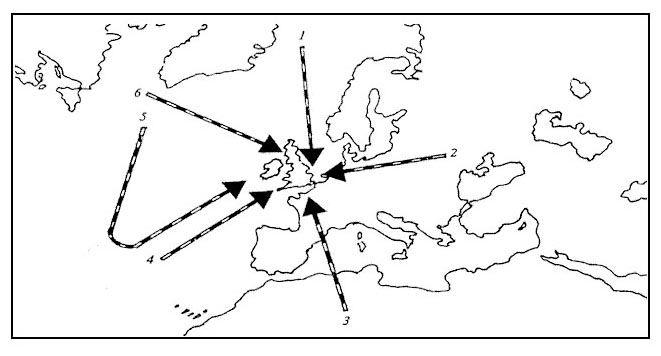 With the exception of meridians and the equator, they are curves concave to the equator.
With the exception of meridians and the equator, they are curves concave to the equator. On a lambert conformal conic chart the distance between parallels of latitude ?
Question 164-24 : Is smaller between the standard parallels than outside them is constant throughout the chart is larger between the standard parallels and is smaller outside them is constant between the standard parallels and is greater outside them
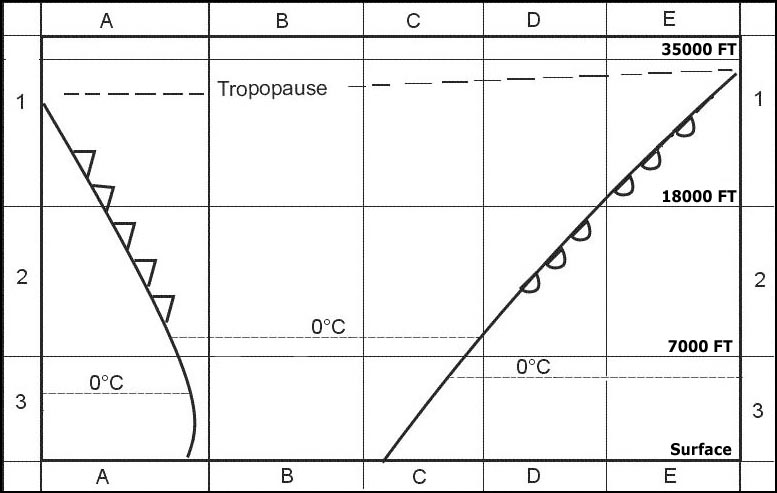 Is smaller between the standard parallels than outside them.
Is smaller between the standard parallels than outside them. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning the appearance of ?
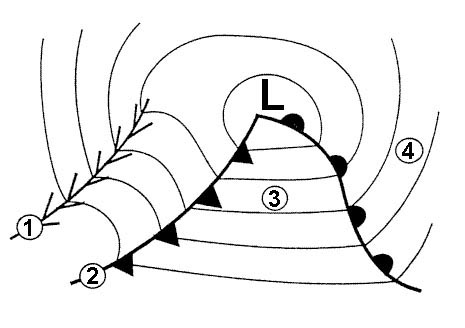
Question 164-25 : The higher the latitude the closer they approximate to a straight line any straight line is a great circle they are complex curves that can be convex and/or concave to the pole they are curves convex to the pole
 The higher the latitude the closer they approximate to a straight line.
The higher the latitude the closer they approximate to a straight line. Which one of the following describes the appearance of rhumb lines except ?
Question 164-26 : Curves concave to the pole ellipses around the pole curves convex to the pole straight lines
 Curves concave to the pole.
Curves concave to the pole. What is the value of the convergence factor on a polar stereographic chart ?
Question 164-27 : 1 0 0 866 0 5
 1.
1. A course of 120° t is drawn between 'x' 61°30'n and 'y' 58°30'n on a lambert ?
Question 164-28 : 66 7 cm 33 4 cm 38 5 cm 36 0 cm
 66.7 cm.
66.7 cm. Given .direct mercator chart with a scale of 1 200 000 at equator.chart length ?
Question 164-29 : 12 nm 21 nm 22 nm 14 nm
 12 nm.
12 nm. What is the radial and dme distance from crk vor/dme n5150 4 w00829 7 to ?
Question 164-30 : 030° 33 nm 048° 40 nm 014° 33 nm 220° 40 nm
 030° - 33 nm.
030° - 33 nm. What is the radial and dme distance from crk vor/dme n5150 4 w00829 7 to ?
Question 164-31 : 039° 48 nm 024° 43 nm 023° 48 nm 017° 43 nm
 039° - 48 nm
039° - 48 nm What is the radial and dme distance from sha vor/dme n5243 3 w00853 1 to ?
Question 164-32 : 309° 33 nm 057° 27 nm 293° 33 nm 324° 17 nm
 309° - 33 nm
309° - 33 nm What is the radial and dme distance from sha vor/dme n5243 3 w00853 1 to ?
Question 164-33 : 139° 35 nm 129° 46 nm 132° 36 nm 212° 26 nm
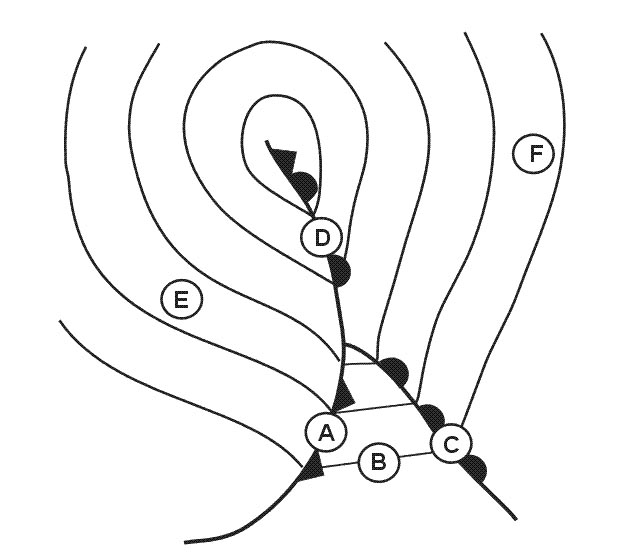 139° - 35 nm.
139° - 35 nm. What is the radial and dme distance from con vor/dme n5354 8 w00849 1 to ?
Question 164-34 : 358° 36 nm 214° 26 nm 049° 45 nm 169° 35 nm
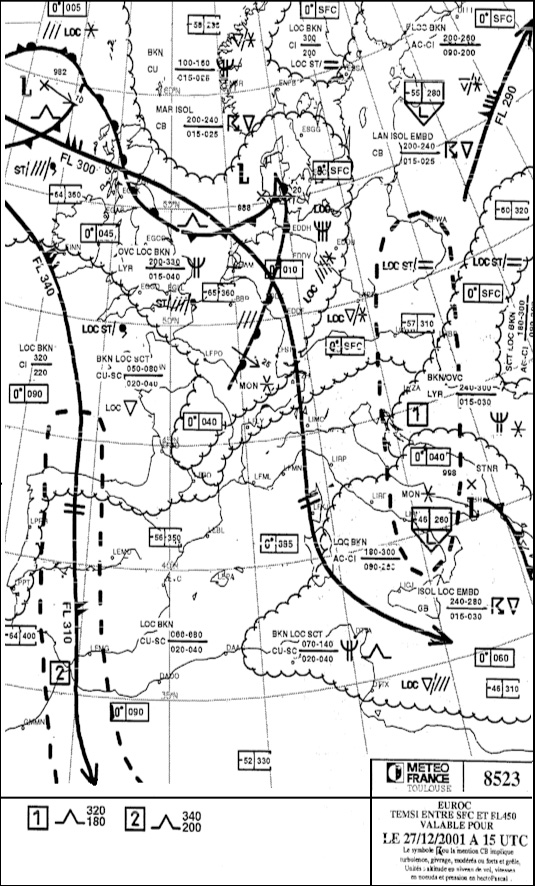 358° - 36 nm
358° - 36 nm What is the radial and dme distance from con vor/dme n5354 8 w00849 1 to ?
Question 164-35 : 140° 23 nm 119° 42 nm 311° 22 nm 240° 24 nm
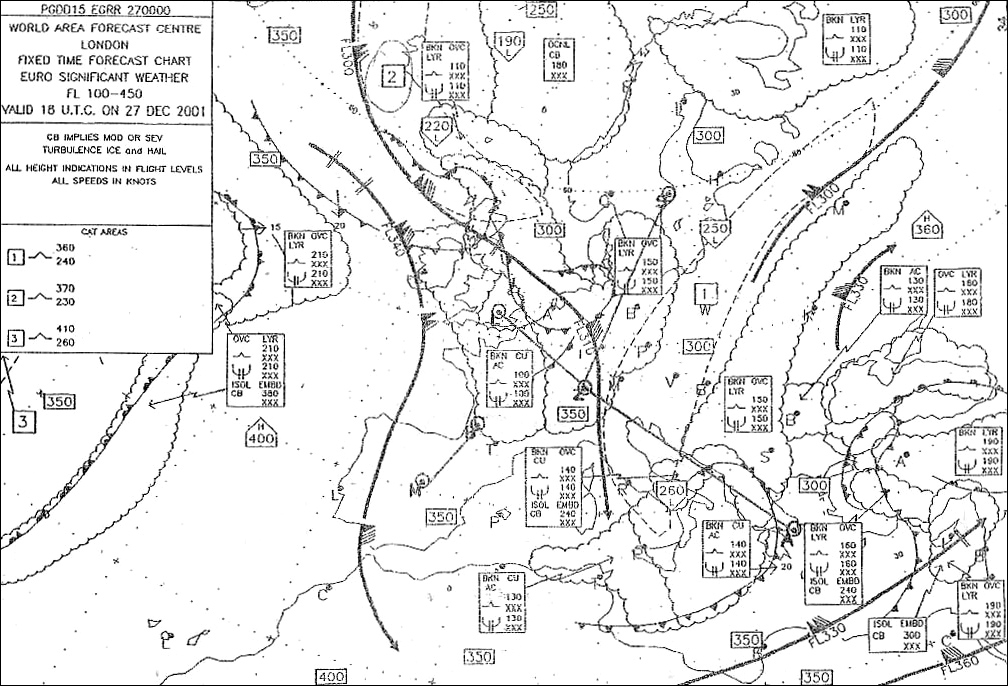 140° - 23 nm
140° - 23 nm What is the average track °m and distance between crn ndb n5318 1 w00856 5 and ?
Question 164-36 : 058° 128 nm 229° 125 nm 237° 130 nm 089° 95 nm
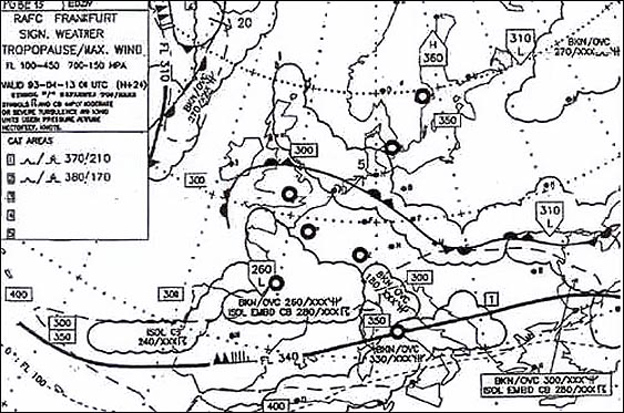 058° - 128 nm.
058° - 128 nm. What is the average track °t and distance between slg ndb n5416 7 w00836 0 and ?
Question 164-37 : 011° 47 nm 020° 46 nm 348° 46 nm 191° 45 nm
 011° - 47 nm
011° - 47 nm What is the average track °t and distance between wtd ndb n5211 3 w00705 0 and ?
Question 164-38 : 336° 137 nm 344° 139 nm 156° 136 nm 164° 138 nm
 336° - 137 nm
336° - 137 nm What is the average track °t and distance between bal vor n5318 0 w00626 9 and ?
Question 164-39 : 270° 90 nm 278° 89 nm 268° 91 nm 272° 89 nm
 270° - 90 nm
270° - 90 nm What is the average track °t and distance between crn ndb n5318 1 w00856 5 and ?
Question 164-40 : 035° 80 nm 042° 83 nm 031° 81 nm 044° 82 nm
 035° - 80 nm
035° - 80 nm ~
Exclusive rights reserved. Reproduction prohibited under penalty of prosecution.
6519 Free Training Exam
